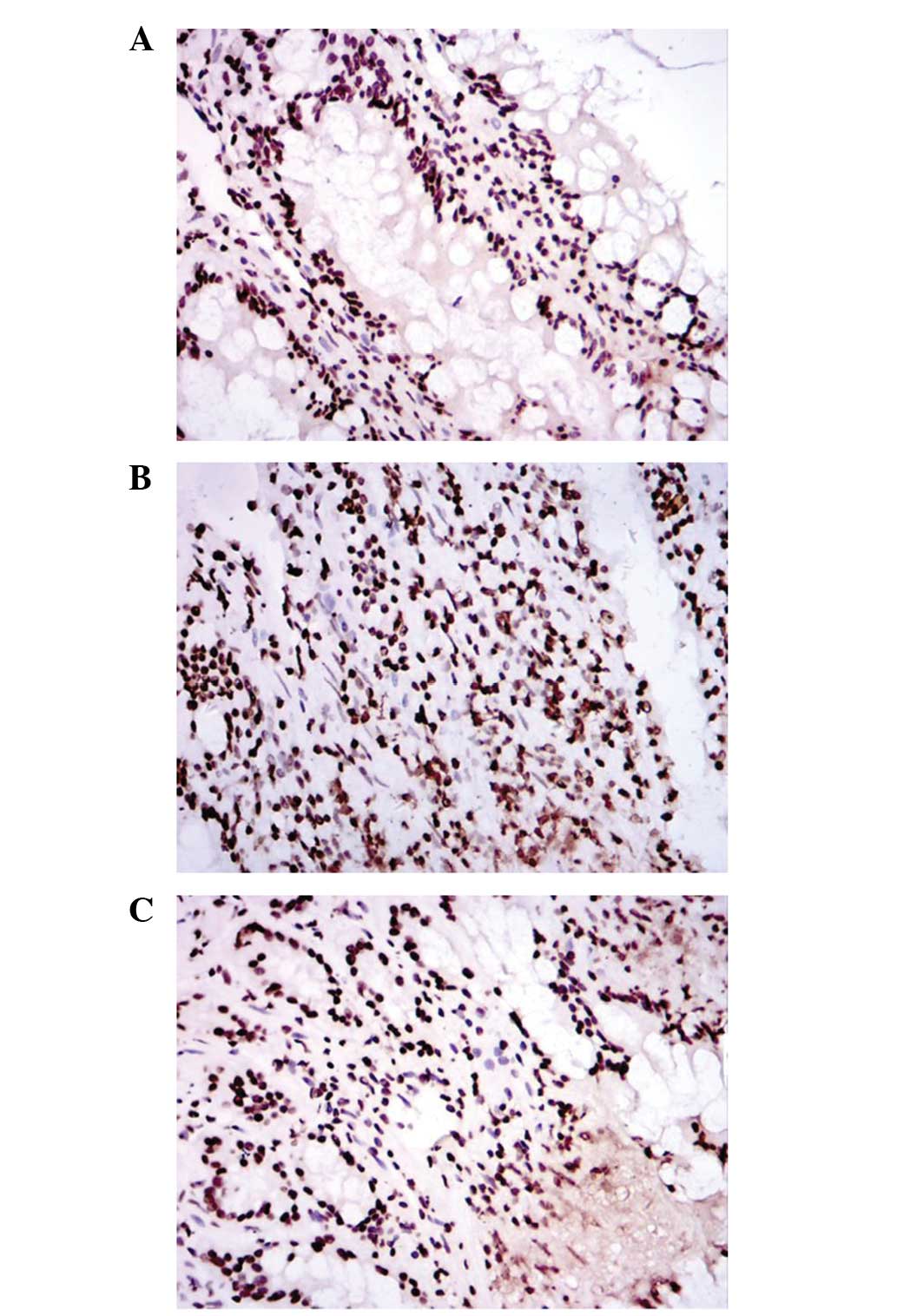
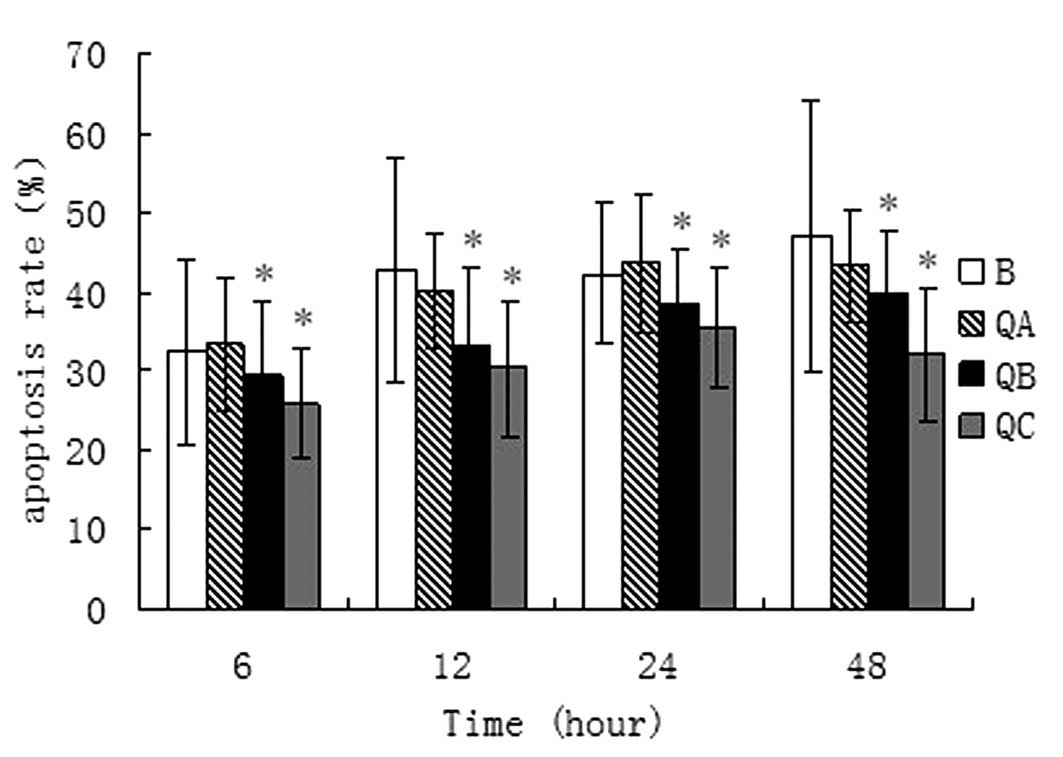
