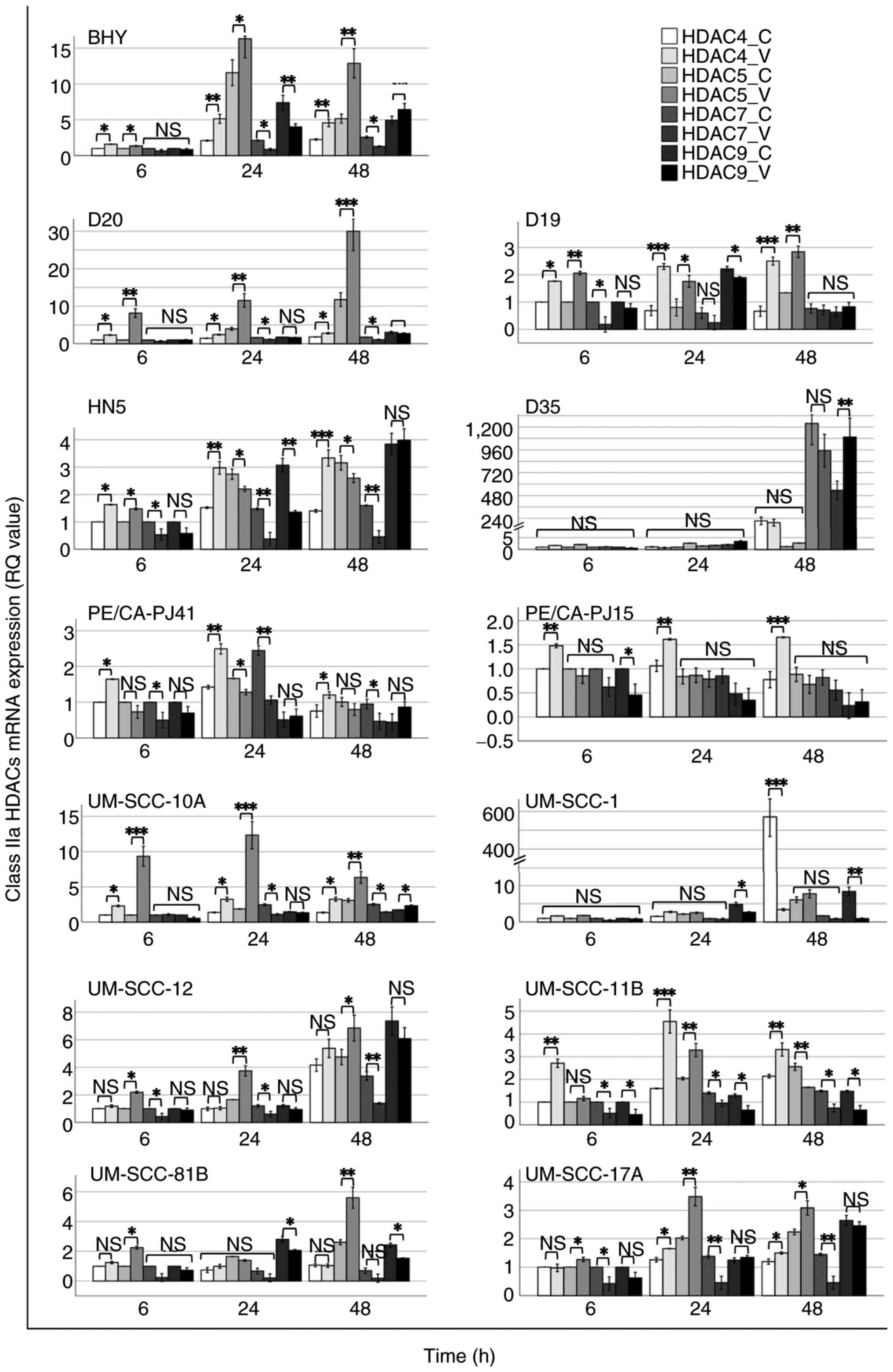
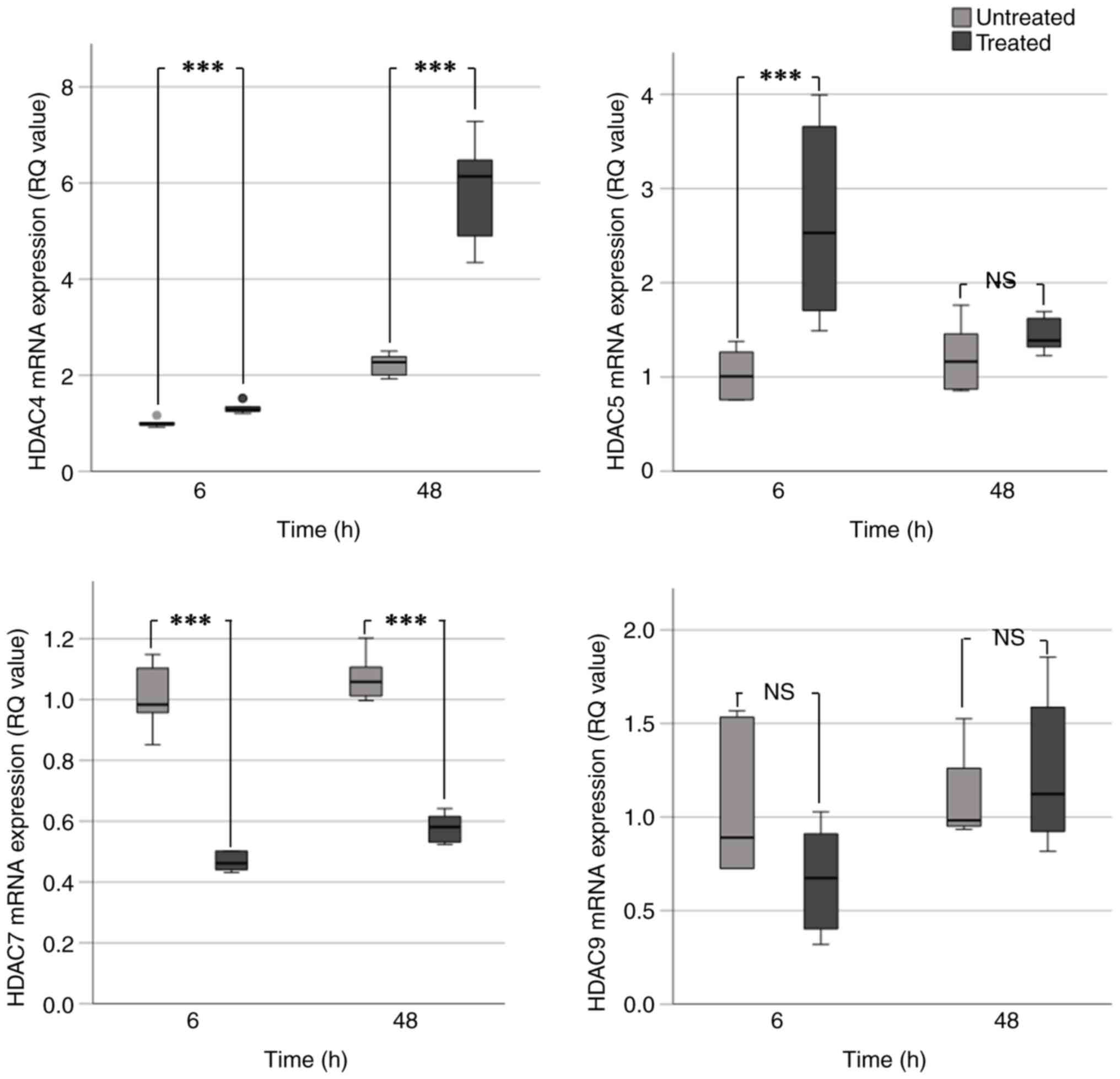
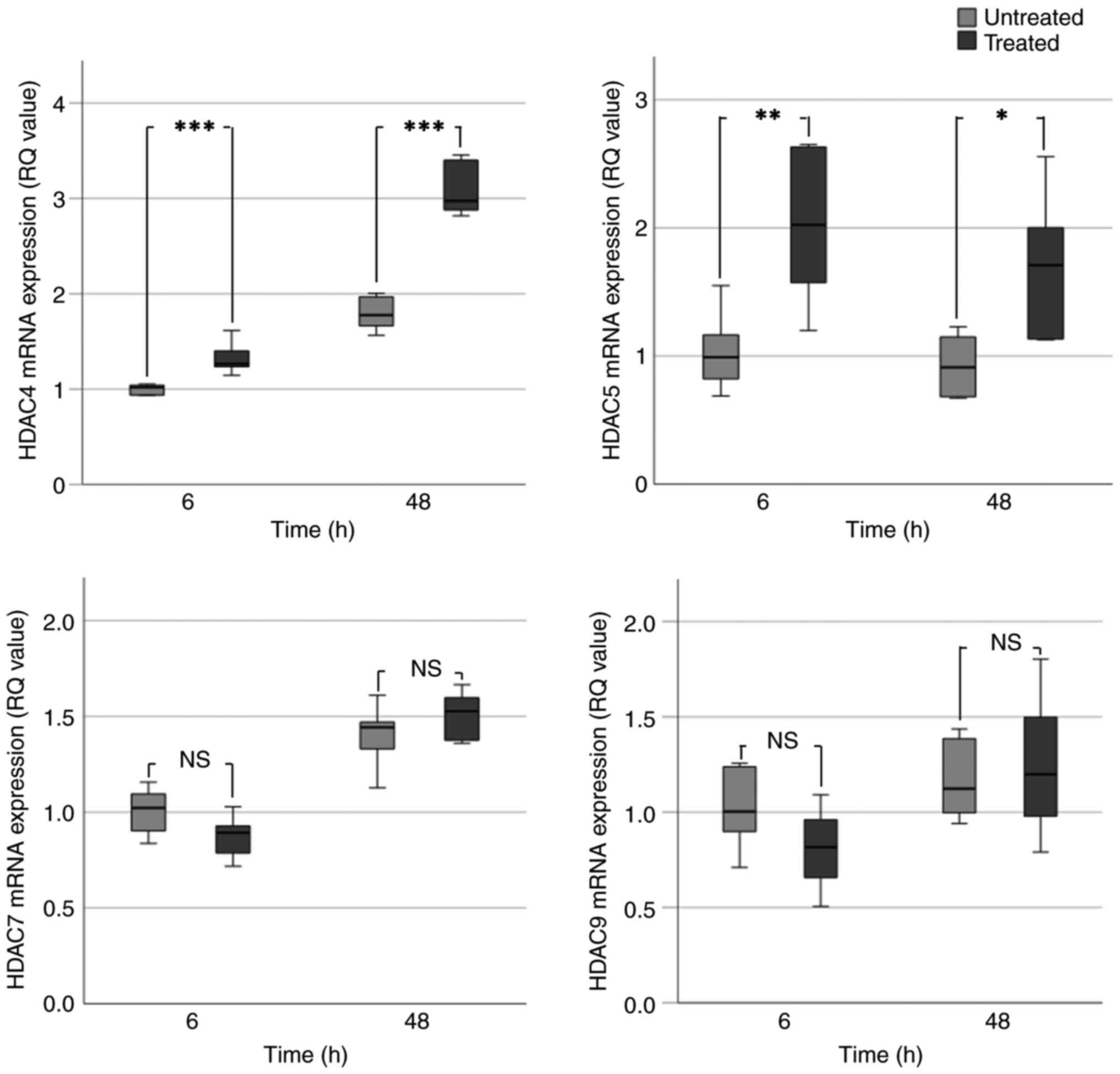
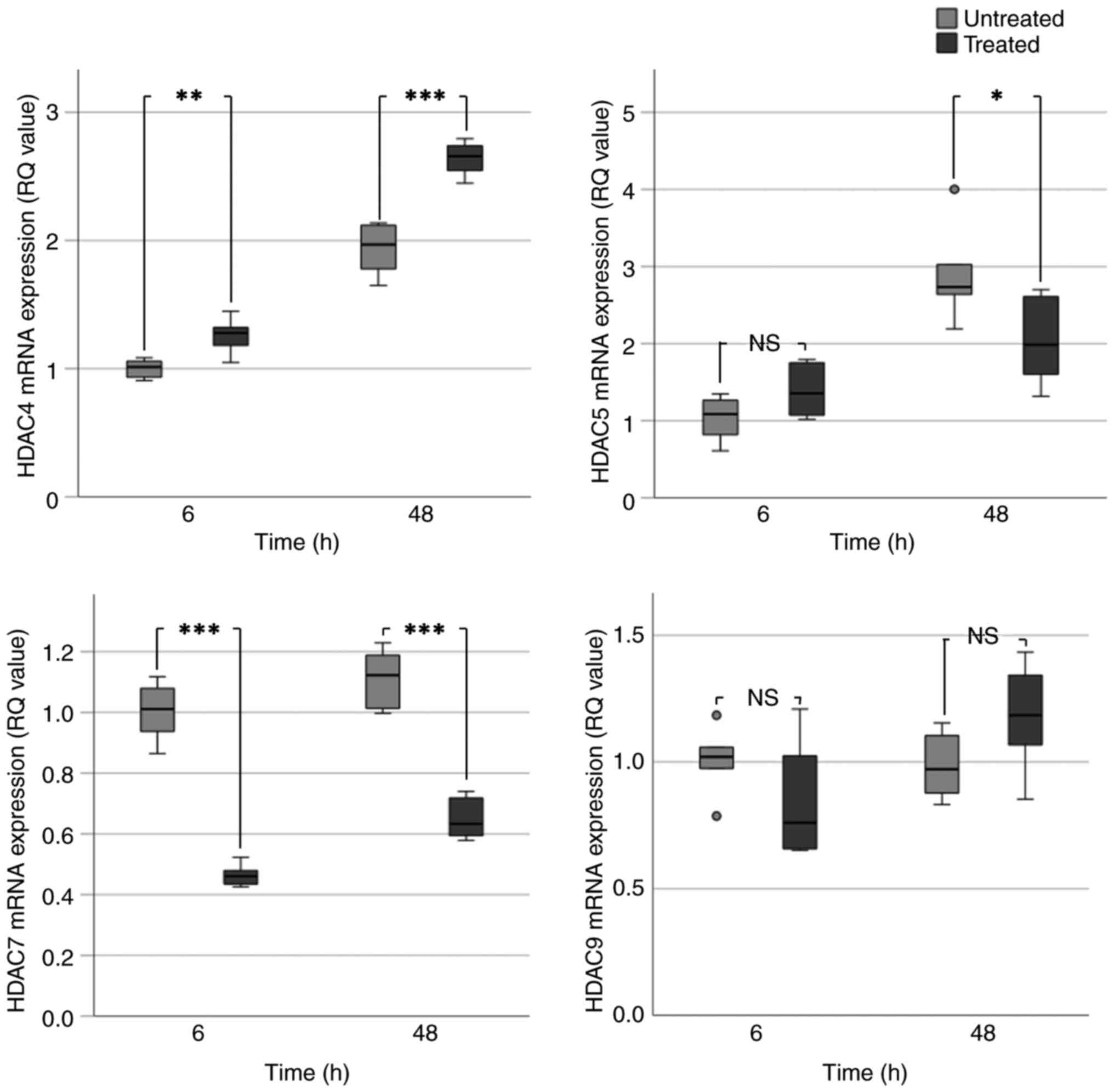
|
1
|
Ho MW, Field EA, Field JK, Risk JM,
Rajlawat BP, Rogers SN, Steele JC, Triantafyllou A, Woolgar JA,
Lowe D and Shaw RJ: Outcomes of oral squamous cell carcinoma
arising from oral epithelial dysplasia: Rationale for monitoring
premalignant oral lesions in a multidisciplinary clinic. Br J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 51:594–599. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sciubba JJ: Oral Cancer. The importance of
