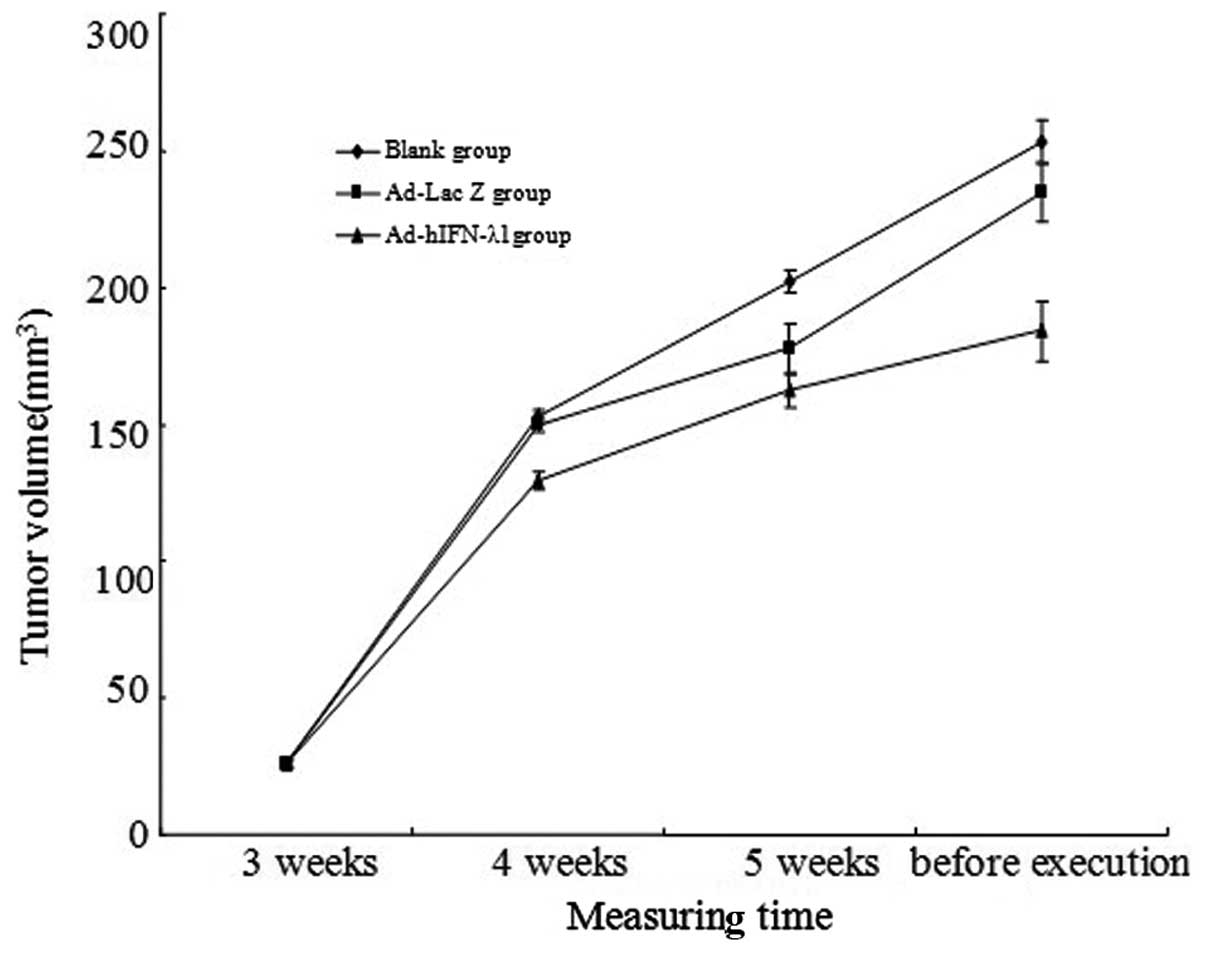
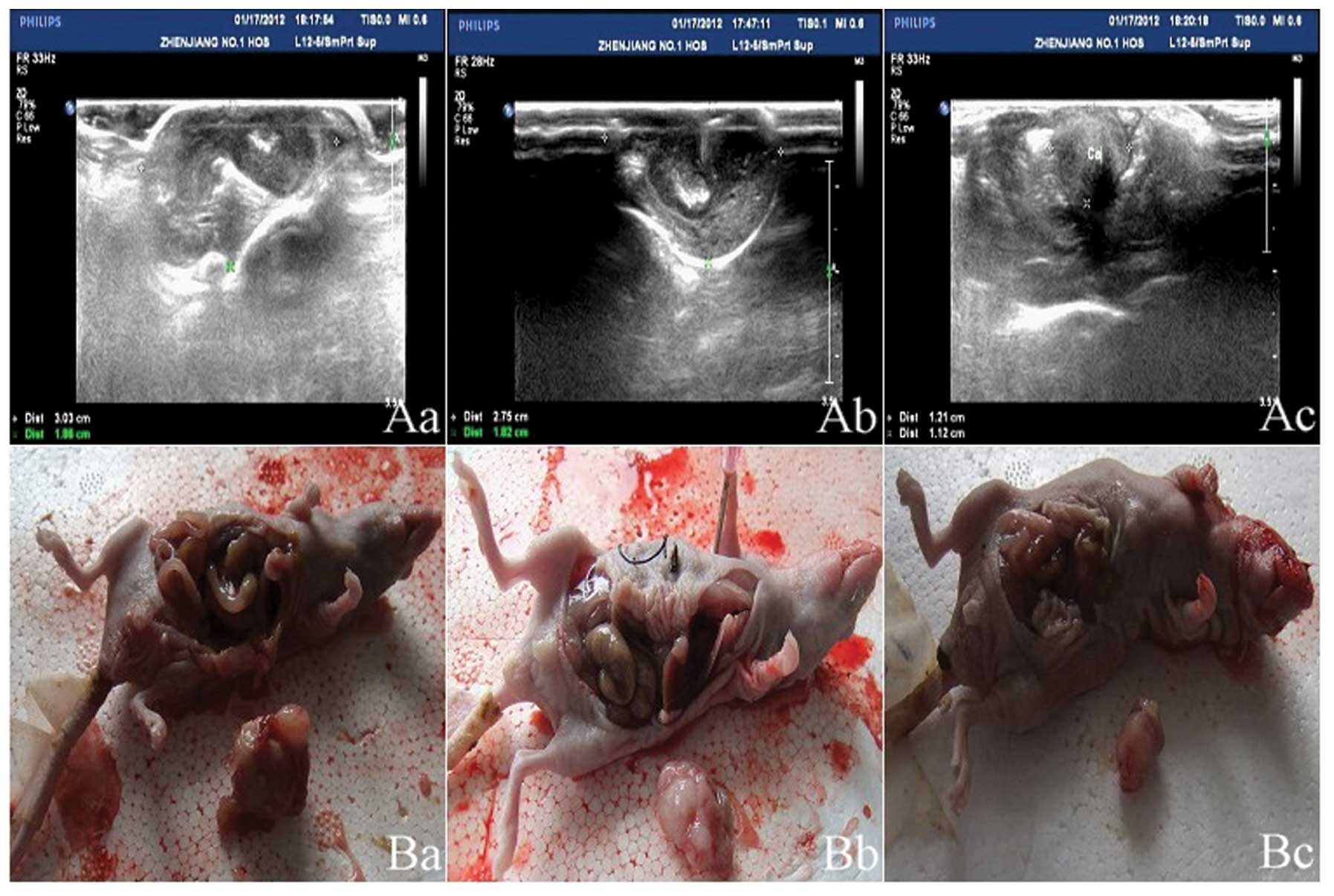
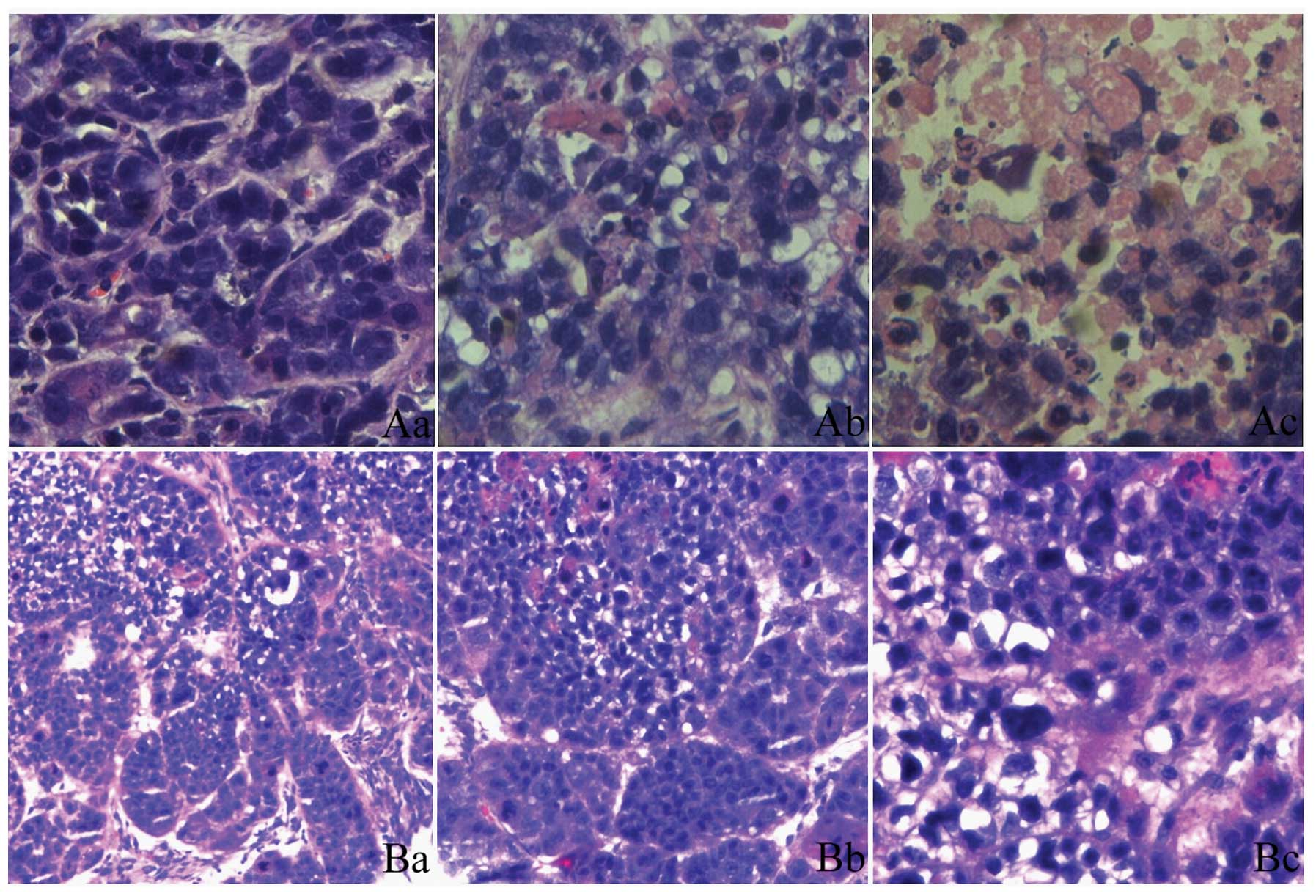
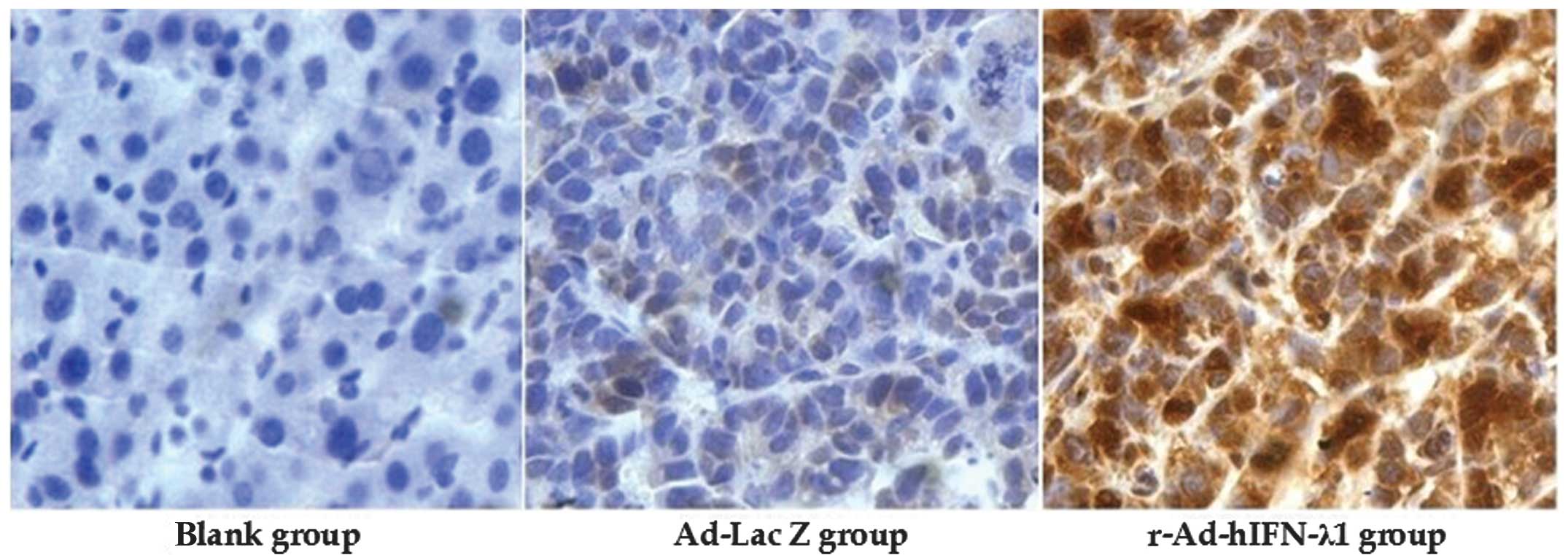
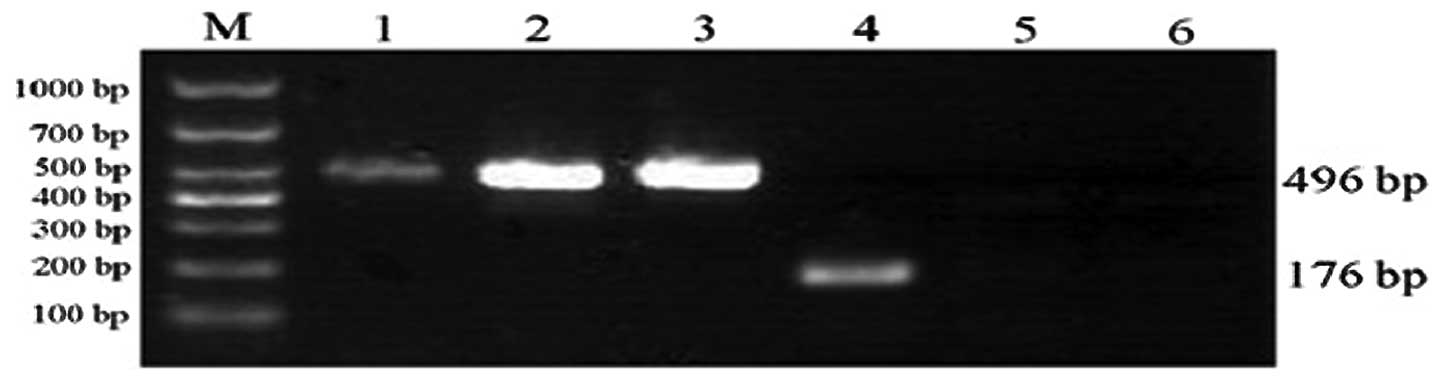
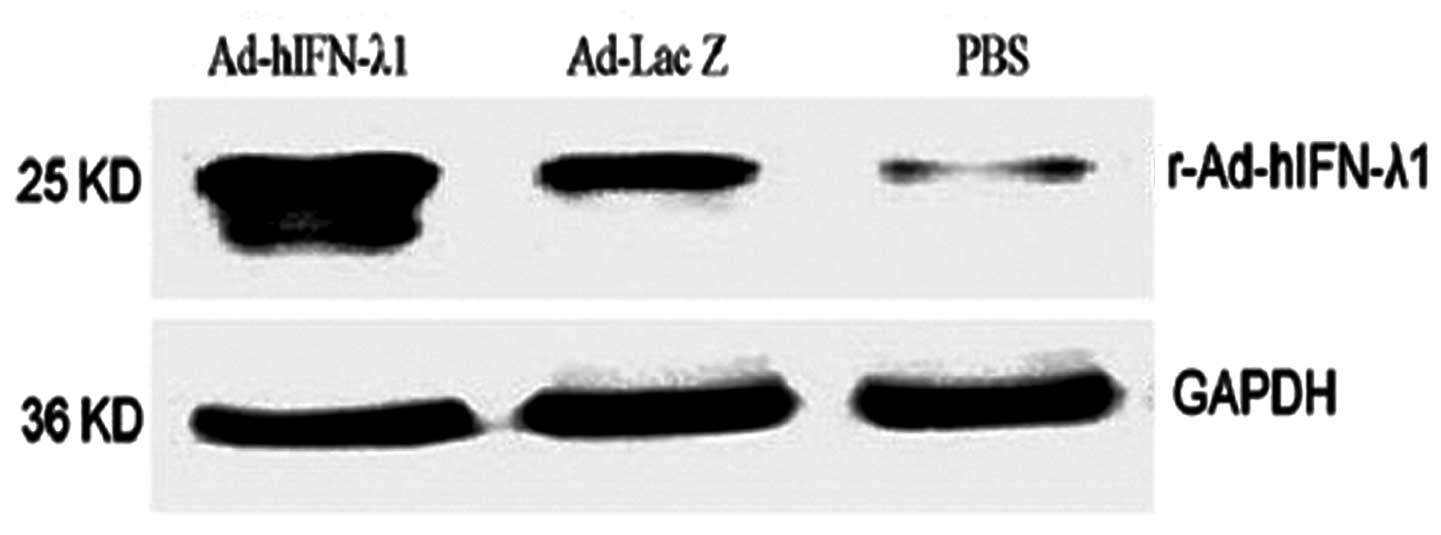
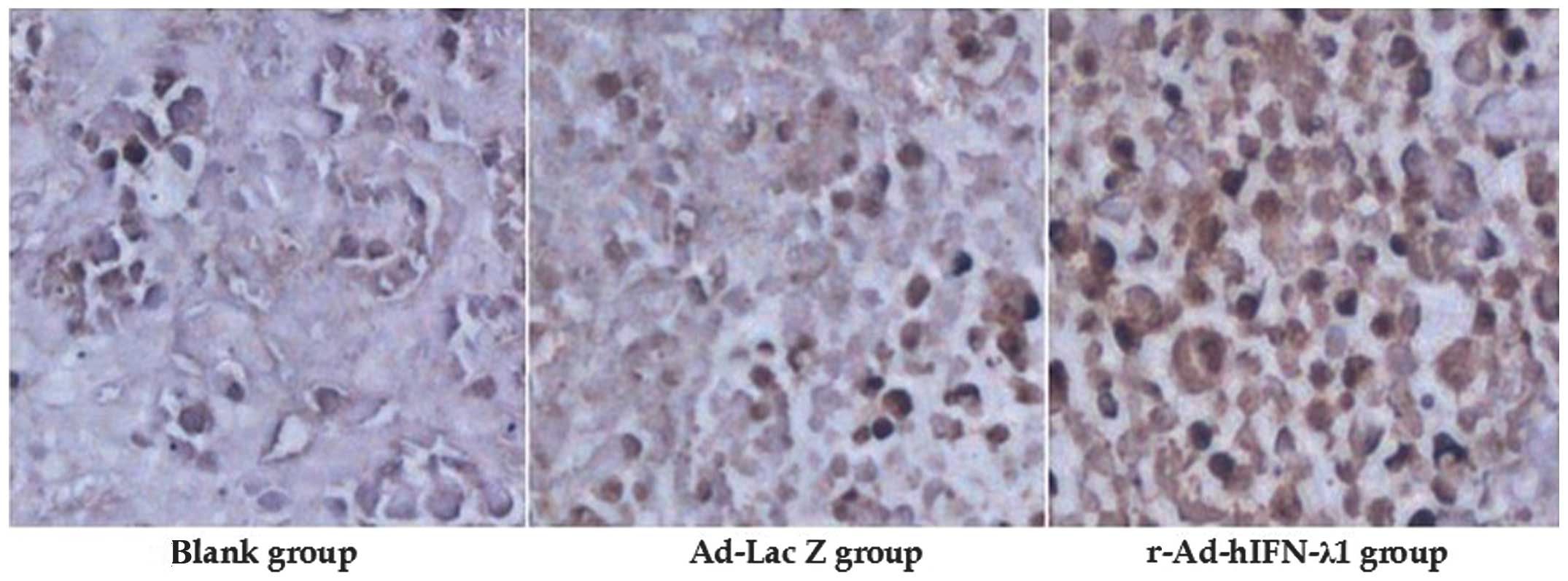
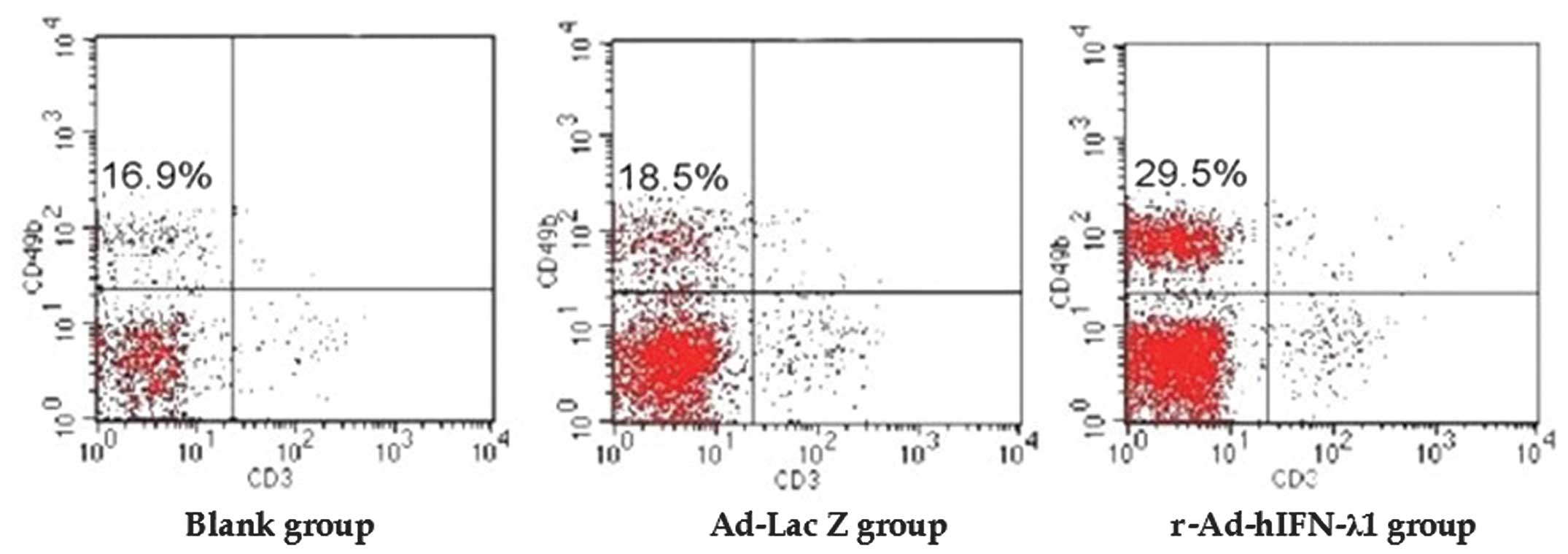
|
1
|
Sheppard P, Kindsvogel W, Xu W, et al:
IL-28, IL-29 and their class II cytokine receptor IL-28R. Nat
Immunol. 4:63–68. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kotenko SV, Gallagher G, Baurin VV, et al:
IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class
II cytokine receptor complex. Nat Immunol. 4:69–77. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meager A, Visvalingam K, Dilger P, Bryan D
