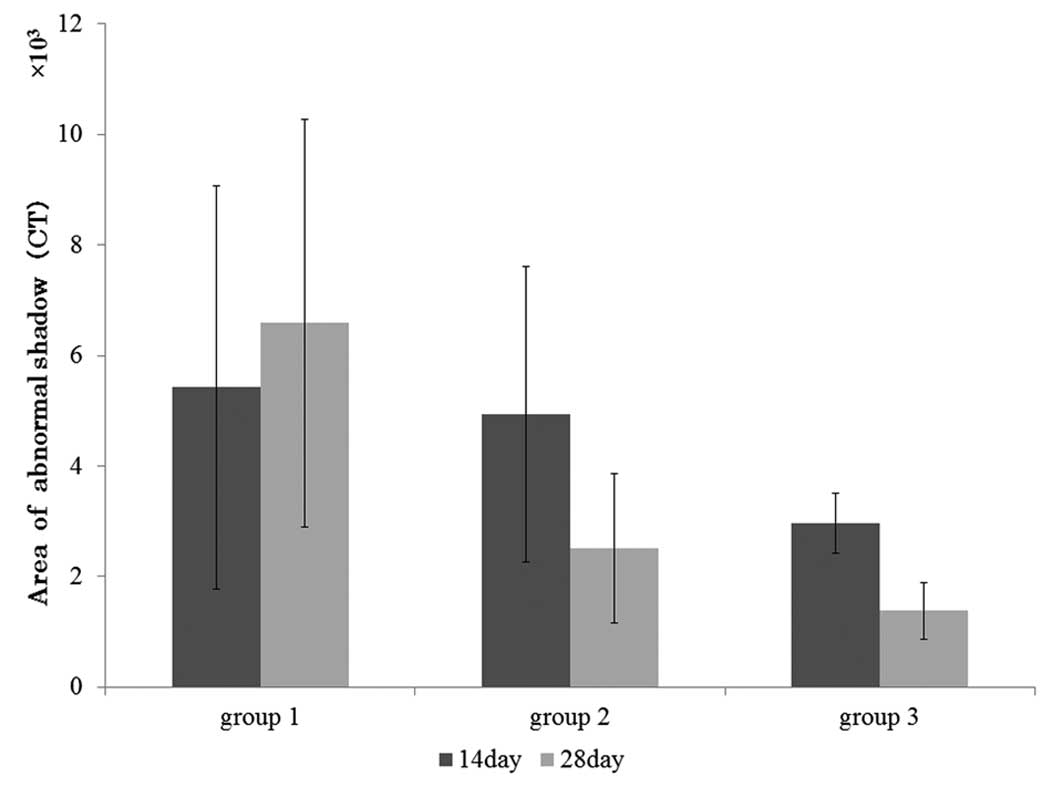
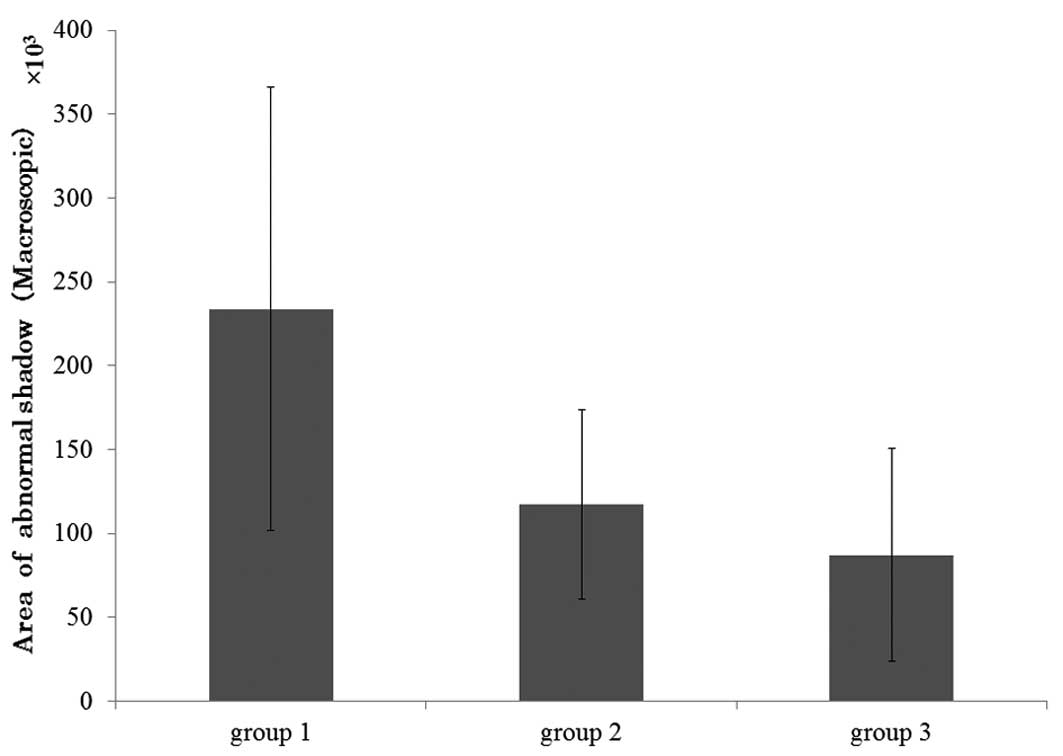
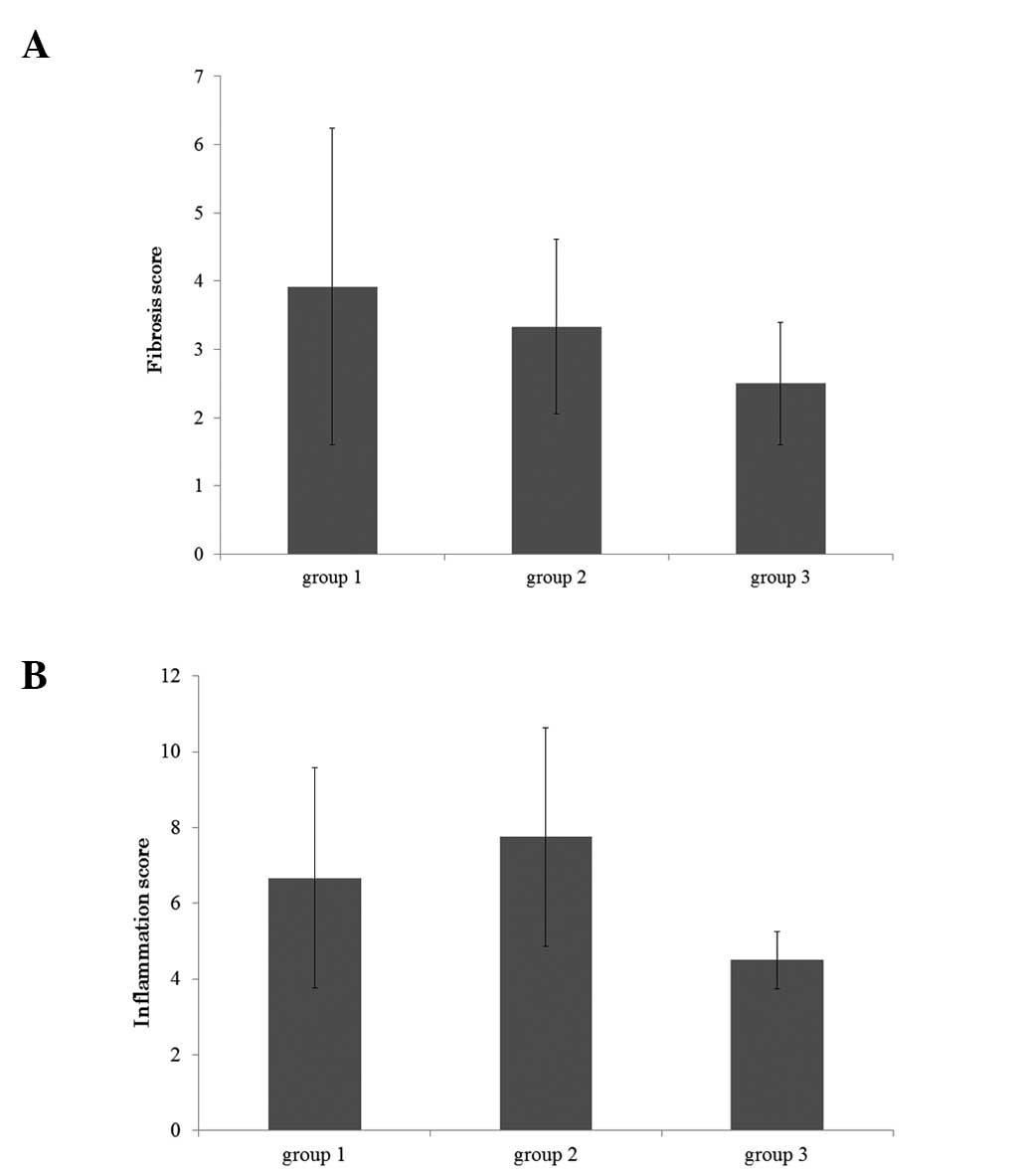
|
1.
|
Inoue A, Saijo Y, Maemondo M, Gomi K,
Tokue Y, et al: Severe acute interstitial pneumonia and gefitinib.
Lancet. 361:137–139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Camus P, Kudoh S and Ebina M: Interstitial
lung disease associated with drug therapy. Br J Cancer. 91(Suppl
2): S18–S23. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Camus PH, Foucher P, Bonniaud P and Ask K:
Drug-induced infiltrative lung disease. Eur Respir J Suppl.
32:93s–100s. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Matsuno O: Drug-induced interstitial lung
disease: mechanisms and best diagnostic approaches. Respir Res.
13:392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Cooper JA Jr, Zitnik RJ and Matthay RA:
Mechanisms of drug-induced pulmonary disease. Annu Rev Med.
