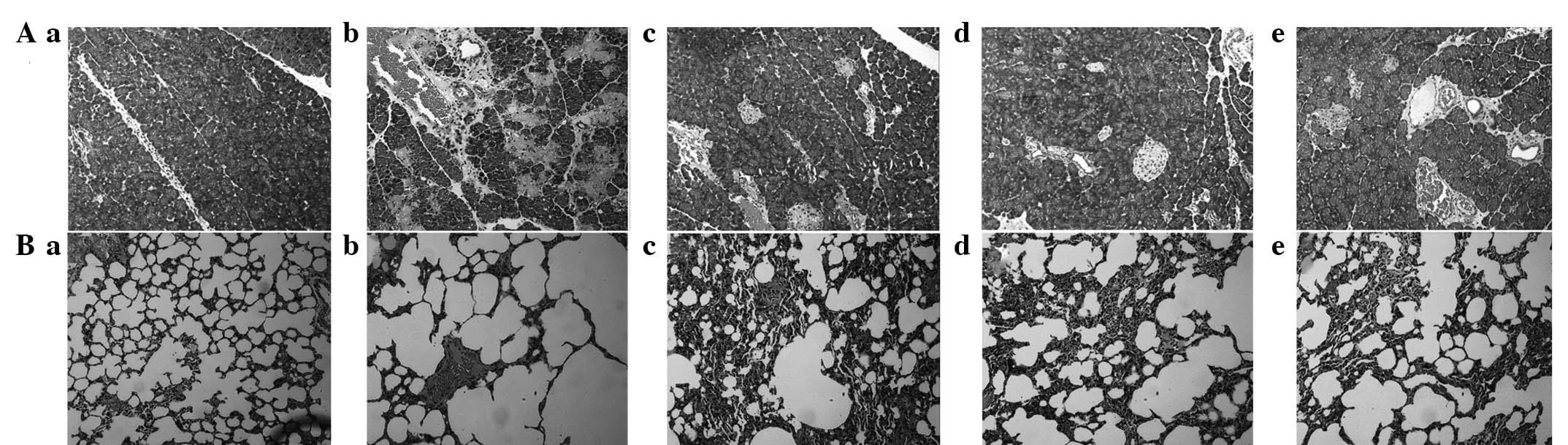
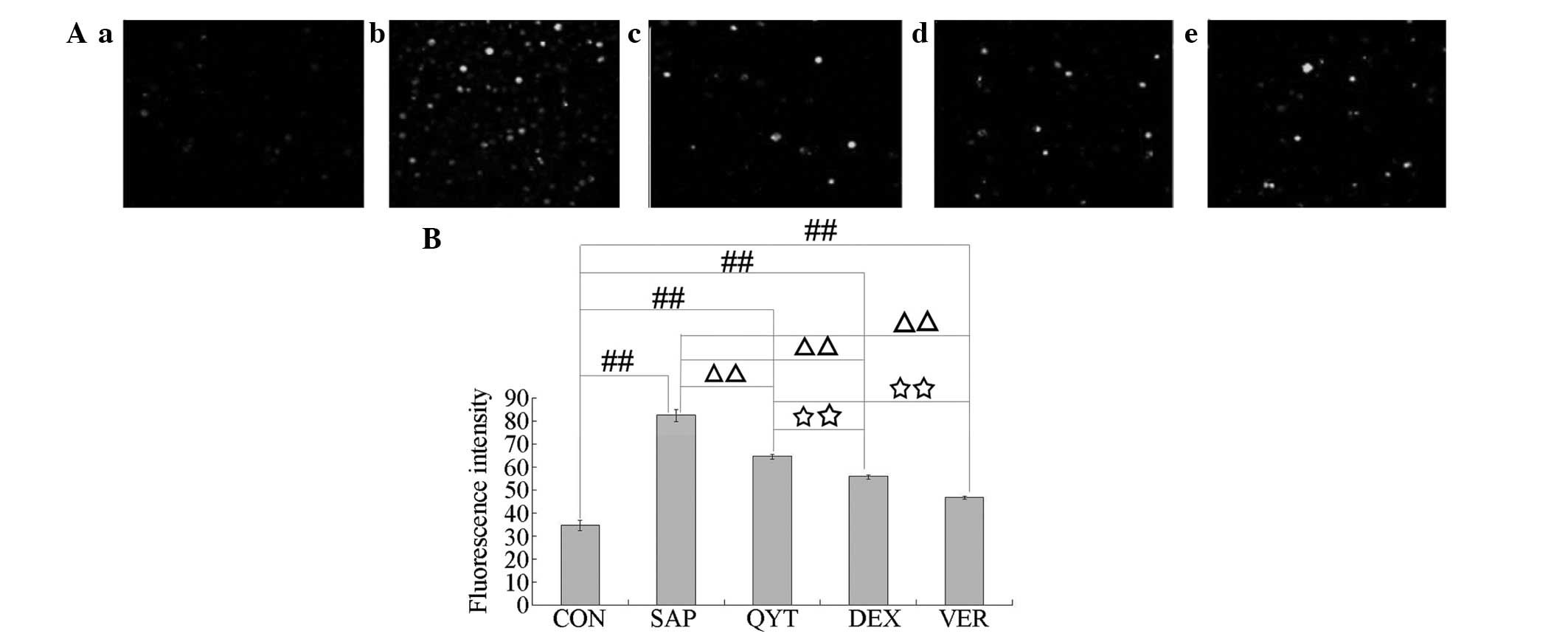
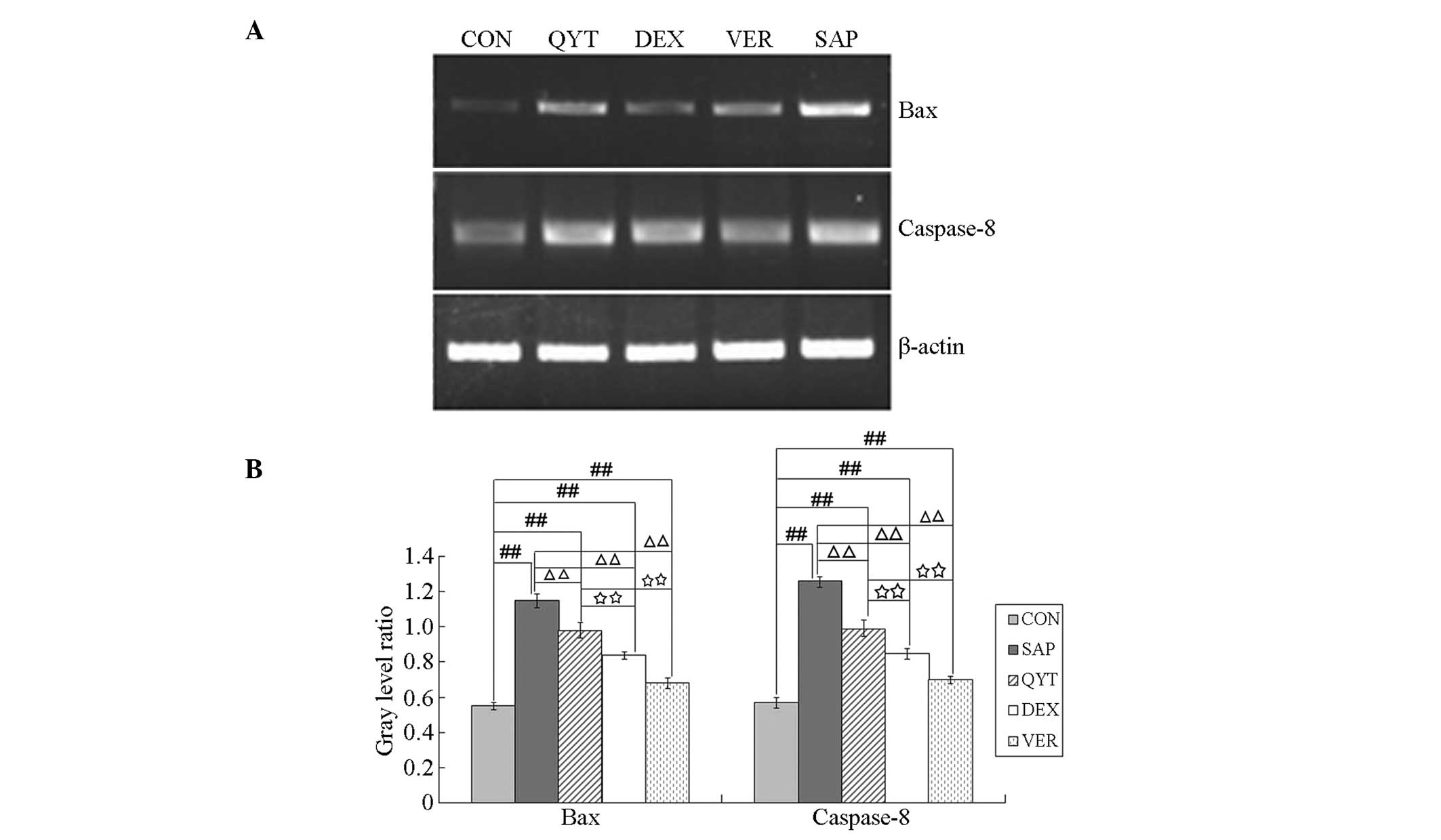
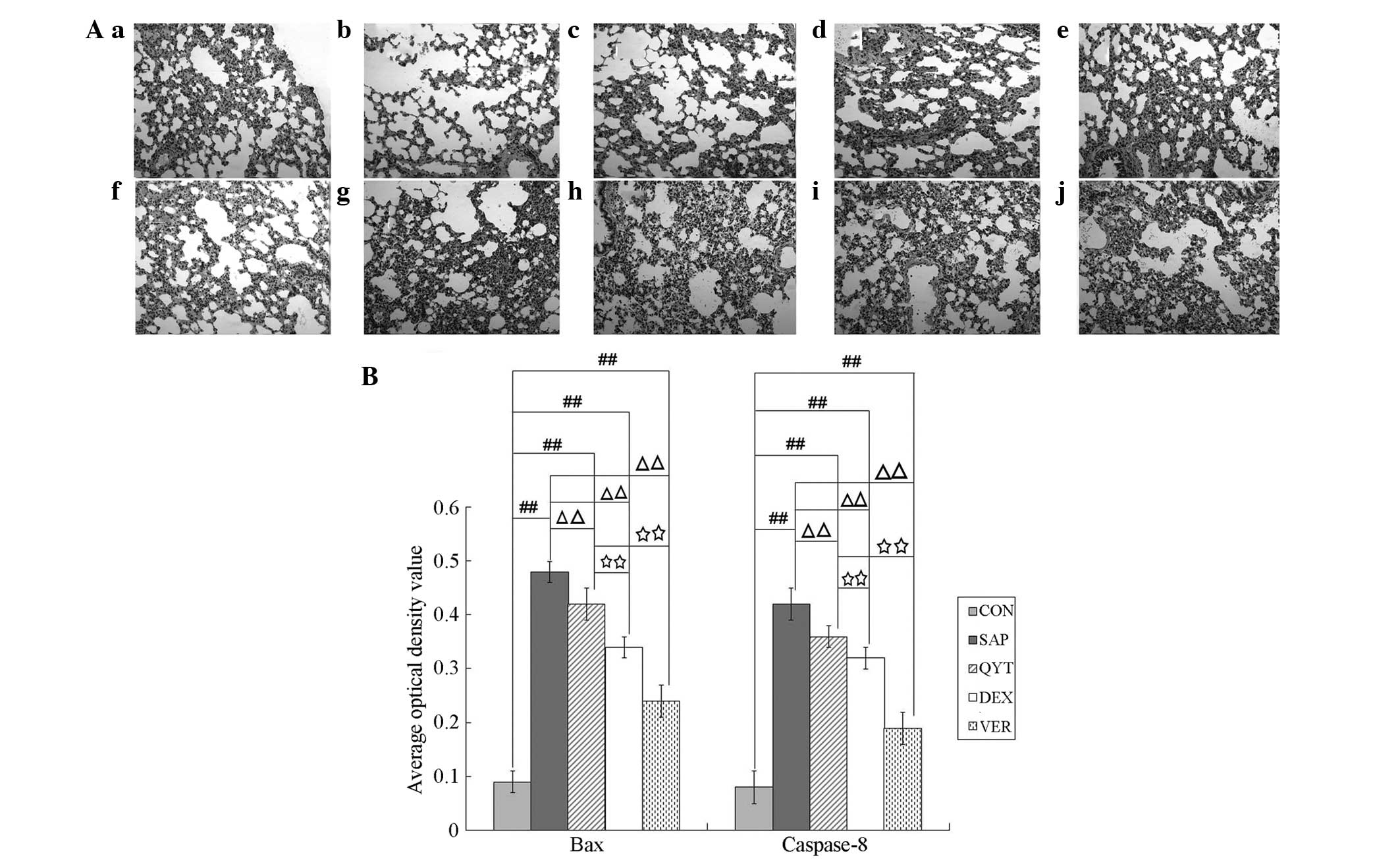
|
1
|
Akbarshahi H, Rosendahl AH,
Westergren-Thorsson G and Andersson R: Acute lung injury in acute
pancreatitis - awaiting the big leap. Respir Med. 106:1199–1210.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Surbatović M, Jovanović K, Radaković S and
Filipović N: Pathophysiological aspects of severe acute
pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 133:76–81.
2005.(In Serbian).
|
|
3
|
Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Rumpf JJ, et al:
NFkappaB activation by Fas is mediated through FADD, caspase-8, and
