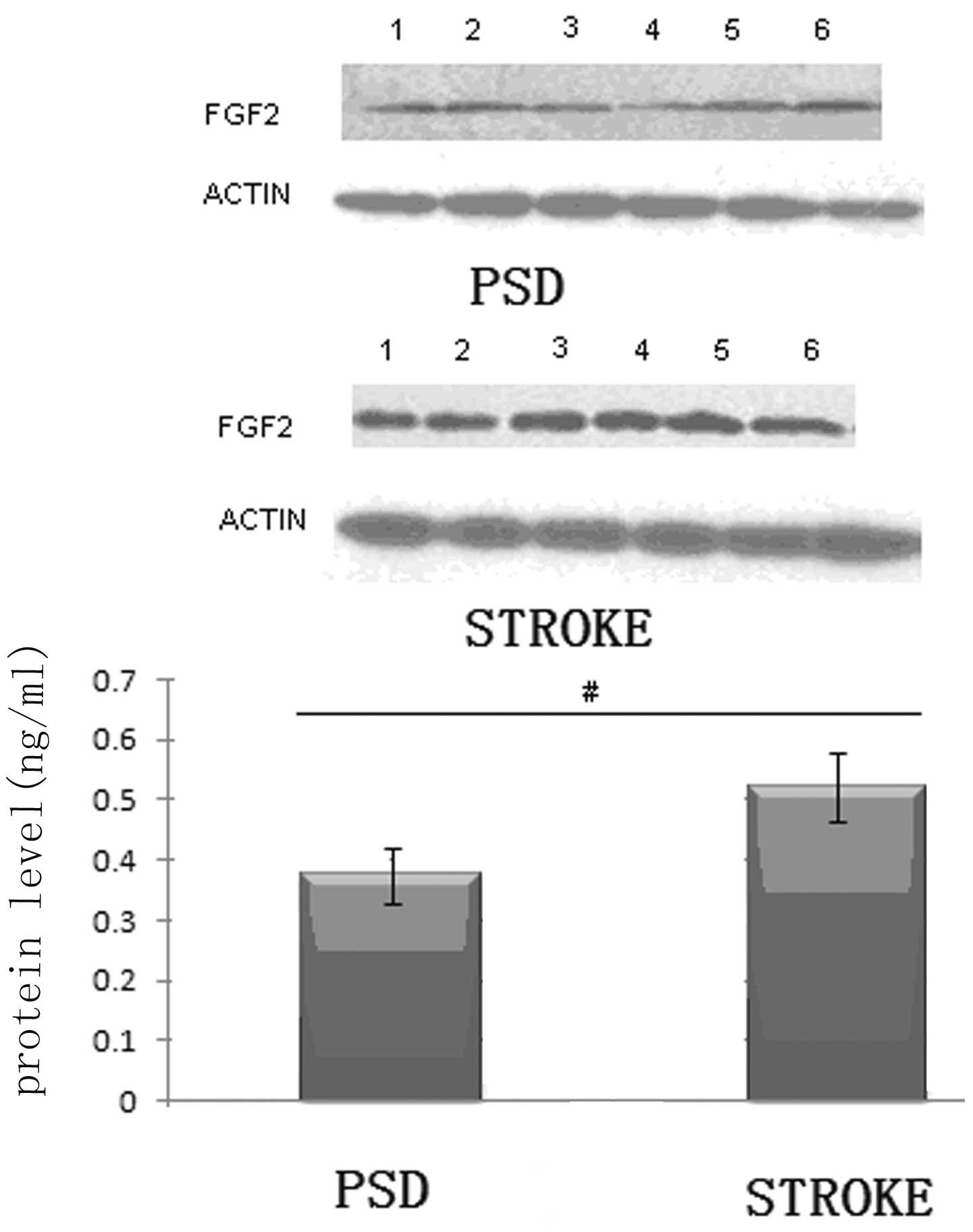
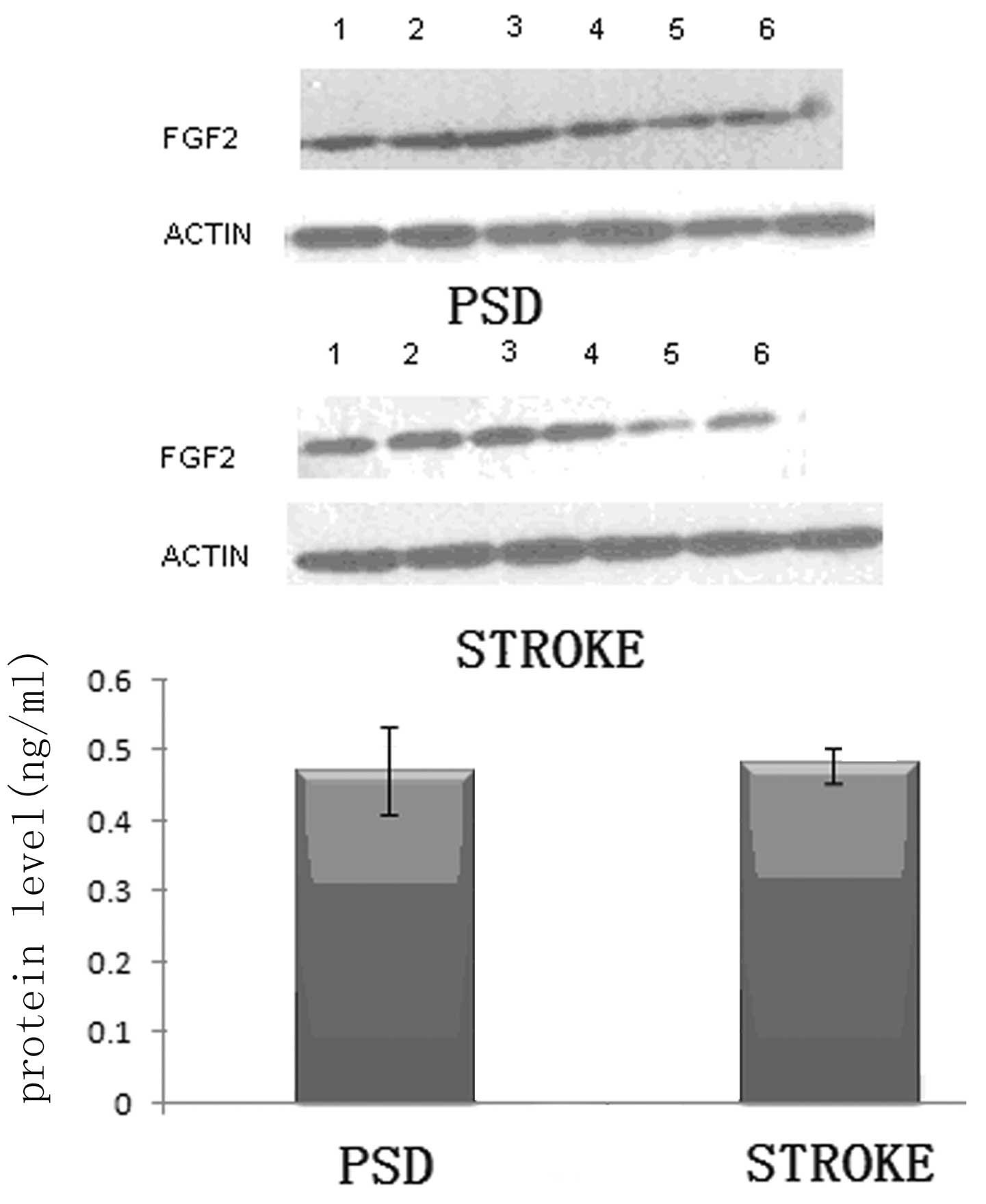
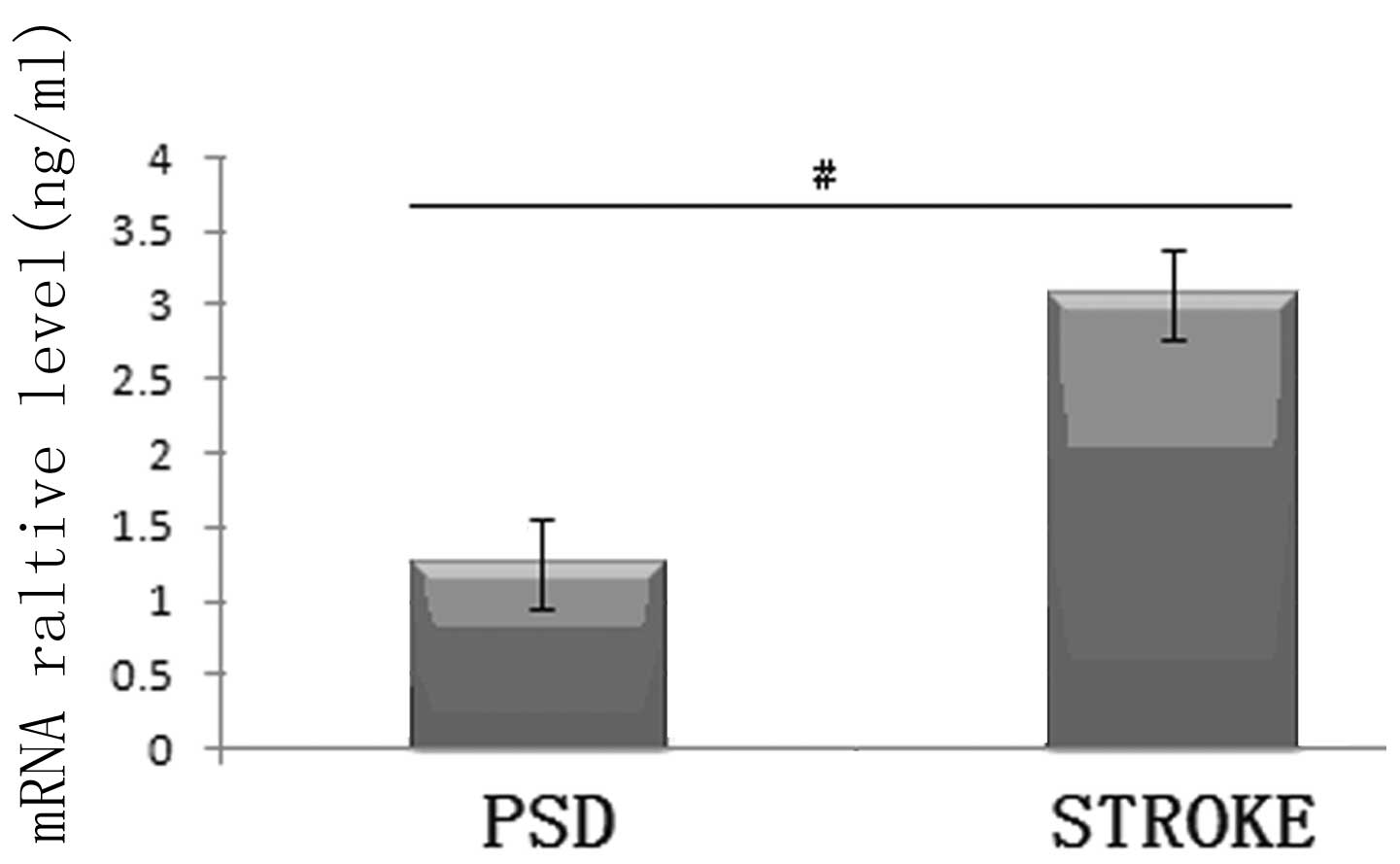
|
1
|
Yang LL, Zhang ZJ and Sun DM: Incidence
and its risk factors of post-stroke depression in cerebral stroke
patients at acute stage. Lin Chuang Shen Jing Bing Xue Za Zhi.
23:185–187. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
2
|
Berg C, Backström T, Winberg S, et al:
Developmental exposure to fluoxetine modulates the serotonin system
in hypothalamus. PLoS One. 8:e550532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sullivan GM, Ogden RT, Huang YY, et al:
Higher in vivo serotonin-1a binding in posttraumatic stress
disorder: a PET study with [11C]WAY-100635. Depress Anxiety.
