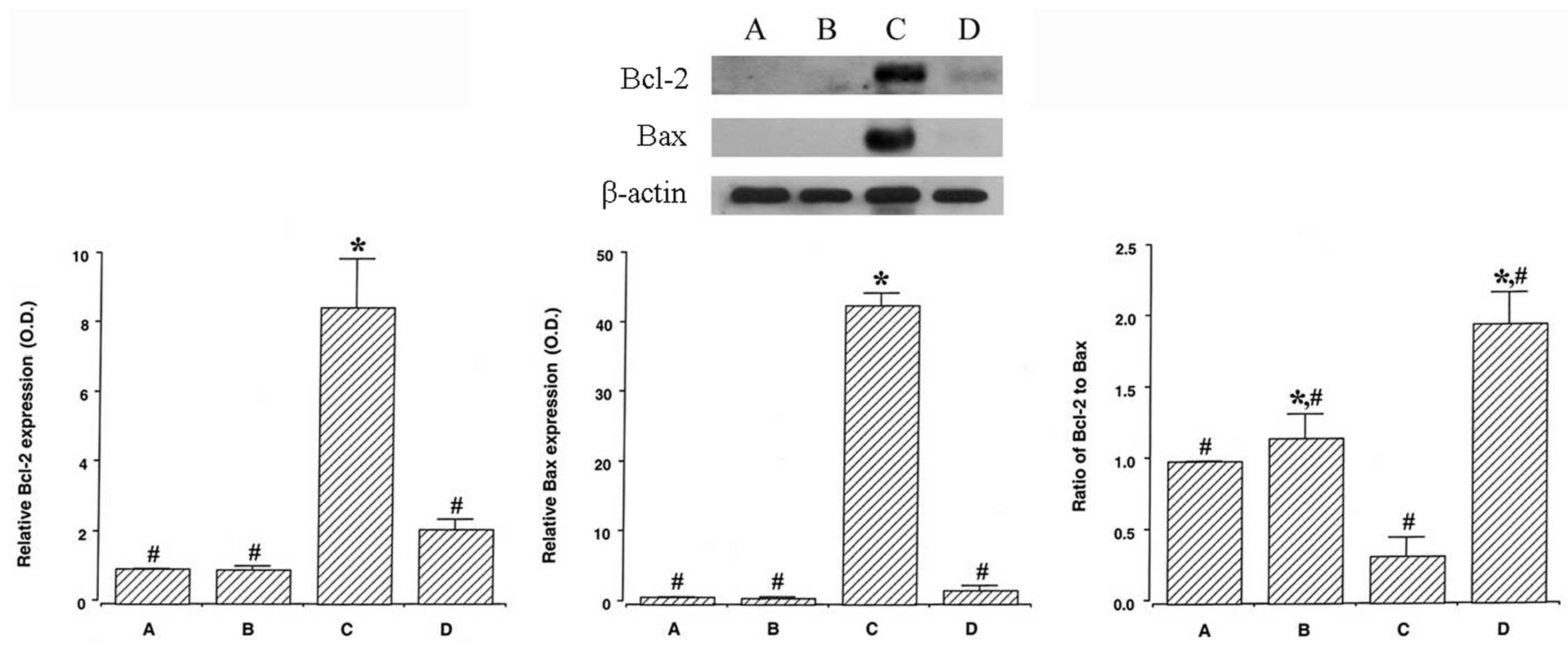
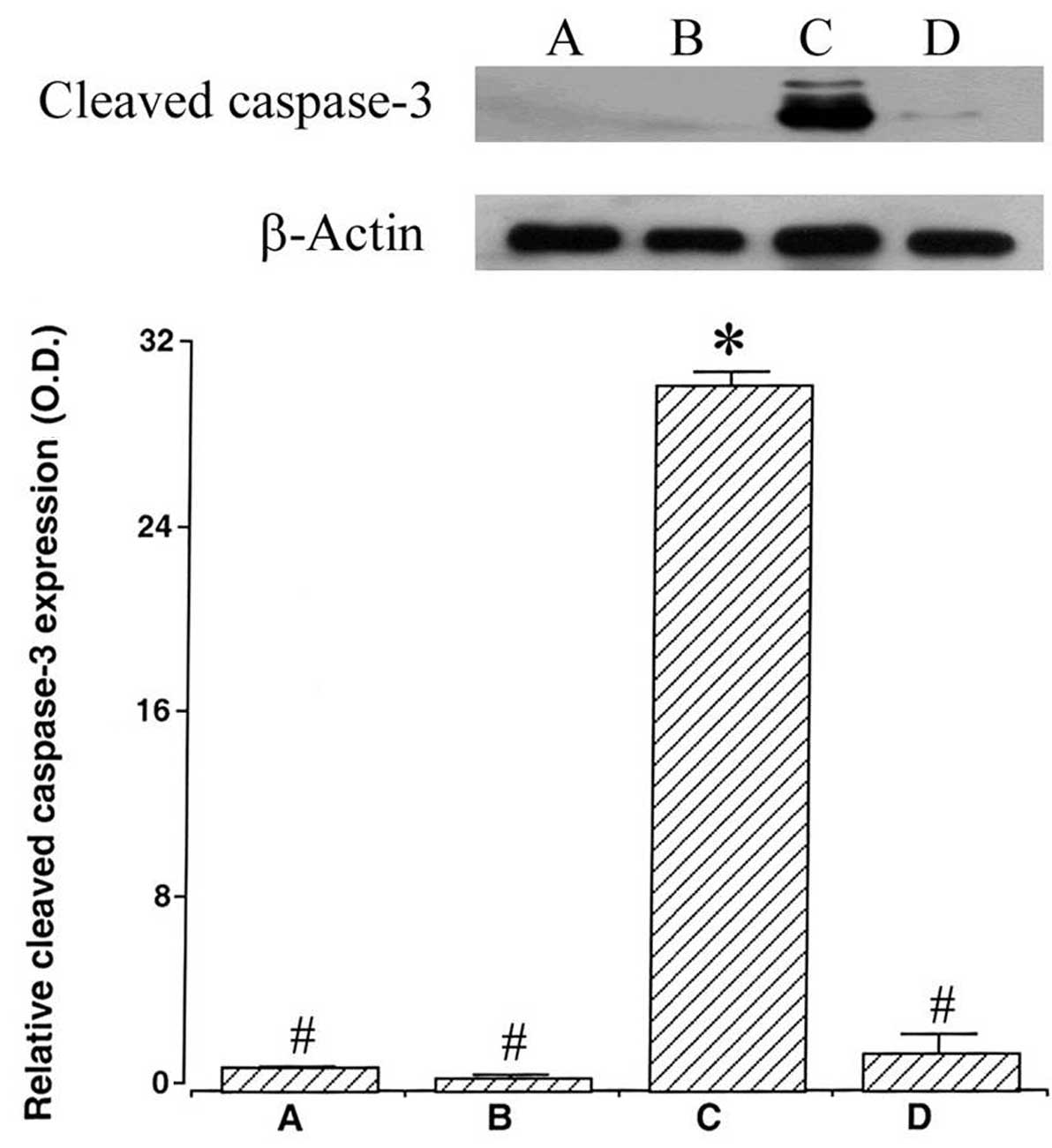
|
1
|
Tator CH and Fehlings MG: Review of the
secondary injury theory of acute spinal cord trauma with emphasis
on vascular mechanisms. J Neurosurg. 75:15–26. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hwang L, Choi IY, Kim SE, Ko IG, Shin MS,
Kim CJ, Kim SH, Jin JJ, Chung JY and Yi JW: Dexmedetomidine
ameliorates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced memory impairment by
inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic
factor expression in the rat hippocampus. Int J Mol Med.
