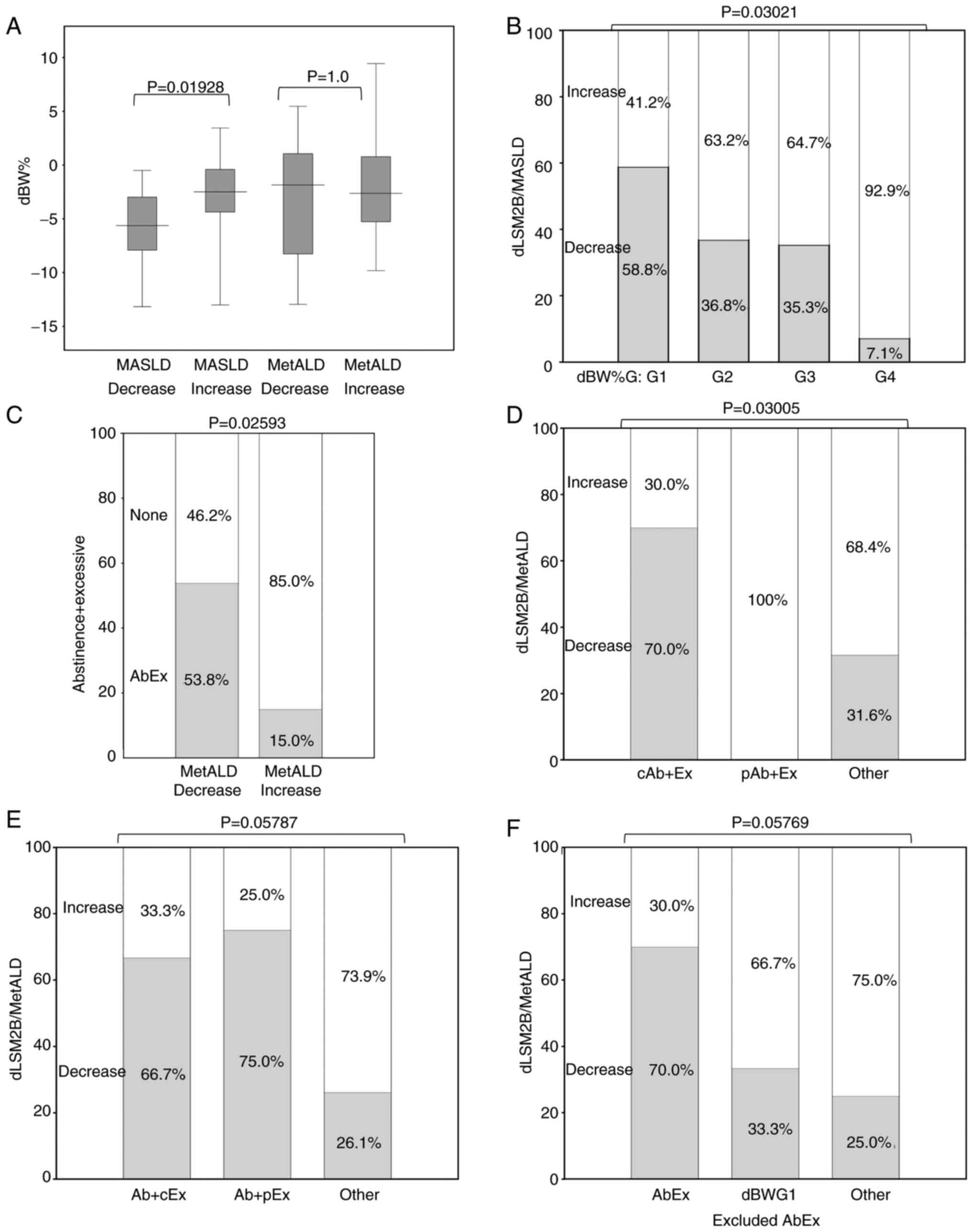
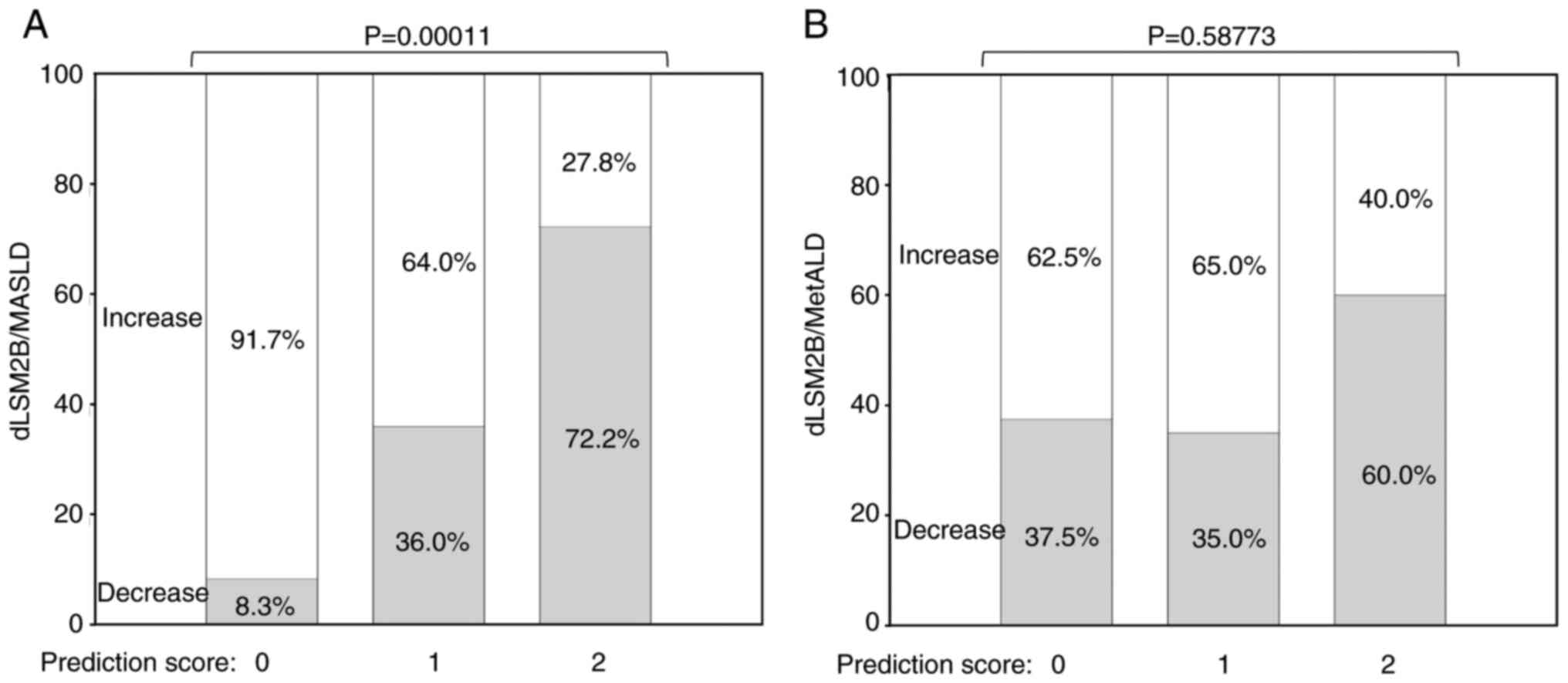
|
1
|
Rinella ME, Lazarus JV, Ratziu V, Francque
SM, Sanyal AJ, Kanwal F, Romero D, Abdelmalek MF, Anstee QM, Arab
JP, et al: A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty
liver disease nomenclature. J Hepatol. 79:1542–1556.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Marek GW and Malhi H: MetALD: Does it
require a different therapeutic option? Hepatology. 80:1424–1440.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gratacós-Ginès J, Ariño S, Sancho-Bru P,
Bataller R and Pose E: MetALD: Clinical aspects, pathophysiology
and treatment. JHEP Rep. 7(101250)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fukunaga S, Mukasa M, Nakane T, Nakano D,
Tsutsumi T, Chou T, Tanaka H, Hayashi D, Minami S, Ohuchi A, et al:
Impact of non-obese metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver
disease on risk factors for the recurrence of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma treated with endoscopic submucosal dissection: A
multicenter study. Hepatol Res. 54:201–212. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver (EASL). Tacke F, Horn P, Wai-Sun Wong V, Ratziu V, Bugianesi
E, Francque S, Zelber-Sagi S, Valenti L, Roden M, et al:
EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines on the management of
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J
Hepatol. 81:492–542. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu X, Zhang W, Ma B, Lv C, Sun M and
Shang Q: The value of serum Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation
isomer in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 15(1382293)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shephard DA: The 1975 declaration of
Helsinki and consent. Can Med Assoc J. 115:1191–1192.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B,
Verkarre V, Nalpas A, Dhalluin-Venier V, Fontaine H and Pol S:
FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV
infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology.
