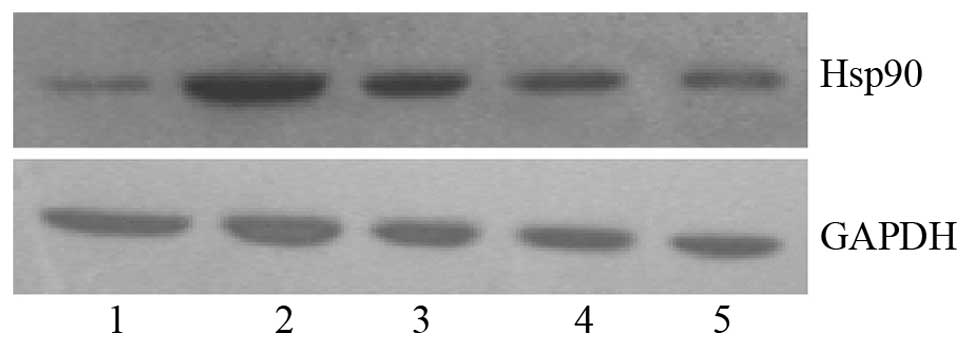
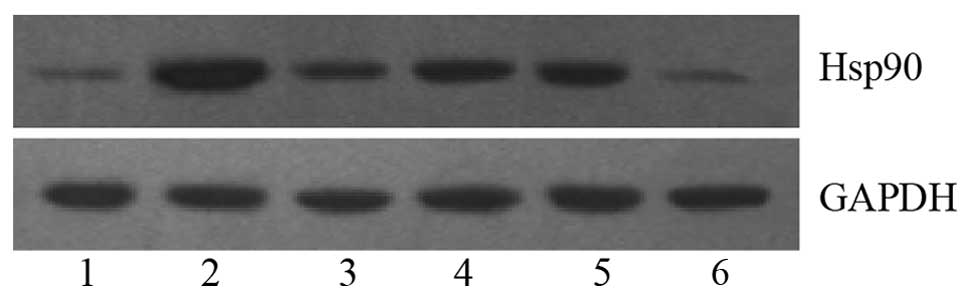
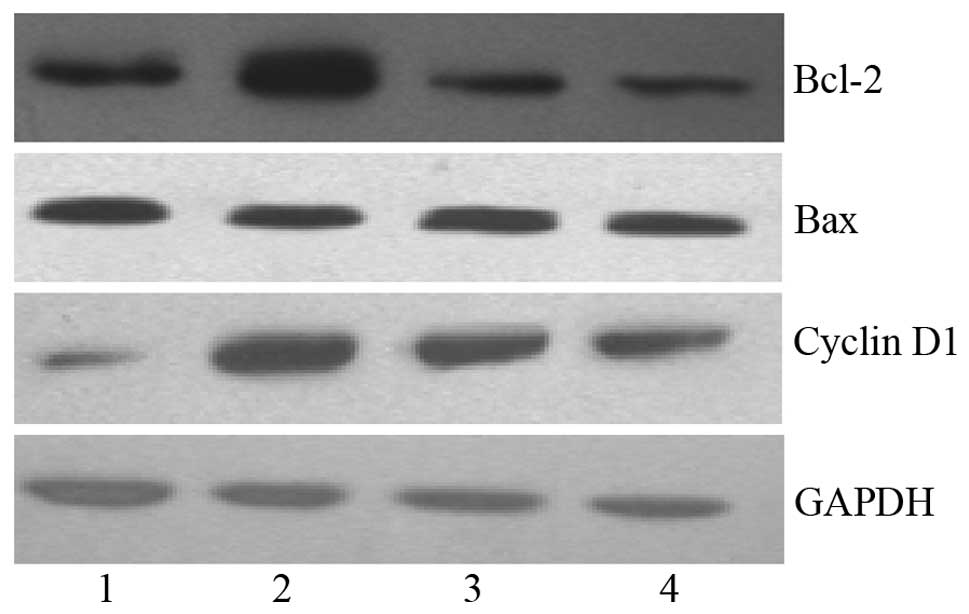
|
1
|
Bishop SC, Burlison JA and Blagg BS:
Hsp90: a novel target for the disruption of multiple signaling
cascades. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 7:369–388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Trepel J, Mollapour M, Giaccone G and
Neckers L: Targeting the dynamic HSP90 complex in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 10:537–549. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chiosis G, Dickey CA and Johnson JL: A
global view of Hsp90 functions. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 20:1–4. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee WY, Chen YC, Shih CM, et al: The
induction of heme oxygenase-1 suppresses heat shock protein 90 and
the proliferation of human breast cancer cells through its
byproduct carbon monoxide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 274:55–62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schwock J, Pham NA, Cao MP and Hedley DW:
Efficacy of Hsp90 inhibition for induction of apoptosis and
inhibition of growth in cervical carcinoma cells in vitro and in
vivo. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 61:669–681. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Neckers L: Chaperoning oncogenes: Hsp90 as
a target of geldanamycin. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 172:259–277. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mehta PP, Kung PP, Yamazaki S, et al: A
novel class of specific Hsp90 small molecule inhibitors demonstrate
in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity in human melanoma cells.
