|
1
|
Collard HR and Pantilat SZ: Dyspnea in
interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care.
2:100–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hou N, Torii S, Saito N, Hosaka M and
Takeuchi T: Reactive oxygen species-mediated pancreatic beta-cell
death is regulated by interactions between stress-activated protein
kinases, p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and mitogen-activated
protein kinase phosphatases. Endocrinology. 149:1654–1665. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Horton MR, Santopietro V, Mathew L, et al:
Thalidomide for the treatment of cough in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 157:398–406. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smith JL, Schaffner AE, Hofmeister JK, et
al: ets-2 is a target for an akt (Protein kinase B)/jun N-terminal
kinase signaling pathway in macrophages of motheaten-viable mutant
mice. Mol Cell Biol. 20:8026–8034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choe JY, Jung HJ, Park KY, et al:
Anti-fibrotic effect of thalidomide through inhibiting
TGF-beta-induced ERK1/2 pathways in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis
in mice. Inflamm Res. 59:177–188. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
D’Amato RJ, Loughnan MS, Flynn E and
Folkman J: Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 91:4082–4085. 1994.
|
|
7
|
Moreira AL, Sampaio EP, Zmuidzinas A,
Frindt P, Smith KA and Kaplan G: Thalidomide exerts its inhibitory
action on tumor necrosis factor alpha by enhancing mRNA
degradation. J Exp Med. 177:1675–1680. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koch HP: Thalidomide and congeners as
anti-inflammatory agents. Prog Med Chem. 22:165–242. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Takeshita I, Matsumoto
K, Maruoka S and Horie T: Transforming growth Factor-betal induces
phenotypic modulation of human lung fibroblasts to myofibroblast
through a c-Jun-NH2- terminal kinase-dependent pathway. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 163:152–157. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Alcorn JF, Guala AS, van der Velden J, et
al: Jun N-terminal kinase 1 regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition induced by TGF-beta1. J Cell Sci. 121:1036–1045. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kapoun AM, Gaspar NJ, Wang Y, et al:
Transforming growth factor-beta receptor type 1 (TGFbetaRI) kinase
activity but not p38 activation is required for TGF betaRI-induced
myofibroblast differentiation and profibrotic gene expression. Mol