RIP and is inhibited by FLIP. J Cell Biol. 166:369–380. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Donepudi M, Mac Sweeney A, Briand C and
Grütter MG: Insights into the regulatory mechanism for caspase-8
activation. Mol Cell. 11:543–549. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gogvadze V, Robertson JD, Zhivotovsky B
and Orrenius S: Cytochrome c release occurs via
Ca2+-dependent and Ca2+-independent
mechanisms that are regulated by Bax. J Biol Chem. 276:19066–19071.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schild L, Keilhoff G, Augustin W, Reiser G
and Striggow F: Distinct Ca2+ thresholds determine
cytochrome c release or permeability transition pore opening in
brain mitochondria. FASEB J. 15:565–567. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang G, Chen HL, Ren F, Li J and Li YQ:
Expression of Cav-1, AQP1 and AQP5 in lung of acute
pancreatitis-associated lung injury rats and the therapeutic role
of Qingyitang. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 90:2564–2569. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Zhang XM, Chen HL and Wang ZH: Expression
of secretory type II phospholipase A2in acute lung
injury following acute pancreatitis and interventional effect of
Qingyi decoction on it. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
22:518–521. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Cornélio Favarin D, Martins Teixeira M,
Lemos de Andrade E, et al: Anti-inflammatory effects of ellagic
acid on acute lung injury induced by acid in mice. Mediators
Inflamm. 2013:1642022013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bi XD, Zhao J and Fu XG: Experimental
study of the effects QingYi decoction combination with
Dexamethasone on early systemic inflammatory response syndrome
(SIRS) of severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). China Journal of Modern
Medicine. 20:2760–2766. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Mirghazanfari SM, Keshavarz M, Nabavizadeh
F, Soltani N and Kamalinejad M: The effect of ‘Teucrium
polium L.’ extracts on insulin release from in situ isolated
perfused rat pancreas in a newly modified isolation method:the role
of Ca2+ and K+ channels. Iran Biomed J.