early diagnosis and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2:239–251.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
National Cancer Institute: Cancer Stat
Facts: Oral Cavity and Pharynx Cancer. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/oralcav.html.
|
|
4
|
González-Moles MÁ, Aguilar-Ruiz M and
Ramos-García P: Challenges in the early diagnosis of oral cancer,
evidence gaps and strategies for improvement: A scoping review of
systematic reviews. Cancers (Basel). 14(4967)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
van der Waal I: Potentially malignant
disorders of the oral and oropharyngeal mucosa; terminology,
classification and present concepts of management. Oral Oncol.
45:317–323. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Warnakulasuriya S: Oral potentially
malignant disorders: A comprehensive review on clinical aspects and
management. Oral Oncol. 102(104550)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Field EA, McCarthy CE, Ho MW, Rajlawat BP,
Holt D, Rogers SN, Triantafyllou A, Field JK and Shaw RJ: The
management of oral epithelial dysplasia: The Liverpool algorithm.
Oral Oncol. 51:883–887. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zaini ZM, McParland H, Møller H, Husband K
and Odell EW: Predicting malignant progression in clinically
high-risk lesions by DNA ploidy analysis and dysplasia grading. Sci
Rep. 8(15874)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Al-Khafaji AS, Pantazi P, Acha-Sagredo A,
Schache A, Risk JM, Shaw RJ and Liloglou T: Overexpression of HURP
mRNA in head and neck carcinoma and association with in vitro
response to vinorelbine. Oncol Lett. 19:2502–2507. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rivera C, Gallegos R and Figueroa C:
Biomarkers of progression to oral cancer in patients with
dysplasia: A systematic review. Mol Clin Oncol.
