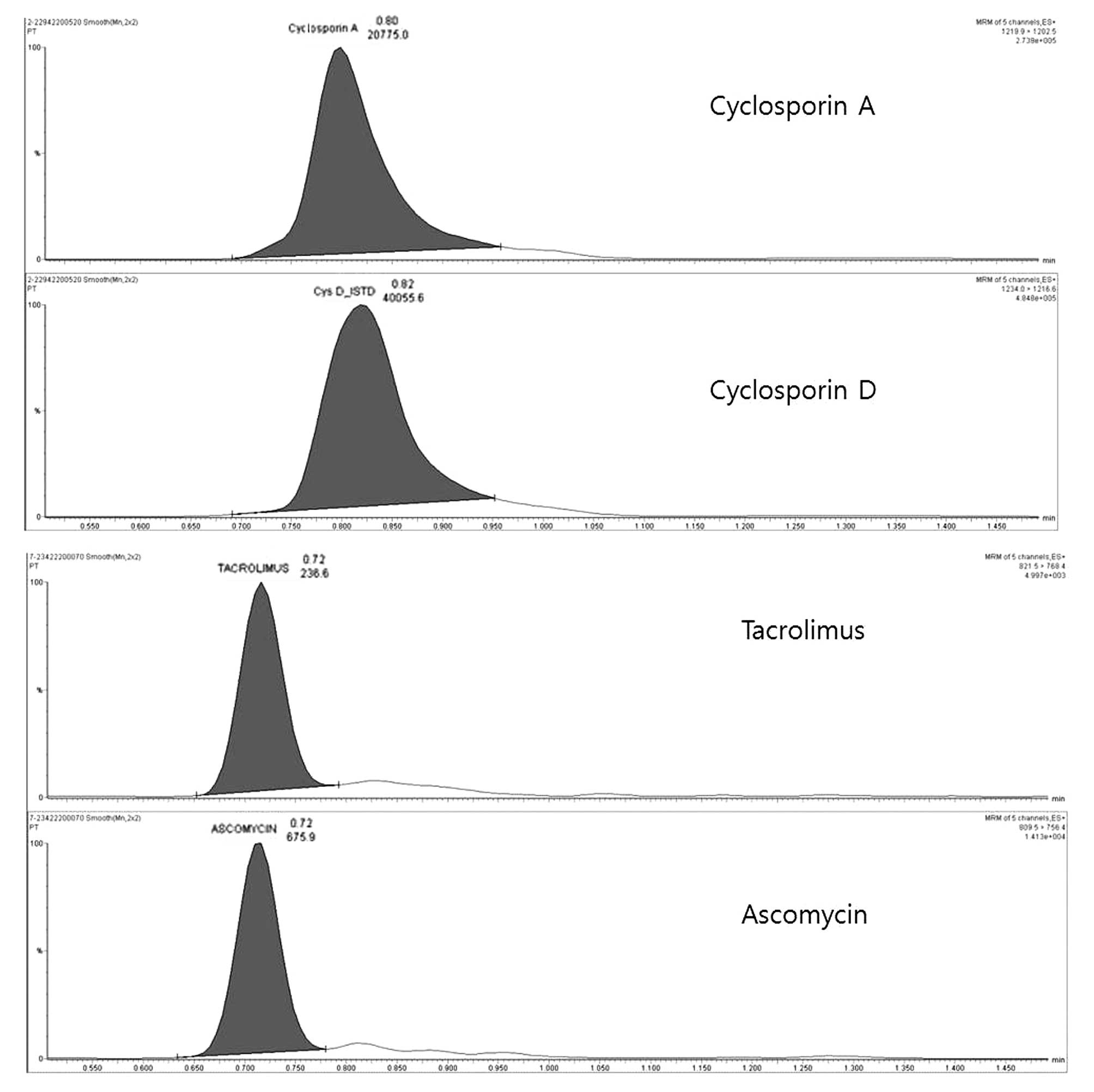
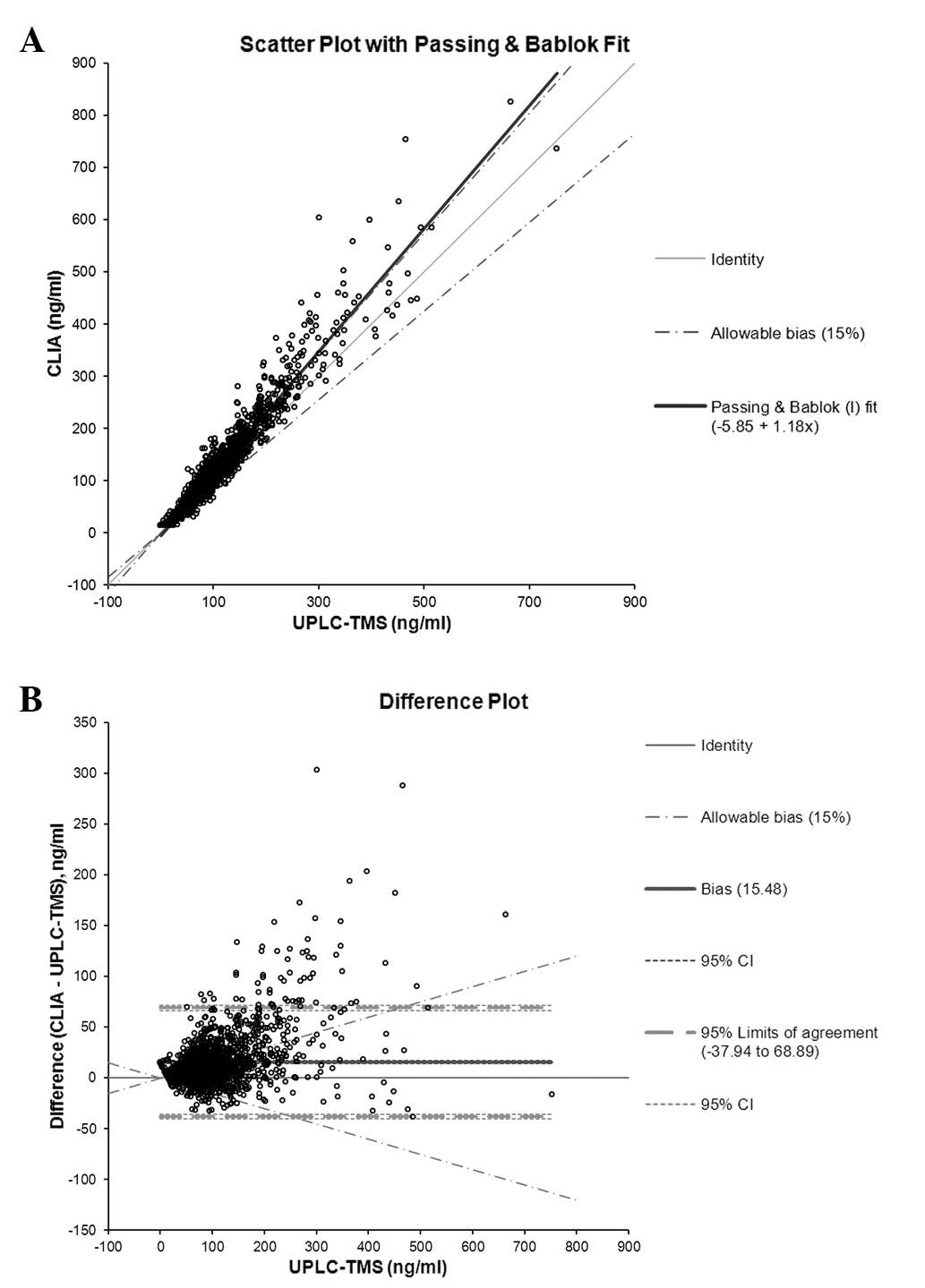
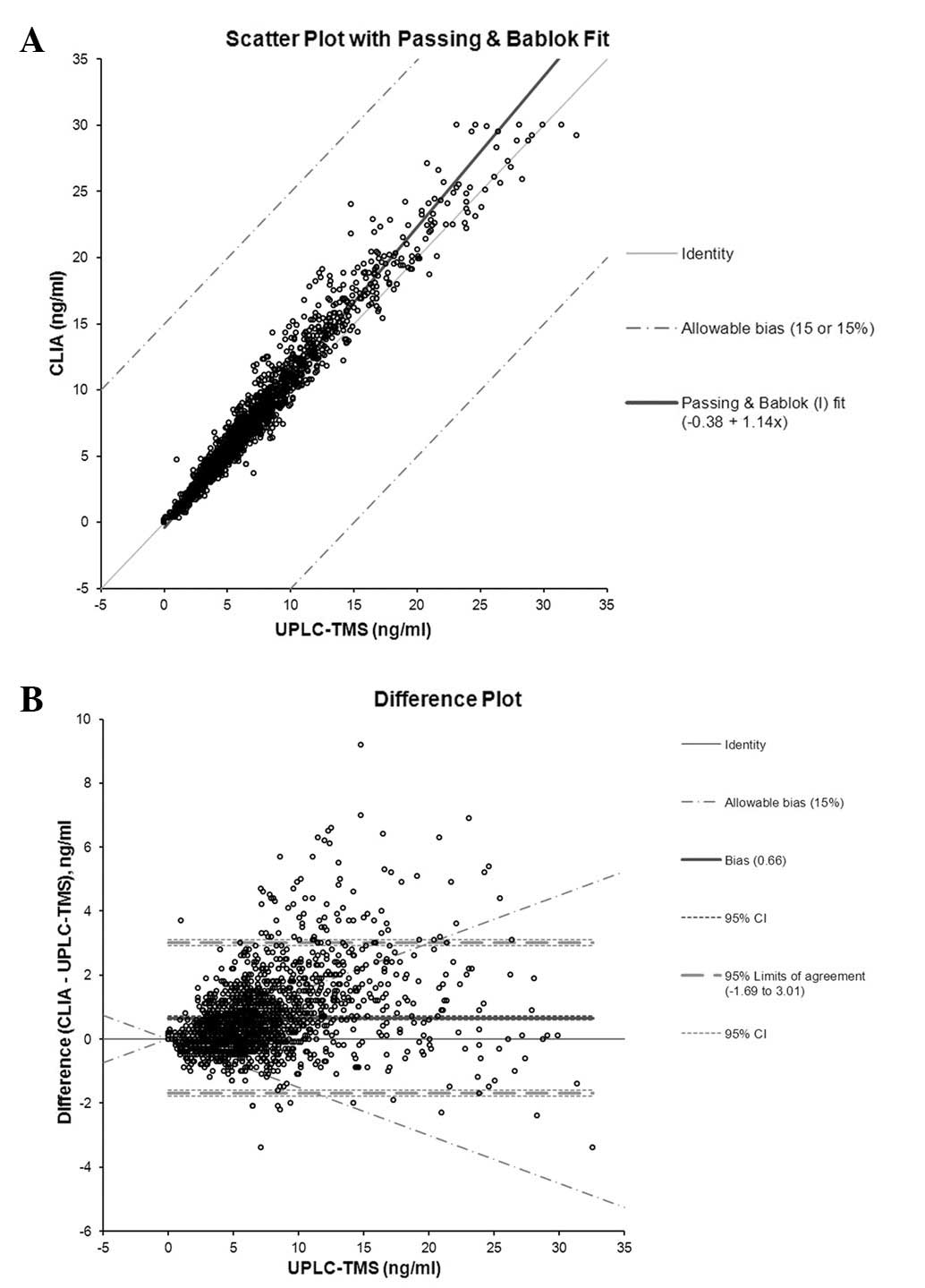
|
1
|
Ferrara JL and Deeg HJ: Graft-versus-host
disease. N Engl J Med. 324:667–674. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kahan BD, Keown P, Levy GA and Johnston A:
Therapeutic drug monitoring of immunosuppressant drugs in clinical
practice. Clin Ther. 24:330–350. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jusko WJ, Thomson AW, Fung J, et al:
Consensus document: therapeutic monitoring of tacrolimus (FK-506).
Ther Drug Monit. 17:606–614. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ansermot N, Fathi M, Veuthey JL, Desmeules
J, Rudaz S and Hochstrasser D: Simultaneous quantification of
cyclosporine, tacrolimus, sirolimus and everolimus in whole blood
by liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. Clin
Biochem. 41:728–735. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chung JW, An D, Song J, et al: Performance
evaluation of affinity column mediated immunometric assay for
tacrolimus. Korean J Lab Med. 29:415–422. 2009.(In Korean).
|
|
6
|
Oellerich M and Armstrong VW: The role of
therapeutic drug monitoring in individualizing immunosuppressive
drug therapy: recent developments. Ther Drug Monit. 28:720–725.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Taylor PJ: Therapeutic drug monitoring of
immunosuppressant drugs by high-performance liquid
