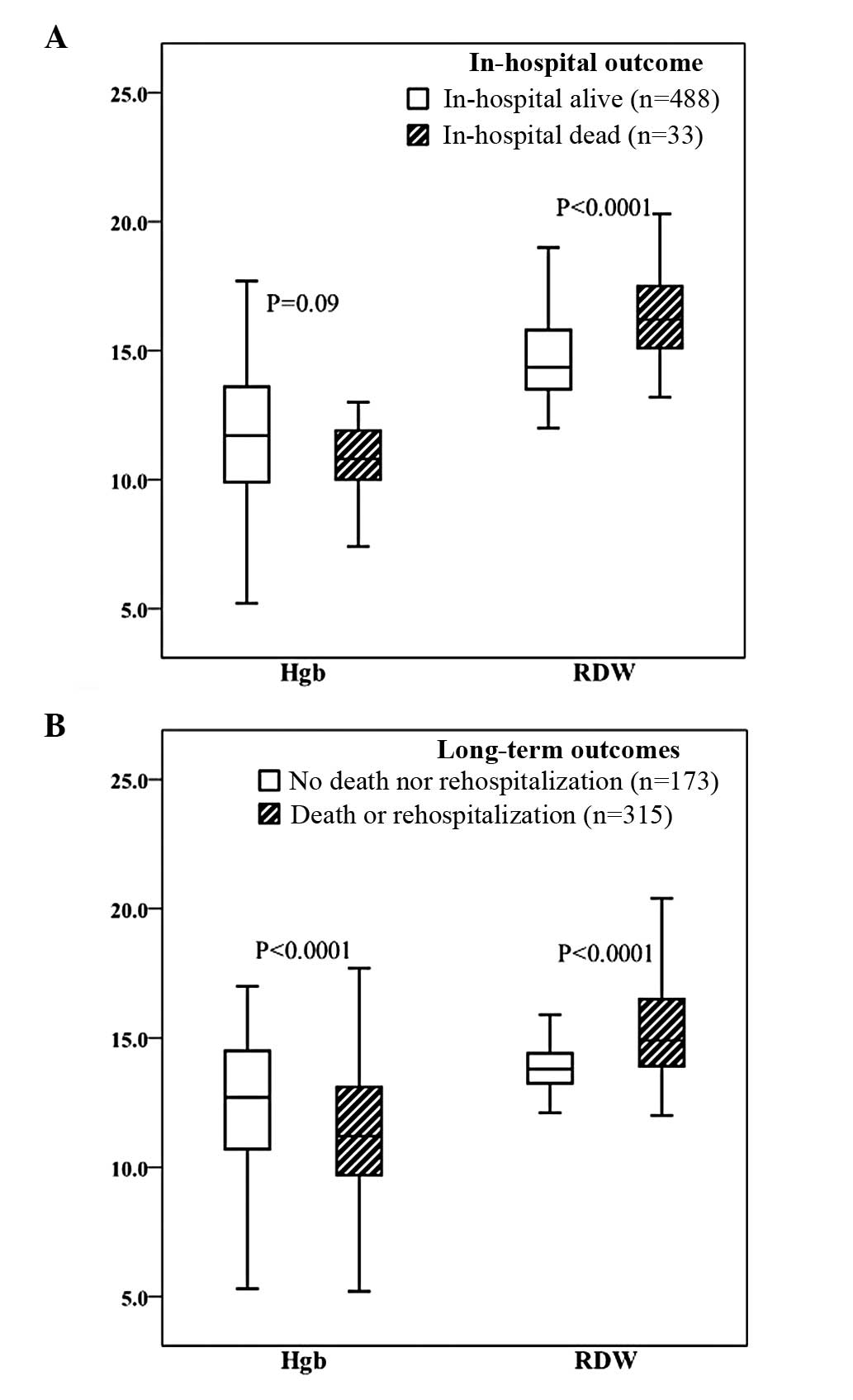
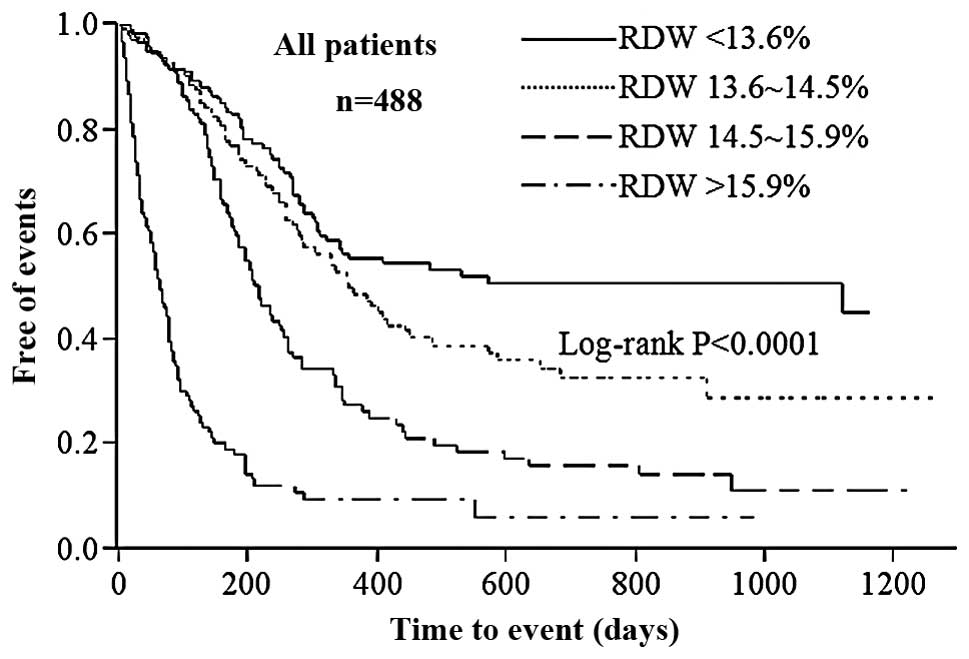
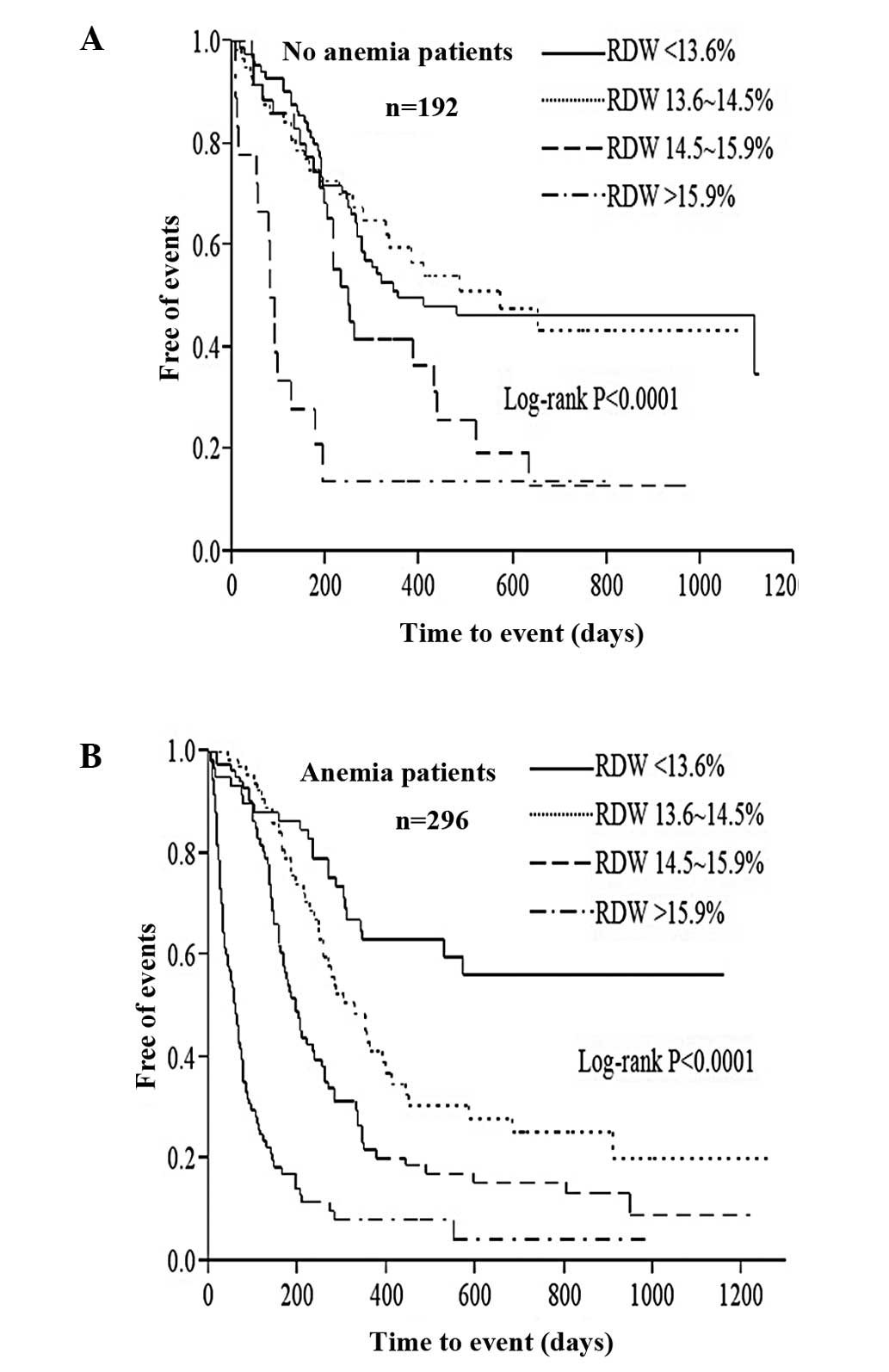
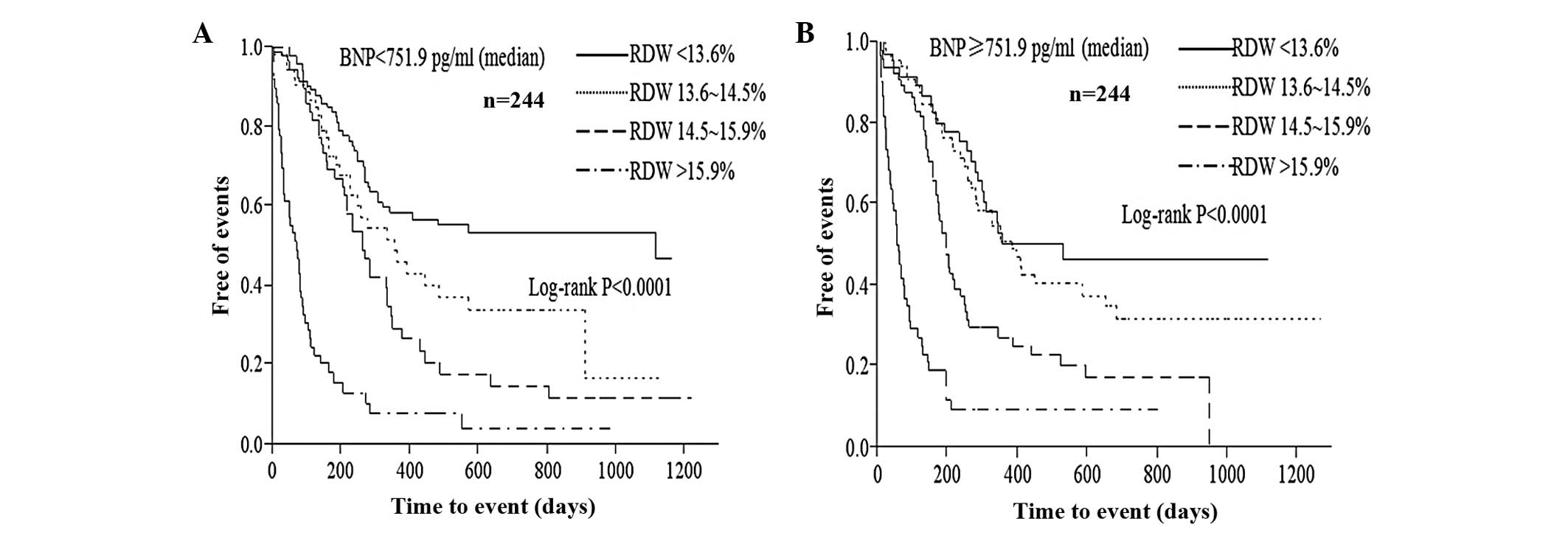
|
1
|
Levy D, Kenchaiah S, Larson MG, et al:
Long-term trends in the incidence of and survival with heart
failure. N Engl J Med. 347:1397–1402. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mueller C, Laule-Kilian K, Christ A, et
al: Inflammation and long-term mortality in acute congestive heart
failure. Am Heart J. 151:845–850. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roger VL, Weston SA, Redfield MM, et al:
Trends in heart failure incidence and survival in a community-based
population. JAMA. 292:344–350. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cowie MR, Wood DA, Coats AJ, et al:
Survival of patients with a new diagnosis of heart failure: a
population based study. Heart. 83:505–510. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xue Y, Chan J, Sakariya S and Maisel A:
Biomarker-guided treatment of congestive heart failure. Congest
Heart Fail. 16(Suppl 1): S62–S67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Allen LA: Use of multiple biomarkers in
heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rep. 12:230–236. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vistnes M, Christensen G and Omland T:
Multiple cytokine biomarkers in heart failure. Expert Rev Mol
Diagn. 10:147–157. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bozkurt B, Mann DL and Deswal A:
Biomarkers of inflammation in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev.