and Wadhwa M: Biological activity of interleukins-28 and -29:
comparison with type I interferons. Cytokine. 31:109–118. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zheng Y, Li H, Yu J, Zhao H, Wang SE and
Ren X: Interferon-λs: special immunomodulatory agents and potential
therapeutic targets. J Innate Immun. 5:209–218. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Witte K, Gruetz G, Volk HD, et al: Despite
IFN-lambda receptor expression, blood immune cells, but not
keratinocytes or melanocytes, have an impaired response to type III
interferons: implications for therapeutic applications of these
cytokines. Genes Immun. 10:702–714. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Brand S, Beigel F, Olszak T, et al: IL-28A
and IL-29 mediate antiproliferative and antiviral signals in
intestinal epithelial cells and murine CMV infection increases
colonic IL-28A expression. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
289:G960–G968. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sato A, Ohtsuki M, Hata M, Kobayashi E and
Murakami T: Antitumor activity of IFN-lambda in murine tumor
models. J Immunol. 176:7686–7694. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Halter R, Carnwath J, Espanion G, et al:
Strategies to express factor VIII gene constructs in the ovine
mammary gland. Theriogenology. 39:137–149. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yan YL, Liu Y, Cao WY, Bu XF, Bu ZG and
Zheng JX: Human lamada-interferon expressed in BHK-21 cell line and