13(42)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Balasundaram I, Payne KF, Al-Hadad I,
Alibhai M, Thomas S and Bhandari R: Is there any benefit in surgery
for potentially malignant disorders of the oral cavity? J Oral
Pathol Med. 43:239–244. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sundberg J, Korytowska M, Holmberg E,
Bratel J, Wallström M, Kjellström E, Blomgren J, Kovács A, Öhman J,
Sand L, et al: Recurrence rates after surgical removal of oral
leukoplakia-A prospective longitudinal multi-centre study. PLoS
One. 14(e0225682)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ranganathan K and Kavitha L: Oral
epithelial dysplasia: Classifications and clinical relevance in
risk assessment of oral potentially malignant disorders. J Oral
Maxillofac Pathol. 23:19–27. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Siemianowicz K, Likus W, Dorecka M, Wilk
R, Dziubdziela W and Markowski J: Chemoprevention of head and neck
cancers: Does it have only one face? Biomed Res Int.
2018(9051854)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Park SY and Kim JS: A short guide to
histone deacetylases including recent progress on class II enzymes.
Exp Mol Med. 52:204–212. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Seto E and Yoshida M: Erasers of histone
acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 6(a018713)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Audia JE and Campbell RM: Histone
modifications and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
8(a019521)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Glozak MA and Seto E: Histone deacetylases
and cancer. Oncogene. 26:5420–5432. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li Y and Seto E: HDACs and HDAC inhibitors
in cancer development and therapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
6(a026831)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zheng YC, Kang HQ, Wang B, Zhu YZ, Mamun
MAA, Zhao LF, Nie HQ, Liu Y, Zhao LJ, Zhang XN, et al: Curriculum
vitae of HDAC6 in solid tumors. Int J Biol Macromol.
230(123219)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang P, Wang Z and Liu J: Role of HDACs in
normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Mol Cancer.
19(5)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Saito H, Yatabe Y,
Mitsudomi T and Takahashi T: Reduced expression of class II histone
deacetylase genes is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer
patients. Int J Cancer. 112:26–32. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cao LL, Song X, Pei L, Liu L, Wang H and
Jia M: Histone deacetylase HDAC1 expression correlates with the
progression and prognosis of lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 96(e7663)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Müller BM, Jana L, Kasajima A, Lehmann A,
Prinzler J, Budczies J, Winzer KJ, Dietel M, Weichert W and Denkert
C: Differential expression of histone deacetylases HDAC1, 2 and 3
in human breast cancer-overexpression of HDAC2 and HDAC3 is
associated with clinicopathological indicators of disease
progression. BMC Cancer. 13(215)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Qaddoori YB, Al-Khafaji ASK, Khashman BM
and Abdulghafour KH: The study of histone deacetylases
immunoexpression in relation to regulating vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF) implicated in malignant progression of
colorectal cancer. Iraqi J Sci. 66:1861–1875. 2025.
|
|
26
|
Qaddoori YB, Al-Khafaji ASK, Khashman BM
and Abdulghafour KH: The potential role of HDAC1 and HDAC3
Immunoexpression in P53 downregulation and tumor aggressiveness of
colon and rectum carcinomas patients. Exp Oncol. 46:393–401.
2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Rastogi B, Raut SK, Panda NK, Rattan V,
Radotra BD and Khullar M: Overexpression of HDAC9 promotes oral
squamous cell carcinoma growth, regulates cell cycle progression,
and inhibits apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 415:183–196.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chang HH, Chiang CP, Hung HC, Lin CY, Deng
YT and Kuo MY: Histone deacetylase 2 expression predicts poorer
prognosis in oral cancer patients. Oral Oncol. 45:610–614.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kelly WK, Richon VM, O'Connor O, Curley T,
MacGregor-Curtelli B, Tong W, Klang M, Schwartz L, Richardson S,
Rosa E, et al: Phase I clinical trial of histone deacetylase
inhibitor: Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid administered
intravenously. Clin Cancer Res. 9 (10 Pt 1):3578–3588.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Duvic M, Talpur R, Ni X, Zhang C, Hazarika
P, Kelly C, Chiao JH, Reilly JF, Ricker JL, Richon VM and Frankel
SR: Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic
acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood.
