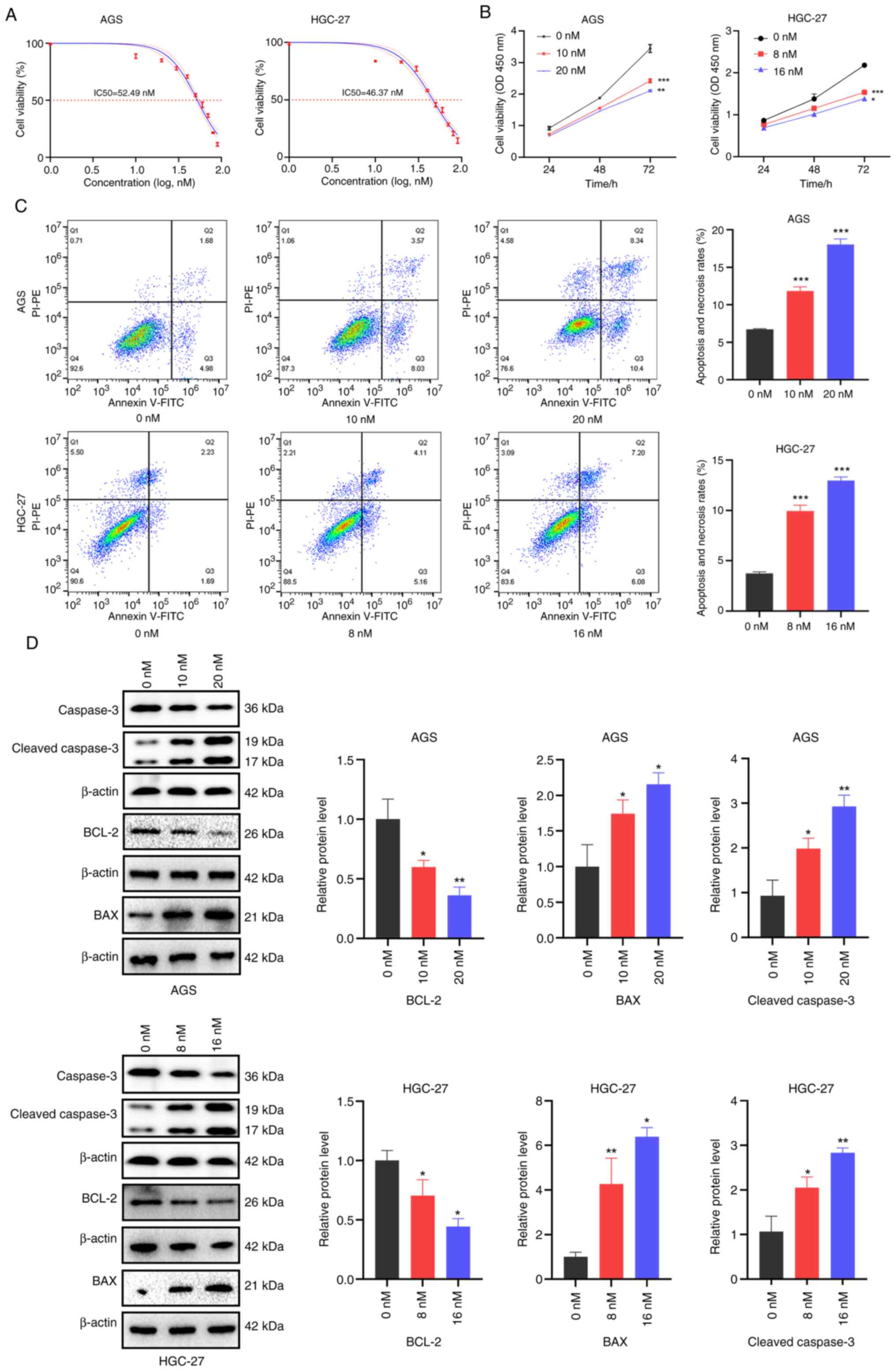
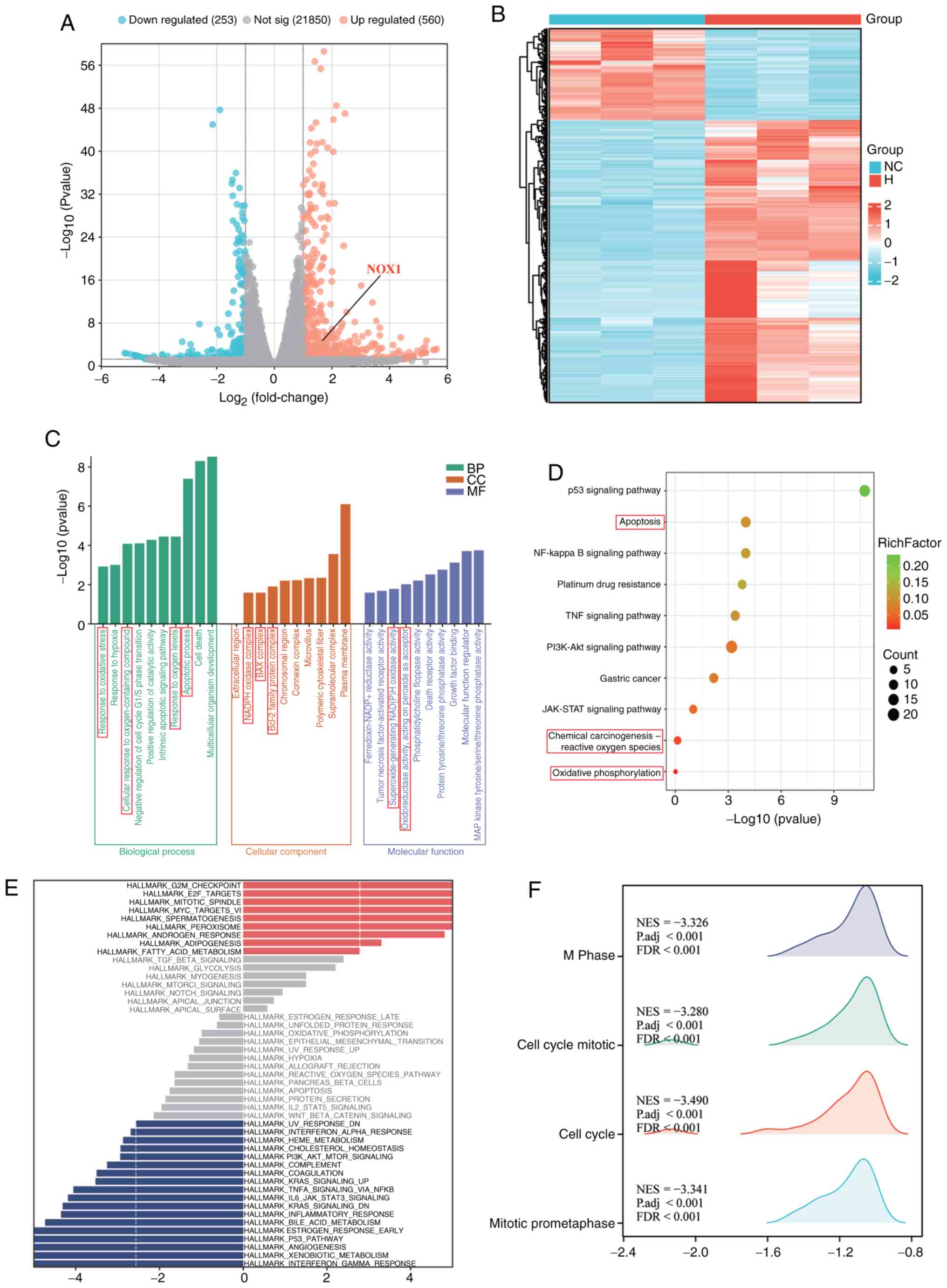
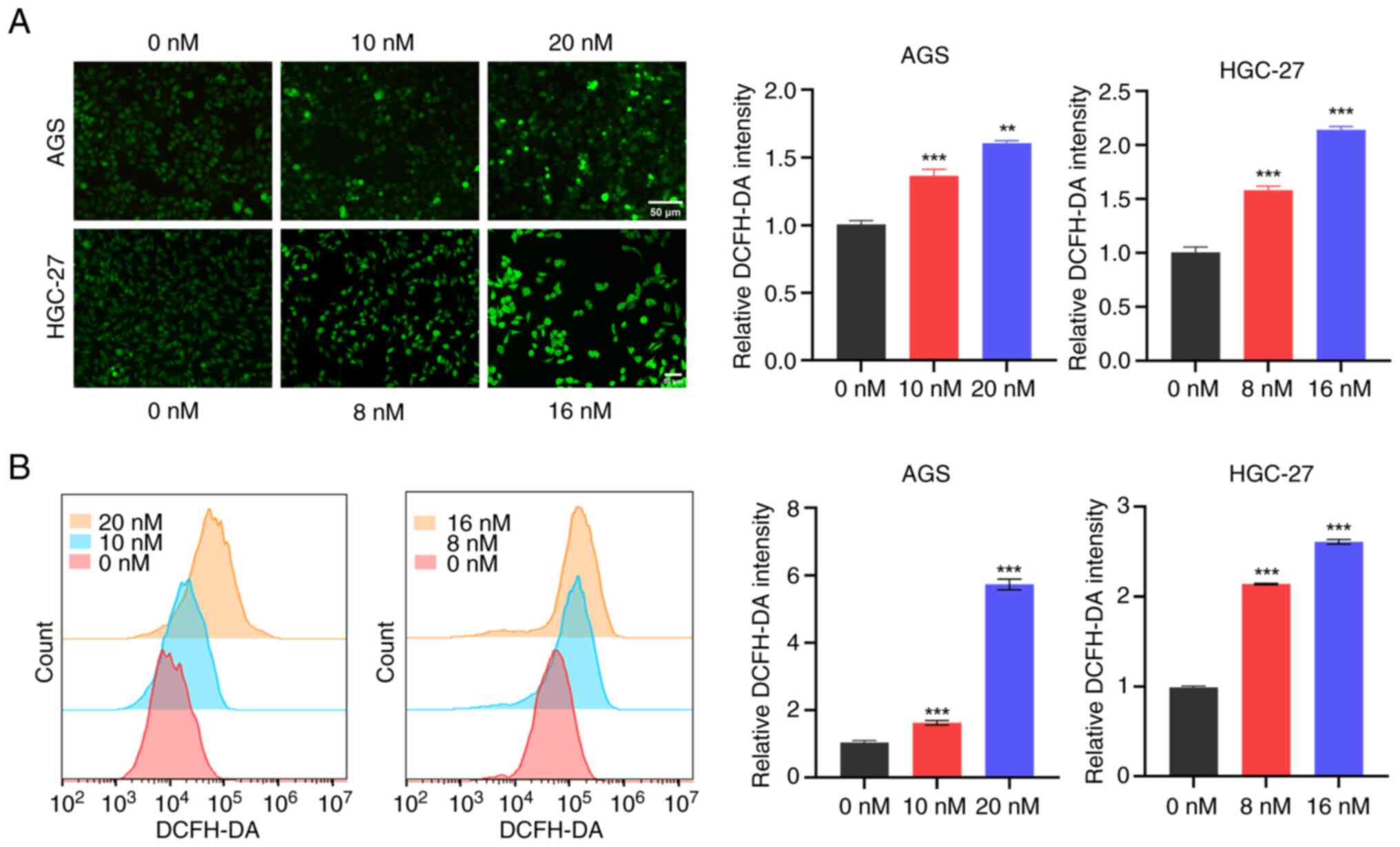
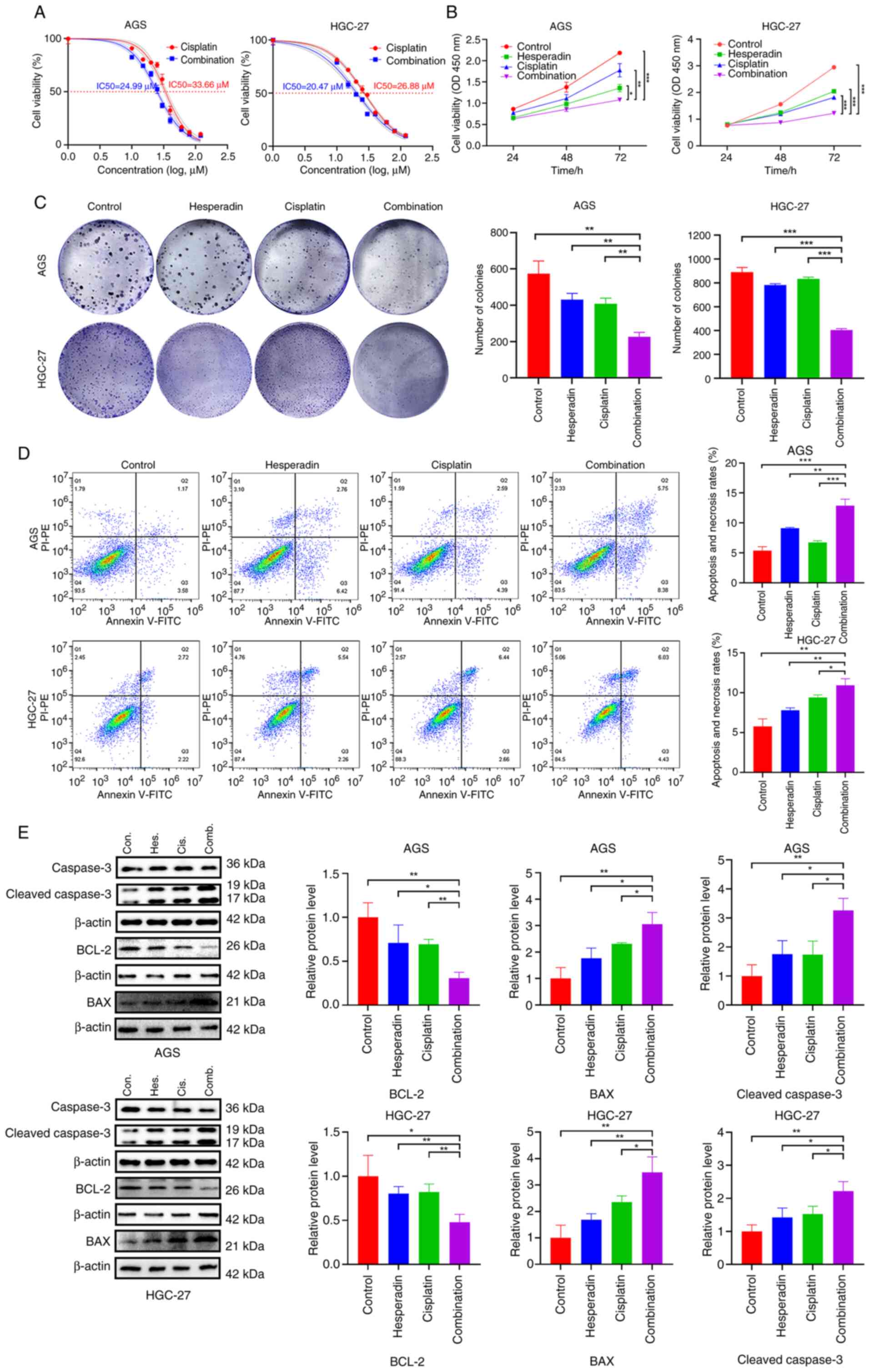
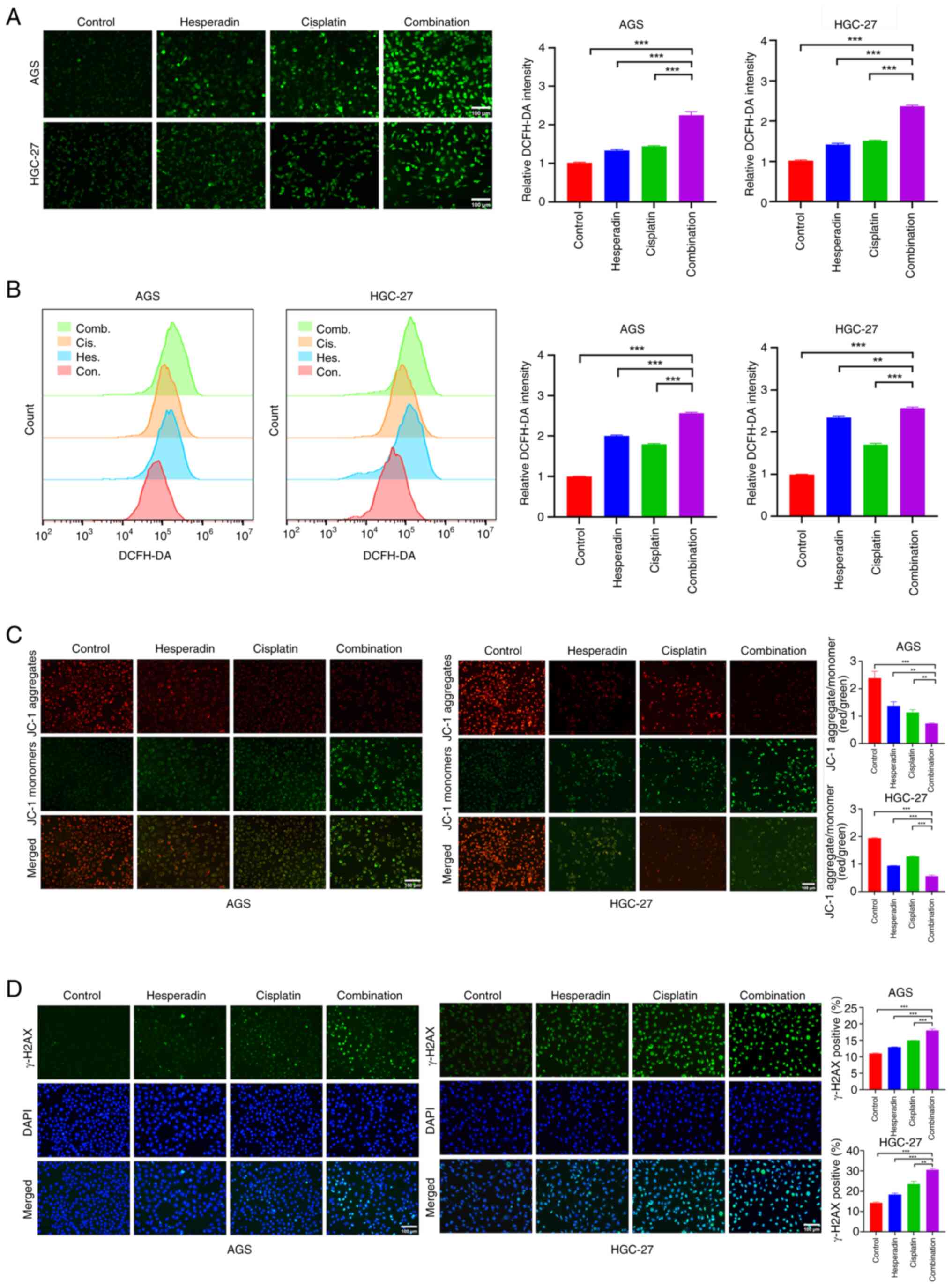
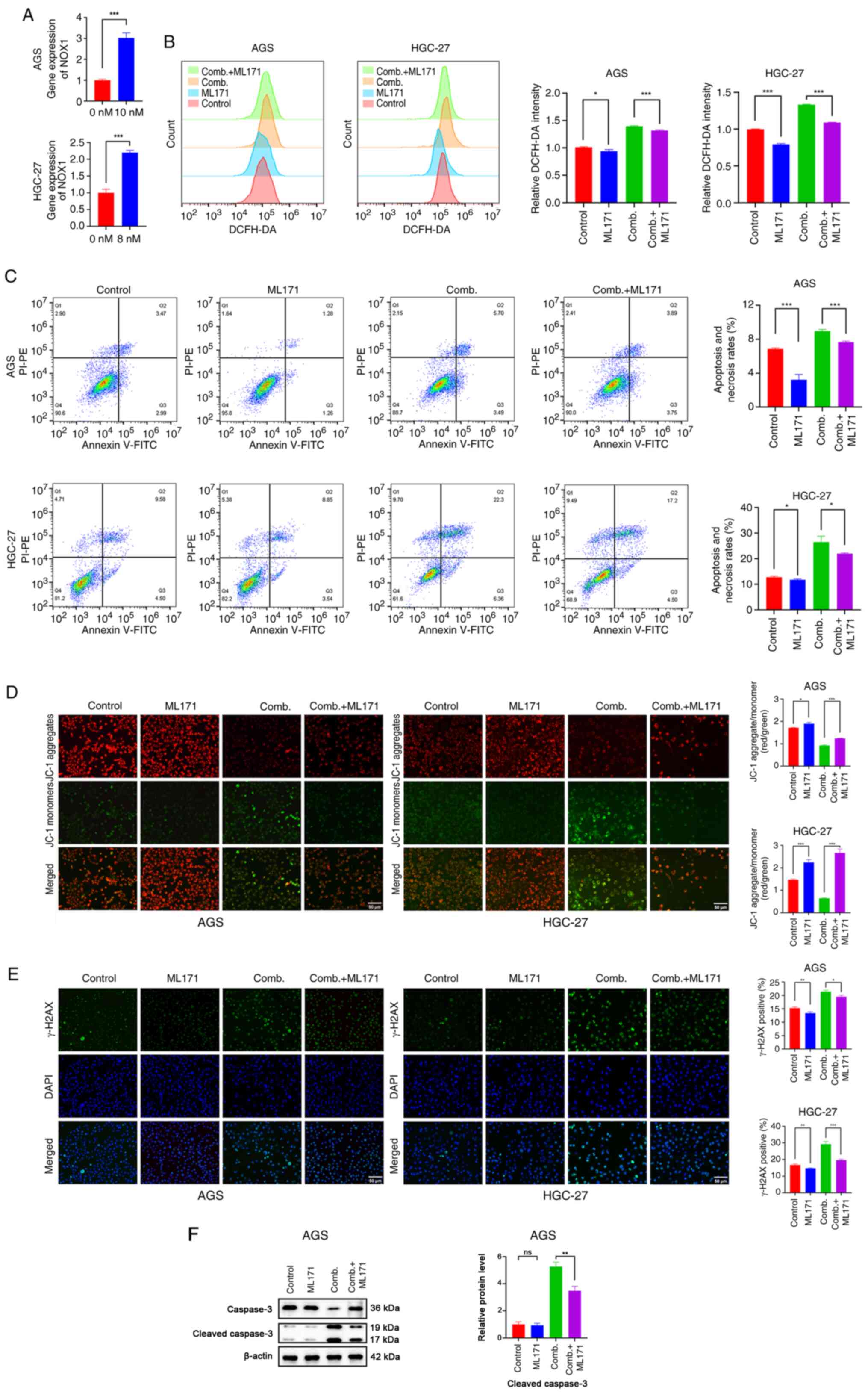
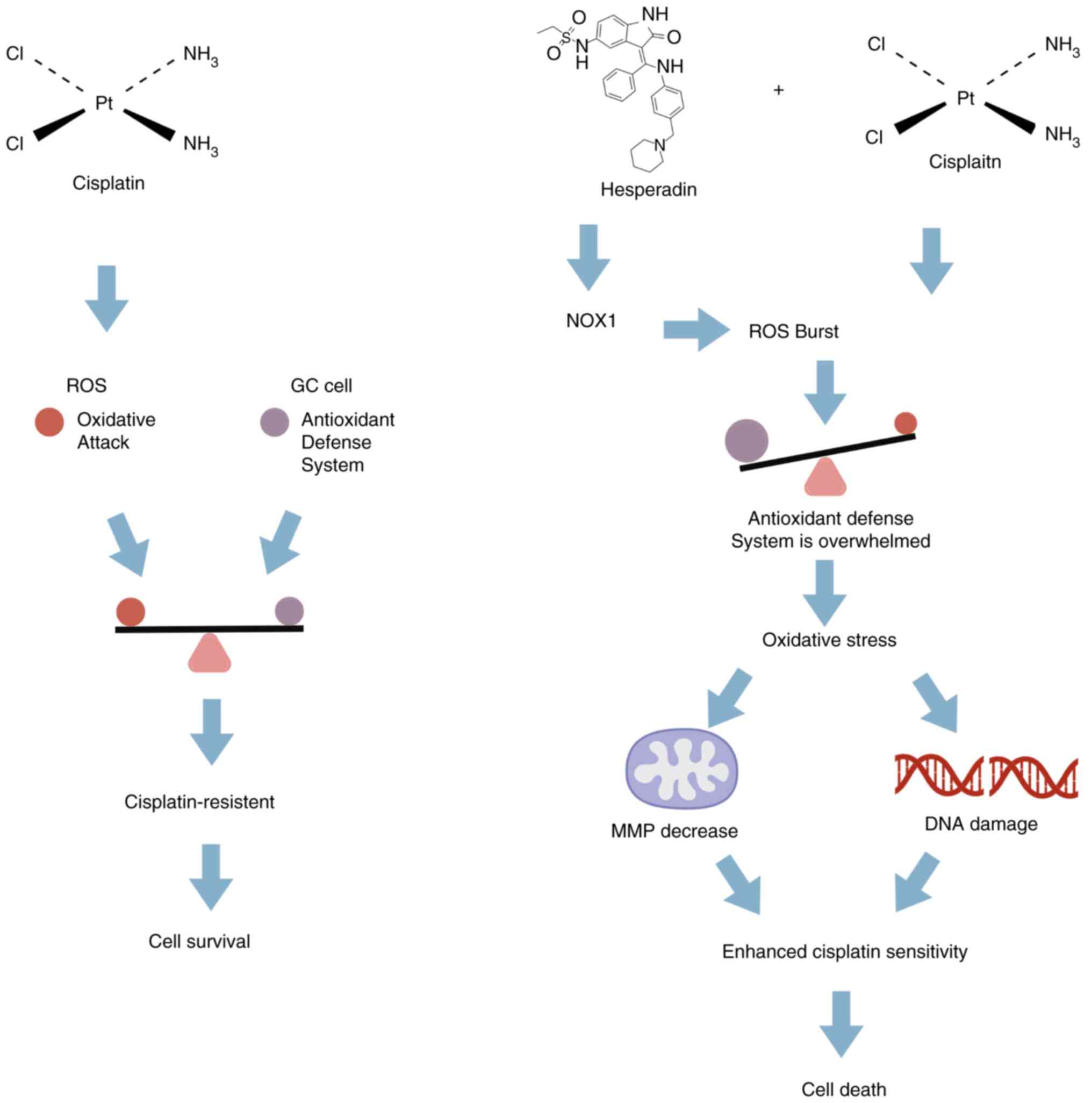
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Digklia A and Wagner AD: Advanced gastric
cancer: Current treatment landscape and future perspectives. World
J Gastroenterol. 22:2403–2414. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lei ZN, Teng QX, Tian Q, Chen W, Xie Y, Wu