its bioactivity. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 24:950–953.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Ferrantini M, Capone I and Belardelli F:
Interferon-alpha and cancer: mechanisms of action and new
perspectives of clinical use. Biochimie. 89:884–893. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Billiau A: Interferon: the pathways of
discovery I. Molecular and cellular aspects. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 17:381–409. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raison CL, Demetrashvili M, Capuron L and
Miller AH: Neuropsychiatric adverse effects of interferon-alpha:
recognition and management. CNS Drugs. 19:105–123. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brand S, Zitzmann K, Dambacher J, et al:
SOCS-1 inhibits expression of the antiviral proteins 2′,5′-OAS and
MxA induced by the novel interferon-lambdas IL-28A and IL-29.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 331:543–548. 2005.
|
|
14
|
Langer JA, Cutrone EC and Kotenko S: The
Class II cytokine receptor (CRF2) family: overview and patterns of
receptor-ligand interactions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:33–48.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dumoutier L, Tounsi A, Michiels T,
Sommereyns C, Kotenko SV and Renauld JC: Role of the interleukin
(IL)-28 receptor tyrosine residues for antiviral and
antiproliferative activity of IL-29/interferon-lambda 1:
similarities with type I interferon signaling. J Biol Chem.
279:32269–32274. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sommereyns C, Paul S, Staeheli P and