14:178–185. 2010.
|
|
12
|
Rzepka JP, Haick AK and Miura TA:
Virus-infected alveolar epithelial cells direct neutrophil
chemotaxis and inhibit their apoptosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
46:833–841. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Domínguez-Fandos D, Peinado VI, Puig-Pey
R, et al: Pulmonary inflammatory reaction and structural changes
induced by cigarette smoke exposure in the Guinea pig. COPD.
9:473–484. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stewart JP, Kipar A, Cox H, Payne C,
Vasiliou S and Quinn JP: Induction of tachykinin production in
airway epithelia in response to viral infection. PLoS One.
3:e16732008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lahm T, Crisostomo PR, Markel TA, Wang M,
Lillemoe KD and Meldrum DR: The critical role of vascular
endothelial growth factor in pulmonary vascular remodeling after
lung injury. Shock. 28:4–14. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang L, Taneja R, Wang W, et al: Human
alveolar epithelial cells attenuate pulmonary microvascular
endothelial cell permeability under septic conditions. PLoS One.
8:e553112013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Han F, Luo Y, Li Y, et al: Seawater
induces apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells via the
Fas/FasL-mediated pathway. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 182:71–80.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsukahara S, Yamamoto S, Tin-Tin-Win-Shwe,
et al: Inhalation of low-level formaldehyde increases the Bcl-2/Bax
expression ratio in the hippocampus of immunologically sensitized
mice. Neuroimmunomodulation. 13:63–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leung PO, Lee HH, Kung YC, Tsai MF and
Chou TC: Therapeutic effect of C-phycocyanin extracted from blue
green algae in a rat model of acute lung injury induced by
lipopolysaccharide. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:9165902013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li L, Wu W, Huang W, Hu G, Yuan W and Li
W: NF-κB RNAi decreases the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and inhibits
TNF-α-induced apoptosis in human alveolar epithelial cells. Inflamm
Res. 62:387–397. 2013.
|
|
21
|
Aguirre A, Shoji KF, Sáez JC, Henríquez M
and Quest AF: FasL-triggered death of Jurkat cells requires caspase
8-induced, ATP-dependent. J Cell Physiol. 228:458–493. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim HA, Park JH, Lee S, Choi JS, Rhim T
and Lee M: Combined delivery of dexamethasone and plasmid DNA in an
animal model of LPS-induced acute lung injury. J Control Release.
156:60–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nutt LK, Chandra J, Pataer A, et al:
Bax-mediated Ca2+ mobilization promotes cytochrome
c release during apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 277:20301–20308.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shan HL, Wang Y, Wu JW, et al: Verapamil
reverses cardiac iron overload in streptozocin-induced diabetic
rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 386:645–650. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu G, Chen J, Jing G and Shalev A:
Preventing β-cell loss and diabetes with calcium channel blockers.
Diabetes. 61:848–856. 2012.
|
|
26
|
Suzuki K, Saito SY and Ishikawa T:
Involvement of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C in
thromboxane A2 receptor-mediated extracellular
Ca2+ influx in rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 677:123–130.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Long S, Wilson M, Bengtén E, Clem LW,
Miller NW and Chinchar VG: Identification and characterization of a
FasL-like protein and cDNAs encoding the channel catfish
death-inducing signaling complex. Immunogenetics. 56:518–530. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nomura J, Matsumoto K, Iguchi-Ariga SM and
Ariga H: Mitochondria-independent induction of Fas-mediated
apoptosis by MSSP. Oncol Rep. 14:1305–1309. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang S: Rhubarb Gardenia Treated 28 cases
of acute edematous pancreatitis. Chinese Journal of Integrated
Traditional and Western Medicine. 3:1831999.(In Chinese).
|