Introduction
Acute urinary retention (AUR) is a common
complication in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
(1,2). Previous studies have shown that
>10% of men >70 years old experience at least one episode of
AUR over a 5-year period and this risk increases to one-third of
men over a 10-year period (3).
Urinary retention induces an increase of
intravesical pressure, which may affect renal function and
morphology. Chronic urinary retention may impair renal function and
lead to terminal kidney failure within a few years (4). Whether AUR results in an impairment
of renal function and morphology requires investigation. A previous
study observed that AUR affects glomerular and tubular renal
function, which results in elevated urinary albumin excretion.
Following AUR, glomerular permeability and tubular damage persists
in the majority of patients (5).
Data concerning renal function and morphology, however, remain
scarce for AUR.
In clinical practice, the majority of patients with
AUR are treated with catheterization (6). However, the durations of AUR prior to
intervention differ markedly among patients due to differences in
medical history and pain tolerance. Whether different AUR durations
result in different impairments of renal function or morphology
remains unclear; little has been published in the literature. In
the current study, a rat model was used to investigate the effect
of the duration of bladder overdistention (DOBO) on renal function
and morphology, which may partly clarify this clinical uncertainty
and provide information concerning the mechanisms involved in the
impairment.
Materials and methods
Animal model
Studies were performed on male Sprague-Dawley rats
weighing 200–250 g (n=40). All rats received a standard diet, water
ad libitum and were housed in a 12 h light/dark cycle. All
animal care and experimental protocols were in accordance with the
guidelines of Zhejiang University (Hangzhou, China). The 40 rats
were allocated to five groups: the sham-operated control and DOBO
1, 2, 4 and 8 h groups (each n=8). Rats were anesthetized with
urethane (1.0 g/kg i.p.) and anesthesia was maintained by
supplementary injections of the same anesthetic. Once anesthetized,
the rats were shaved for kidney Doppler ultrasound. The rat bladder
was identified with a low midline abdominal incision. After
emptying the bladder, the foreskin was ligated using 3-0 silk
thread. A 24-G catheter was inserted into the apex of the bladder
dome. The catheter was connected to an infusion pump, then 37°C
0.9% saline was infused (0.1 ml/min) until the total volume reached
1 ml. This was twice the mean bladder capacity of 0.5 ml
established in preliminary experiments. The status of
overdistention was maintained for 1, 2, 4 and 8 h, respectively. In
the rats of the control group, the bladder was exposed and
punctured but no saline was infused.
Doppler ultrasound detection
Kidney ultrasound was applied to all rats 0.5 h
after the overdistention was relieved. The kidney length, width and
cortex thickness were measured. Renal size was calculated using the
following formula: Renal size (cm3) = renal length (cm)
× renal width (cm) × cortex thickness (cm)/6. At the same time, the
thicknesses of the cortex and hydronephrosis levels were measured.
Furthermore, Doppler ultrasound with a V4 MHz transducer was used
to calculate the resistant index (RI) of the main renal artery
(MRA), inter lobular artery (IRA) and segmental renal artery (SRA).
The RI was calculated with the following formula: RI = (peak
systolic shift − minimum diastolic shift)/peak systolic shift
(4).
Renal function test
Blood samples were collected and stored at 4°C until
examination. Serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
were measured by the Department of Clinical Chemistry using an
enzymatic method.
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl
transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) assay
Apoptosis was detected using the TUNEL assay.
Formalin-fixed, paraffin wax-embedded tissue sections were
deparaffinized and stained using the TUNEL-avidin-biotin-complex
method. Ten high-power (×400) fields were randomly selected in one
section. The numbers of apoptotic cells, defined by chromatin
condensation or nuclear fragmentation were counted. The apoptotic
index was calculated as follows: Apoptotic index = number of
positive cells/total number of cells × 100.
Transmission electron microscopy
(TEM)
To observe the ultra-structure of the bladder
tissues, sections were stained with uranyl acetate and plumbic
citrate and examined using TEM (TECNAI 10, Philips, Amsterdam, The
Netherlands).