Michiels T: IFN-lambda (IFN-lambda) is expressed in a
tissue-dependent fashion and primarily acts on epithelial cells in
vivo. PLoS Pathog. 4:e10000172008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pekarek V, Srinivas S, Eskdale J and
Gallagher G: Interferon lambda-1 (IFN-lambda1/IL-29) induces ELR(-)
CXC chemokine mRNA in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, in
an IFN-gamma-independent manner. Genes Immun. 8:177–180. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Numasaki M, Tagawa M, Iwata F, et al:
IL-28 elicits antitumor responses against murine fibrosarcoma. J
Immunol. 178:5086–5098. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mennechet FJ and Uzé G:
Interferon-lambda-treated dendritic cells specifically induce
proliferation of FOXP3-expressing suppressor T cells. Blood.
107:4417–4423. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Uzé G and Monneron D: IL-28 and IL-29:
newcomers to the interferon family. Biochimie. 89:729–734.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Porta C, Hadj-Slimane R, Nejmeddine M, et
al: Interferons alpha and gamma induce p53-dependent and
p53-independent apoptosis, respectively. Oncogene. 24:605–615.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lasfar A, Lewis-Antes A, Smirnov SV, et
al: Characterization of the mouse IFN-lambda ligand-receptor
system: IFN-lambdas exhibit antitumor activity against B16
melanoma. Cancer Res. 66:4468–4477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|