chromatography-mass spectrometry. Ther Drug Monit. 26:215–219.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Poquette MA, Lensmeyer GL and Doran TC:
Effective use of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC/MS) in
the routine clinical laboratory for monitoring sirolimus,
tacrolimus, and cyclosporine. Ther Drug Monit. 27:144–150. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Korecka M, Solari SG and Shaw LM:
Sensitive, high throughput HPLC-MS/MS method with on-line sample
clean-up for everolimus measurement. Ther Drug Monit. 28:484–490.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Christians U, Jacobsen W, Serkova N, et
al: Automated, fast and sensitive quantification of drugs in blood
by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with on-line extraction:
immunosuppressants. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 748:41–53.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deters M, Kirchner G, Resch K and Kaever
V: Simultaneous quantification of sirolimus, everolimus, tacrolimus
and cyclosporine by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
(LC-MS). Clin Chem Lab Med. 40:285–292. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ceglarek U, Lembcke J, Fiedler GM, et al:
Rapid simultaneous quantification of immunosuppressants in
transplant patients by turbulent flow chromatography combined with
tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 346:181–190. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wallemacq P, Goffinet JS, O’Morchoe S, et
al: Multi-site analytical evaluation of the Abbott ARCHITECT
tacrolimus assay. Ther Drug Monit. 31:198–204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wallemacq P, Armstrong VW, Brunet M, et
al: Opportunities to optimize tacrolimus therapy in solid organ
transplantation: report of the European consensus conference. Ther
Drug Monit. 31:139–152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Napoli KL: 12-hour area under the curve
cyclosporine concentrations determined by a validated liquid
chromatography-mass spectrometry procedure compared with
fluorescence polarization immunoassay reveals sirolimus effect on
cyclosporine pharmacokinetics. Ther Drug Monit. 28:726–736. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang S, Magill JE and Vicente FB: A fast
and simple high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry
method for simultaneous measurement of whole blood tacrolimus and
sirolimus. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 129:661–665. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kaptein EM, Yi SS, Endres DB, Kaptein JS
and Chan LS: Vitamin D deficiency in urban indigent patients in
Southern California. Endocr Pract. 19:404–413. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|