Statistical analysis
All results are expressed as the mean ± standard
error of the mean (SEM). The statistical significance of the
difference between two variables was determined using the unpaired
Student’s t-test. One-way ANOVA was used to compare variables among
more than two groups. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant result.
Results
Survival
All rats survived and data were collected, with the
exception of one rat in the 8 h overdistention group.
Doppler ultrasound detection
DOBO had significant effects on renal volume, the
degree of separation of the pelvis and cortical thickness (Table I). Compared with the control, the
renal size in the rats with 2, 4 or 8 h DOBO was significantly
increased (P<0.05). Compared with the DOBO 1 h group, the DOBO 4
and 8 h groups demonstrated significant increases in renal size
(P<0.05). A significant difference was also observed between the
DOBO 2 h group and the DOBO 4 and 8 h groups (P<0.05).
Furthermore, rats with a DOBO of 2, 4 or 8 h showed a significantly
higher degree of separation of the pelvis than the controls
(P<0.05); significant differences were also observed between the
DOBO 1 h group and the 2, 4 and 8 h groups (P<0.05). Cortical
thicknesses showed no significant differences among the groups,
however. Different overdistention durations had different effects
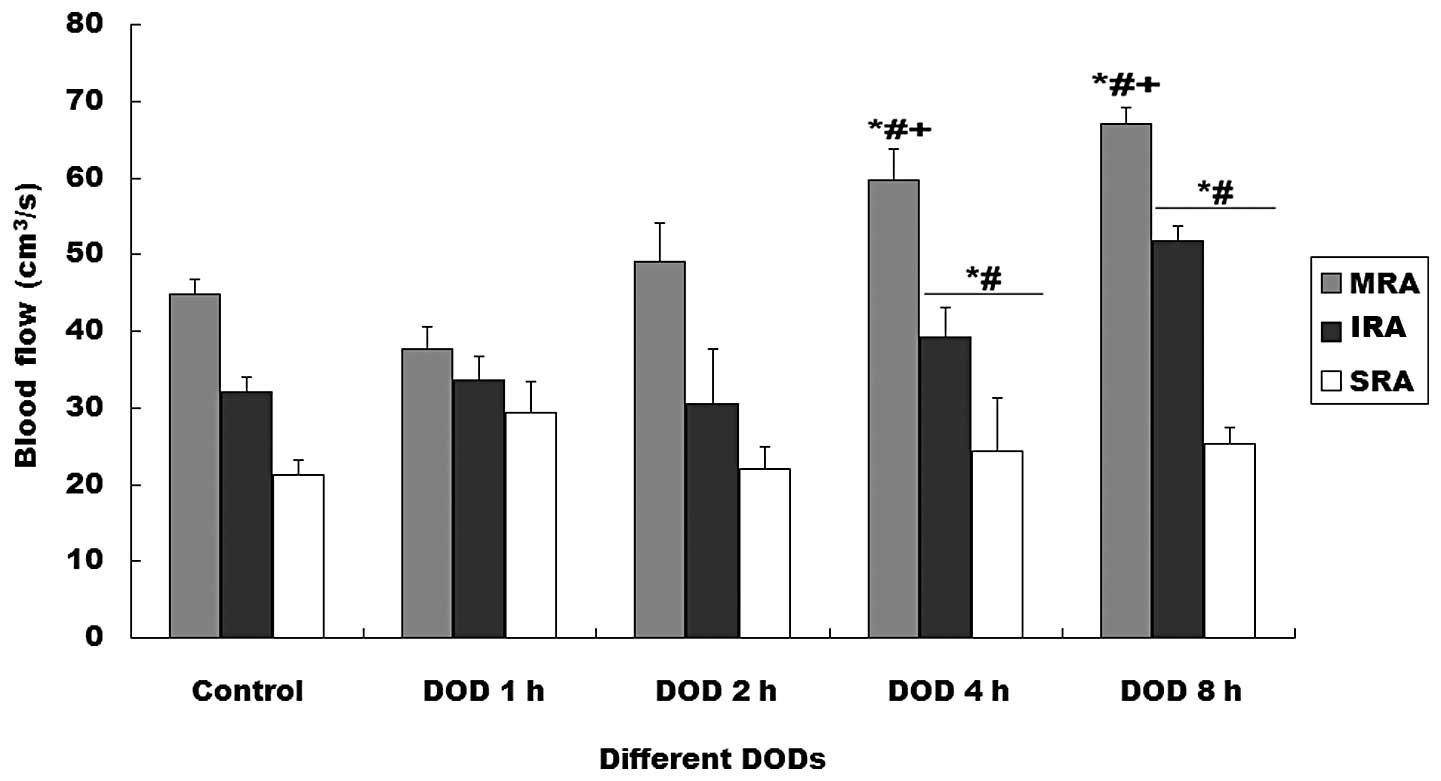
on the blood flow of the renal arteries (Fig. 1). Blood flow in the MRA, IRA and
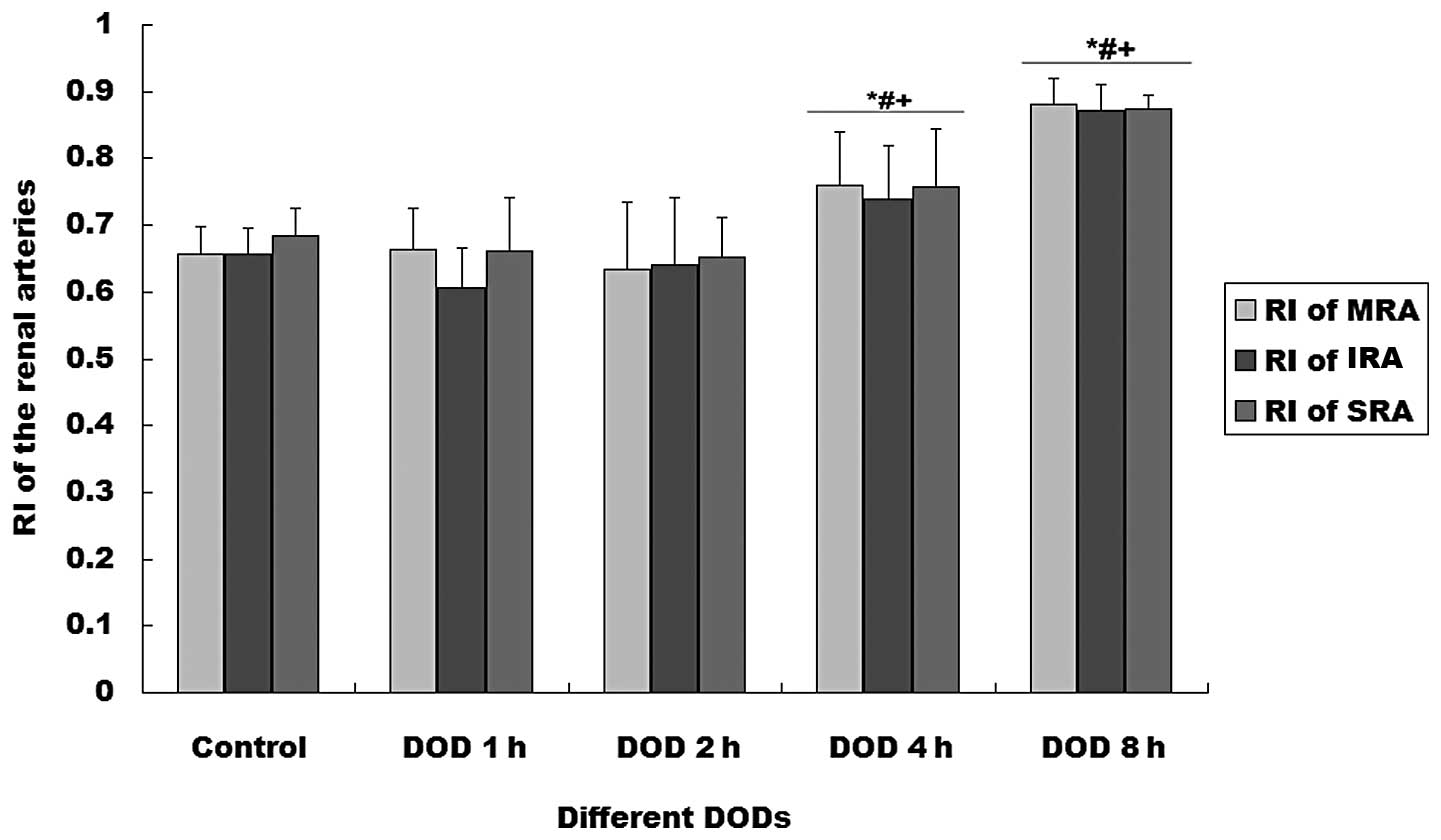
SRA increased with distention time (P<0.01). The RIs of the MRA
and SRA were significantly higher in the rats with 4 or 8 h DOBO
than in the other groups (P<0.01, Fig. 2).