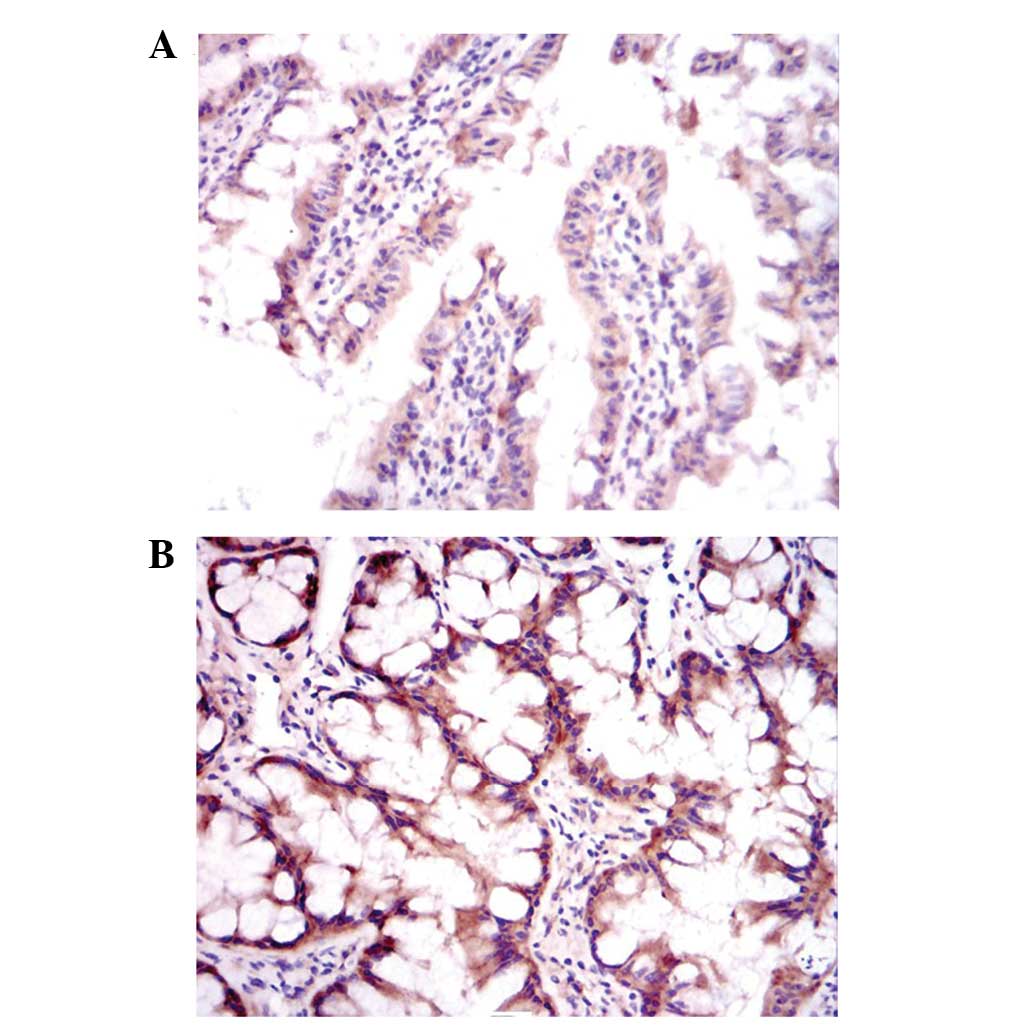
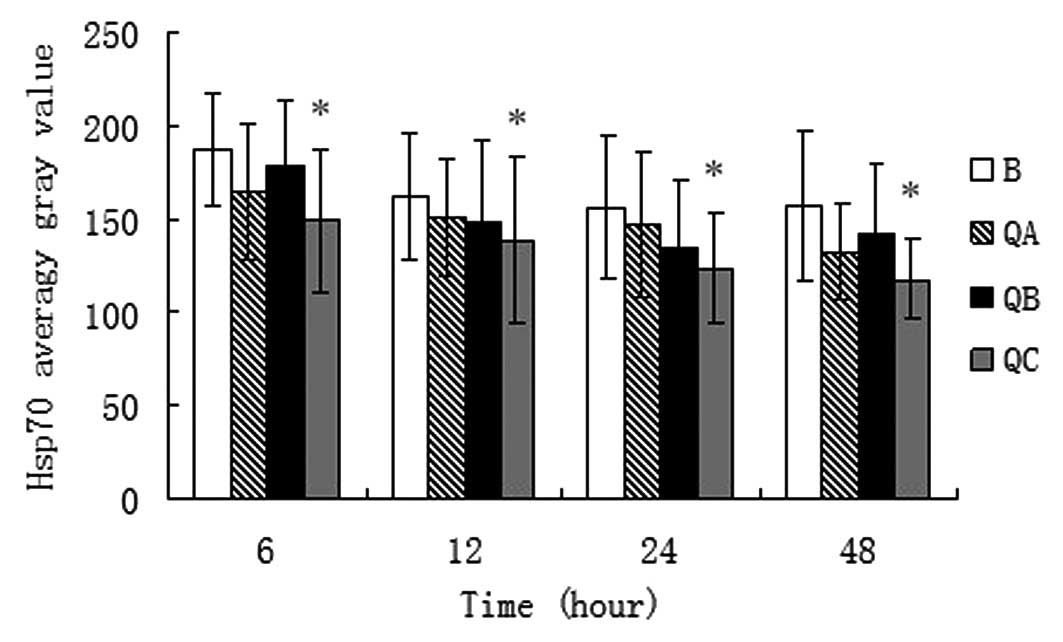