109:31–39. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
O'Connor OA, Horwitz S, Masszi T, Van Hoof
A, Brown P, Doorduijn J, Hess G, Jurczak W, Knoblauch P, Chawla S,
et al: Belinostat in patients with relapsed or refractory
peripheral T-Cell lymphoma: Results of the pivotal phase II BELIEF
(CLN-19) study. J Clin Oncol. 33:2492–2499. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Piekarz RL, Frye R, Turner M, Wright JJ,
Allen SL, Kirschbaum MH, Zain J, Prince HM, Leonard JP, Geskin LJ,
et al: Phase II multi-institutional trial of the histone
deacetylase inhibitor romidepsin as monotherapy for patients with
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 27:5410–5417.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
San-Miguel JF, Hungria VT, Yoon SS, Beksac
M, Dimopoulos MA, Elghandour A, Jedrzejczak WW, Günther A, Nakorn
TN, Siritanaratkul N, et al: Panobinostat plus bortezomib and
dexamethasone versus placebo plus bortezomib and dexamethasone in
patients with relapsed or relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma:
A multicentre, randomised, double-blind phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 15:1195–1206. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Eckschlager T, Plch J, Stiborova M and
Hrabeta J: Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int
J Mol Sci. 18(1414)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
National Library of Medicine (NIH):
Chemoprevention of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC)
With Valproic Acid (GAMA). NIH, Bethesda, MD, 2018. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02608736. Accessed
March 16, 2025.
|
|
36
|
Romoli M, Mazzocchetti P, D'Alonzo R,
Siliquini S, Rinaldi VE, Verrotti A, Calabresi P and Costa C:
Valproic acid and epilepsy: From molecular mechanisms to clinical
evidences. Curr Neuropharmacol. 17:926–946. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gurvich N, Tsygankova OM, Meinkoth JL and
Klein PS: Histone deacetylase is a target of valproic acid-mediated
cellular differentiation. Cancer Res. 64:1079–1086. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Duenas-Gonzalez A, Candelaria M,
Perez-Plascencia C, Perez-Cardenas E, de la Cruz-Hernandez E and
Herrera LA: Valproic acid as epigenetic cancer drug: Preclinical,
clinical and transcriptional effects on solid tumors. Cancer Treat
Rev. 34:206–222. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sang Z, Sun Y, Ruan H, Cheng Y, Ding X and
Yu Y: Anticancer effects of valproic acid on oral squamous cell
carcinoma via SUMOylation in vivo and in vitro. Exp Ther Med.
12:3979–3987. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
National Library of Medicine (NIH):
MAGE-C2 TCR T Cell Trial to Treat Melanoma and Head and Neck Cancer
(MC2TCR). NIH, Bethesda, MD, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04729543?cond=(head%20OR%20neck)%20AND%20cancer&term=(head%20OR%20neck)%20AND%20cancer&intr=Valproic%20Acid&page=1&rank=5).
Accessed March 16, 2025.
|
|
41
|
National Library of Medicine (NIH):
Repurposed Drugs to Improve Haematological Responses in
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (REPAIR-MDS). NIH, Bethesda, MD, 2023.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04997811?cond=Haematological%20Malignancy&term=Haematological%20Malignancy&intr=Valproic%20Acid&rank=1.
Accessed March 16, 2025.
|
|
42
|
Brodie SA and Brandes JC: Could valproic
acid be an effective anticancer agent? The evidence so far. Expert
Rev Anticancer Ther. 14:1097–1100. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kang H, Gillespie TW, Goodman M, Brodie
SA, Brandes M, Ribeiro M, Ramalingam SS, Shin DM, Khuri FR and
Brandes JC: Long-term use of valproic acid in US veterans is
associated with a reduced risk of smoking-related cases of head and
neck cancer. Cancer. 120:1394–1400. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Theocharis S, Klijanienko J, Giaginis C,
Rodriguez J, Jouffroy T, Girod A, Alexandrou P and Sastre-Garau X:
Histone deacetylase-1 and -2 expression in mobile tongue squamous
cell carcinoma: Associations with clinicopathological parameters
and patients survival. J Oral Pathol Med. 40:706–714.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
McCarthy C, Sacco J, Fedele S, Ho M,
Porter S, Liloglou T, Greenhalf B, Robinson M, Young B, Cicconi S,
et al: SAVER: Sodium valproate for the epigenetic reprogramming of
high-risk oral epithelial dysplasia-a phase II randomised control
trial study protocol. Trials. 22(428)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Al-Khafaji ASK, Wang LM, Alabdei HH and
Liloglou T: Effect of valproic acid on histone deacetylase
expression in oral cancer (Review). Oncol Lett.
