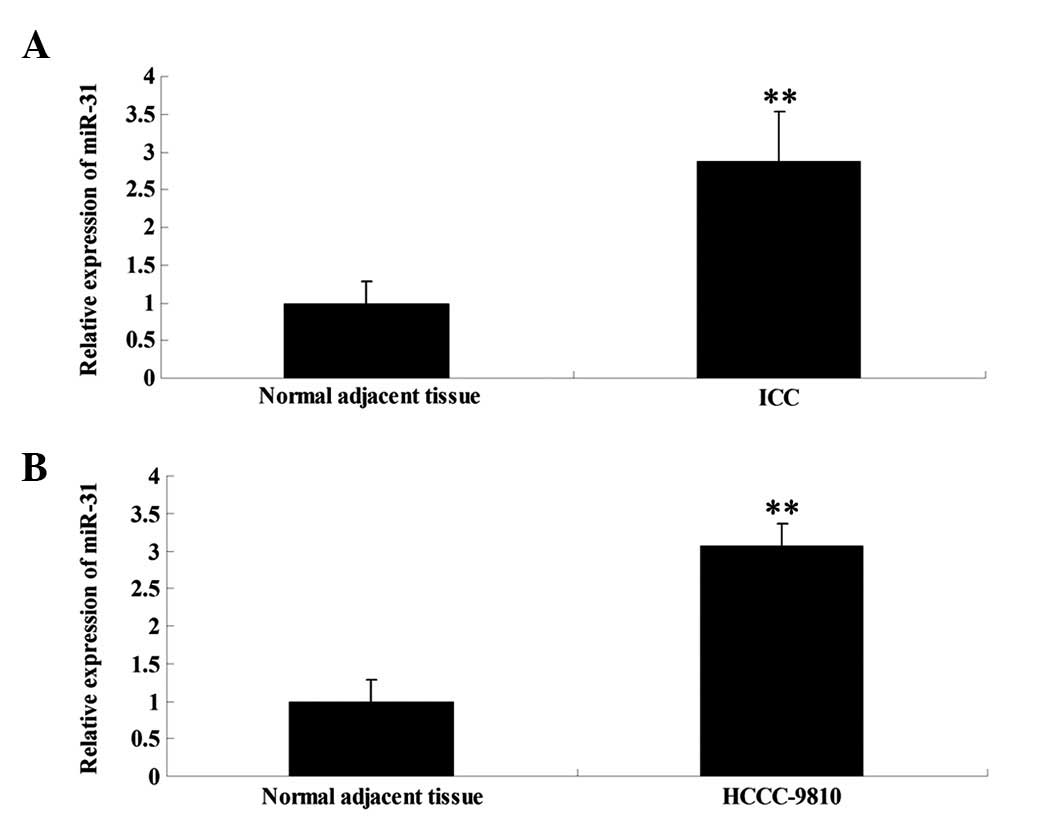
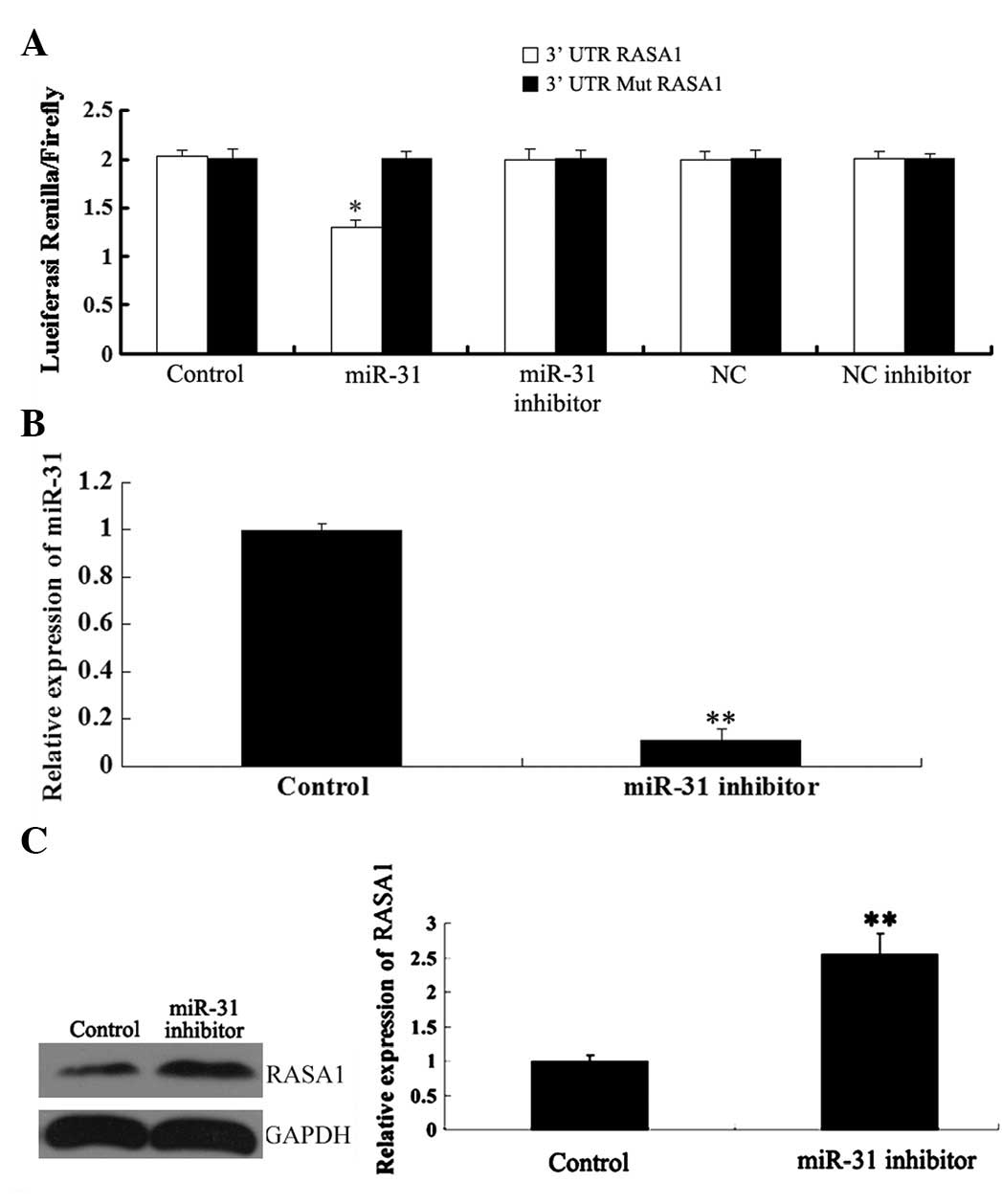
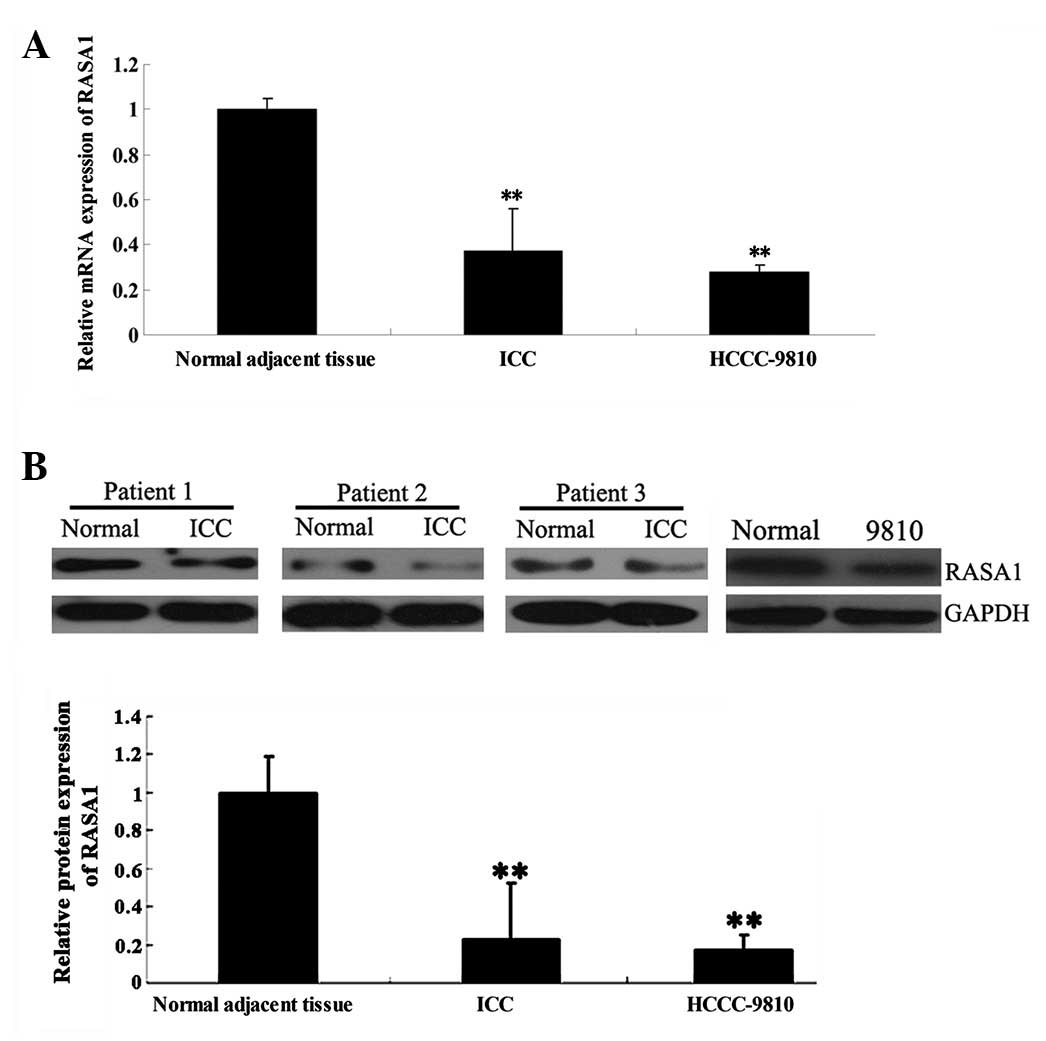
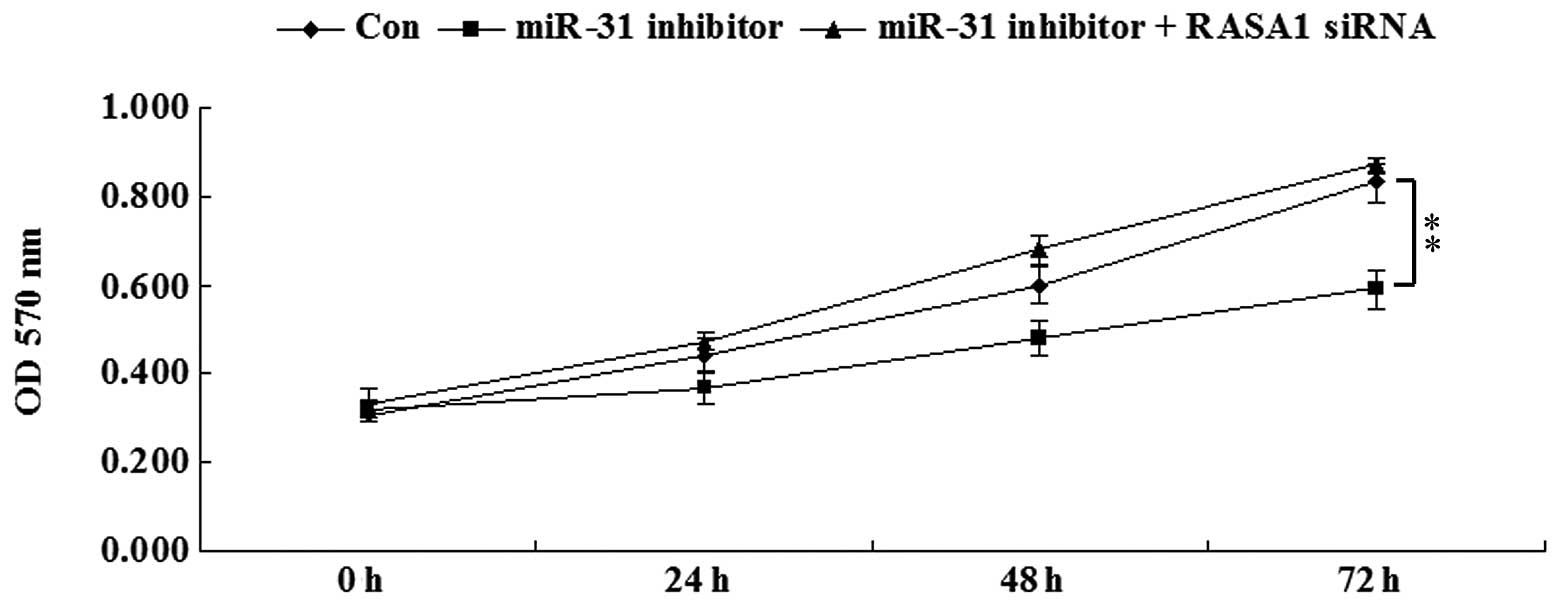
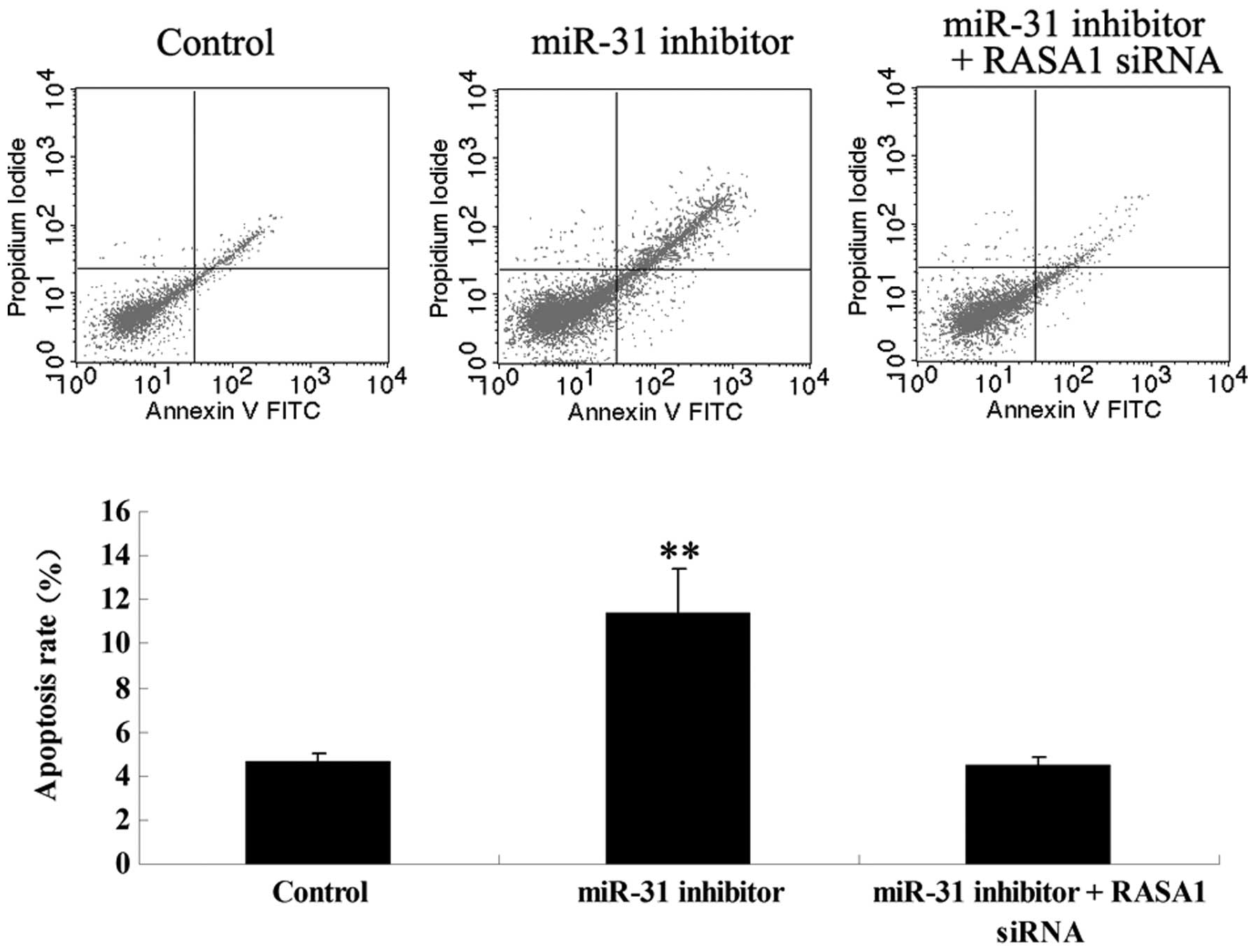
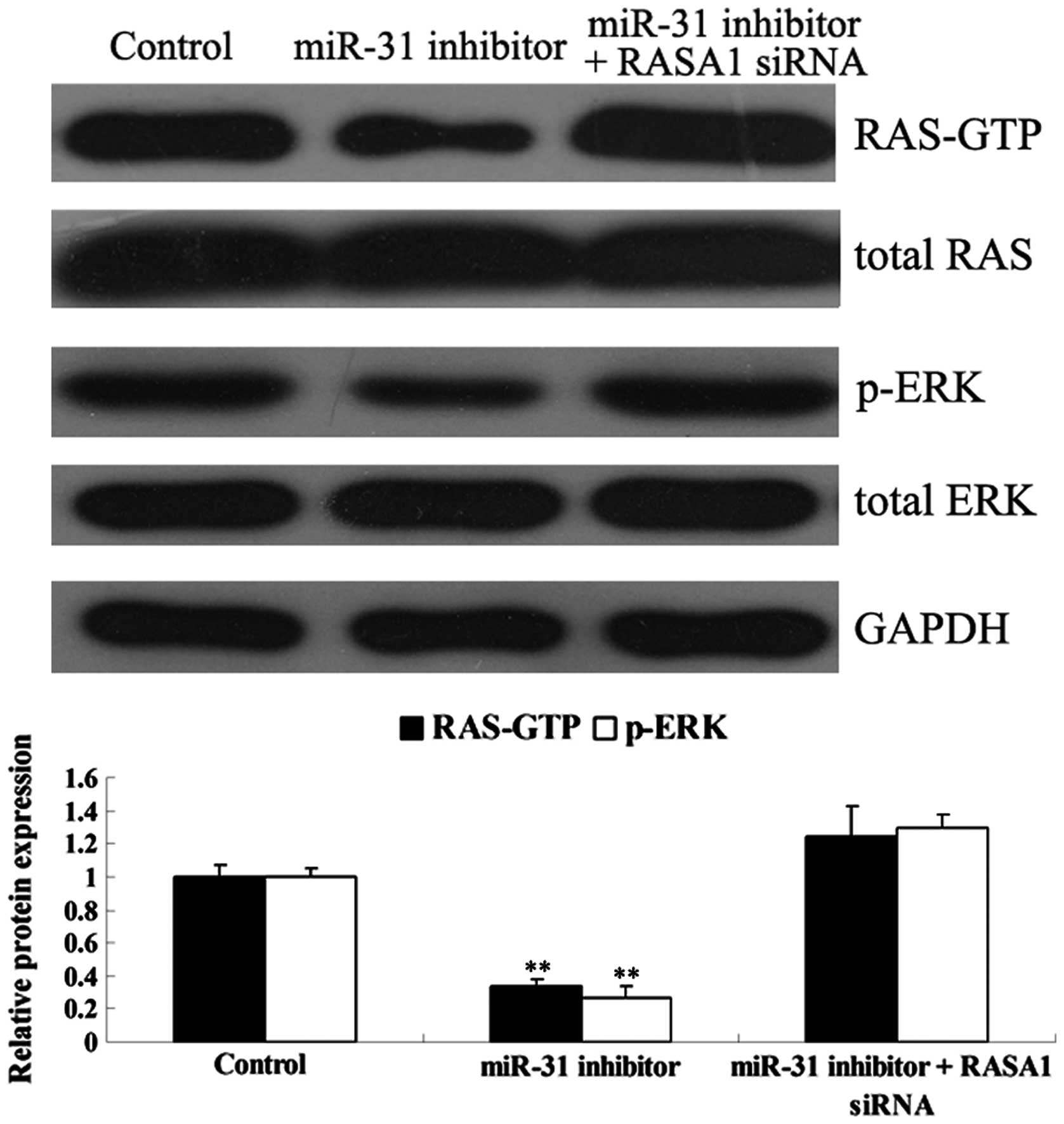
|
1.
|
Farges O and Fuks D: Clinical presentation
and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterol
Clin Biol. 34:191–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Luh F, Kuei A, Fann P, Chu P and Yen Y:
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatitis: case study and
literature review. Anticancer Res. 29:3239–3243. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Sempoux C, Jibara G, Ward SC, et al:
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: new insights in pathology. Semin
Liver Dis. 31:49–60. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Isomoto H: Epigenetic alterations
associated with cholangiocarcinoma (review). Oncol Rep. 22:227–232.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Zhou L, Yang ZX, Song WJ, et al:
MicroRNA-21 regulates the migration and invasion of a stem-like
population in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 43:661–669.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Guo P, Lan J, Ge J, Nie Q, Mao Q and Qiu
Y: miR-708 acts as a tumor suppressor in human glioblastoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 30:870–876. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Brunet Vega A, Pericay C, Moya I, et al:
microRNA expression profile in stage III colorectal cancer:
Circulating miR-18a and miR-29a as promising biomarkers. Oncol Rep.