39:395–404. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Cooper JA Jr, White DA and Matthay RA:
Drug-induced pulmonary disease. Part 1: Cytotoxic drugs. Am Rev
Respir Dis. 133:321–340. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Cooper JA Jr, White DA and Matthay RA:
Drug-induced pulmonary disease. Part 2: Noncytotoxic drugs. Am Rev
Respir Dis. 133:488–505. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Cleverley JR, Screaton NJ, Hiorns MP, et
al: Drug-induced lung disease: high-resolution CT and histological
findings. Clin Radiol. 57:292–299. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Ohnishi H, Yokoyama A, Yasuhara Y,
Watanabe A, Naka T, et al: Circulating KL-6 levels in patients with
drug induced pneumonitis. Thorax. 58:872–875. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Gan Y, Herzog EL and Gomer RH: Pirfenidone
treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag.
7:39–47. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Asai T, Ohno Y, Minatoguchi S, Funaguchi
N, Yuhgetsu H, et al: The specific free radical scavenger edaravone
suppresses bleomycin-induced acute pulmonary injury in rabbits.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 34:22–26. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Kakavas S, Demestiha T, Vasileiou P and
Xanthos T: Erythropoetin as a novel agent with pleiotropic effects
against acute lung injury. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 67:1–9. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Markarian B and Dailey ET: Preparation of
inflated lung specimens. Heitzman’s the Lung: Radiologic-Pathologic
Correlations. Groskin SA: 3rd edition. Mosby; St. Louis, MO: pp.
4–12. 1993
|
|
14.
|
Hirose N, Lynch DA, Cherniack RM and
Doherty DE: Correlation between high resolution computed tomography
and tissue morphometry of the lung in bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis in the rabbit. Am Rev Respir Dis. 147:730–738. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Du M, Irani RA, Stivers DN, Lee SJ and
Travis EL: H2-Ea deficiency is a risk factor for bleomycin-induced
lung fibrosis in mice. Cancer Res. 64:6835–6839. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Galvan L, Huang CH, Prestayko AW, Stout
JT, Evans JE and Crooke ST: Inhibition of bleomycin-induced DNA
breakage by superoxide dismutase. Cancer Res. 41:5103–5106.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Cunningham ML, Ringrose PS and Lokesh BR:
Inhibition of the genotoxicity of bleomycin by superoxide
dismutase. Mutat Res. 135:199–202. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Tajima S, Bando M, Ishii Y, Hosono T,
Yamasawa H, et al: Effects of edaravone, a free-radical scavenger,
on bleomycin-induced lung injury in mice. Eur Respir J.
32:1337–1343. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Martin WJ II and Kachel DL:
Bleomycin-induced pulmonary endothelial cell injury: evidence for
the role of iron-catalyzed toxic oxygen-derived species. J Lab Clin
Med. 110:153–158. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Iyer SN, Gurujeyalakshmi G and Giri SN:
Effects of pirfenidone on transforming growth factor-beta gene
expression at the transcriptional level in bleomycin hamster model
of lung fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 291:367–373.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Raghu G, Johnson WC, Lockhart D and Mageto
Y: Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with a new
antifibrotic agent, pirfenidone: results of a prospective,
open-label Phase II study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
159:1061–1069. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Azuma A, Nukiwa T, Tsuboi E, Suga M, Abe
S, Nakata K, et al: Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 171:1040–1047. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Shichinohe H, Kuroda S, Yasuda H, Ishikawa
T, Iwai M, Horiuchi M and Iwasaki Y: Neuroprotective effects of the
free radical scavenger edaravone (MCI-186) in mice permanent focal
brain ischemia. Brain Res. 1029:200–206. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
MacRedmond R, Singhera GK and Dorscheid
DR: Erythropoietin inhibits respiratory epithelial cell apoptosis
in a model of acute lung injury. Eur Respir J. 33:1403–1414. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Ozer EA, Kumral A, Ozer E, Yilmaz O, Duman
N, Ozkal S, et al: Effects of erythropoietin on hyperoxic lung
injury in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res. 58:38–41. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Nagatani Y, Nitta N, Otani H, Mukaisho K,
Sonoda A, Nitta-Seko A, et al: Quantitative measurement of
bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rabbits using sequential in vivo
regional analysis and high-resolution computed tomography:
correlation with pathologic findings. Acad Radiol. 18:672–681.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Izbicki G, Segel MJ, Christensen TG,
Conner MW and Breuer R: Time course of bleomycin-induced lung
fibrosis. Int J Exp Pathol. 83:111–119. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Ozkan M, Dweik RA and Ahmad M:
Drug-induced lung disease. Cleve Clin J Med. 68:782–795. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Gruchalla RS: Drug metabolism, danger
signals, and drug induced hypersensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
108:475–488. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Foucher P, Biour M, Blayac JP, Godard P,
Sgro C, et al: Drugs that may injure the respiratory system. Eur
Respir J. 10:265–279. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Camus P, Fanton A, Bonniaud P, Camus C and
Foucher P: Interstitial lung disease induced by drugs and
radiation. Respiration. 71:301–326. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Schnabel A, Richter C, Bauerfeind S and
Gross WL: Bronchoalveolar lavage cell profile in methotrexate
induced pneumonitis. Thorax. 52:377–379. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
du Bois RM: An earlier and more confident
diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir Rev.
21:141–146. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|