K, Zeng Q, Zeng L, Pan Y, Chen ZS and He Y: Signaling pathways and
therapeutic interventions in gastric cancer. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 7(358)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Huang R and Zhou PK: DNA damage repair:
Historical perspectives, mechanistic pathways and clinical
translation for targeted cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 6(254)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Peña Q, Wang A, Zaremba O, Shi Y, Scheeren
HW, Metselaar JM, Kiessling F, Pallares RM, Wuttke S and Lammers T:
Metallodrugs in cancer nanomedicine. Chem Soc Rev. 51:2544–2582.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ruhlmann CH, Iversen TZ, Okera M, Muhic A,
Kristensen G, Feyer P, Hansen O and Herrstedt J: Multinational
study exploring patients' perceptions of side-effects induced by
chemo-radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 117:333–337. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shahid M, Subhan F, Ahmad N and Sewell
RDE: The flavonoid 6-methoxyflavone allays cisplatin-induced
neuropathic allodynia and hypoalgesia. Biomed Pharmacother.
95:1725–1733. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yu C, Dong H, Wang Q, Bai J, Li YN, Zhao
JJ and Li JZ: Danshensu attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity
through activation of Nrf2 pathway and inhibition of NF-κB. Biomed
Pharmacother. 142(111995)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang H, Zhang Z, Wei X and Dai R:
Small-molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2 (TW-37) suppresses growth and
enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. J
Ovarian Res. 8(3)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shi S, Bai X, Ji Q, Wan H, An H, Kang X
and Guo S: Molecular mechanism of ion channel protein TMEM16A
regulated by natural product of narirutin for lung cancer adjuvant
treatment. Int J Biol Macromol. 223:1145–1157. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bai X, Liu Y, Cao Y, Ma Z, Chen Y and Guo
S: Exploring the potential of cryptochlorogenic acid as a dietary
adjuvant for multi-target combined lung cancer treatment.
Phytomedicine. 132(155907)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Morahan BJ, Abrie C, Al-Hasani K, Batty
MB, Corey V, Cowell AN, Niemand J, Winzeler EA, Birkholtz LM,
Doerig C and Garcia-Bustos JF: Human Aurora kinase inhibitor
hesperadin reveals epistatic interaction between Plasmodium
falciparum PfArk1 and PfNek1 kinases. Commun Biol.
3(701)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wu X, Wu J, Hu W, Wang Q, Liu H, Chu Z, Lv
K and Xu Y: MST4 kinase inhibitor Hesperadin attenuates autophagy
and behavioral disorder via the MST4/AKT pathway in intracerebral
hemorrhage mice. Behav Neurol. 2020(2476861)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chhajer R, Bhattacharyya A and Ali N: Cell
death in Leishmania donovani promastigotes in response to Mammalian
Aurora kinase B inhibitor-Hesperadin. Biomed Pharmacother.