30:320–326. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Karakatsanis A, Papaconstantinou I,
Gazouli M, Lyberopoulou A, Polymeneas G and Voros D: Expression of
microRNAs, miR-21, miR-31, miR-122, miR-145, miR-146a, miR-200c,
miR-221, miR-222, and miR-223 in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its prognostic
significance. Mol Carcinog. 52:297–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Oishi N, Kumar MR, Roessler S, et al:
Transcriptomic profiling reveals hepatic stem-like gene signatures
and interplay of miR-200c and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 56:1792–1803. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Zeng B, Li Z, Chen R, et al: Epigenetic
regulation of miR-124 by hepatitis C virus core protein promotes
migration and invasion of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells by
targeting SMYD3. FEBS Lett. 586:3271–3278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Boon LM, Mulliken JB and Vikkula M: RASA1:
variable phenotype with capillary and arteriovenous malformations.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 15:265–269. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Sun D, Yu F, Ma Y, et al: MicroRNA-31
activates the RAS pathway and functions as an oncogenic MicroRNA in
human colorectal cancer by repressing RAS p21 GTPase activating
protein 1 (RASA1). J Biol Chem. 288:9508–9518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Conner EA, et al:
Inactivation of Ras GTPase-activating proteins promotes
unrestrained activity of wild-type Ras in human liver cancer. J
Hepatol. 54:311–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Hu X, Stern HM, Ge L, et al: Genetic
alterations and oncogenic pathways associated with breast cancer
subtypes. Mol Cancer Res. 7:511–522. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Ulger C, Toruner GA, Alkan M, et al:
Comprehensive genome-wide comparison of DNA and RNA level scan
using microarray technology for identification of candidate
cancer-related genes in the HL-60 cell line. Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 147:28–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Yang XY, Guan M, Vigil D, Der CJ, Lowy DR
and Popescu NC: p120Ras-GAP binds the DLC1 Rho-GAP tumor suppressor
protein and inhibits its RhoA GTPase and growth-suppressing
activities. Oncogene. 28:1401–1409. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011.
|
|
19.
|
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M and
Giegerich R: Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target
duplexes. RNA. 10:1507–1517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, et al:
Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet. 37:495–500.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Lapinski PE, Qiao Y, Chang CH and King PD:
A role for p120 RasGAP in thymocyte positive selection and survival
of naive T cells. J Immunol. 187:151–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Osman MA, Sarkar FH and Rodriguez-Boulan
E: A molecular rheostat at the interface of cancer and diabetes.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1836:166–176. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Kawahigashi Y, Mishima T, Mizuguchi Y, et
al: MicroRNA profiling of human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
cell lines reveals biliary epithelial cell-specific microRNAs. J
Nippon Med Sch. 76:188–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Chen L, Yan HX, Yang W, et al: The role of
microRNA expression pattern in human intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 50:358–369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Xu RS, Wu XD, Zhang SQ, et al: The tumor
suppressor gene RhoBTB1 is a novel target of miR-31 in human colon
cancer. Int J Oncol. 42:676–682. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Tu HF, Lin SC and Chang KW: MicroRNA
aberrances in head and neck cancer: pathogenetic and clinical
significance. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 21:104–111.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Liu CJ, Lin SC, Yang CC, Cheng HW and
Chang KW: Exploiting salivary miR-31 as a clinical biomarker of
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 34:219–224. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Zhang Y, Guo J, Li D, et al:
Down-regulation of miR-31 expression in gastric cancer tissues and
its clinical significance. Med Oncol. 27:685–689. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, et al:
Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in
prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:1166–1176. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Creighton CJ, Fountain MD, Yu Z, et al:
Molecular profiling uncovers a p53-associated role for microRNA-31
in inhibiting the proliferation of serous ovarian carcinomas and
other cancers. Cancer Res. 70:1906–1915. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Lu Z, Ye Y, Jiao D, Qiao J, Cui S and Liu
Z: miR-155 and miR-31 are differentially expressed in breast cancer
patients and are correlated with the estrogen receptor and
progesterone receptor status. Oncol Lett. 4:1027–1032. 2012.
|
|
33.
|
Veerla S, Lindgren D, Kvist A, et al:
MiRNA expression in urothelial carcinomas: important roles of
miR-10a, miR-222, miR-125b, miR-7 and miR-452 for tumor stage and
metastasis, and frequent homozygous losses of miR-31. Int J Cancer.
124:2236–2242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Wang C, Cigliano A, Delogu S, et al:
Functional crosstalk between AKT/mTOR and Ras/MAPK pathways in
hepatocarcinogenesis: Implications for the treatment of human liver
cancer. Cell Cycle. 12:1999–2010. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|