30:197–206. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Spasojevic N, Jovanovic P and Dronjak S:
Chronic fluoxetine treatment affects gene expression of
catecholamine enzymes in the heart of depression model rats. Indian
J Exp Biol. 50:771–775. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vergaño-Vera E, Méndez-Gómez HR,
Hurtado-Chong A, et al: Fibroblast growth factor-2 increases the
expression of neurogenic genes and promotes the migration and
differentiation of neurons derived from transplanted neural
stem/progenitor cells. Neuroscience. 162:39–54. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reynolds BA and Weiss S: Generation of
neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian
central nervous system. Science. 255:1707–1710. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vicario-Abejón C, Yusta-Boyo MJ,
Fernández-Moreno C and de Pablo F: Locally born olfactory bulb stem
cells proliferate in response to insulin-related factors and
require endogenous insulin-like growth factor-I for differentiation
into neurons and glia. J Neurosci. 23:895–906. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gritti A, Parati EA, Cova L, Frolichsthal
P, et al: Multipotential stem cells from the adult mouse brain
proliferate and self-renew in response to basic fibroblast growth
factor. J Neurosci. 16:1091–1100. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Turner CA, Watson SJ and Akil H: The
fibroblast growth factor family: neuromodulation of affective
behavior. Neuron. 76:160–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fukuchi-Shimogori T and Grove EA:
Neocortex patterning by the secreted signaling molecule FGF8.
Science. 294:1071–1074. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shin DM, Korada S, Raballo R, et al: Loss
of glutamatergic pyramidal neurons in frontal and temporal cortex
resulting from attenuation of FGFR1 signaling is associated with
spontaneous hyperactivity in mice. J Neurosci. 24:2247–2258. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guillemot F and Zimmer C: From cradle to
grave: the multiple roles of fibroblast growth factors in neural
development. Neuron. 71:574–588. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vaccarino FM, Schwartz ML, Raballo R, et
al: Changes in cerebral cortex size are governed by fibroblast
growth factor during embryogenesis. Nat Neurosci. 2:246–253. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Raballo R, Rhee J, Lyn-Cook R, et al:
Basic fibroblast growth factor (Fgf2) is necessary for cell
proliferation and neurogenesis in the developing cerebral cortex. J
Neurosci. 20:5012–5023
|
|
15
|
Mason I: Initiation to end point: the
multiple roles of fibroblast growth factors in neural development.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 8:583–596. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ciccolini F and Svendsen CN: Fibroblast
growth factor 2 (FGF-2) promotes acquisition of epidermal growth
factor (EGF) responsiveness in mouse striatal precursor cells:
identification of neural precursors responding to both EGF and
FGF-2. J Neurosci. 18:7869–7880. 1998.
|
|
17
|
Ito Y, Tsurushima H, Sato M, et al:
Angiogenesis therapy for brain infarction using a slow-releasing
drug delivery system for fibroblast growth factor 2. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 432:182–187. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maric D, Fiorio Pla A, Chang YH and Barker
JL: Self-renewing and differentiating properties of cortical neural
stem cells are selectively regulated by basic fibroblast growth
factor (FGF) signaling via specific FGF receptors. J Neurosci.
27:1836–1852. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sun Y, Hu J, Zhou L, et al: Interplay
between FGF2 and BMP controls the self-renewal, dormancy and
differentiation of rat neural stem cells. J Cell Sci.
124:1867–1877. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vicario-Abejón C, Johe KK, Hazel TG, et
al: Functions of basic fibroblast growth factor and neurotrophins
in the differentiation of hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 15:105–114.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cattaneo E and McKay R: Proliferation and
differentiation of neuronal stem cells regulated by nerve growth
factor. Nature. 347:762–765. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gillen R, Tennen H, McKee TE, et al:
Depressive symptoms and history of depression predict
rehabilitation efficiency in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med
Rehabil. 82:1645–1649. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh A, Black SE, Herrmann N, et al:
Functional and neuroanatomic correlations in poststroke depression:
the Sunnybrook Stroke Study. Stroke. 31:637–644. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vataja R, Pohjasvaara T, Mäntylä R, et al:
Depression-executive dysfunction syndrome in stroke patients. Am J
Geriatr Psychiatry. 13:99–107. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kishi Y, Kosier T and Robinson RG:
Suicidal plans in patients with acute stroke. J Nerv Ment Dis.