177(116960)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Liang R, Wang K, Zhang W, Zhang
M, Jin L, Xie P, Zheng W, Shang H, Hu Q, et al: Novel CaMKII-δ
inhibitor Hesperadin exerts dual functions to ameliorate cardiac
ischemia/reperfusion injury and inhibit tumor growth. Circulation.
145:1154–1168. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Wu J, Fu Y, Yu R, Su H, Zheng Q,
Wu H, Zhou S, Wang K, Zhao J, et al: Hesperadin suppresses
pancreatic cancer through ATF4/GADD45A axis at nanomolar
concentrations. Oncogene. 41:3394–3408. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li J, Jia YC, Ding YX, Bai J, Cao F and Li
F: The crosstalk between ferroptosis and mitochondrial dynamic
regulatory networks. Int J Biol Sci. 19:2756–2771. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
To TL, Cuadros AM, Shah H, Hung WHW, Li Y,
Kim SH, Rubin DHF, Boe RH, Rath S, Eaton JK, et al: A compendium of
genetic modifiers of mitochondrial dysfunction reveals
intra-organelle buffering. Cell. 179:1222–1238.e17. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wagner AD, Syn NL, Moehler M, Grothe W,
Yong WP, Tai BC, Ho J and Unverzagt S: Chemotherapy for advanced
gastric cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
8(CD004064)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Al-Batran SE, Homann N, Pauligk C, Goetze
TO, Meiler J, Kasper S, Kopp HG, Mayer F, Haag GM, Luley K, et al:
Perioperative chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus leucovorin,
oxaliplatin, and docetaxel versus fluorouracil or capecitabine plus
cisplatin and epirubicin for locally advanced, resectable gastric
or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (FLOT4): A
randomised, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet. 393:1948–1957. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hauf S, Cole RW, LaTerra S, Zimmer C,
Schnapp G, Walter R, Heckel A, van Meel J, Rieder CL and Peters JM:
The small molecule Hesperadin reveals a role for Aurora B in
correcting kinetochore-microtubule attachment and in maintaining
the spindle assembly checkpoint. J Cell Biol. 161:281–294.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ladygina NG, Latsis RV and Yen T: Effect
of the pharmacological agent hesperadin on breast and prostate
tumor cultured cells. Biomed Khim. 51:170–176. 2005.PubMed/NCBI(In Russian).
|
|
25
|
Hu Y, Zhang J, Musharrafieh R, Hau R, Ma C
and Wang J: Chemical genomics approach leads to the identification
of Hesperadin, an Aurora B kinase inhibitor, as a broad-spectrum
influenza antiviral. Int J Mol Sci. 18(1929)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim HJ, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Oh GS, Moon HD,
Kwon KB, Park C, Park BH, Lee HK, Chung SY, et al: Roles of NADPH
oxidases in cisplatin-induced reactive oxygen species generation
and ototoxicity. J Neurosci. 30:3933–3946. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen TM, Huang CM, Setiawan SA, Hsieh MS,
Sheen CC and Yeh CT: KDM5D histone demethylase identifies
platinum-tolerant head and neck cancer cells vulnerable to mitotic
catastrophe. Int J Mol Sci. 24(5310)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Han X, Zhang JJ, Han ZQ, Zhang HB and Wang
ZA: Let-7b attenuates cisplatin resistance and tumor growth in
gastric cancer by targeting AURKB. Cancer Gene Ther. 25:300–308.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Erickson JR, Joiner ML, Guan X, Kutschke
W, Yang J, Oddis CV, Bartlett RK, Lowe JS, O'Donnell SE,
Aykin-Burns N, et al: A dynamic pathway for calcium-independent
activation of CaMKII by methionine oxidation. Cell. 133:462–474.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Anderson ME, Brown JH and Bers DM: CaMKII
in myocardial hypertrophy and heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
51:468–473. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang Z, Zhao X, Gao M, Xu L, Qi Y, Wang J
and Yin L: Dioscin alleviates myocardial infarction injury via
regulating BMP4/NOX1-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation.
Phytomedicine. 103(154222)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Drummond GR, Selemidis S, Griendling KK
and Sobey CG: Combating oxidative stress in vascular disease: NADPH
oxidases as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 10:453–471.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jiang S, Li H, Zhang L, Mu W, Zhang Y,
Chen T, Wu J, Tang H, Zheng S, Liu Y, et al: Generic diagramming
platform (GDP): A comprehensive database of high-quality biomedical
graphics. Nucleic Acids Res. 53 (D1):D1670–D1676. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|