 | Table IEffect of the duration of bladder
overdistention (DOBO) on renal size, degree of separation of the
renal pelvis and the thickness of the renal cortex. |
Table I
Effect of the duration of bladder
overdistention (DOBO) on renal size, degree of separation of the
renal pelvis and the thickness of the renal cortex.
| Group | Renal size
(cm3) | Separation of the
pelvis (cm) | Thickness of the
renal cortex (cm) |
|---|
| Control (n=8) | 1.041±0.159 | 0.000±0.000 | 0.263±0.037 |
| 1 h DOBO (n=8) | 1.146±0.162 | 0.223±0.059a | 0.259±0.058 |
| 2 h DOBO (n=8) | 1.472±0.145a |
0.320±0.029a,b | 0.276±0.032 |
| 4 h DOBO (n=8) |
1.484±0.193a–c |
0.308±0.044a–c | 0.251±0.052 |
| 8 h DOBO (n=7) |
1.634±0.155a–c |
0.277±0.028a–c | 0.256±0.035 |
Renal function test
Rats with 2, 4 or 8 h DOBO showed significant,
time-dependent increases in SCr and BUN levels compared with
sham-operated controls (P<0.01, Table II).
 | Table IIEffect of the duration of bladder
overdistention (DOBO) on serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea
nitrogen (BUN) levels. |
Table II
Effect of the duration of bladder
overdistention (DOBO) on serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea
nitrogen (BUN) levels.
| Group | SCr
(μmol/l) | BUN (mmol/l) |
|---|
| Control (n=8) | 12.375±1.302 | 6.980±1.072 |
| 1 h DOBO (n=8) | 18.250±1.669 | 11.481±1.474a |
| 2 h DOBO (n=8) |
23.125±2.532a,b |
18.689±1.100a,b |
| 4 h DOBO (n=8) |
34.375±2.200a–c |
25.184±1.760a–c |
| 8 h DOBO (n=7) |
51.500±3.423a–d |
32.079±5.592a–d |
TUNEL assay
Increasing DOBO also promoted apoptosis within renal
tissues. Compared with controls, the rats with 4 or 8 h DOBO showed
significant increases in the apoptotic index (P<0.01). This
effect was time-dependent (Figs. 3
and 4).
