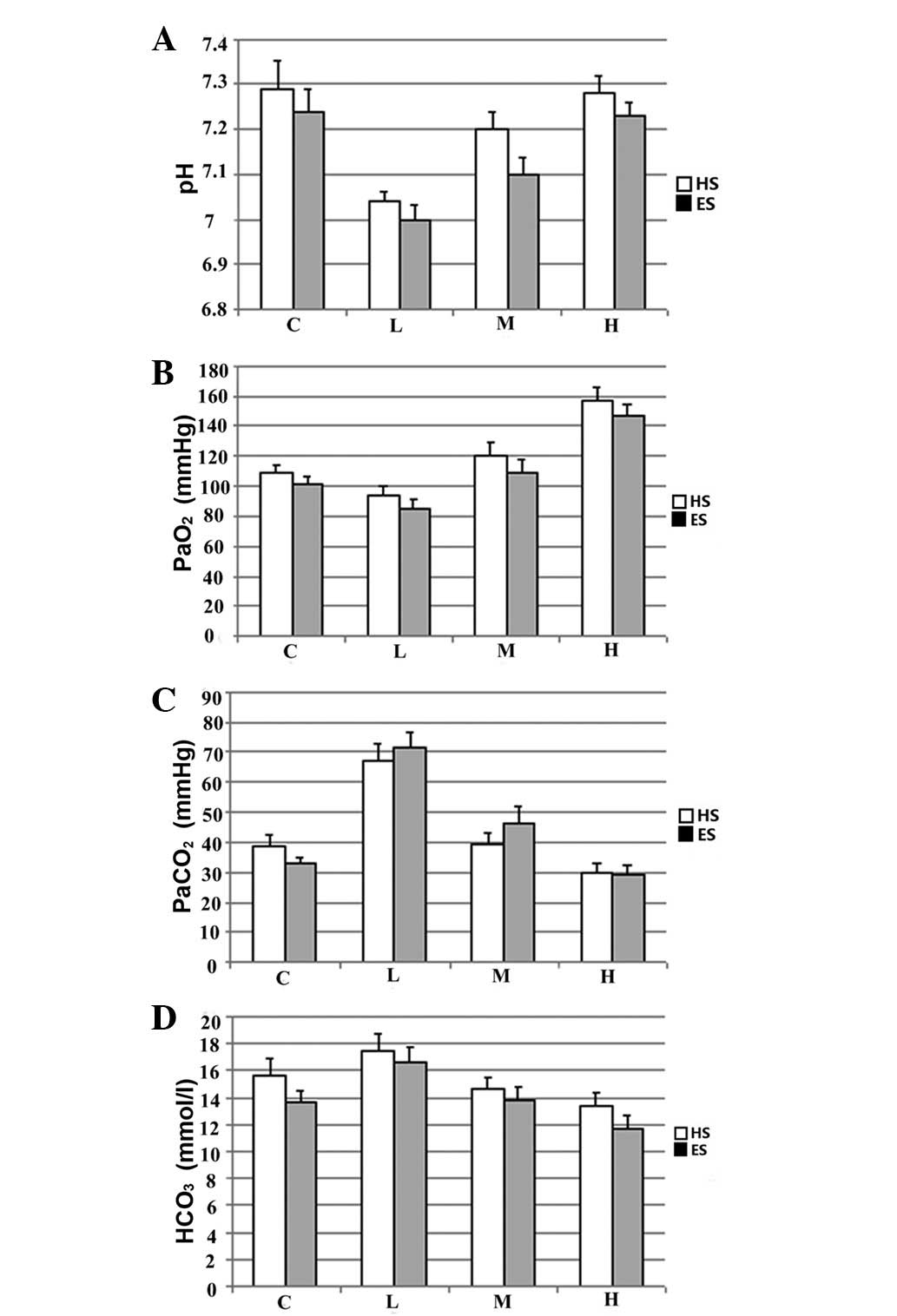
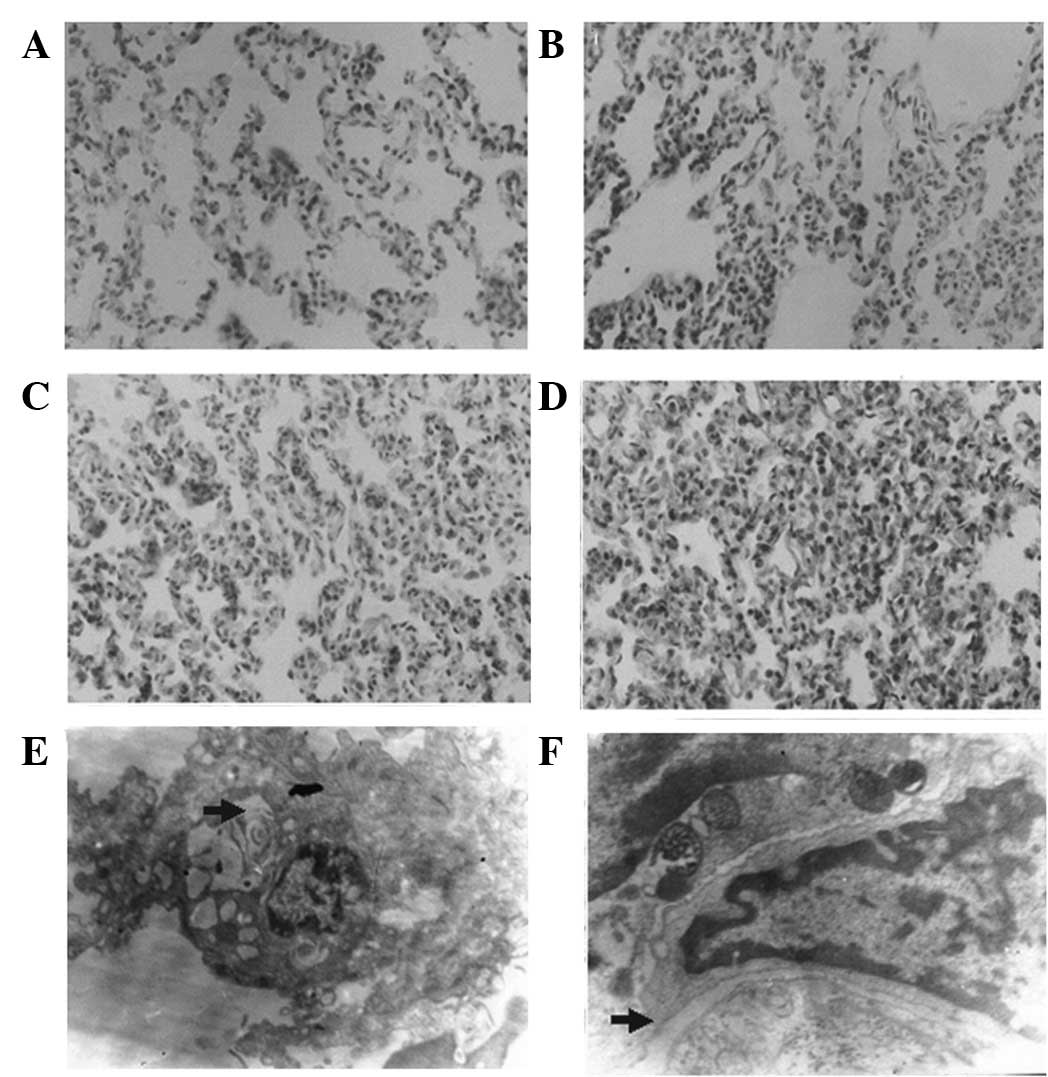
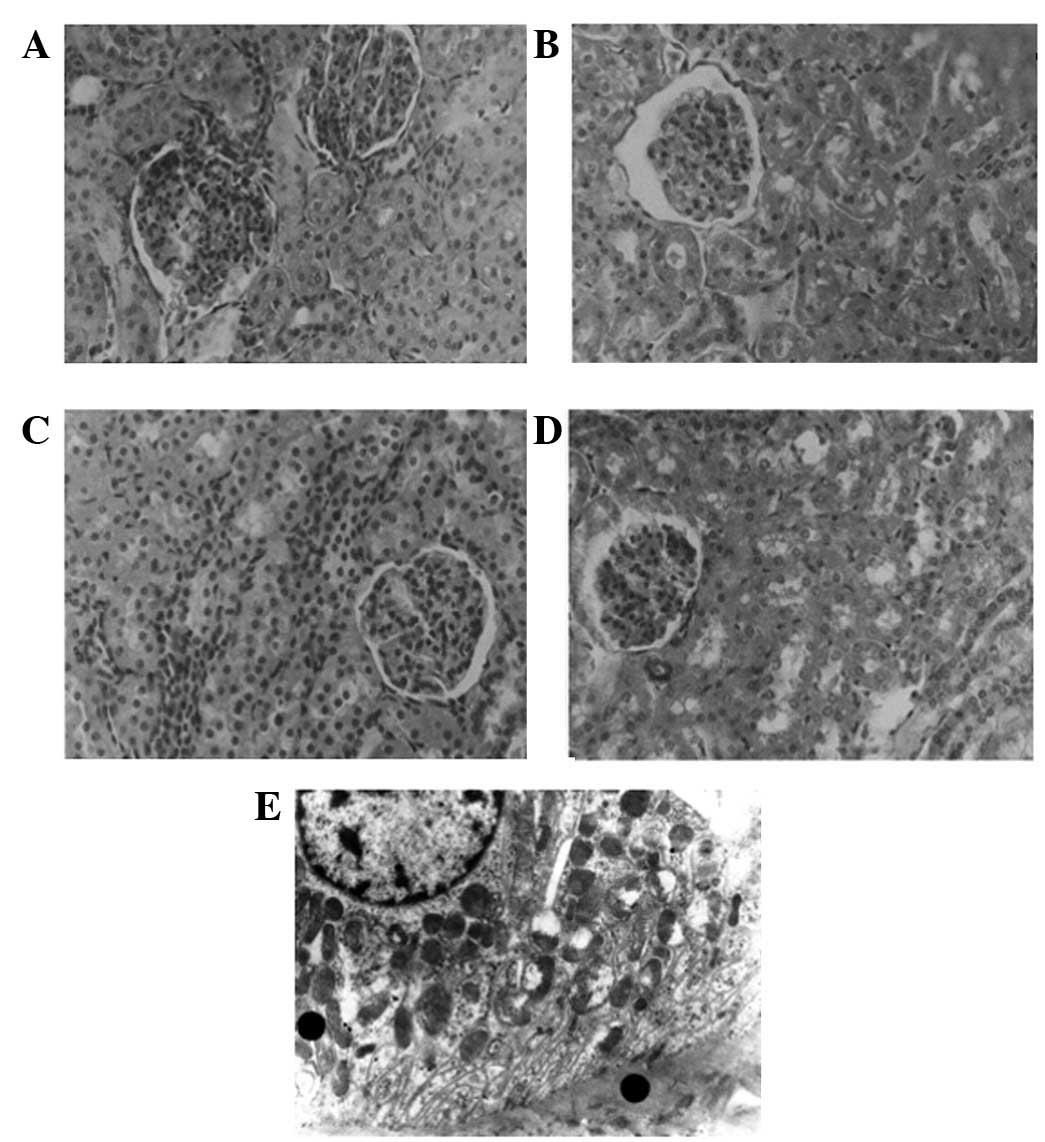
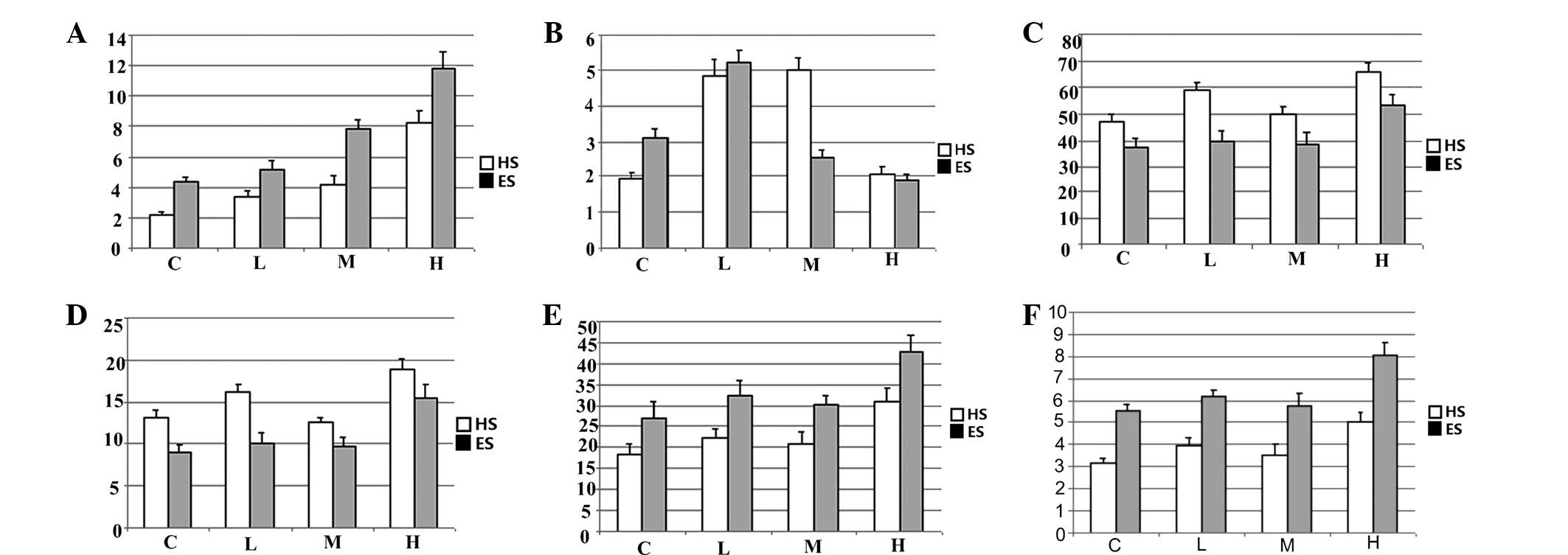
|
1
|
Giuliani D, Mioni C, Bazzani C, et al:
Selective melanocortin MC4 receptor agonists reverse haemorrhagic
shock and prevent multiple organ damage. Br J Pharmacol.
150:595–603. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Madách K, Aladzsity I, Szilágyi A, et al:
4G/5G polymorphism of PAI-1 gene is associated with multiple organ
dysfunction and septic shock in pneumonia induced severe sepsis:
prospective, observational, genetic study. Crit Care.
14:R792010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, et al:
Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management
of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Intensive Care Med.
34:17–60. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wheeler AP: Recent developments in the
diagnosis and management of severe sepsis. Chest. 132:1967–1976.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
No authors listed. Ventilation with lower
tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute
lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Acute
Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. N Engl J Med. 342:1301–1308.
2000.
|
|
6
|
Parsons PE, Eisner MD, Thompson BT, et al:
Lower tidal volume ventilation and plasma cytokine markers of
inflammation in patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med.
33:1–6. 2005.
|
|
7
|
Ragaller M and Richter T: Acute lung
injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Emerg Trauma
Shock. 3:43–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Imai Y, Parodo J, Kajikawa O, et al:
Injurious mechanical ventilation and end-organ epithelial cell
apoptosis and organ dysfunction in an experimental model of acute
respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA. 289:2104–2112. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dhanireddy S, Altemeier WA, Matute-Bello
G, et al: Mechanical ventilation induces inflammation, lung injury,
and extra-pulmonary organ dysfunction in experimental pneumonia.
Lab Invest. 86:790–799. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O’Mahony DS, Liles WC, Altemeier WA, et
al: Mechanical ventilation interacts with endotoxemia to induce
extrapulmonary organ dysfunction. Crit Care. 10:R1362006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wolthuis EK, Vlaar AP, Choi G, Roelofs JJ,
Juffermans NP and Schultz MJ: Mechanical ventilation using
non-injurious ventilation settings causes lung injury in the
absence of pre-existing lung injury in healthy mice. Crit Care.
