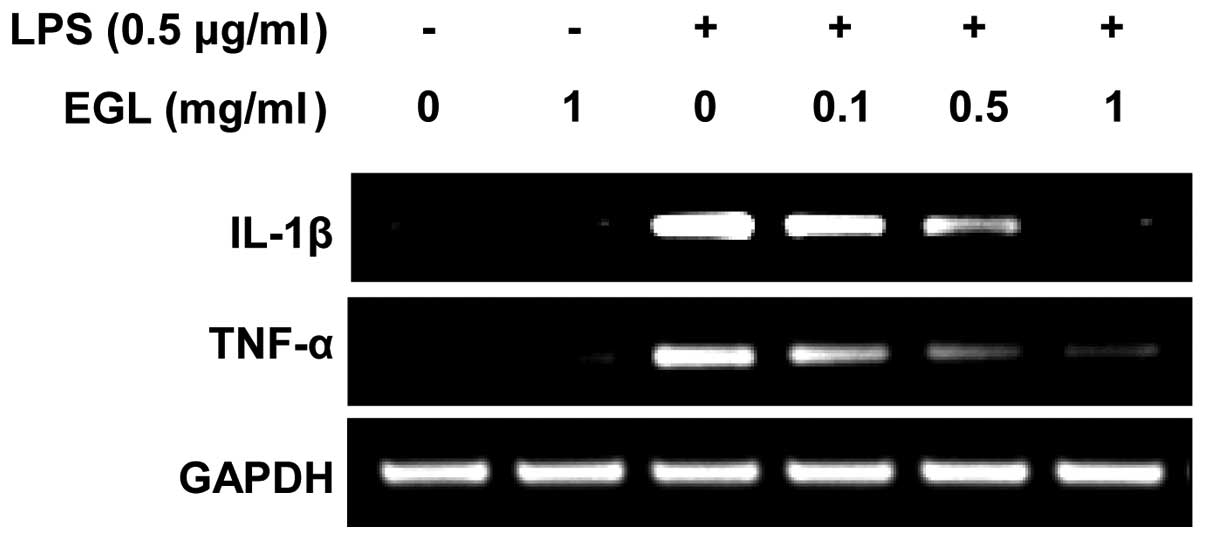
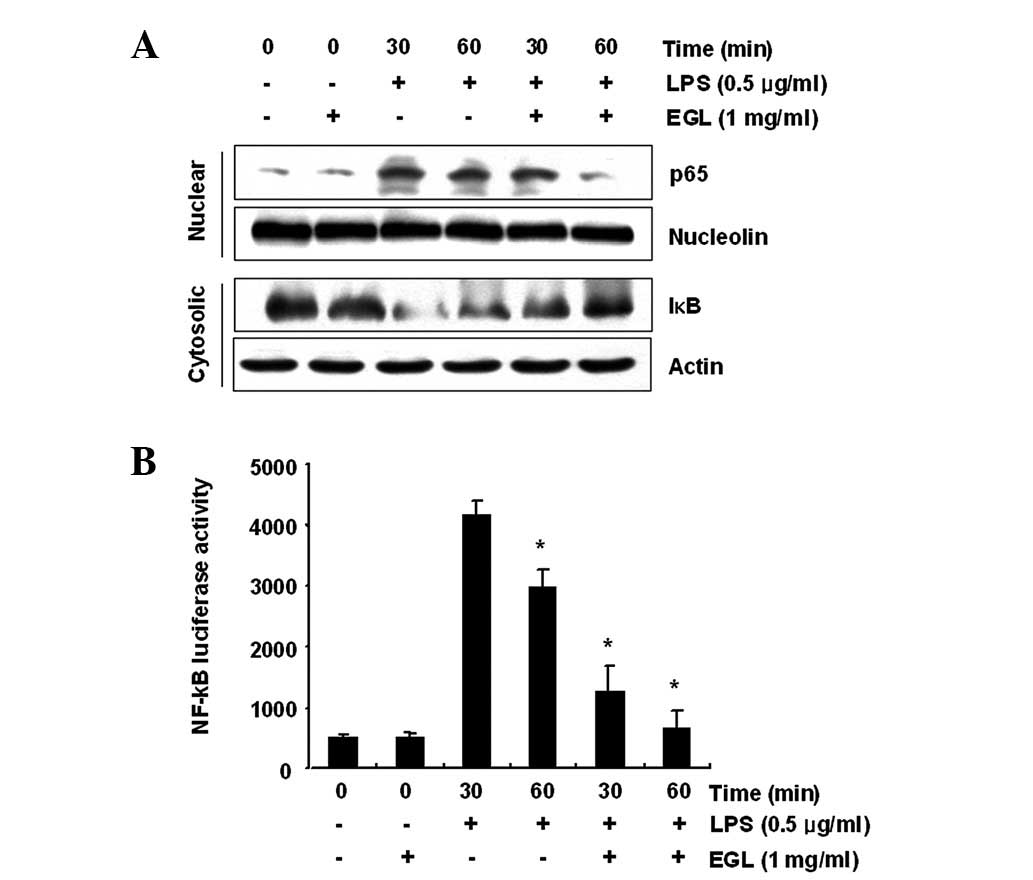
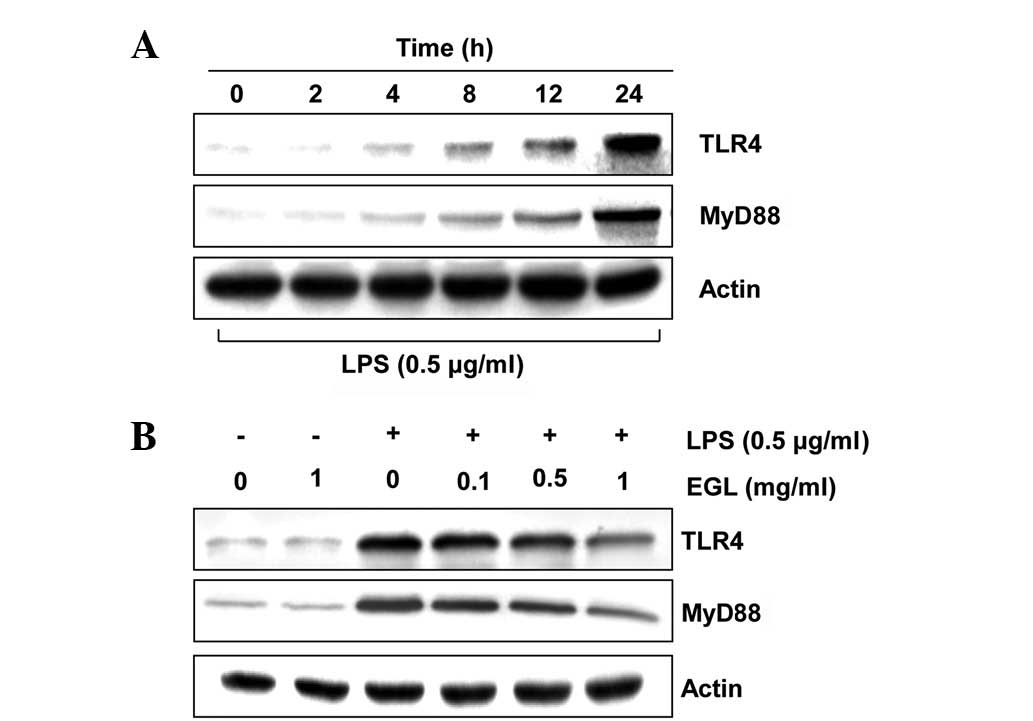
|
1.
|
Mahajna J, Dotan N, Zaidman BZ, Petrova RD
and Wasser SP: Pharmacological values of medicinal mushrooms for
prostate cancer therapy: the case of Ganoderma lucidum. Nutr
Cancer. 61:16–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Boh B, Berovic M, Zhang J and Zhi-Bin L:
Ganoderma lucidum and its pharmaceutically active compounds.
Biotechnol Annu Rev. 13:265–301. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Paterson RR: Ganoderma - a
therapeutic fungal biofactory. Phytochemistry. 67:1985–2001. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Yuen JW and Gohel MD: Anticancer effects
of Ganoderma lucidum: a review of scientific evidence. Nutr
Cancer. 53:11–17. 2005.
|
|
5.
|
Chien CM, Cheng JL, Chang WT, Tien MH,
Tsao CM, Chang YH, Chang HY, Hsieh JF, Wong CH and Chen ST:
Polysaccharides of Ganoderma lucidum alter cell
immunophenotypic expression and enhance CD56+ NK-cell
cytotoxicity in cord blood. Bioorg Med Chem. 12:5603–5609.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Hu H, Ahn NS, Yang X, Lee YS and Kang KS:
Ganoderma lucidum extract induces cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cell. Int J Cancer.