27(197)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Dokmanovic M, Clarke C and Marks PA:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Overview and perspectives. Mol
Cancer Res. 5:981–989. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Iskar M, Campillos M, Kuhn M, Jensen LJ,
van Noort V and Bork P: Drug-induced regulation of target
expression. PLoS Comput Biol. 6(e1000925)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
McGregor F, Muntoni A, Fleming J, Brown J,
Felix DH, MacDonald DG, Parkinson EK and Harrison PR: Molecular
changes associated with oral dysplasia progression and acquisition
of immortality: Potential for its reversal by 5-azacytidine. Cancer
Res. 62:4757–4766. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Al-Khafaji ASK, Alnefaie G and Al-Shammari
AM: Valproic acid enhances the paclitaxel activity in respiratory
tract cancer cells. J Contemp Med Sci. 4:208–213. 2019.
|
|
51
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yoo CB and Jones PA: Epigenetic therapy of
cancer: Past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:37–50.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Gu M, Ren B, Fang Y, Ren J, Liu X, Wang X,
Zhou F, Xiao R, Luo X, You L and Zhao Y: Epigenetic regulation in
cancer. MedComm (2020). 5(e495)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Karagiannis TC, Kn H and El-Osta A: The
epigenetic modifier, valproic acid, enhances radiation sensitivity.
Epigenetics. 1:131–137. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Avallone A, Piccirillo MC, Di Gennaro E,
Romano C, Calabrese F, Roca MS, Tatangelo F, Granata V, Cassata A,
Cavalcanti E, et al: Randomized phase II study of valproic acid in
combination with bevacizumab and oxaliplatin/fluoropyrimidine
regimens in patients with RAS-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer:
The REVOLUTION study protocol. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
12(1758835920929589)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Ukey S, Ramteke A, Choudhury C, Purohit P
and Sharma P: Differential expression of zinc-dependent HDAC
subtypes and their involvement in unique pathways associated with
carcinogenesis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 23:877–883.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Castro LM, Gallant M and Niles LP: Novel
targets for valproic acid: Up-regulation of melatonin receptors and
neurotrophic factors in C6 glioma cells. J Neurochem. 95:1227–1236.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Ajamian F, Salminen A and Reeben M:
Selective regulation of class I and class II histone deacetylases
expression by inhibitors of histone deacetylases in cultured mouse
neural cells. Neurosci Lett. 365:64–68. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Jurkin J, Zupkovitz G, Lagger S,
Grausenburger R, Hagelkruys A, Kenner L and Seiser C: Distinct and
redundant functions of histone deacetylases HDAC1 and HDAC2 in
proliferation and tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle. 10:406–412.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Pinkerneil M, Hoffmann MJ, Deenen R,
Köhrer K, Arent T, Schulz WA and Niegisch G: Inhibition of Class I
Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 promotes urothelial carcinoma cell
death by various mechanisms. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:299–312.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Yang H, Maddipoti S, Quesada A, Bohannan
Z, Cabrero Calvo M, Colla S, Wei Y, Estecio M, Wierda W,
Bueso-Ramos C and Garcia-Manero G: Analysis of class I and II
histone deacetylase gene expression in human leukemia. Leuk
Lymphoma. 56:3426–3433. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Duong V, Bret C, Altucci L, Mai A,
Duraffourd C, Loubersac J, Harmand PO, Bonnet S, Valente S,
Maudelonde T, et al: Specific activity of class II histone
deacetylases in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res.
6:1908–1919. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Kwon HY, Kang NY, Dae HM, Kim KS, Kim CH,
Do SI and Lee Y: Valproic acid-mediated transcriptional regulation
of human GM3 synthase (hST3Gal V) in SK-N-BE(2)-C human
neuroblastoma cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:999–1005.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Li H, Wawrose JS, Gooding WE, Garraway LA,
Lui VWY, Peyser ND and Grandis JR: Genomic analysis of head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines and human tumors: A
rational approach to preclinical model selection. Mol Cancer Res.
12:571–582. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|