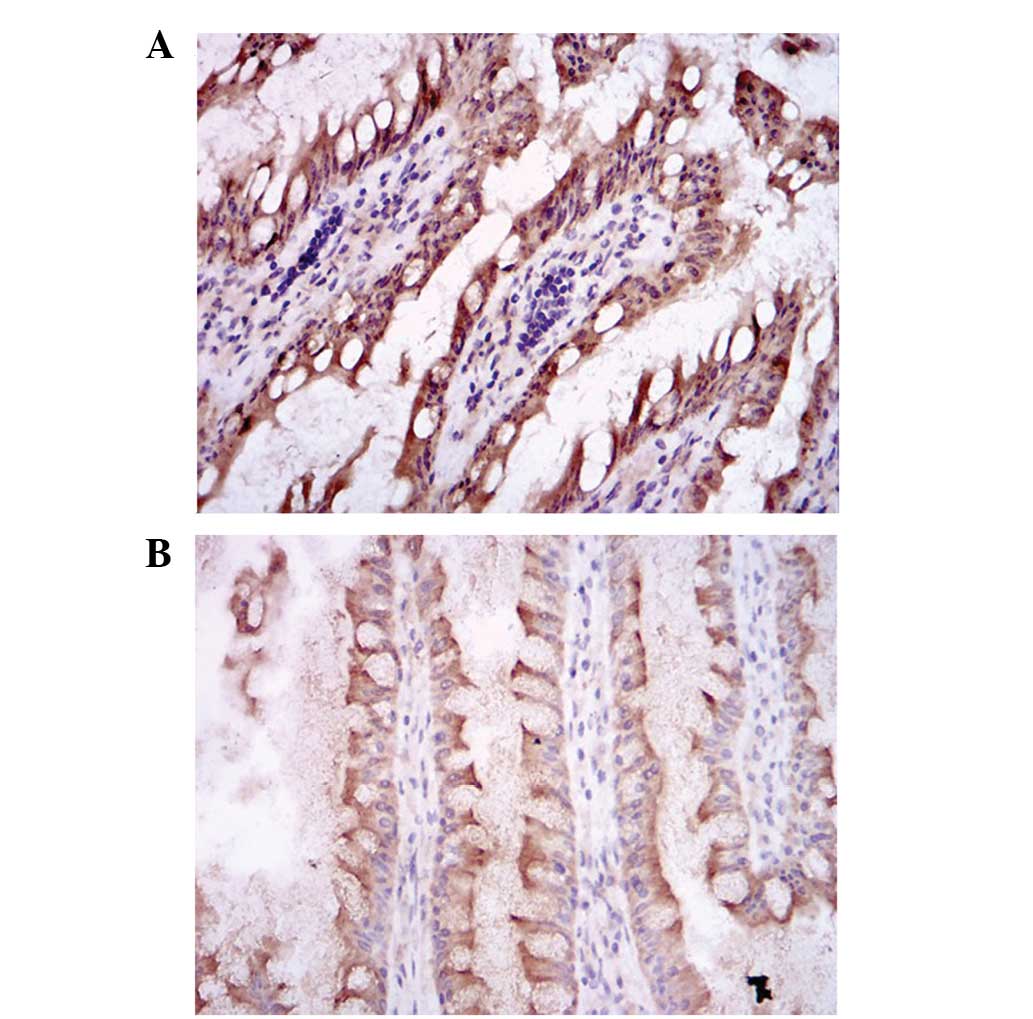
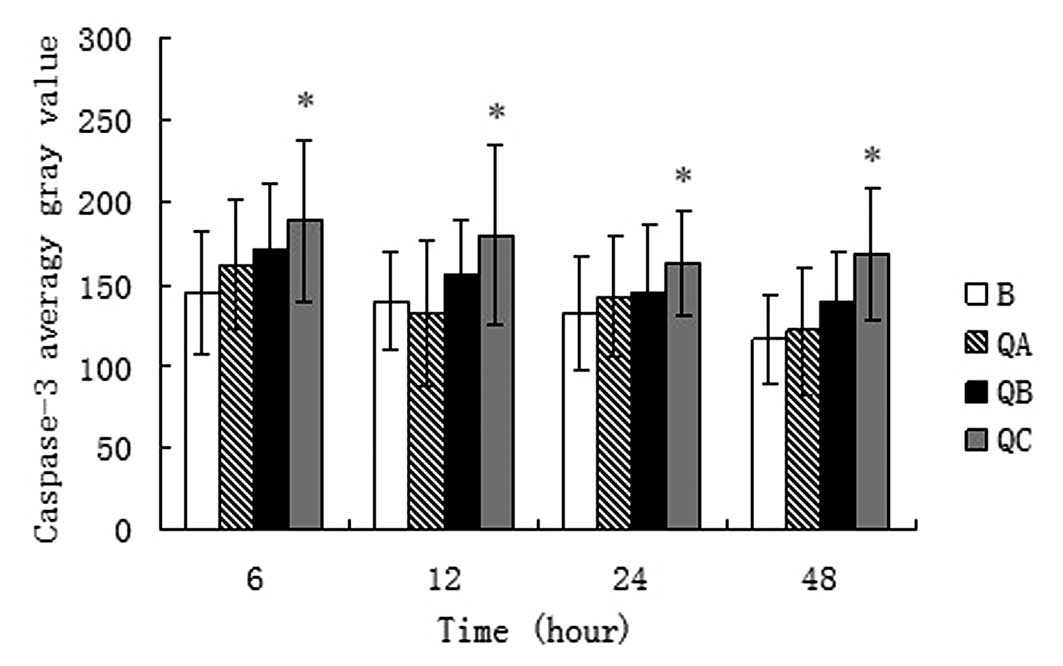