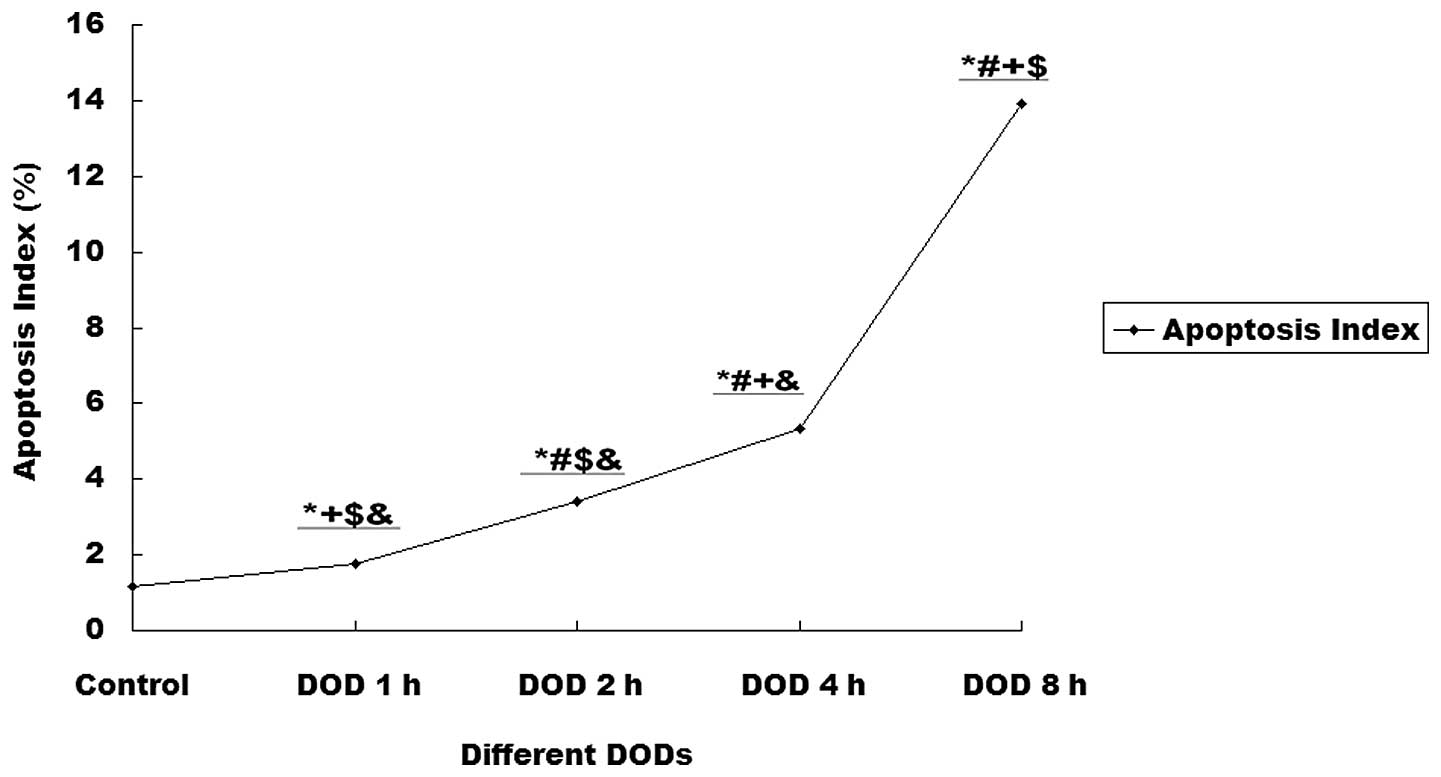 | Figure 3Effect of the duration of bladder
overdistention (DOBO) on the apoptotic index of renal cells.
Compared with the control, rats with 1, 2, 4 or 8 h DOBO showed a
significant increase in apoptotic index (1.15 vs. 1.77, 3.4, 5.34
and 13.91%, respectively; P<0.01) and this effect was
time-dependent. *P<0.01 vs. control group,
#P<0.01 vs. 1 h DOBO group, +P<0.01 vs.
