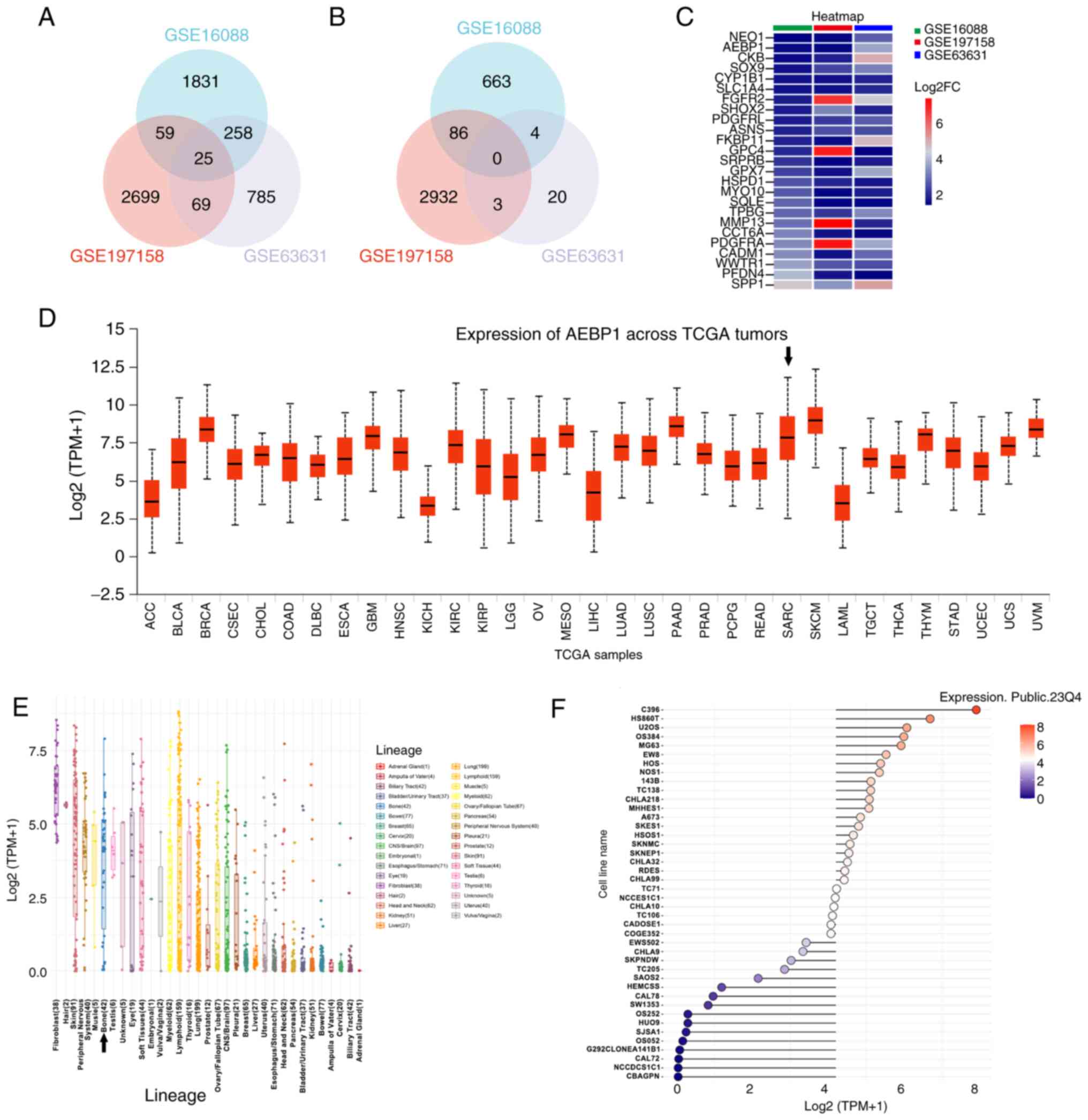
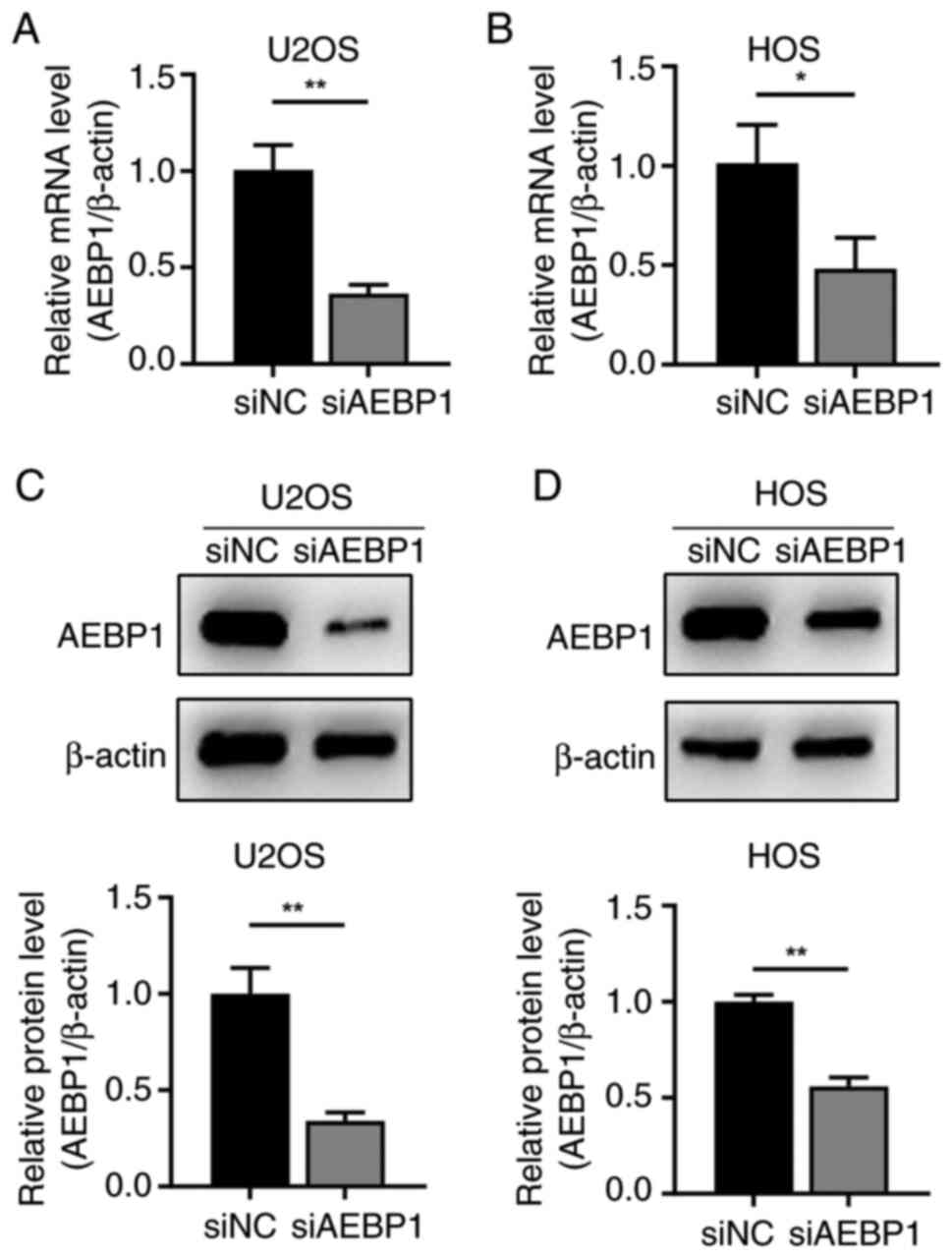
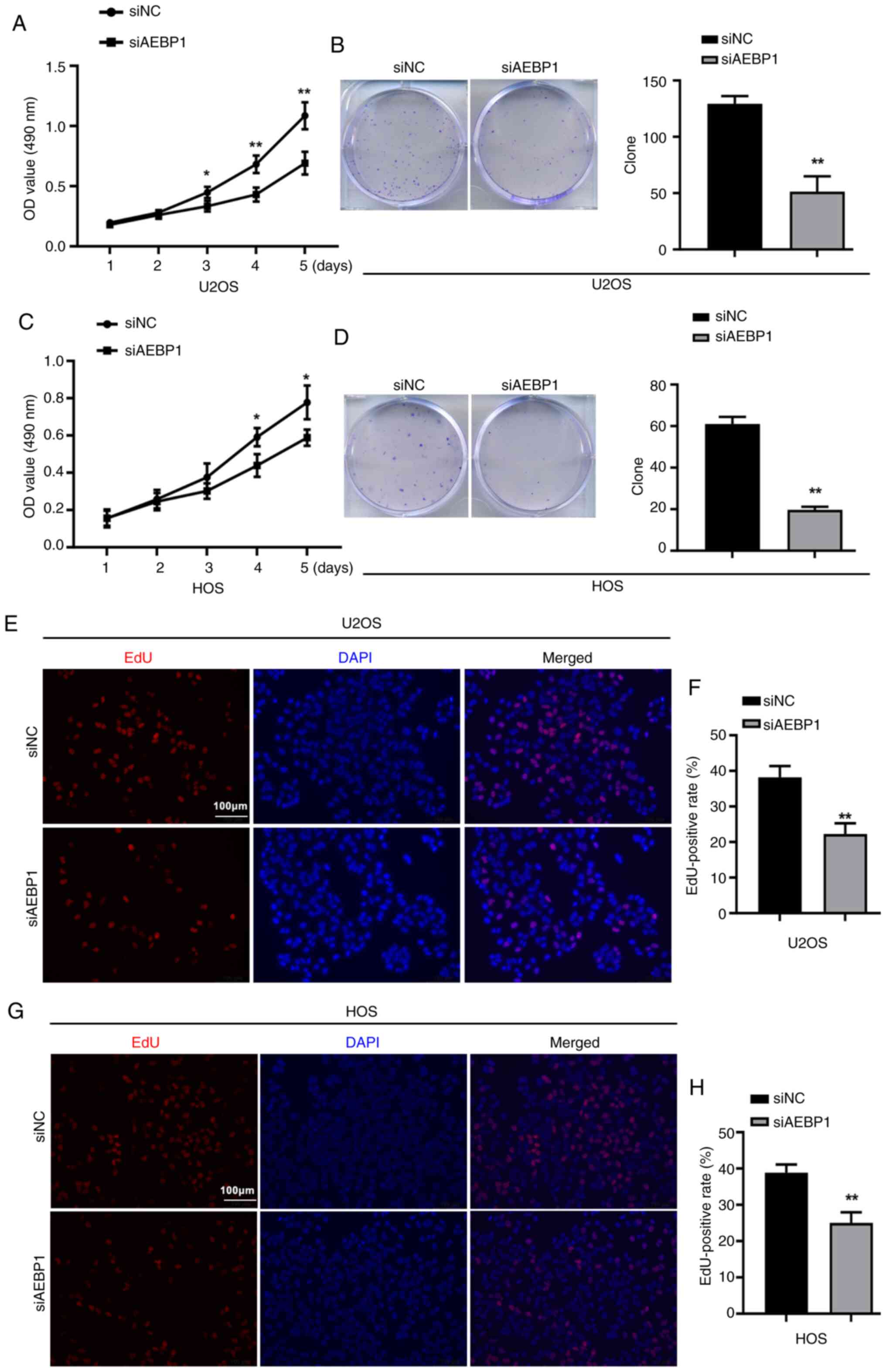
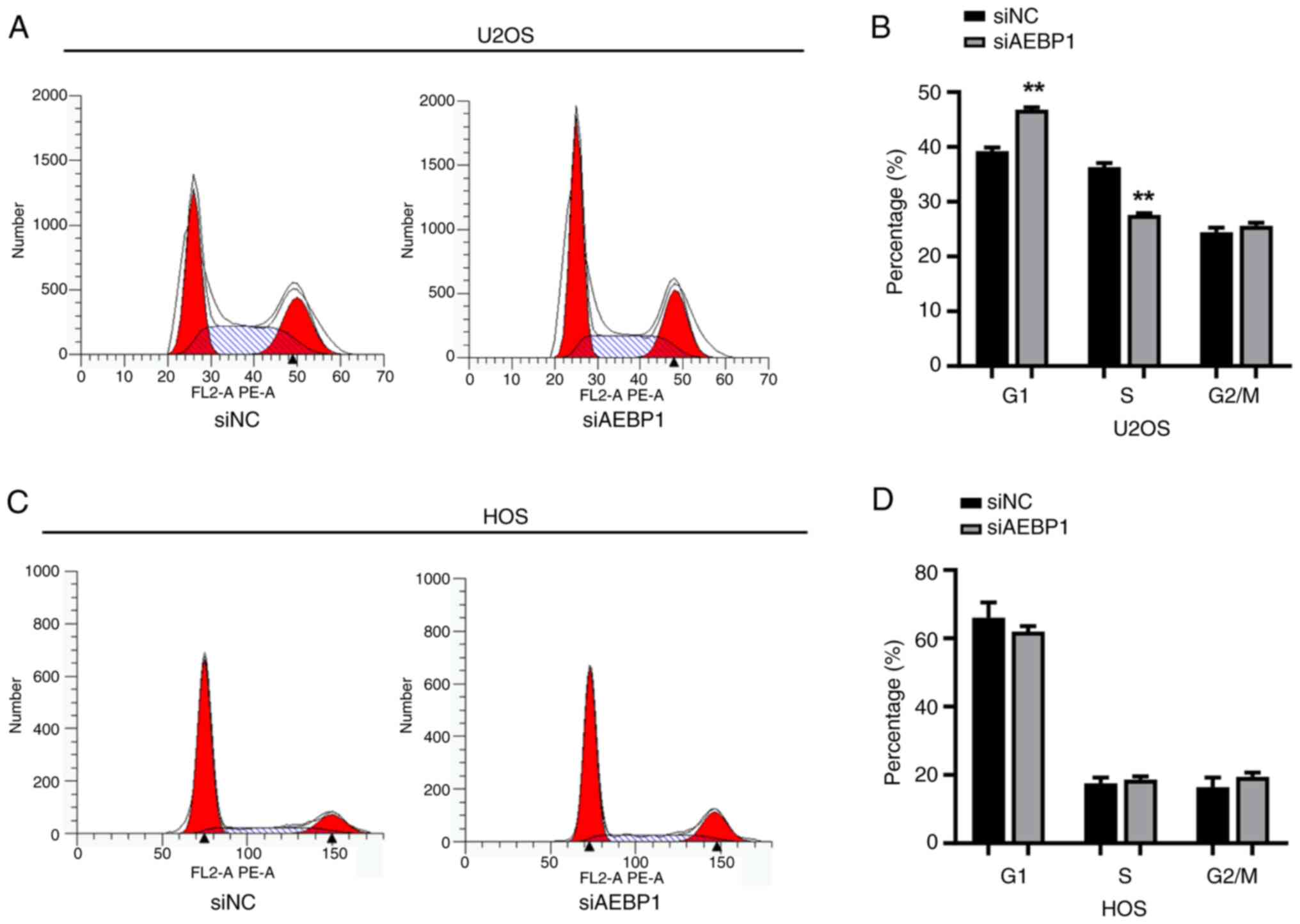
|
1
|
Li Z, Li X, Xu D, Chen X, Li S, Zhang L,
Chan MTV and Wu WKK: An update on the roles of circular RNAs in
osteosarcoma. Cell Prolif. 54(e12936)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Whelan J, McTiernan A, Cooper N, Wong YK,
Francis M, Vernon S and Strauss SJ: Incidence and survival of
malignant bone sarcomas in England 1979-2007. Int J Cancer.
131:E508–E517. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sheng G, Gao Y, Yang Y and Wu H:
Osteosarcoma and metastasis. Front Oncol. 11(780264)2021.
|
|
5
|
Chen C, Xie L, Ren T, Huang Y, Xu J and
Guo W: Immunotherapy for osteosarcoma: Fundamental mechanism,
rationale, and recent breakthroughs. Cancer Lett. 500:1–10.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
He GP, Muise A, Li AW and Ro HS: A
eukaryotic transcriptional repressor with carboxypeptidase
activity. Nature. 378:92–96. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sugai T, Yamada N, Osakabe M, Hashimoto M,
Uesugi N, Eizuka M, Tanaka Y, Sugimoto R, Yanagawa N and Matsumoto
T: Microenvironmental markers are correlated with lymph node
metastasis in invasive submucosal colorectal cancer.
Histopathology. 79:584–598. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li S, Liu X, Liu T, Meng X, Yin X, Fang C,
Huang D, Cao Y, Weng H, Zeng X and Wang X: Identification of
biomarkers correlated with the TNM staging and overall survival of
patients with bladder cancer. Front Physiol. 8(947)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li J, Ruan Y, Zheng C, Pan Y, Lin B, Chen
Q and Zheng Z: AEBP1 contributes to breast cancer progression by
facilitating cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and blocking
apoptosis. Discov Med. 35:45–56. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lyons PJ, Mattatall NR and Ro HS: Modeling
and functional analysis of AEBP1, a transcriptional repressor.
Proteins. 63:1069–1083. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ladha J, Sinha S, Bhat V, Donakonda S and
Rao SMR: Identification of genomic targets of transcription factor
AEBP1 and its role in survival of glioma cells. Mol Cancer Res.
10:1039–1051. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu JY, Jiang L, Liu JJ, He T, Cui YH,
Qian F and Yu PW: AEBP1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of gastric cancer cells by activating the NF-κB pathway and
predicts poor outcome of the patients. Sci Rep.