15:331–341. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Araújo JP, Lourenço P, Azevedo A, et al:
Prognostic value of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in heart
failure: a systematic review. J Card Fail. 15:256–266.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rehman SU and Januzzi JL Jr: Natriuretic
peptides for guiding heart failure therapy. Compr Ther. 34:32–40.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Adams KF Jr, Felker GM, Fraij G, et al:
Biomarker guided therapy for heart failure: focus on natriuretic
peptides. Heart Fail Rev. 15:351–370. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Odedra K and Ferro A: Neurohormones and
heart failure: the importance of aldosterone. Int J Clin Pract.
60:835–846. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Trachtenberg BH and Hare JM: Biomarkers of
oxidative stress in heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. 5:561–577.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Belziti CA: Prevalence of anemia in heart
failure and its effects on prognosis. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther.
7:131–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Salisbury AC and Kosiborod M: Outcomes
associated with anemia in patients with heart failure. Heart Fail
Clin. 6:359–372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He SW and Wang LX: The impact of anemia on
the prognosis of chronic heart failure: a meta-analysis and
systemic review. Congest Heart Fail. 15:123–130. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ghali JK: Anemia and heart failure. Curr
Opin Cardiol. 24:172–178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dabbah S, Hammerman H, Markiewicz W and
Aronson D: Relation between red cell distribution width and
clinical outcomes after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol.
105:312–317. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nabais S, Losa N, Gaspar A, et al:
Association between red blood cell distribution width and outcomes
at six months in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Rev Port
Cardiol. 28:905–924. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Förhécz Z, Gombos T, Borgulya G, et al:
Red cell distribution width: a powerful prognostic marker in heart
failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 12:4152010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Al-Najjar Y, Goode KM, Zhang J, et al: Red
cell distribution width: an inexpensive and powerful prognostic
marker in heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 11:1155–1162. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Kimmenade RR, Mohammed AA,
Uthamalingam S, et al: Red blood cell distribution width and 1-year
mortality in acute heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 12:129–136.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pascual-Figal DA, Bonaque JC, Redondo B,
Caro C, Manzano-Fernandez S, Sánchez-Mas J, Garrido IP and Valdes
M: Red blood cell distribution width predicts long-term outcome
regardless of anaemia status in acute heart failure patients. Eur J
Heart Fail. 11:840–846. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Evans TC and Jehle D: The red blood cell
distribution width. J Emerg Med. 9:71–74. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Viswanath D, Hegde R, Murthy V, et al: Red
cell distribution width in the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia.
Indian J Pediatr. 68:1117–1119. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Crosato M, Steinborn W and Anker SD:
Anemia in chronic congestive heart failure: frequency, prognosis,
and treatment. Heart Fail Monit. 4:2–6. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Terrovitis JV, Anastasiou-Nana M, Kaldara
E, et al: Anemia in heart failure: pathophysiologic insights and
treatment options. Future Cardiol. 5:71–81. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Felker GM, Adams KF Jr, Gattis WA and
O’Connor CM: Anemia as a risk factor and therapeutic target in
heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 44:959–966. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pierce CN and Larson DF: Inflammatory
cytokine inhibition of erythropoiesis in patients implanted with a
mechanical circulatory assist device. Perfusion. 20:83–90. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Felker GM, Allen LA, Pocock SJ, et al;
CHARM Investigators. Red cell distribution width as a novel
prognostic marker in heart failure: data from the CHARM Program and
the Duke Databank. J Am Coll Cardiol. 50:40–47. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maisel A: B-type natriuretic peptide
levels: diagnostic and prognostic in congestive heart failure:
what’s next? Circulation. 105:2328–2331. 2002.
|
|
32
|
Ikonomidis I, Michalakeas CA, Lekakis J,
et al: Multimarker approach in cardiovascular risk prediction. Dis
Markers. 26:273–285. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Velagaleti RS, Gona P, Larson MG, et al:
Multimarker approach for the prediction of heart failure incidence
in the community. Circulation. 122:1700–1706. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yin WH, Chen JW, Feng AN, et al:
Multimarker approach to risk stratification among patients with
advanced chronic heart failure. Clin Cardiol. 30:397–402. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|