102:250–253. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Lin SB, Li CH, Lee SS and Kan LS:
Triterpene-enriched extracts from Ganoderma lucidum inhibit
growth of hepatoma cells via suppressing protein kinase C,
activating mitogen-activated protein kinases and G2-phase cell
cycle arrest. Life Sci. 72:2381–2390. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Hong KJ, Dunn DM, Shen CL and Pence BC:
Effects of Ganoderma lucidum on apoptotic and
anti-inflammatory function in HT-29 human colonic carcinoma cells.
Phytother Res. 18:768–770. 2004.
|
|
9.
|
Stanley G, Harvey K, Slivova V, Jiang J
and Sliva D: Ganoderma lucidum suppresses angiogenesis
through the inhibition of secretion of VEGF and TGF-β1 from
prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 330:46–52. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Müller CI, Kumagai T, O’Kelly J, Seeram
NP, Heber D and Koeffler HP: Ganoderma lucidum causes
apoptosis in leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma cells. Leuk
Res. 30:841–848. 2006.
|
|
11.
|
Jang KJ, Han MH, Lee BH, Kim BW, Kim CH,
Yoon HM and Choi YH: Induction of apoptosis by ethanol extracts of
Ganoderma lucidum in human gastric carcinoma cells. J
Acupunct Meridian Stud. 3:24–31. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Cheung WM, Hui WS, Chu PW, Chiu SW and Ip
NY: Ganoderma extract activates MAP kinases and induces the
neuronal differentiation of rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. FEBS
Lett. 486:291–296. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Zhao HB, Lin SQ, Liu JH and Lin ZB:
Polysaccharide extract isolated from Ganoderma lucidum
protects rat cerebral cortical neurons from hypoxia/reoxygenation
injury. J Pharmacol Sci. 95:294–298. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Lai CS, Yu MS, Yuen WH, So KF, Zee SY and
Chang RC: Antagonizing beta-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity of the
anti-aging fungus Ganoderma lucidum. Brain Res.
1190:215–224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Zhou ZY, Tang YP, Xiang J, Wua P, Jin HM,
Wang Z, Mori M and Cai DF: Neuroprotective effects of water-soluble
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on cerebral ischemic
injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 131:154–164. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Perry VH and Gordon S: Macrophages and
microglia in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 92:273–274.
1998.
|
|
17.
|
Sawada M, Kondo N, Suzumura A and
Marunouchi T: Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by
microglia and astrocytes in culture. Brain Res. 491:394–397. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Meda L, Cassatella MA, Szendrei GI, Otvos
L Jr, Baron P, Villalba M, Ferrari D and Rossi F: Activation of
microglial cells by β-amyloid protein and interferon-γ. Nature.
373:647–650. 1995.
|
|
19.
|
Dandona P, Ghanim H, Chaudhuri A, Dhindsa
S and Kim SS: Macronutrient intake induces oxidative and
inflammatory stress: potential relevance to atherosclerosis and
insulin resistance. Exp Mol Med. 42:245–253. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Gonzalez-Scarano F and Baltuch G:
Microglia as mediators of inflammatory and degenerative diseases.
Annu Rev Neurosci. 22:219–240. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Amor S, Puentes F, Baker D and van der
Valk P: Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology.
129:154–169. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Dheen ST, Kaur C and Ling EA: Microglial
activation and its implications in the brain diseases. Curr Med
Chem. 14:1189–1197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Eikelenboom P and van Gool WA:
Neuroinflammatory perspectives on the two faces of Alzheimer’s
disease. J Neural Transm. 111:281–294. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Gao HM, Liu B, Zhang W and Hong JS: Novel
anti-inflammatory therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 24:395–401. 2003.
|
|
25.
|
Liu B and Hong JS: Role of microglia in
inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and
strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
304:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Bae DS, Kim YH, Pan CH, Nho CW, Samdan J,
Yansan J and Lee JK: Protopine reduces the inflammatory activity of
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophages. BMB Rep.
45:108–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Jin CY, Moon DO, Lee KJ, Kim MO, Lee JD,
Choi YH, Park YM and Kim GY: Piceatannol attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB activation and
NF-kappaB-related proinflammatory mediators in BV2 microglia.
Pharmacol Res. 54:461–467. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Lee JW, Lee MS, Kim TH, Lee HJ, Hong SS,
Noh YH, Hwang BY, Ro JS and Hong JT: Inhibitory effect of
inflexinol on nitric oxide generation and iNOS expression via
inhibition of NF-κB activation. Mediators Inflamm.
