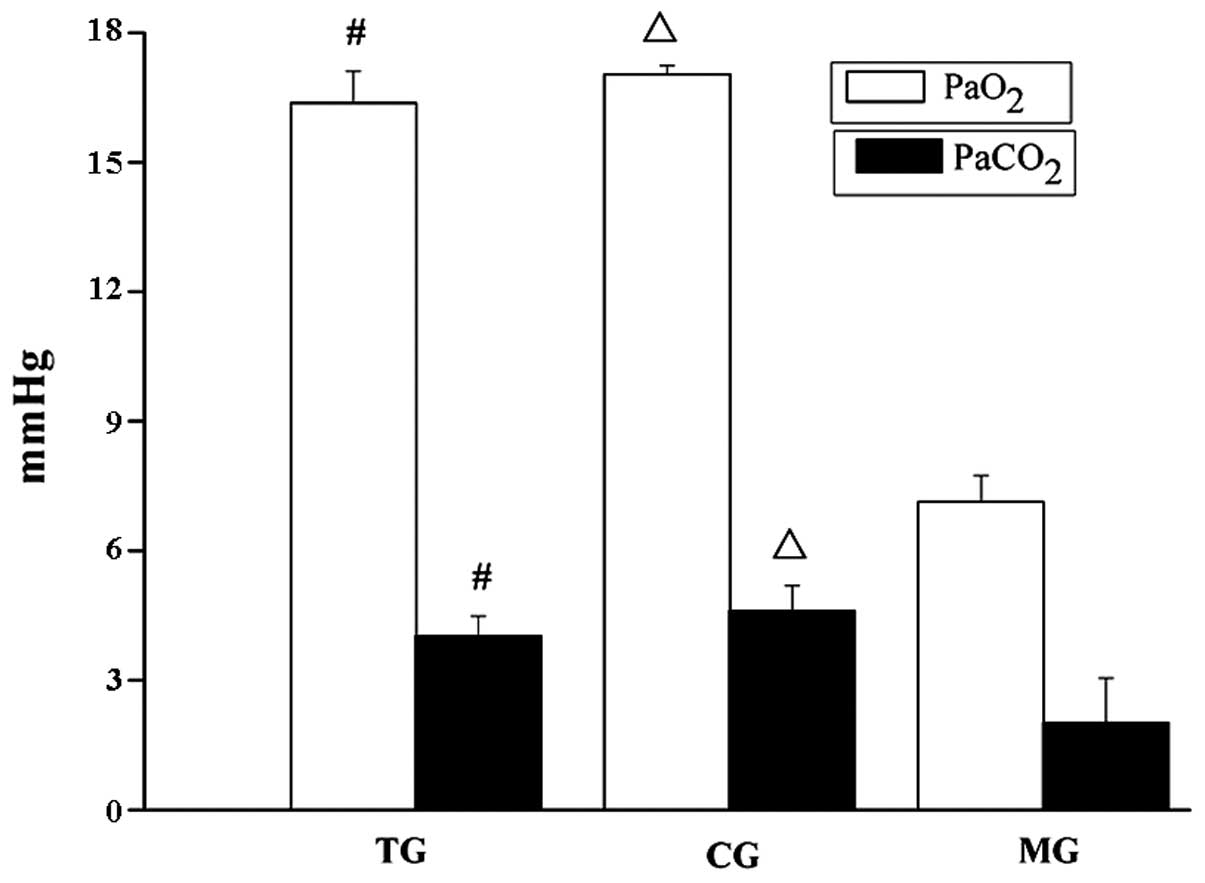
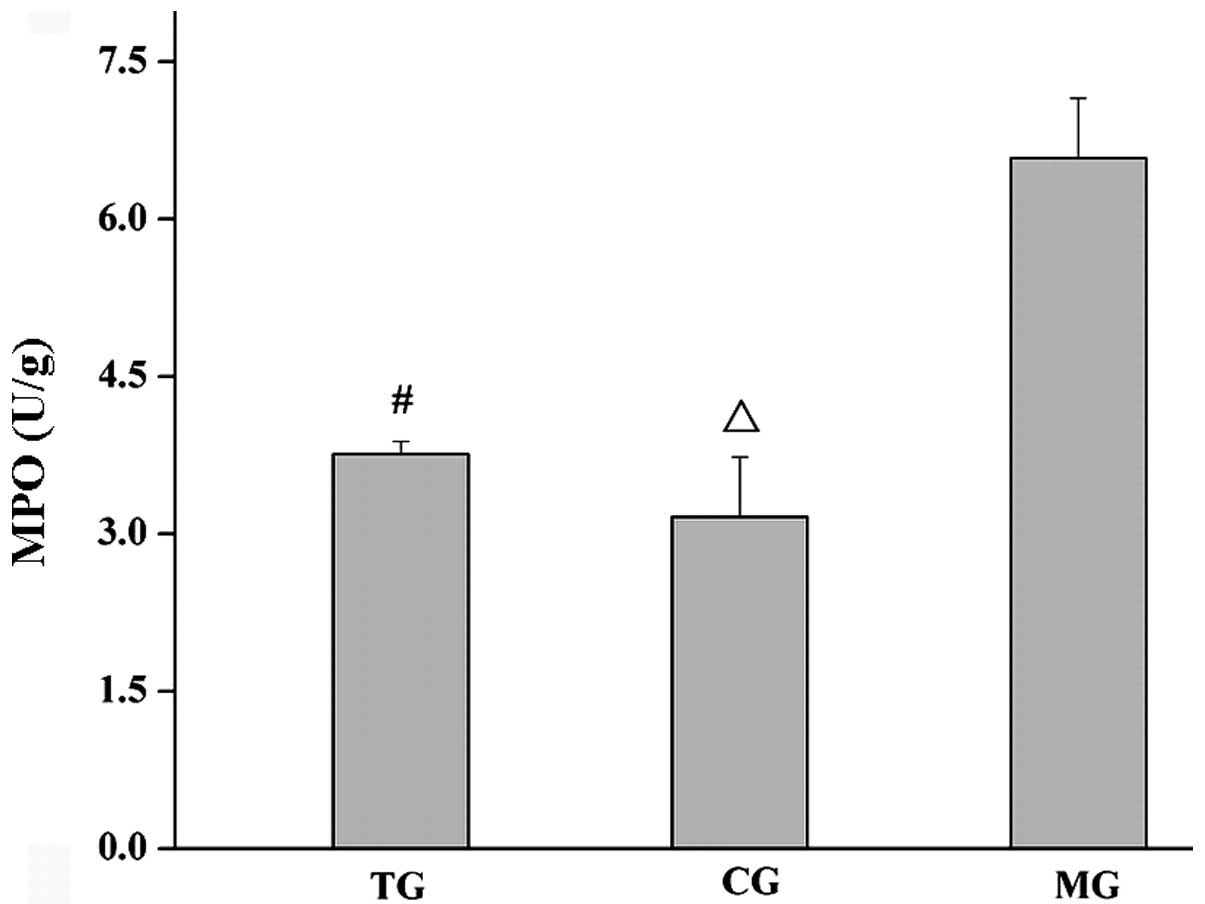
