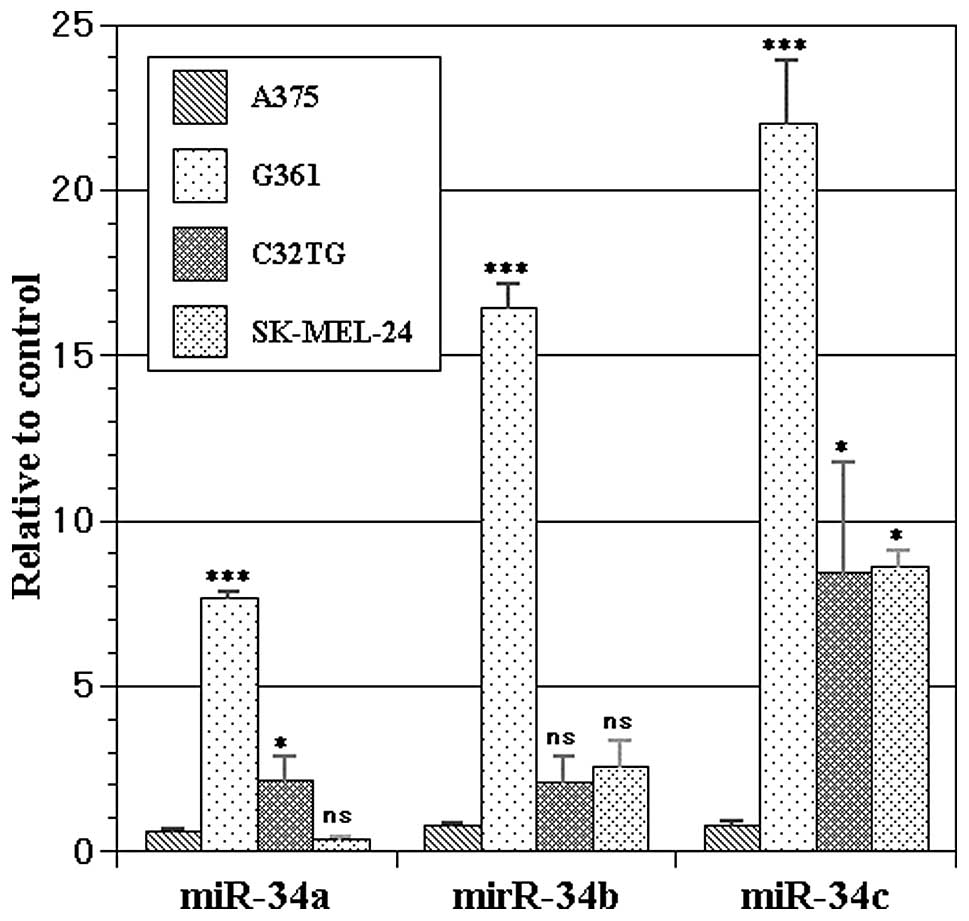
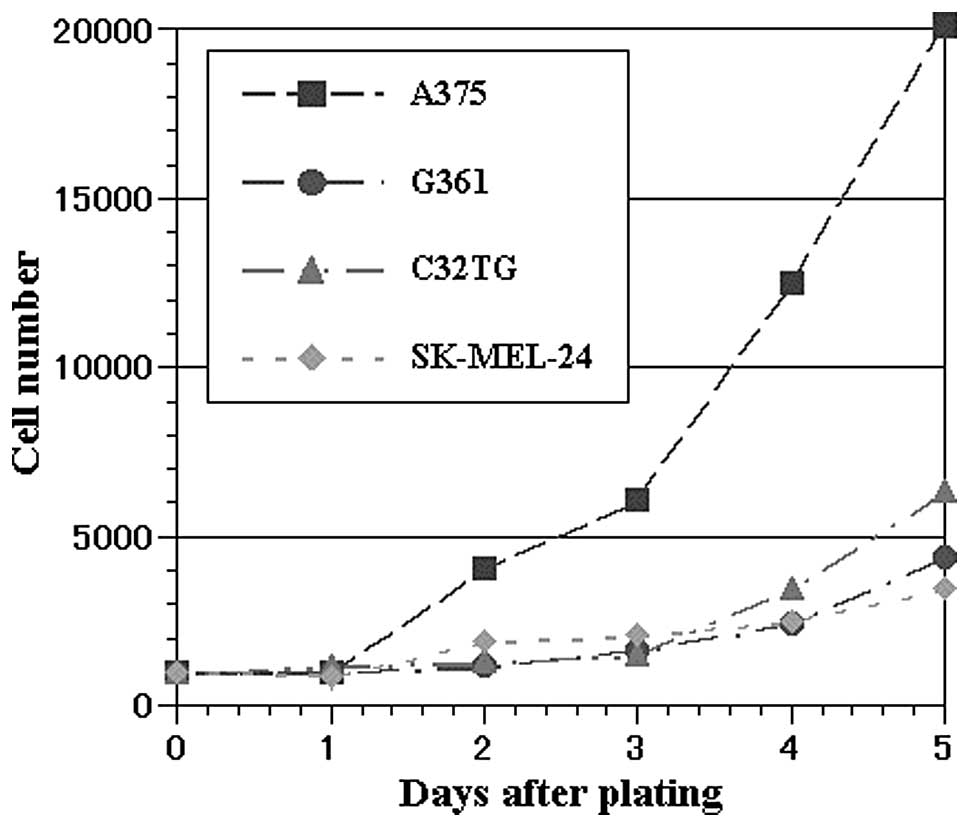
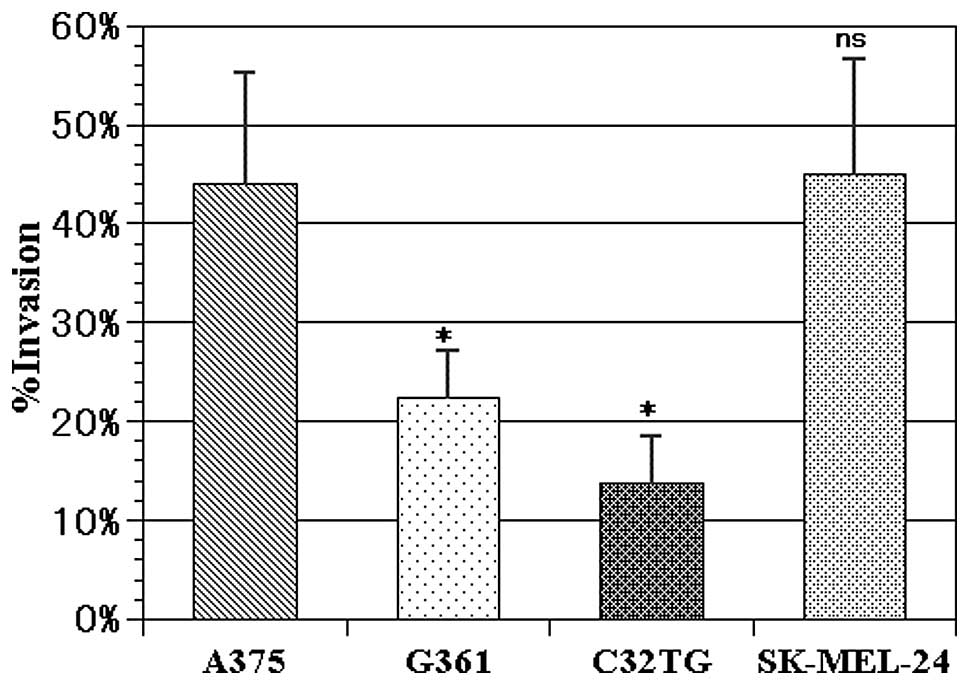
|
1.
|
Hermeking H: p53 enters the microRNA
world. Cancer Cell. 12:414–418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Fabbri M, Croce CM and Calin GA:
MicroRNAs. Cancer J. 14:1–6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Mueller DW and Bosserhoff AK: Role of
miRNAs in the progression of malignant melanoma. Br J Cancer.