2 h DOBO group, $P<0.01 vs. 4 h DOBO group,
&P<0.01 vs. 8 h DOBO group. |
TEM
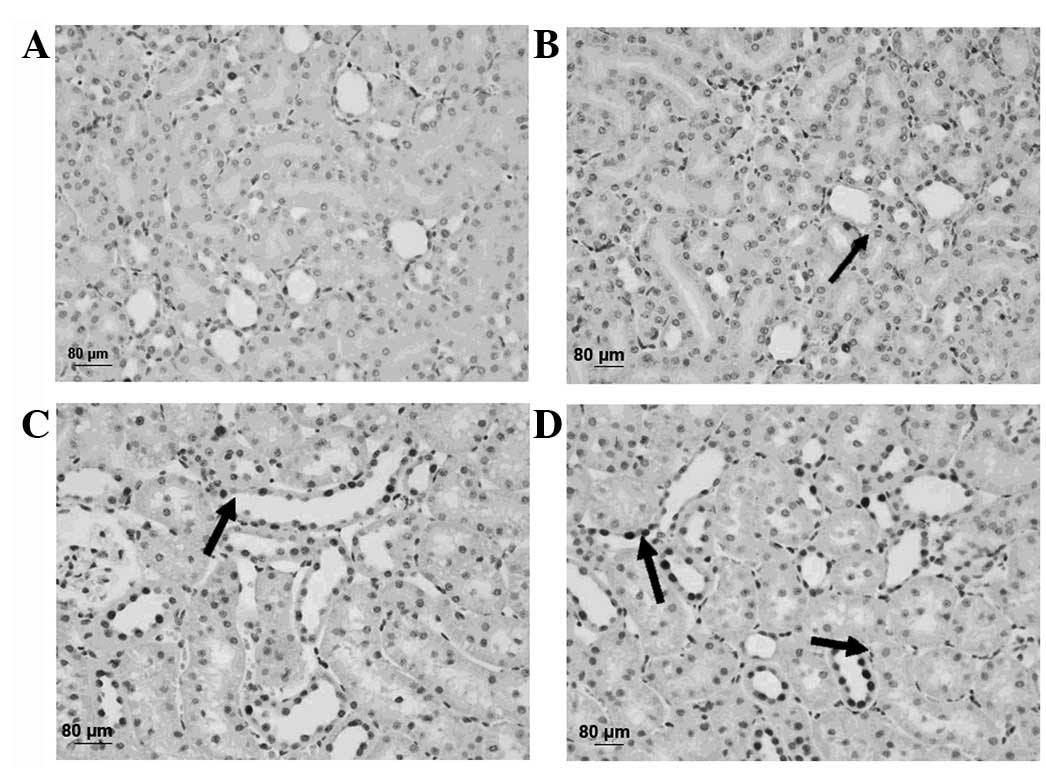
Electron microscopy revealed that increasing DOBO
led to increasingly aggravated cellular and tissue injury. Evidence
of injury included mitochondrial breakdown, tubular vacuolization
and dilation, mesangial proliferation, necrosis, podocyte swelling
and inosculation and slit pores were clearly visible. These
injuries became more pronounced as the DOBO increased (Fig. 5).
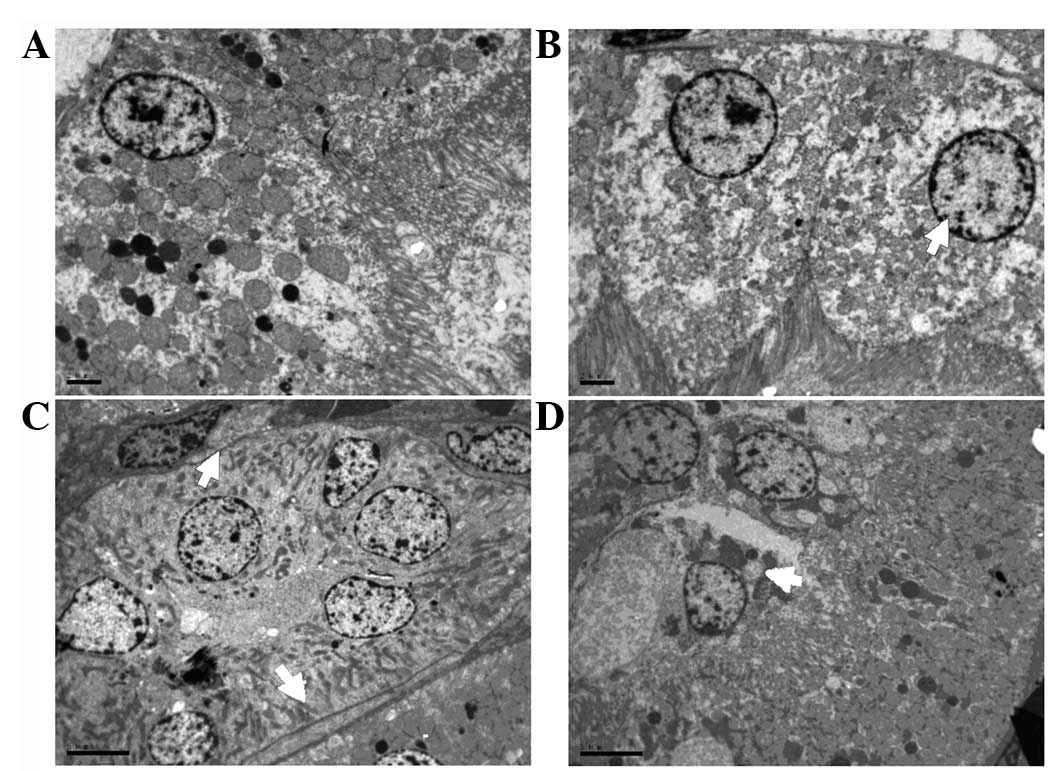 | Figure 5Representative microscopic findings
indicating the effect of the duration of bladder overdistention
(DOBO) on renal ultrastructure. (A) Control group (magnification,
×2,550). (B) 1 h DOBO group (magnification, ×2,550). (C) 4 h DOBO
group (magnification, ×1,850). (D) 8 h DOBO group (magnification,
×1,850). Electron microscopy revealed that an increase in the DOBO
led to increasingly aggravated cellular and tissue injury. Evidence
of injury included mitochondrial breakdown, tubular vacuolization
and dilation, mesangial proliferation, necrosis, podocyte swelling
and inosculation and clearly visible slit pores (arrows). |
Discussion
It is well known that BPH is a progressive disease,
with risk of urinary retention and renal insufficiency (5). Renal impairment caused by BPH is
usually a chronic disorder, which takes several years, even decades
to develop (9). In the current
study, it was identified that rats with bladder overdistention had
significant, time-dependent reductions in SCr and BUN levels.
Renal hemodynamic alterations and the consequences
of progression to irreversible renal injury following unilateral
ureteral obstruction (UUO) have been studied in detail (6). In animals with UUO, both renal blood
flow (RBF) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decrease and remain
depressed without intervention (7). The degree of damage to renal function
depends on the duration of UUO and the species being examined
(1,12,13).
In the current study, the blood flow rate was observed to increase
in the renal arteries during overdistention in a time-dependent
manner, which was associated with increasingly severe
hydronephrosis and increasing renal size. Kidney length is
traditionally used to predict kidney size; however, length alone is