2007:93148–93157. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Baima ET, Guzova JA, Mathialagan S, Nagiec
EE, Hardy MM, Song LR, Bonar SL, Weinberg RA, Selness SR, Woodard
SS, Chrencik J, Hood WF, Schindler JF, Kishore N and Mbalaviele G:
Novel insights into the cellular mechanisms of the
anti-inflammatory effects of NF-κB essential modulator binding
domain peptides. J Biol Chem. 285:13498–13506. 2010.
|
|
30.
|
Miller SI, Ernst RK and Bader MW: LPS,
TLR4 and infectious disease diversity. Nat Rev Microbiol. 3:36–46.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Lee YH, Jeon SH, Kim SH, Kim C, Lee SJ,
Koh D, Lim Y, Ha K and Shin SY: A new synthetic chalcone
derivative, 2-hydroxy-3′,5,5′-trimethoxychalcone (DK-139),
suppresses the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory response
through inhibition of the Akt/NF-κB pathway in BV2 microglial
cells. Exp Mol Med. 44:369–377. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Romanovsky AA, Steiner AA and Matsumura K:
Cells that trigger fever. Cell Cycle. 5:2195–2197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Fukuzawa M, Yamaguchi R, Hide I, Chen Z,
Hirai Y, Sugimoto A, Yasuhara T and Nakata Y: Possible involvement
of long chain fatty acids in the spores of Ganoderma lucidum
(Reishi Houshi) to its anti-tumor activity. Biol Pharm Bull.
31:1933–1937. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Sanodiya BS, Thakur GS, Baghel RK, Prasad
GB and Bisen PS: Ganoderma lucidum: a potent pharmacological
macrofungus. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 10:717–742. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Xu Z, Chen X, Zhong Z, Chen L and Wang Y:
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides: immunomodulation and
potential anti-tumor activities. Am J Chin Med. 39:15–27. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Vane JR, Mitchell JA, Appleton I,
Tomlinson A, Bishop-Bailey D, Croxtall J and Willoughby DA:
Inducible isoforms of cyclooxygenase and nitric-oxide synthase in
inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:2046–2050. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Hawkey CJ: Cox-2 inhibitors. Lancet.
353:307–314. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Giovannini MG, Scali C, Prosperi C,
Bellucci A, Pepeu G and Casamenti G: Experimental brain
inflammation and neurode-generation as model of Alzheimer’s
disease: protective effects of selective COX-2 inhibitors. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 16:31–40. 2003.
|
|
39.
|
MacMicking J, Xie QW and Nathan C: Nitric
oxide and macrophage function. Ann Rev Immunol. 15:323–330. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Mitchell JA, Larkin S and Williams TJ:
Cyclooxygenase-2: regulation and relevance in inflammation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 50:1535–1542. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Boka G, Anglade P, Wallach D, Javoy-Agid
F, Agid Y and Hirsch EC: Immunocytochemical analysis of tumor
necrosis factor and its receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci
Lett. 172:151–154. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Murphy S: Production of nitric oxide by
glial cells: regulation and potential roles in the CNS. Glia.
29:1–13. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Akassoglou K, Bauer J, Kassiotis G,
Pasparakis M, Lassmann H, Kollias G and Probert L: Oligodendrocyte
apoptosis and primary demyelination induced by local TNF/p55TNF
receptor signaling in the central nervous system of transgenic
mice: models for multiple sclerosis with primary
oligodendrogliopathy. Am J Pathol. 153:801–813. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44.
|
Sriram K, Matheson JM, Benkovic SA, Miller
DB, Luster MI and O’Callaghan JP: Mice deficient in TNF receptors
are protected against dopaminergic neurotoxicity: implications for
Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J. 16:1474–1476. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Rothwell N, Allan S and Toulmond S: The
role of interleukin 1 in acute neurodegeneration and stroke:
pathophysiological and therapeutic implications. J Clin Invest.
100:2648–2652. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-kappaB and I-kappaB
proteins: new discoveries and insights. Ann Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Moon DO, Choi YH, Kim ND, Park YM and Kim
GY: Anti-inflammatory effects of β-lapachone in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol.
7:506–514. 2007.
|
|
48.
|
Trinchieri G and Sher A: Cooperation of
Toll-like receptor signals in innate immune defence. Nat Rev
Immunol. 7:179–190. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Medzhitov R: Toll-like receptors and
innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:135–145. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Seki E, Tsutsui H, Iimuro Y, Naka T, Son
G, Akira S, Kishimoto T, Nakanishi K and Fujimoto J: Contribution
of Toll-like receptor/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signaling
to murine liver regeneration. Hepatology. 41:443–450. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|