46:32–36. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Oh JH, Ahn SB, Cho S, Nah EH, Yoon EL and
Jun DW: Diagnostic performance of non-invasive tests in patients
with MetALD in a health check-up cohort. J Hepatol. 81:772–780.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Männistö V, Salomaa V, Jula A, Lundqvist
A, Männistö S, Perola M and Åberg F: ALT levels, alcohol use, and
metabolic risk factors have prognostic relevance for liver-related
outcomes in the general population. JHEP Rep.
6(101172)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Díaz LA, Lazarus JV, Fuentes-López E,
Idalsoaga F, Ayares G, Desaleng H, Danpanichkul P, Cotter TG, Dunn
W, Barrera F, et al: Disparities in steatosis prevalence in the
United States by Race or Ethnicity according to the 2023 criteria.
Commun Med (Lond). 4(219)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Choe HJ, Moon JH, Kim W, Koo BK and Cho
NH: Steatotic liver disease predicts cardiovascular disease and
advanced liver fibrosis: A community-dwelling cohort study with
20-year follow-up. Metabolism. 153(155800)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Israelsen M, Francque S, Tsochatzis EA and
Krag A: Steatotic liver disease. Lancet. 404:1761–1778.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Moon JH, Jeong S, Jang H, Koo BK and Kim
W: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
increases the risk of incident cardiovascular disease: A nationwide
cohort study. EClinicalMedicine. 65(102292)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rinella ME, Neuschwander-Tetri BA,
Siddiqui MS, Abdelmalek MF, Caldwell S, Barb D, Kleiner DE and
Loomba R: AASLD practice guidance on the clinical assessment and
management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.
77:1797–1835. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Huttasch M, Roden M and Kahl S: Obesity
and MASLD: Is weight loss the (only) key to treat metabolic liver
disease? Metabolism 157:. 155937(155937)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ogawa Y, Tomeno W, Imamura Y, Baba M, Ueno
T, Kobayashi T, Iwaki M, Nogami A, Kessoku T, Honda Y, et al:
Distribution of Fibrosis-4 index and vibration-controlled transient
elastography-derived liver stiffness measurement for patients with
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in health
check-up. Hepatol Res: Oct 4, 2024 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
18
|
Kaplan DE, Teerlink CC, Schwantes-An TH,
Norden-Krichmar TM, DuVall SL, Morgan TR, Tsao PS, Voight BF, Lynch
JA, Vujković M and Chang KM: Clinical and genetic risk factors for
progressive fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic
liver disease. Hepatol Commun. 8(e0487)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Younossi ZM, Paik JM, Henry L, Stepanova M
and Nader F: Pharmaco-economic assessment of screening strategies
for high-risk MASLD in primary care. Liver Int.