31:1047–1056. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Kim DH, Ko IG, Kim BK, Kim TW, Kim SE,
Shin MS, Kim CJ, Kim H, Kim KM and Baek SS: Treadmill exercise
inhibits traumatic brain injury-induced hippocampal apoptosis.
Physiol Behav. 101:660–665. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Savitz SI and Rosenbaum DM: Apoptosis in
neurological disease. Neurosurgery. 42:555–574. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sung YH, Kim SC, Hong HP, Park CY, Shin
MS, Kim CJ, Seo JH, Kim DY, Kim DJ and Cho HJ: Treadmill exercise
ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal loss through suppressing
microglial activation in Parkinson’s disease mice. Life Sci.
91:1309–1316. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Crowe MJ, Bresnahan JC, Shuman SL, Masters
JN and Beattie MS: Apoptosis and delayed degeneration after spinal
cord injury in rats and monkeys. Nat Med. 3:73–76. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li GL, Brodin G, Farooque M, Funa K, Holtz
A, Wang WL and Olsson Y: Apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2 after
compression trauma to rat spinal cord. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
55:280–289. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yong C, Arnold PM, Zoubine MN, Citron BA,
Watanabe I, Berman NE and Festoff BW: Apoptosis in cellular
compartments of rat spinal cord after severe contusion injury. J
Neurotrauma. 15:459–472. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Emery E, Aldana P, Bunge MB, Puckett W,
Srinivasan A, Keane RW, Bethea J and Levi AD: Apoptosis after
traumatic human spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg. 89:911–920. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nathoo N, Narotam PK, Agrawal DK, Connolly
CA, van Dellen JR, Barnett GH and Chetty R: Influence of apoptosis
on neurological outcome following traumatic cerebral contusion. J
Neurosurg. 101:233–240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsuchiya D, Hong S, Matsumori Y, Kayama T,
Swanson RA, Dillman WH, Liu J, Panter SS and Weinstein PR:
Overexpression of rat heat shock protein 70 reduces neuronal injury
after transient focal ischemia, transient global ischemia, or
kainic acid-induced seizures. Neurosurgery. 53:1179–1188. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: a review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin Z and El-Deiry WS: Overview of cell
death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:139–163.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schorey JS and Cooper AM: Macrophage
signaling upon mycobacterial infection: the MAP kinases lead the
way. Cell Microbiol. 5:133–142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen
GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S and Reed JC: Regulation of
cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science.
282:1318–1321. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H,
Gotoh Y and Greenberg ME: Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples
survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell.
91:231–241. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shin DY, Kim GY, Lee JH, Choi BT, Yoo YH
and Choi YH: Apoptosis induction of human prostate carcinoma DU145
cells by diallyl disulfide via modulation of JNK and PI3K/AKT
signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 13:14158–14171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Jiang Y, Wan Y, Zhang L, Tang W, Ma
J, Wu S and Cheng W: Medroxyprogestogen enhances apoptosis of
SKOV-3 cells via inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Biomed Res. 27:43–50. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barber AJ, Nakamura M, Wolpert EB, Reiter
CE, Seigel GM, Antonetti DA and Gardner TW: Insulin rescues retinal
neurons from apoptosis by a phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt-mediated mechanism that reduces the activation of
caspase-3. J Biol Chem. 276:32814–32821. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lobner D and Ali C: Mechanisms of bFGF and
NT-4 potentiation of necrotic neuronal death. Brain Res. 954:42–50.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou L and Shine HD: Neurotrophic factors
expressed in both cortex and spinal cord induce axonal plasticity
after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci Res. 74:221–226. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guan J, Bennet L, Gluckman PD and Gunn AJ:
Insulin-like growth factor-1 and post-ischemic brain injury. Prog
Neurobiol. 70:443–462. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pierchala BA, Ahrens RC, Paden AJ and
Johnson EM Jr: Nerve growth factor promotes the survival of
sympathetic neurons through the cooperative function of the protein
kinase C and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways. J Biol Chem.