Cancer Lett. 300:30–39. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du X and Mi R: Study on the cell signal
transductions of cell proliferation and apoptosis induced by VEGF-C
in cervical carcinoma. Xian Dai Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 11:877–880.
8852011.
|
|
9
|
Chinnaiyan P, Allen GW and Harari PM:
Radiation and new molecular agents, part II: targeting HDAC, HSP90,
IGF-1R, PI3K, and Ras. Semin Radiat Oncol. 16:59–64. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Park JW, Yeh MW, Wong MG, et al: The heat
shock protein 90-binding geldanamycin inhibits cancer cell
proliferation, down-regulates oncoproteins, and inhibits epidermal
growth factor-induced invasion in thyroid cancer cell lines. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 88:3346–3353. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sreedhar AS, Kalmár E, Csermely P and Shen
YF: Hsp90 isoforms: functions, expression and clinical importance.
FEBS Lett. 562:11–15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schmitt E, Gehrmann M, Brunet M, Multhoff
G and Garrido C: Intracellular and extracellular functions of heat
shock proteins: repercussions in cancer therapy. J Leukoc Biol.
81:15–27. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Polier S, Samant RS, Clarke PA, et al:
ATP-competitive inhibitors block protein kinase recruitment to the
Hsp90-Cdc37 system. Nat Chem Biol. 9:307–312. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Richter K and Buchner J: Hsp90:
chaperoning signal transduction. J Cell Physiol. 188:281–290. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cappello F, David S, Rappa F, et al: The
expression of HSP60 and HSP10 in large bowel carcinomas with lymph
node metastase. BMC Cancer. 5:1392005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Powers MV and Workman P: Targeting of
multiple signalling pathways by heat shock protein 90 molecular
chaperone inhibitors. Endocr Relat Cancer. 13(Suppl 1): 125–135.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Georgakis GV, Li Y, Rassidakis GZ, et al:
Inhibition of heat shock protein 90 function by
17-allylamino-17-demethoxy-geldanamycin in Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells
down-regulates Akt kinase, dephosphorylates extracellular
signal-regulated kinase, and induces cell cycle arrest and cell
death. Clin Cancer Res. 12:584–590. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades NS, McMullan CJ,
et al: Antimyeloma activity of heat shock protein-90 inhibition.
Blood. 107:1092–1100. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ferrario A, Rucker N, Wong S, Luna M and
Gomer CJ: Survivin, a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis family,
is induced by photodynamic therapy and is a target for improving
treatment response. Cancer Res. 67:4989–4995. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Röhl A, Rohrberg J and Buchner J: The
chaperone Hsp90: changing partners for demanding clients. Trends
Biochem Sci. 38:253–262. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sidera K and Patsavoudi E: HSP90
Inhibitors: current development and potential in cancer therapy.
Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 9:1–20. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gooljarsingh LT, Fernandes C, Yan K, et
al: A biochemical rationale for the anticancer effects of Hsp90
inhibitors: slow, tight binding inhibition by geldanamycin and its
analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:7625–7630. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duus J, Bahar HI, Venkataraman G, et al:
Analysis of expression of heat shock protein-90 (HSP90) and the
effects of HSP90 inhibitor (17-AAG) in multiple myeloma. Leuk
Lymphoma. 47:1369–1378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|