101:551–556. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Yamashita T, Tokino T, Tonoki H, et al:
Induction of apoptosis in melanoma cell lines by p53 and its
related proteins. J Invest Dermatol. 117:914–919. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Min FL, Zhang H, Li WJ, Gao QX and Zhou
GM: Effect of exogenous wild-type p53 on melanoma cell death
pathways induced by irradiation at different linear energy
transfer. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 41:284–288. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Miyato Y and Ando K: Apoptosis of human
melanoma cells by a combination of lonidamine and radiation. J
Radiat Res (Tokyo). 45:189–194. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Monney L, Sabatos CA, Gaglia JL, et al:
Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates macrophage
activation and severity of an autoimmune disease. Nature.
415:536–541. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Chijiwa T, Abe Y, Ikoma N, et al:
Thrombospondin 2 inhibits metastasis of human malignant melanoma
through microenvironment-modification in NOD/SCID/γCnull (NOG)
mice. Int J Oncol. 34:5–13. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ikoma N, Yamazaki H, Abe Y, et al: S100A4
expression with reduced E-cadherin expression predicts distant
metastasis of human malignant melanoma cell lines in the
NOD/SCID/γCnull (NOG) mouse model. Oncol Rep. 14:633–637.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Dominguez-Sola D, Ying CY, Grandori C, et
al: Non-transcriptional control of DNA replication by c-Myc.
Nature. 448:445–451. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Ho J and Benchimol S: Transcriptional
repression mediated by the p53 tumour suppressor. Cell Death
Differ. 10:404–408. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Chen K and Rajewsky N: The evolution of
gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev
Genet. 8:93–103. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
siRNAs. Genes Dev. 20:515–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Bommer GT, Gerin I, Feng Y, et al:
p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor
genes. Curr Biol. 17:1298–1307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Chang TC, Wentzel EA, Kent OA, et al:
Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene
expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol Cell. 26:745–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Corney DC, Flesken-Nikitin A, Godwin AK,
Wang W and Nikitin AY: MicroRNA-34b and microRNA-34c are targets of
p53 and cooperate in control of cell proliferation and
adhesion-independent growth. Cancer Res. 67:8433–8438. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Raver-Shapira N, Marciano E, Meiri E, et
al: Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to
p53-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell. 26:731–743. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Tarasov V, Jung P, Verdoodt B, et al:
Differential regulation of microRNAs by p53 revealed by massively
parallel sequencing: miR-34a is a p53 target that induces apoptosis
and G1-arrest. Cell Cycle. 6:1586–1593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M and
Nakagama H: Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like
growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15472–15477. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Bagchi A and Mills AA: The quest for the
1p36 tumor suppressor. Cancer Res. 68:2551–2556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Zhou Z, Flesken-Nikitin A, Corney DC, et
al: Synergy of p53 and Rb deficiency in a conditional mouse model
for metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 66:7889–7898. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Sun F, Fu H, Liu Q, et al: Downregulation
of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett.
582:1564–1568. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Pigazzi M, Manara E, Baron E and Basso G:
miR-34b targets cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein in
acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 69:2471–2478. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Bemis LT, Chen R, Amato CM, et al:
MicroRNA-137 targets microphthalmia-associated transcription factor
in melanoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 68:1362–1368. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Segura MF, Hanniford D, Menendez S, et al:
Aberrant miR-182 expression promotes melanoma metastasis by
repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated transcription
factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:1814–1819. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Lodygin D, Tarasov V, Epanchintsev A, et
al: Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple
types of cancer. Cell Cycle. 7:2591–2600. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Migliore C, Petrelli A, Ghiso E, et al:
MicroRNAs impair MET-mediated invasive growth. Cancer Res.
68:10128–10136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Yan D, Zhou X, Chen X, et al: MicroRNA-34a
inhibits uveal melanoma cell proliferation and migration through
downregulation of c-Met. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:1559–1565.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Fujita Y, Kojima K, Hamada N, et al:
Effects of miR-34a on cell growth and chemoresistance in prostate
cancer PC3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 377:114–119. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Kozaki K, Imoto I, Mogi S, Omura K and
Inazawa J: Exploration of tumor-suppressive microRNAs silenced by
DNA hypermethylation in oral cancer. Cancer Res. 68:2094–2105.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Toyota M, Suzuki H, Sasaki Y, et al:
Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-34b/c and B-cell translocation
gene 4 is associated with CpG island methylation in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 68:4123–4132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|