184:274–280. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
House A, Knapp E, Bamford J and Vail A:
Mortality at 12 and 24 months after stroke may be associated with
depressive symptoms at 1 month. Stroke. 32:696–701. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Everson SA, Roberts RE, Goldberg DE and
Kaplan GA: Depressive symptoms and increased risk of stroke
mortality over a 29-year period. Arch Intern Med. 158:1133–1138.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Robinson RG, Bolduc PL and Price TR:
Two-year longitudinal study of poststroke mood disorders:diagnosis
and outcome at one and two years. Stroke. 18:837–843.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Simonsick EM, Wallace RB, Blazer DG and
Berkman LF: Depressive symptomatology and hypertension-associated
morbidity and mortality in older adults. Psychosom Med. 57:427–435.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vescovi AL, Reynolds BA, Fraser DD and
Weiss S: bFGF regulates the proliferative fate of unipotent
(neuronal) and bipotent (neuronal/astroglial) EGF-generated CNS
progenitor cells. Neuron. 11:951–966. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lukaszewicz A, Savatier P, Cortay V, et
al: Contrasting effects of basic fibroblast growth factor and
neurotrophin 3 on cell cycle kinetics of mouse cortical stem cells.
J Neurosci. 22:6610–6622. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lillien L and Raphael H: BMP and FGF
regulate the development of EGF-responsive neural progenitor cells.
Development. 127:4993–5005. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ikeda N, Nonoguchi N, Zhao MZ, et al: Bone
marrow stromal cells that enhanced fibroblast growth factor-2
secretion by herpes simplex virus vector improve neurological
outcome after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke.
36:2725–2730. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yi ZH, Fang YR and Yu SY: Research
progress of gene differential expression of depression brain
tissue. Zhongguo Shen Jing Jing Shen Ji Bing Za Zhi. 36:56–59.
2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Ay I, Sugimori H and Finkelstein SP:
Intravenous basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) decreases DNA
fragmentation and prevents downregulation of Bcl-2 expression in
the ischemic brain following middle cerebral artery occlusion in
rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 87:71–80. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Rosenblatt S, Irikura K, Caday CG, et al:
Basic fibroblast growth factor dilates rat pial arterioles. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 14:70–74. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Koizumi J, Yoshida Y, Nakazawa T and
Ooneda G: Experimental studies of ischemic brain edema: A new
experimental model of cerebral embolism in rats in which
recirculation can be introduced in the ischemic area. Jpn J Stroke.
16:1–8. 1986.(In Japanese).
|
|
39
|
Willner P, Towell A, Sampson D, et al:
Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic mild unpredictable
stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant.
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 93:358–364. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rasul A, El-Nour H, Blakely RD, et al:
Effect of chronic mild stress on serotonergic markers in the skin
and brain of the NC/Nga atopic-like mouse strain. Arch Dermatol
Res. 303:625–633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ji YH and Song JG: Relevance among
cognition function, autonomic nerve function and the serum levels
of monoamine neurotransmitter in patients with post-stroke
depression. Lin Chuang Shen Jing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 20:426–428.
2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
42
|
Loubinoux I, Kronenberg G, Endres M, et
al: Post-stroke depression: mechanisms, translation and therapy. J
Cell Mol Med. 16:1961–1969. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Haneda E, Higuchi M, Maeda J, et al: In
vivo mapping of substance P receptors in brains of laboratory
animals by high-resolution imaging systems. Synapse. 61:205–215.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chatterjee K, Fall S and Barer D: Mood
after stroke: a case control study of biochemical, neuro-imaging
and socio-economic risk factors for major depression in stroke
survivors. BMC Neurol. 10:1252010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Evans SJ, Choudary PV, Neal CR, et al:
Dysregulation of the fibroblast growth factor system in major
depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:15506–15511. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|