45(e16119)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Patel S, Kim RG, Shui AM, Magee C, Lu M,
Chen J, Tana M, Huang CY and Khalili M: Fatty liver education
promotes physical activity in vulnerable groups, including those
with unhealthy alcohol use. Gastro Hep Adv. 3:84–94.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shay JES, Vannier A, Tsai S, Mahle R, Diaz
PML, Przybyszewski E, Challa PK, Patel SJ, Suzuki J, Schaefer E, et
al: Moderate-high intensity exercise associates with reduced
incident alcohol-associated liver disease in high-risk patients.
Alcohol Alcohol. 58:472–477. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Frith J, Day CP, Robinson L, Elliott C,
Jones DEJ and Newton JL: Potential strategies to improve uptake of
exercise interventions in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J
Hepatol. 52:112–116. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Beygi M, Ahi S, Zolghadri S and Stanek A:
Management of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease/metabolic
dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: From medication
therapy to nutritional interventions. Nutrients.
16(2220)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Marti-Aguado D, Calleja JL, Vilar-Gomez E,
Iruzubieta P, Rodríguez-Duque JC, Del Barrio M, Puchades L,
Rivera-Esteban J, Perelló C, Puente A, et al: Low-to-moderate
alcohol consumption is associated with increased fibrosis in
individuals with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver
disease. J Hepatol. 81:930–940. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Griswold MG, Fullman N, Hawley C, Arian N,
Zimsen SRM, Tymeson HD, Venkateswaran V, Tapp AD, Forouzanfar MH,
Salama JS and Abate KH: Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries
and territories, 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the global
burden of disease study 2016. Lancet. 392:1015–1035.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Díaz LA, Arab JP, Louvet A, Bataller R and
Arrese M: The intersection between alcohol-related liver disease
and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 20:764–783. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Arab JP, Díaz LA, Rehm J, Im G, Arrese M,
Kamath PS, Lucey MR, Mellinger J, Thiele M, Thursz M, et al:
Metabolic dysfunction and alcohol-related liver disease (MetALD):
Position statement by an expert panel on alcohol-related liver
disease. J Hepatol. 82:744–756. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Adamson SJ, Heather N, Morton V and
Raistrick D: UKATT Research Team. Initial preference for drinking
goal in the treatment of Alcohol problems: II. Treatment outcomes.
Alcohol Alcohol. 45:136–142. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Haber PS: Identification and treatment of
alcohol use disorder. N Engl J Med. 392:258–266. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu M, Ye Z, Zhang Y, He P, Zhou C, Yang
S, Zhang Y, Gan X and Qin X: Accelerometer-derived
moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and incident nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. BMC Med. 22(398)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Stine JG, Schreibman IR, Faust AJ, Dahmus
J, Stern B, Soriano C, Rivas G, Hummer B, Kimball SR, Geyer NR, et
al: NASHFit: A randomized controlled trial of an exercise training
program to reduce clotting risk in patients with NASH. Hepatology.
76:172–185. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Nakano M, Kawaguchi M, Kawaguchi T and
Yoshiji H: Profiles associated with significant hepatic fibrosis
consisting of alanine aminotransferase >30 U/l, exercise habits,
and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
Hepatol Res. 54:655–666. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim SY and Kim HJ: Obesity risk was
associated with alcohol intake and sleep duration among Korean men:
The 2016-2020 Korea national health and nutrition examination
survey. Nutrients. 16(3950)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Miller-Matero LR, Yeh HH, Ma L, Jones RA,
Nadolsky S, Medcalf A, Foster GD and Cardel MI: Alcohol use and
antiobesity medication treatment. JAMA Netw Open.
7(e2447644)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Avitabile E, Gratacós-Ginès J,
Pérez-Guasch M, Belén Rubio A, Herms Q, Cervera M, Nadal R, Carol
M, Fabrellas N, Bruguera P, et al: Liver fibrosis screening
increases alcohol abstinence. JHEP Rep. 6(101165)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|