8(11955)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liu M, Yu Y, Zhang Z, Chen Z, Chen B,
Cheng Y, Wei Y, Li J and Shang H: AEBP1 as a potential
immune-related prognostic biomarker in glioblastoma: A
bioinformatic analyses. Ann Transl Med. 9(1657)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hou Y, Sun B, Liu W, Yu B, Shi Q, Luo F,
Bai Y and Feng H: Targeting of glioma stem-like cells with a
parthenolide derivative ACT001 through inhibition of AEBP1/PI3K/AKT
signaling. Theranostics. 11:555–566. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li S, Li C and Fang Z: MicroRNA 214
inhibits adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1 activity and
increases the sensitivity of chemotherapy in colorectal cancer.
Oncol Lett. 17:55–62. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Paoloni M, Davis S, Lana S, Withrow S,
Sangiorgi L, Picci P, Hewitt S, Triche T, Meltzer P and Khanna C:
Canine tumor cross-species genomics uncovers targets linked to
osteosarcoma progression. BMC Genomics. 10(625)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wood RK, Flory AR, Mann MJ, Talbot LJ and
Hendershot LM: Secretory defects in pediatric osteosarcoma result
from downregulation of selective COPII coatomer proteins. iScience.
25(104100)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sato S, Tang YJ, Wei Q, Hirata M, Weng A,
Han I, Okawa A, Takeda S, Whetstone H, Nadesan P, et al:
Mesenchymal tumors can derive from Ng2/Cspg4-expressing pericytes
with β-catenin modulating the neoplastic phenotype. Cell Rep.
16:917–927. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:D991–D995.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dong M, Yang G, Liu H, Liu X, Lin S, Sun D
and Wang Y: Aged black garlic extract inhibits HT29 colon cancer
cell growth via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomed Rep.
2:250–254. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhu Y, Wu F, Hu J, Xu Y, Zhang J, Li Y,
Lin Y and Liu X: LDHA deficiency inhibits trophoblast proliferation
via the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1/CyclinD1 signaling pathway in unexplained
recurrent spontaneous abortion. FASEB J. 37(e22744)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mills JN, Rutkovsky AC and Giordano A:
Mechanisms of resistance in estrogen receptor positive breast
cancer: Overcoming resistance to tamoxifen/aromatase inhibitors.
Curr Opin Pharmacol. 41:59–65. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Politz O, Siegel F, Bärfacker L, Bömer U,
Hägebarth A, Scott WJ, Michels M, Ince S, Neuhaus R, Meyer K, et
al: BAY 1125976, a selective allosteric AKT1/2 inhibitor, exhibits
high efficacy on AKT signaling-dependent tumor growth in mouse
models. Int J Cancer. 140:449–459. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Holloway RW, Bogachev O, Bharadwaj AG,
McCluskey GD, Majdalawieh AF, Zhang L and Ro HS: Stromal adipocyte
enhancer-binding protein (AEBP1) promotes mammary epithelial cell
hyperplasia via proinflammatory and hedgehog signaling. J Biol
Chem. 287:39171–39181. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Guo Y, Yang K, Harwalkar J, Nye JM, Mason
DR, Garrett MD, Hitomi M and Stacey DW: Phosphorylation of cyclin
D1 at Thr 286 during S phase leads to its proteasomal degradation
and allows efficient DNA synthesis. Oncogene. 24:2599–2612.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Guo X, Li W, Wang Q and Yang HS: AKT
activation by pdcd4 knockdown up-regulates cyclin D1 expression and
promotes cell proliferation. Genes Cancer. 2:818–828.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang Z, Wang Y, Wang S, Meng X, Song F,
Huo W, Zhang S, Chang J, Li J, Zheng B, et al: Coxsackievirus A6
induces cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase for viral production.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 8(279)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li S, Juan CX, Feng AM, Bian HL, Liu WD,
Zhang GQ, Wang CZ, Cao Q and Zhou GP: Attenuating the abnormally
high expression of AEBP1 suppresses the pathogenesis of childhood
acute lymphoblastic leukemia via p53-dependent signaling pathway.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:1184–1195. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lin KN, Zhao W, Huang SY and Li H: Grape
seed proanthocyanidin extract induces apoptosis of HL-60/ADR cells
via the Bax/Bcl-2 caspase-3/9 signaling pathway. Transl Cancer Res.
10:3939–3947. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Choi JH, Bogenberger JM and Tibes R:
Targeting apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia: Current status and
future directions of BCL-2 inhibition with venetoclax and beyond.
Target Oncol. 15:147–162. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|