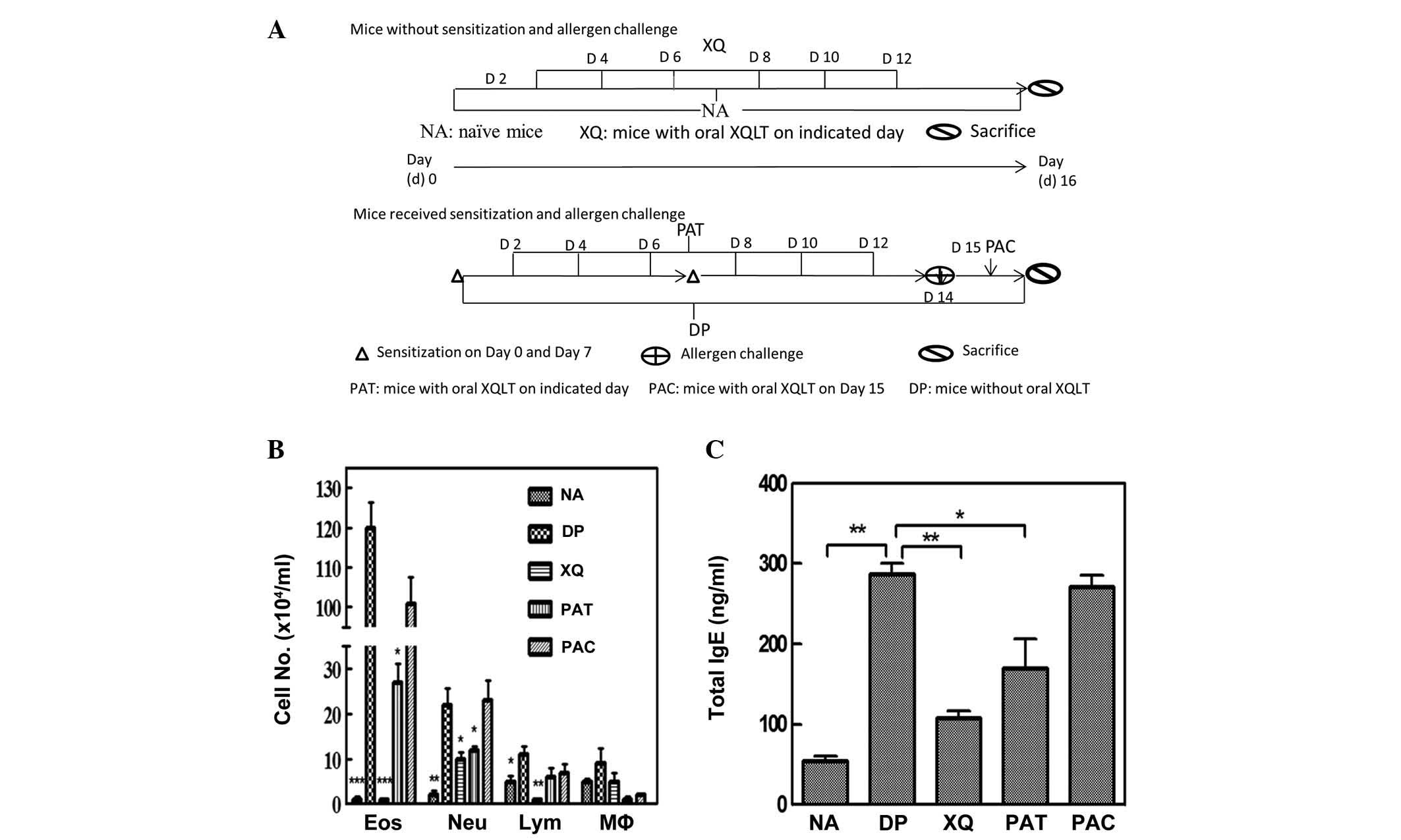
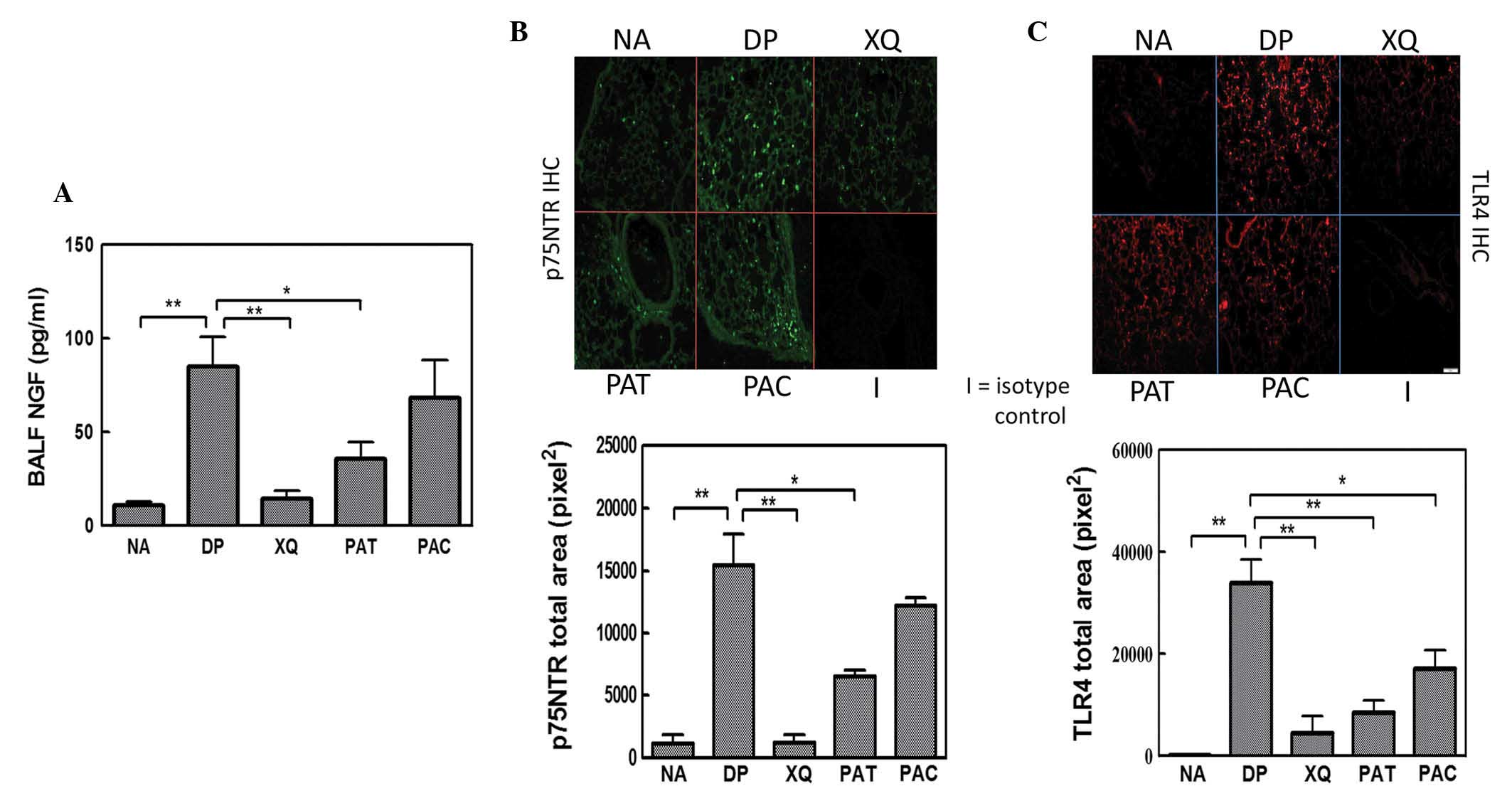
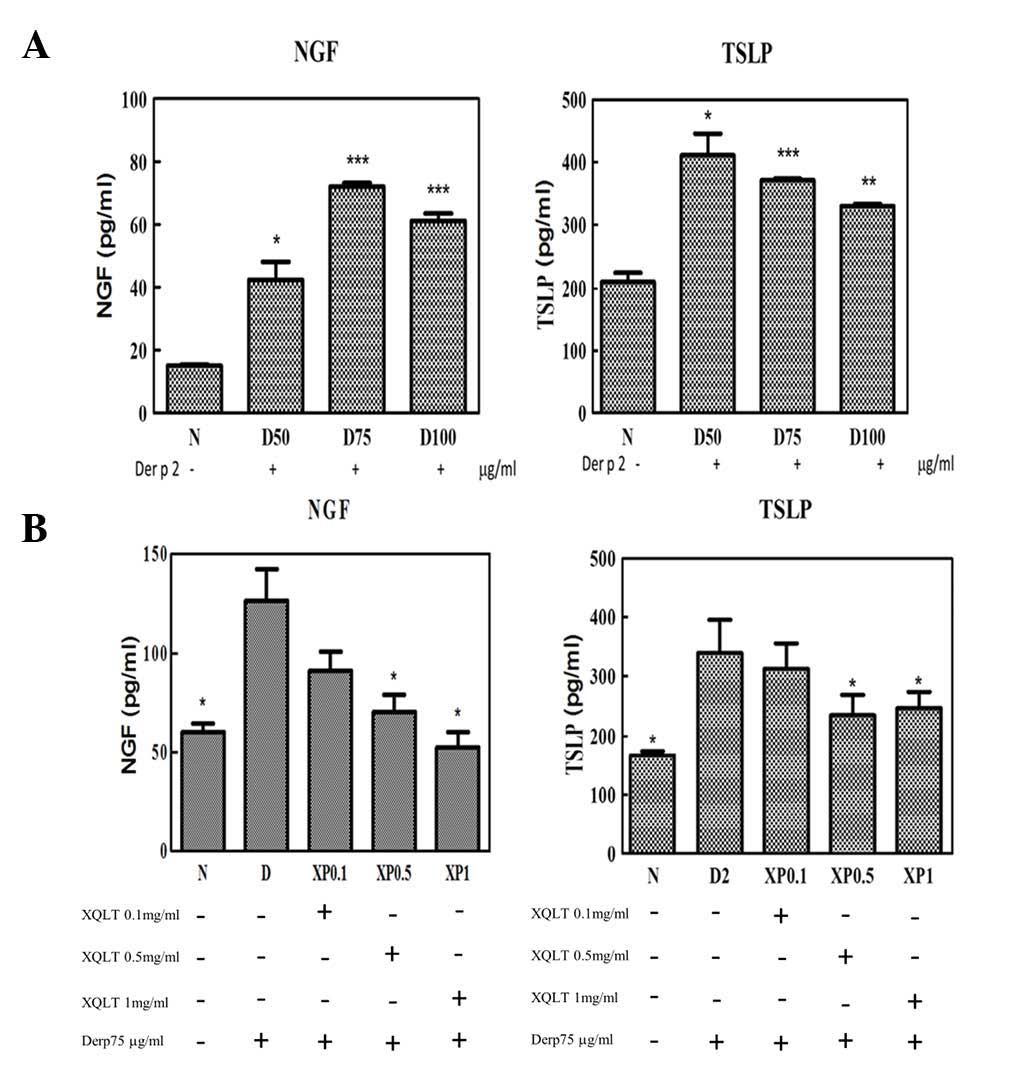
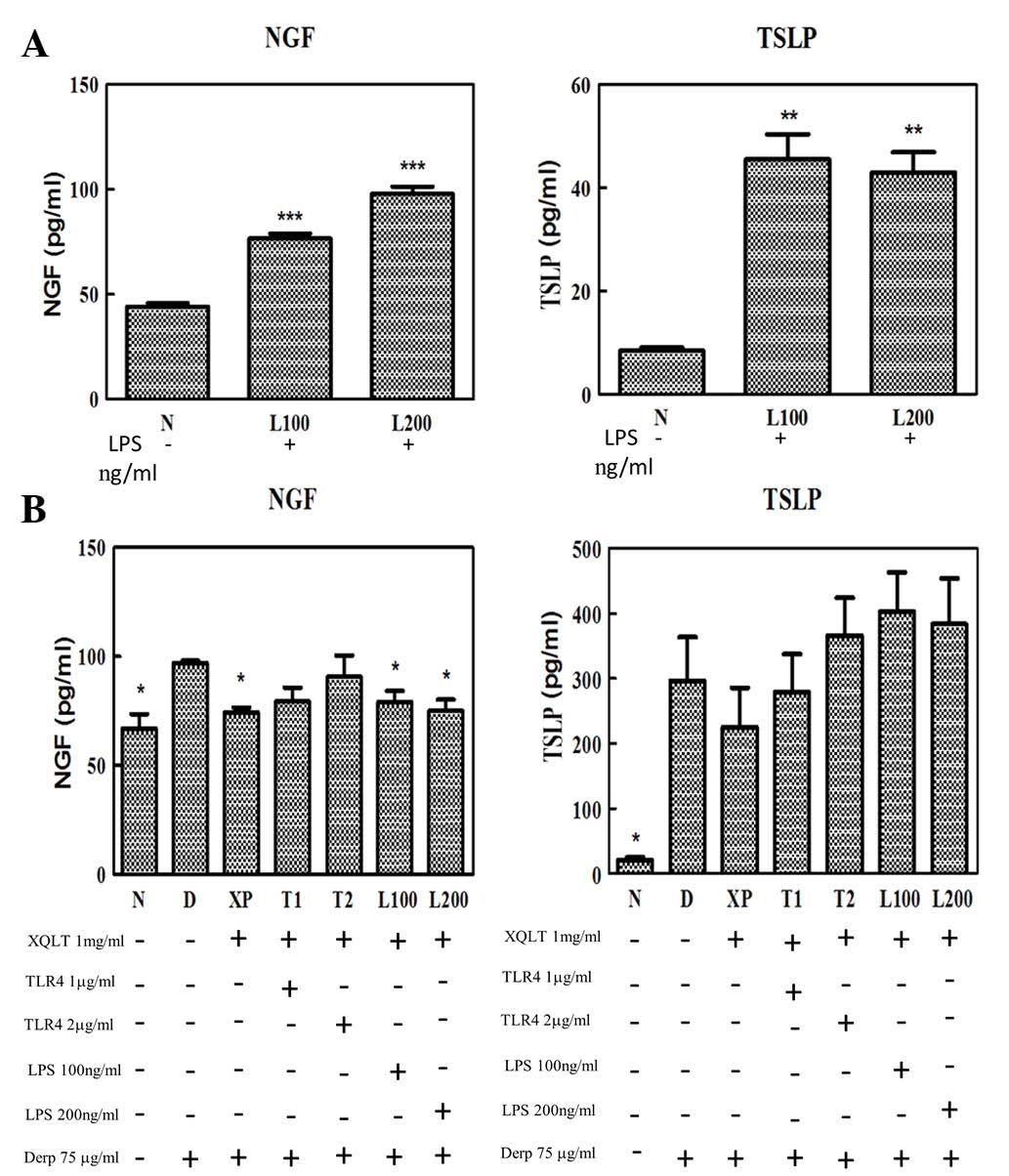
|
1.
|
Kung YY, Chen YC, Hwang SJ, et al: The
prescriptions frequencies and patterns of Chinese herbal medicine
for allergic rhinitis in Taiwan. Allergy. 61:1316–1318. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Nagai T, Nakao M, Shimizu Y, et al:
Proteomic analysis of anti-inflammatory effects of a Kampo
(Japanese herbal) medicine ‘Shoseiryuto (Xiao-Qing-Long-Tang)’ on
airway inflammation in a mouse model. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2011:6041962011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Kao ST, Wang SD, Wang JY, et al: The