Pharmacol. 70:518–531. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bogoyevitch MA, Boehm I, Oakley A,
Ketterman AJ and Barr RK: Targeting the JNK MAPK cascade for
inhibition: basic science and therapeutic potential. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1697:89–101. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu J and Lin A: Role of JNK activation
apoptosis: a double-edged sword. Cell Res. 15:36–42. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, et al:
SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:13681–13686. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
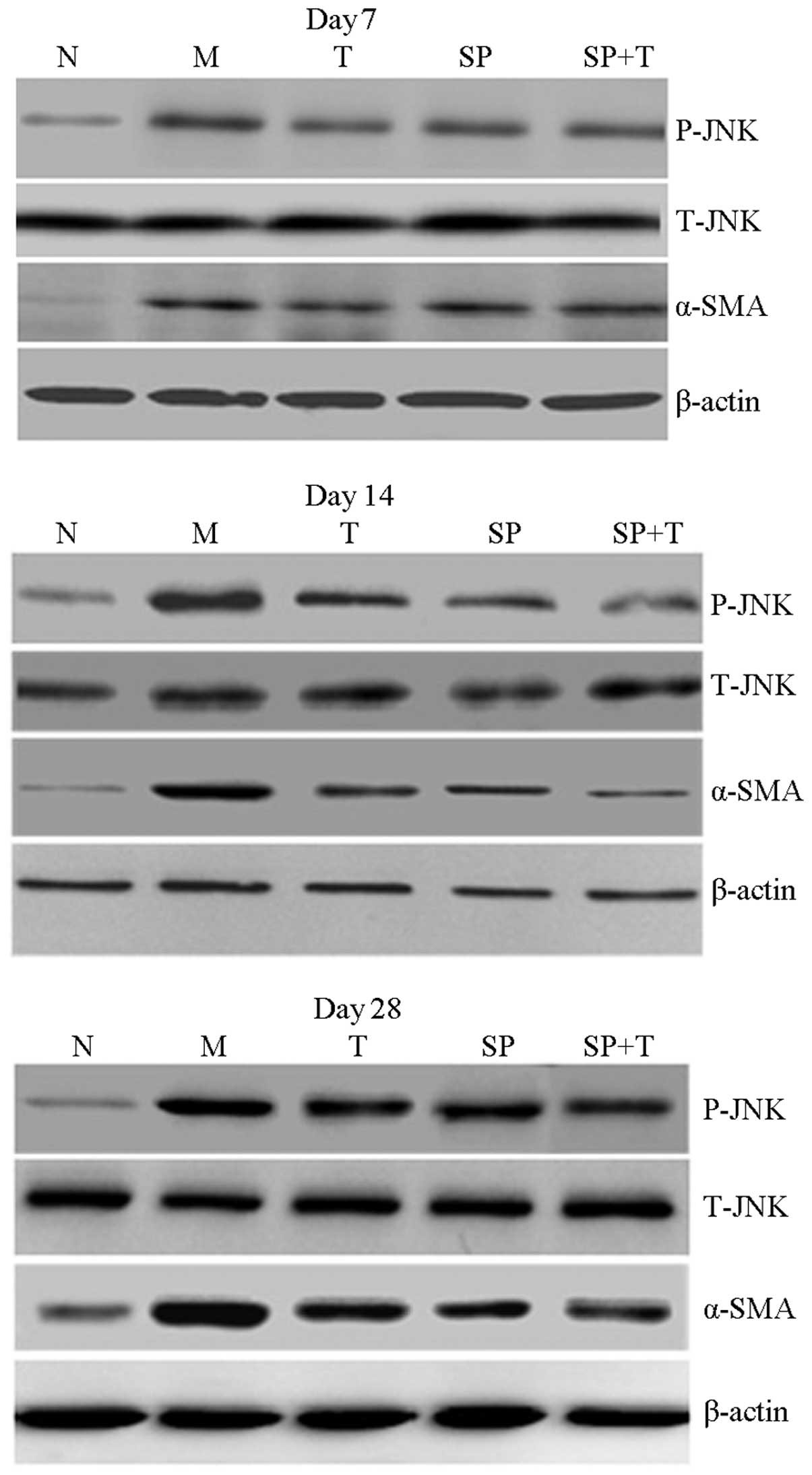
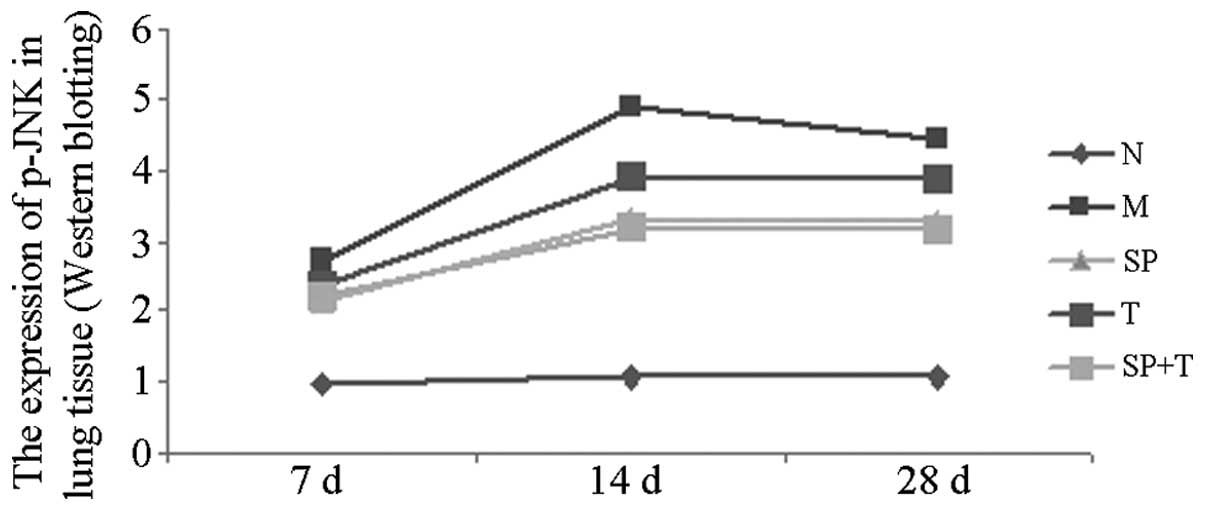
Zhang C-X and Liu X-J: The expression and
significance of p-JNK protein and α-SMA in rats with pulmonary
fibrosis. Chinese Remedies & Clinics. 12:36–38. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Joglekar S and Levin M: The promise of
thalidomide: evolving indications. Drugs Today (Barc). 40:197–204.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arai H, Furusu A, Nishino T, et al:
Thalidomide prevents the progression of peritoneal fibrosis in
mice. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 44:51–60. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chong LW, Hsu YC, Chiu YT, Yang KC and
Huang YT: Anti-fibrotic effects of thalidomide on hepatic stellate
cells and dimethylnitrosamine-intoxicated rats. J Biomed Sci.
13:403–418. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ye Q, Chen B, Tong Z, et al: Thalidomide
reduces IL-18, IL-8 and TNF-alpha release from alveolar macrophages
in interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 28:824–831. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu X, Qian L, Nan H, et al: Thalidomide
inhibits the over-expression of type I collagen in pulmonary
fibrosis rats via inhibition the JNK signaling pathway. Chinese
Journal of Geriatrics. (In Press).
|
|
21
|
Luo X and Liu X-J: Thalidomide suppresses
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by down-regulating expressions
of TGF-β1 and TNF -α in rats. Chinese Remedies & Clinics.
10:1346–1349. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Horton MR and Hallowell RW: Revisiting
thalidomide: fighting with caution against idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Drugs Today (Barc). 48:661–671. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Horton MR, Santopietro V, Mathew L, et al:
Thalidomide for the treatment of cough in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 157:398–406. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|