13:R12009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Douzinas EE, Andrianakis I, Livaditi O, et
al: The level of hypotension during hemorrhagic shock is a major
determinant of the post-resuscitation systemic inflammatory
response: an experimental study. BMC Physiol. 8:152008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brégeon F, Delpierre S, Chetaille B, et
al: Mechanical ventilation affects lung function and cytokine
production in an experimental model of endotoxemia. Anesthesiology.
102:331–339. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paller MS, Hoidal JR and Ferris TF: Oxygen
free radicals in ischemic acute renal failure in the rat. J Clin
Invest. 74:1156–1164. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ and
Gurd FN: Intestinal mucosal lesions in low flow states. A
morphological, hemodynamic, and metabolic reappraisal. Arch Surg.
101:478–483. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu F, Zhang HY and Liu Z: Effects of
mechanical ventilation with different tidal volumes on small
intestine injury of early resuscitated hemorrhagic and endotoxic
shock rabbits. World Chinese Journal of Digestology. 16:833–838.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Ng CS, Wan S, Ho AM and Underwood MJ: Gene
expression changes with a ‘non-injurious’ ventilation strategy.
Crit Care. 13:4032009.
|
|
18
|
Krismer AC, Wenzel V, Lindner KH, et al:
Influence of positive end-expiratory pressure ventilation on
survival during severe hemorrhagic shock. Ann Emerg Med.
46:337–342. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Krismer AC, Wenzel V, Lindner KH, et al:
Influence of negative expiratory pressure ventilation on
hemodynamic variables during severe hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care
Med. 34:2175–2181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Herff H, Paal P, von Goedecke A, Lindner
KH, Severing AC and Wenzel V: Influence of ventilation strategies
on survival in severe controlled hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med.
36:2613–2620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carcoana OV, Mathew JP, Davis E, et al:
Mannitol and dopamine in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary
bypass: a randomized clinical trial. Anesth Analg. 97:1222–1229.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Legrand M, Mik EG, Johannes T, Payen D and
Ince C: Renal hypoxia and dysoxia after reperfusion of the ischemic
kidney. Mol Med. 14:502–516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han X, Fink MP, Uchiyama T, Yang R and
Delude RL: Increased iNOS activity is essential for pulmonary
epithelial tight junction dysfunction in endotoxemic mice. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 286:L259–L267. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moriez R, Salvador-Cartier C, Theodorou V,
Fioramonti J, Eutamene H and Bueno L: Myosin light chain kinase is
involved in lipopolysaccharide-induced disruption of colonic
epithelial barrier and bacterial translocation in rats. Am J
Pathol. 167:1071–1079. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Han X, Fink MP, Yang R and Delude RL:
Increased iNOS activity is essential for intestinal epithelial
tight junction dysfunction in endotoxemic mice. Shock. 21:261–270.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schreiber T, Hueter L, Schwarzkopf K,
Hohlstein S, Schmidt B and Karzai W: Increased susceptibility to
ventilator-associated lung injury persists after clinical recovery
from experimental endotoxemia. Anesthesiology. 104:133–141. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Saldias FJ, Comellas AP, Pesce L, Lecuona
E and Sznajder JI: Dopamine increases lung liquid clearance during
mechanical ventilation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
283:L136–L143. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chamorro-Marín V, García-Delgado M,
Touma-Fernández A, Aguilar-Alonso E and Fernández-Mondejar E:
Intratracheal dopamine attenuates pulmonary edema and improves
survival after ventilator-induced lung injury in rats. Crit Care.
12:R392008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Birnbaum J, Klotz E, Spies CD, et al:
Effects of dopamine on the intestinal microvascular blood flow and
leukocyte activation in a sepsis model in rats. Crit Care.
10:R1172006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Abdelsalam M: Permissive hypoxemia: is it
time to change our approach? Chest. 129:210–211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|