an unreliable predictor of kidney size and the number of functional
nephrons (8), a limitation noted
in both human and animal studies (9). In the present study, renal size and
hydronephrosis were used as indices of renal morphology. During
overdistention, intrapelvic pressure increases until ureteral
regurgitation occurs, resulting in hydronephrosis and a decrease in
renal perfusion without cellular injury (10). In compensation for this, the renal
arteries became constricted, driving an increase in the blood flow
rate. Accordingly, the affected kidney will show reduced ability to
concentrate urine and, if tubular and glomerular damage are allowed
to progress, renal failure may follow (11).
In the present study, it was also observed that
overdistention aggravated ultrastructural changes and increased the
number of apoptotic cells. Early morphological changes in response
to overdistention include the formation of blebs in the apical
membranes of proximal tubule cells, as well as loss of the brush
border (12,13). Proximal tubule cells lost their
polarity and the integrity of their tight junctions was disrupted,
which may have been consequences of alterations in actinomycin-D
microtubule cytoskeleton networks (14). In addition,
Na+/K+-ATPase redistributes from the
basolateral to the apical membrane, contributing to a decrease in
Na+ and Na+-coupled vectorial transport.
Integrins are redistributed to the apical surface (15), and live and dead cells slough off
into the tubular lumen, contributing to the formation of urinary
casts. The casts cause increased intratubular pressure and a
decrease in GFR. Loss of the epithelial cell barrier and tight
junctions between viable cells may result in back-leakage of the
glomerular filtrate, further reducing the effective GFR.
It was postulated that renal injury due to ischemia
may involve the generation of reactive oxygen species, production
of inflammatory cytokines, inflammatory cell infiltration and the
production of fibronectin and collagen, all of which contribute to
interstitial fibrosis and renal microvascular injury. In the
present study, the main ultrastructural changes were mitochondrial
breakdown and disorganized podocytes; these and all other negative
ultrastructural changes were further exacerbated by increasing
durations of overdistention.