effect of Chinese herbal medicine, xiao-qing-long tang (XQLT), on
allergen-induced bronchial inflammation in mite-sensitized mice.
Allergy. 55:1127–1133. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Nagai T, Arai Y, Emori M, et al:
Anti-allergic activity of a Kampo (Japanese herbal) medicine
‘Sho-seiryu-to (Xiao-Qing-Long-Tang)’ on airway inflammation in a
mouse model. Int Immunopharmacol. 4:1353–1365. 2004.
|
|
5.
|
Ko E, Rho S, Cho C, et al:
So-Cheong-Ryong-Tang, tradititional Korean medicine, suppresses Th2
lineage development. Biol Pharm Bull. 27:739–743. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Ko E, Rho S, Lee EJ, et al: Traditional
Korean medicine (SCRT) modulate Th1/Th2 specific cytokine
production in mice CD4+ T cell. J Ethnopharmacol.
92:121–128. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Ehrhard PB, Erb P, Graumann U and Otten U:
Expression of nerve growth factor and nerve growth factor receptor
tyrosine kinase Trk in activated CD4-positive T-cell clones. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:10984–10988. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Ehrhard PB, Erb P, Graumann U, Schmutz B
and Otten U: Expression of functional trk tyrosine kinase receptors
after T cell activation. J Immunol. 152:2705–2709. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Glaab T, Hoymann HG, Hecht M, et al:
Effect of anti-nerve growth factor on early and late airway
responses in allergic rats. Allergy. 58:900–904. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Abram M, Wegmann M, Fokuhl V, et al: Nerve
growth factor and neurotrophin-3 mediate survival of pulmonary
plasma cells during the allergic airway inflammation. J Immunol.
182:4705–4712. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Shi Y, Jin Y, Guo W, et al: Blockage of
nerve growth factor modulates T cell responses and inhibits
allergic inflammation in a mouse model of asthma. Inflamm Res.