279:27986–27993. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cotman CW, Berchtold NC and Christie LA:
Exercise builds brain health: key roles of growth factor cascades
and inflammation. Trends Neurosci. 30:464–472. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tillerson JL, Caudle WM, Reverón ME and
Miller GW: Exercise induces behavioral recovery and attenuates
neurochemical deficits in rodent models of Parkinson’s disease.
Neuroscience. 119:899–911. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Griesbach GS, Hovda DA, Molteni R, Wu A
and Gomez-Pinilla F: Voluntary exercise following traumatic brain
injury: brain-derived neurotrophic factor upregulation and recovery
of function. Neuroscience. 125:129–139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Goldshmit Y, Lythgo N, Galea MP and
Turnley AM: Treadmill training after spinal cord hemisection in
mice promotes axonal sprouting and synapse formation and improves
motor recovery. J Neurotrauma. 25:449–465. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ying Z, Roy RR, Zhong H, Zdunowski S,
Edgerton VR and Gomez-Pinilla F: BDNF-exercise interactions in the
recovery of symmetrical stepping after a cervical hemisection in
rats. Neuroscience. 155:1070–1078. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yune TY, Lee JY, Jung GY, Kim SJ, Jiang
MH, Kim YC, Oh YJ, Markelonis GJ and Oh TH: Minocycline alleviates
death of oligodendrocytes by inhibiting pro-nerve growth factor
production in microglia after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci.
27:7751–7761. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chao OY, Pum ME, Li JS and Huston JP: The
grid-walking test: assessment of sensorimotor deficits after
moderate or severe dopamine depletion by 6-hydroxydopamine lesions
in the dorsal striatum and medial forebrain bundle. Neuroscience.
202:318–325. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
de Leon RD and Acosta CN: Effect of
robotic-assisted treadmill training and chronic quipazine treatment
on hindlimb stepping in spinally transected rats. J Neurotrauma.
23:1147–1163. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hennigan A, O’Callaghan RM and Kelly AM:
Neurotrophins and their receptors: roles in plasticity,
neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Biochem Soc Trans.
35:424–427. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang D, Han Y, Zhang J, Chopp M and
Seyfried DM: Statins enhance expression of growth factors and
activate the PI3K/Akt-mediated signaling pathway after experimental
intracerebral hemorrhage. World J Neurosci. 2:74–80. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yao RQ, Qi DS, Yu HL, Liu J, Yang LH and
Wu XX: Quercetin attenuates cell apoptosis in focal cerebral
ischemia rat brain via activation of BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Neurochem Res. 37:2777–2786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ying Z, Roy RR, Edgerton VR and
Gómez-Pinilla F: Voluntary exercise increases neurotrophin-3 and
its receptor TrkC in the spinal cord. Brain Res. 987:93–99. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tait SW and Green DR: Mitochondria and
cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 11:621–632. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Taylor RC, Cullen SP and Martin SJ:
Apoptosis: controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:231–241. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chan G, Nogalski MT, Bentz GL, Smith MS,
Parmater A and Yurochko AD: Pi3k-dependent upregulation of Mcl-1 by
human cytomegalovirus is mediated by epidermal growth factor
receptor and inhibits apoptosis in short-lived monocytes. J
Immunol. 184:3213–3222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen M and Russo-Neustadt AA: Exercise
activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Mol Brain Res.
135:181–193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cory S, Huang DC and Adams JM: The Bcl-2
family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene.
22:8590–8607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu G, Keeler BE, Zhukareva V and Houlé
JD: Cycling exercise affects the expression of apoptosis-associated
microRNAs after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol.
226:200–206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Upadhyay D, Panduri V, Ghio A and Kamp DW:
Particulate matter induces alveolar epithelial cell DNA damage and
apoptosis: role of free radicals and the mitochondria. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 29:180–187. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|