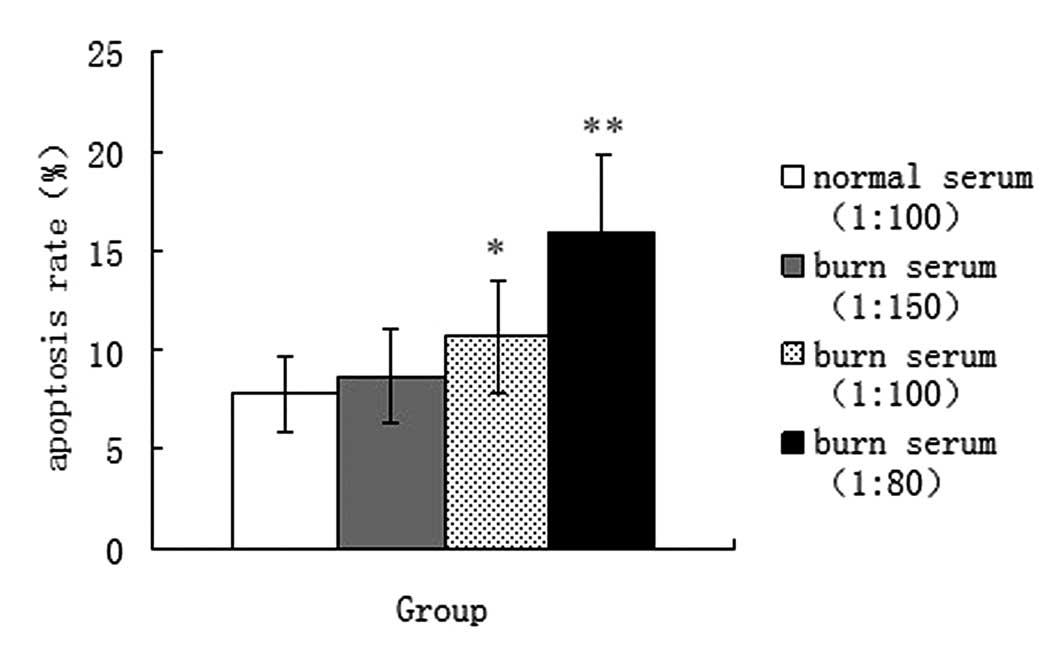
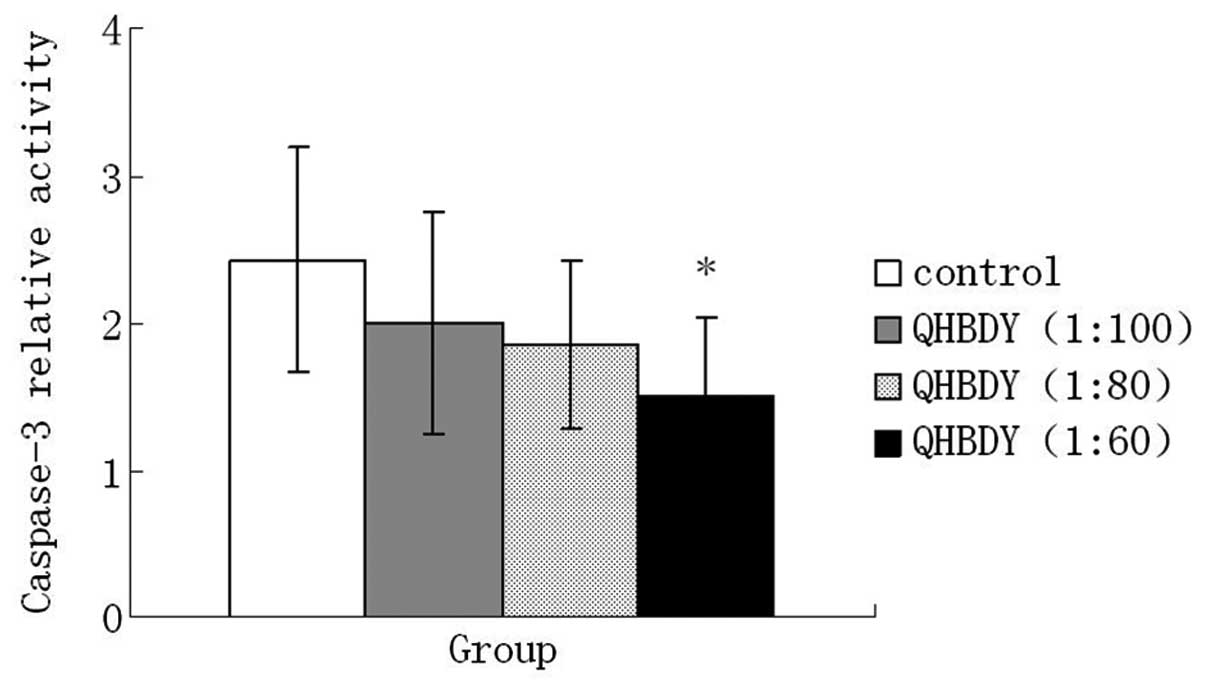
|
1
|
Itoh H, Yagi M, Fushida S, et al:
Activation of immediate early gene, c-fos, and c-jun in the rat
small intestine after ischemia/reperfusion. Transplantion.