61:1369–1378. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Hahn C, Islamian AP, Renz H and Nockher
WA: Airway epithelial cells produce neurotrophins and promote the
survival of eosinophils during allergic airway inflammation. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 117:787–794. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Noga O, Peiser M, Altenähr M, et al:
Differential activation of dendritic cells by nerve growth factor
and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Clin Exp Allergy.
37:1701–1708. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Phipps S, Lam CE, G, Kaiko GE, et al:
Toll/IL-1 signaling is critical for house dust mite-specific helper
T cell type 2 and type 17 responses. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
179:883–893. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Hammad H, Chieppa M, Perros F, et al:
House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4
triggering of airway structural cells. Nat Med. 15:410–416. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ricci A, Greco S, Mariotta S, et al:
Neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors in human lung cancer. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 25:439–446. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Molloy NH, Read DE and Gorman AM: Nerve
growth factor in cancer cell death and survival. Cancers.
3:510–530. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Liu YJ, Soumelis V, Watanabe N, et al:
TSLP: an epithelial cell cytokine that regulates T cell
differentiation by conditioning dendritic cell maturation. Annu Rev
Immunol. 25:193–219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Al-Shami A, Spolski R, Kelly J, et al: A
role for TSLP in the development of inflammation in an asthma
model. J Exp Med. 202:829–839. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Liu YJ: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin:
master switch for allergic inflammation. J Exp Med. 203:269–273.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Roan F, Bell BD, Stoklasek TA, et al: The
multiple facets of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) during
allergic inflammation and beyond. J Leukoc Biol. 91:877–886. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Lu YC, Yeh WC and Ohashi PS: LPS/TLR4
signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 42:145–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Kenny EF and O’Neill LA: Signalling
adaptors used by Toll-like receptors: an update. Cytokine.
43:342–349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Kobayashi T, Takaesu G and Yoshimura A:
Mal-function of TLRs by SOCS. Nat Immunol. 7:123–124. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Wang J, Cai Y, Shao LJ, et al: Activation
of NF-κB by TMPRSS2/ERG fusion isoforms through Toll-like
receptor-4. Cancer Res. 71:1325–1333. 2011.
|
|
26.
|
Jiang Y, Chen G, Zheng Y, et al: TLR4
signaling induces functional nerve growth factor receptor p75NTR on
mouse dendritic cells via p38MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Mol Immunol.
45:1557–1566. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Ye YL, Wu HT, Lin CF, et al:
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus 2 regulates nerve growth
factor release to induce airway inflammation via a reactive oxygen
species-dependent pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
300:L216–L224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Trompette A, Divanovic S, Visintin A, et
al: Allergenicity resulting from functional mimicry of a Toll-like
receptor complex protein. Nature. 457:585–588. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Tokuoka S, Takahashi Y, Masuda T, Tanaka
H, Furukawa S and Nagai H: Disruption of antigen-induced airway
inflammation and airway hyper-responsiveness in low affinity
neurotrophin receptor p75 gene deficient mice. Br J Pharmacol.
134:1580–1586. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Kerzel S, Päth G, Nockher WA, Quarcoo D,
Raap U, Groneberg DA, Dinh QT, Fischer A, Braun A and Renz H:
Pan-neurotrophin receptor p75 contributes to neuronal
hyper-reactivity and airway inflammation in a murine model of
experimental asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 28:170–178. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Bothwell M: p75NTR: a receptor after all.
Science. 272:506–507. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Carter BD, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B,
et al: Selective activation of NF-κB by nerve growth factor through
the neurotrophin receptor p75. Science. 272:542–545. 1996.
|
|
33.
|
Jiang Y, Chen G, Zhang Y, et al: Nerve
growth factor promotes TLR4 signaling-induced maturation of human
dendritic cells in vitro through inducible p75NTR. J Immunol.
179:6297–6304. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Wang SD, Lin LJ, Chen CL, Lee SC, Lin CC,
Wang JJ and Kao ST: Xiao-Qing-Long-Tang attenuates allergic airway
inflammation and remodeling in repetitive Dermatogoides
pteronyssinus challenged chronic asthmatic mice model. J
Ethnopharmacol. 142:531–538. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Muroi M and Tanamoto KI: The
polysaccharide portion plays an indispensable role in
Salmonella lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of NF-κB
through human toll-like receptor 4. Infect Immun. 70:6043–6047.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Nishimura M and Naito S: Tissue-specific
mRNA expression profiles of human toll-like receptors and related
genes. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:886–892. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Zanoni I, Ostuni R, Marek LR, et al: CD14
controls the LPS-induced endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4. Cell.
147:868–880. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|