Based on these results and those reported
previously, bladder overdistention affects not only the structure
and function of the bladder but also of the kidney. Thus, more
attention should be paid to the effects of AUR on the upper urinary
tract. Clinical practice should be expanded to include monitoring
of renal function in patients with AUR, especially in cases of
prolonged AUR. These results indicate that the bladder should be
decompressed as quickly as possible and the duration of AUR should
be shortened to protect renal function in the treatment of AUR.
Certainly, overdistention of the bladder is not the same as AUR and
clinical circumstances are more complicated than animal
experiments. Other factors such as comorbidity, age and physical
conditions also contribute to the severity of impairment and the
recovery of renal function following AUR.
In the present study, there was no recovery of renal
function after the overdistention was relieved. How the duration of
overdistention affects the recovery of renal insufficiency should
be studied further.
DOBO plays an important role in functional and
structural impairment of the kidney. Different overdistention
durations lead to different severities of impairment of the rat
kidney. With increasing duration, the hemodynamic changes, cell
apoptosis and ultrastructural injuries of the kidney are more
evident, all of which may contribute to more serious impairment of
renal function and morphology.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge
Mrs. Li Wang from the Department of Electron Microscopy, Zhejiang
University School of Medicine, for her meticulous technical
assistance with the TEM. This study was supported by a grant from
the Department of Education of Zhejiang Province (No.
491010+G21078) and a grant from the Zhejiang Administration of
Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 2010ZA050).
References
|
1.
|
Fitzpatrick JM and Kirby RS: Management of
acute urinary retention. BJU Int. 97(Suppl 2): 16–20; discussion
21–22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Kaplan SA, Wein AJ, Staskin DR, et al:
Urinary retention and post-void residual urine in men: separating
truth from tradition. J Urol. 180:47–54. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Issa MM, Fenter TC, Black L, et al: An
assessment of the diagnosed prevalence of diseases in men 50 years
of age or older. Am J Manag Care. 12(Suppl): S83–S89.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Platt JF: Duplex Doppler evaluation of
acute renal obstruction. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 18:147–153. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
McConnell JD, Bruskewitz R, Walsh P, et al
Finasteride Long-Term Efficacy and Safety Study Group: The effect
of finasteride on the risk of acute urinary retention and the need
for surgical treatment among men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
N Engl J Med. 338:557–563. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Chan W, Krieg RJ Jr, Ward K, et al:
Progression after release of obstructive nephropathy. Pediatr
Nephrol. 16:238–244. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Chevalier RL, Kim A, Thornhill BA and
Wolstenholme JT: Recovery following relief of unilateral ureteral
obstruction in the neonatal rat. Kidney Int. 55:793–807. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Thakur V, Watkins T, McCarthy K, et al: Is
kidney length a good predictor of kidney volume? Am J Med Sci.
313:85–89. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Ferrer FA, McKenna PH, Bauer MB and Miller
SF: Accuracy of renal ultrasound measurements for predicting actual
kidney size. J Urol. 157:2278–2281. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Mustonen S, Ala-Houhala IO, Vehkalahti P,
et al: Kidney ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound findings during and
after acute urinary retention. Eur J Ultrasound. 12:189–196. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Pope JC IV, Showalter PR, Milam DF and
Brock JW III: Intrapelvic pressure monitoring in the partially
obstructed porcine kidney. Urology. 44:565–571. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Molitoris BA: Ischemia-induced loss of
epithelial polarity: potential role of the actin cytoskeleton. Am J
Physiol. 260:F769–F778. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Spencer AJ, LeFurgey A, Ingram P and
Mandel LJ: Elemental microanalysis of organelles in proximal
tubules. II. Effects of oxygen deprivation. J Am Soc Nephrol.
1:1321–1333. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Fish EM and Molitoris BA: Alterations in
epithelial polarity and the pathogenesis of disease states. N Engl
J Med. 330:1580–1588. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Goligorsky MS and DiBona GF: Pathogenetic
role of Arg-Gly-Asp-recognizing integrins in acute renal failure.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:5700–5704. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|