69:598–604. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang L, Zhou Y, Peng J, Zhang Z, Jiang DJ
and Li YJ: Role of endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in
gastric mucosal injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 86:97–104. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumar V, Mohanty MK and Kanth S: Fatal
burns in Manipal area: a 10 year study. J Forensic Leg Med. 14:3–6.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shinozawa Y: Fluid management and care for
multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in patients with extensive
burns. Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 106:736–739. 2005.(In
Japanese).
|
|
5
|
Duncan DJ, Hopkins PM and Harrison SM:
Negative inotropic effect of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and
interleukin-1beta are ameliorated by alfentanil in rat ventricular
myocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 150:720–726. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin WJ, Wang DL and Pan YQ: Depression
research of psychoneuroimmunology: the role of cytokines. Adv
Psychol Sci. 16:404–410. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Cheng C, Li Z, Huang W, et al: The
influence of the large military exercise on the soldiers’ some
immune-endocrine function. Med J Chin PLA. 32:189–190. 2007.(In
Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Mishima S, Yukioka T, Matsuda H and
Shimazaki S: Mild hypotension and body burns synergistically
increase bacterial translocation in rats consistent with a ‘two-hit
phenomenon’. J Burn Care Rehabil. 18:22–26. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang HY, Lv NH, Xie Y, et al: Protection
of heat shock preconditioning on acute gastric mucosal lesion in
scalded rats and its mechanism. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi.
23:58–61. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Odashima M, Otaka M, Jin M, et al:
Induction of a 72-kDa heat-shock protein in cultured rat gastric
mucosal cells and rat gastric mucosa by zinc L-carnosine. Dig Dis
Sci. 47:2799–2804. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Muñoz J, Albillos A, Pérez-Páramo M, Rossi
I and Alvarez-Mon M: Factors mediating the hemodynamic effects of
tumor necrosis factor-alpha in portal hypertensive rats. Am J
Physiol. 276:G687–G693. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Suemasu S, Tanaka K, Namba T, Ishihara T,
Katsu T, Fujimoto M, Adachi H, Sobue G, Takeuchi K, Nakai A and
Mizushima T: A role for HSP70 in protecting against
indomethacin-induced gastric lesions. J Biol Chem. 284:19705–19715.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Walker HL and Mason AD Jr: A standard
animal burn. J Trauma. 8:1049–1051. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bromberg Z, Raj N, Goloubinoff P,
Deutschman CS and Weiss YG: Enhanced expression of 70-kilodalton
heat shock protein limits cell division in a sepsis-induced model
of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 36:246–255.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wilmore DW and Robinson MK: Metabolism and
nutrition support. Surgical Basic Science. Fischer JE: 7th Edition.
Mosby Press Co; St Louis, MO: pp. 1251993
|
|
16
|
Wang LC: Research progress on chemical
compositions and efficacy of Lonicera spp. J Anhui Agric
Sci. 37:2036–2037. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Wang L, Cui B and Zhang H: Pharmacological
research progress on Lonicera spp. Chin J Anim Husbandry Vet
Med. 34:91–95. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
He X and Lan R: Pharmacological action and
clinical application of honeysuckle. Lishizhen Med Mat Med Res.
15:865–867. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Gong ZZ, Zheng YX, Zheng NG, et al:
Anti-oxidative effect of honeysuckle in vivo: an experimental
study. Prac J Med Pharm. 23:584–585. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Kang OH, Choi JG, Lee JH and Kwon DY:
Luteolin isolated from the flowers of Lonicera japonica
suppresses inflammatory mediator release by blocking NF-κB and
MAPKs activation pathways in HMC-1 cells. Molecules. 15:385–398.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiang Z and Ning Z: Scavenging and
antioxidant properties of compound derived from chlorogenic acid in
South-China honeysuckle. LWT - Food Sci Technol. 41:1189–1203.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Schierenbeck KA: Japanese honeysuckle
(Lonicera japonica) as an invasive species; history,
ecology, and context. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 23:3912004.
|