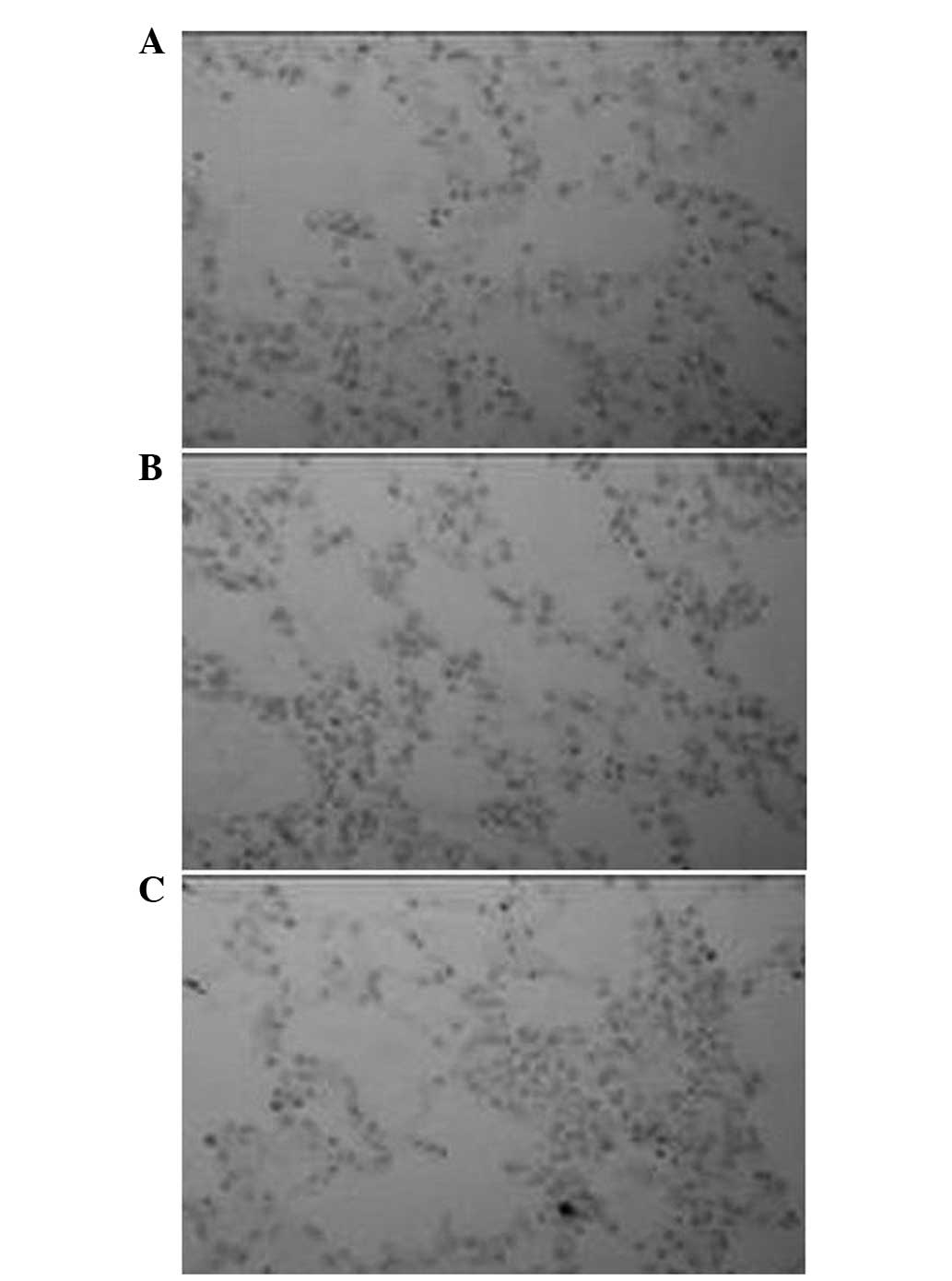
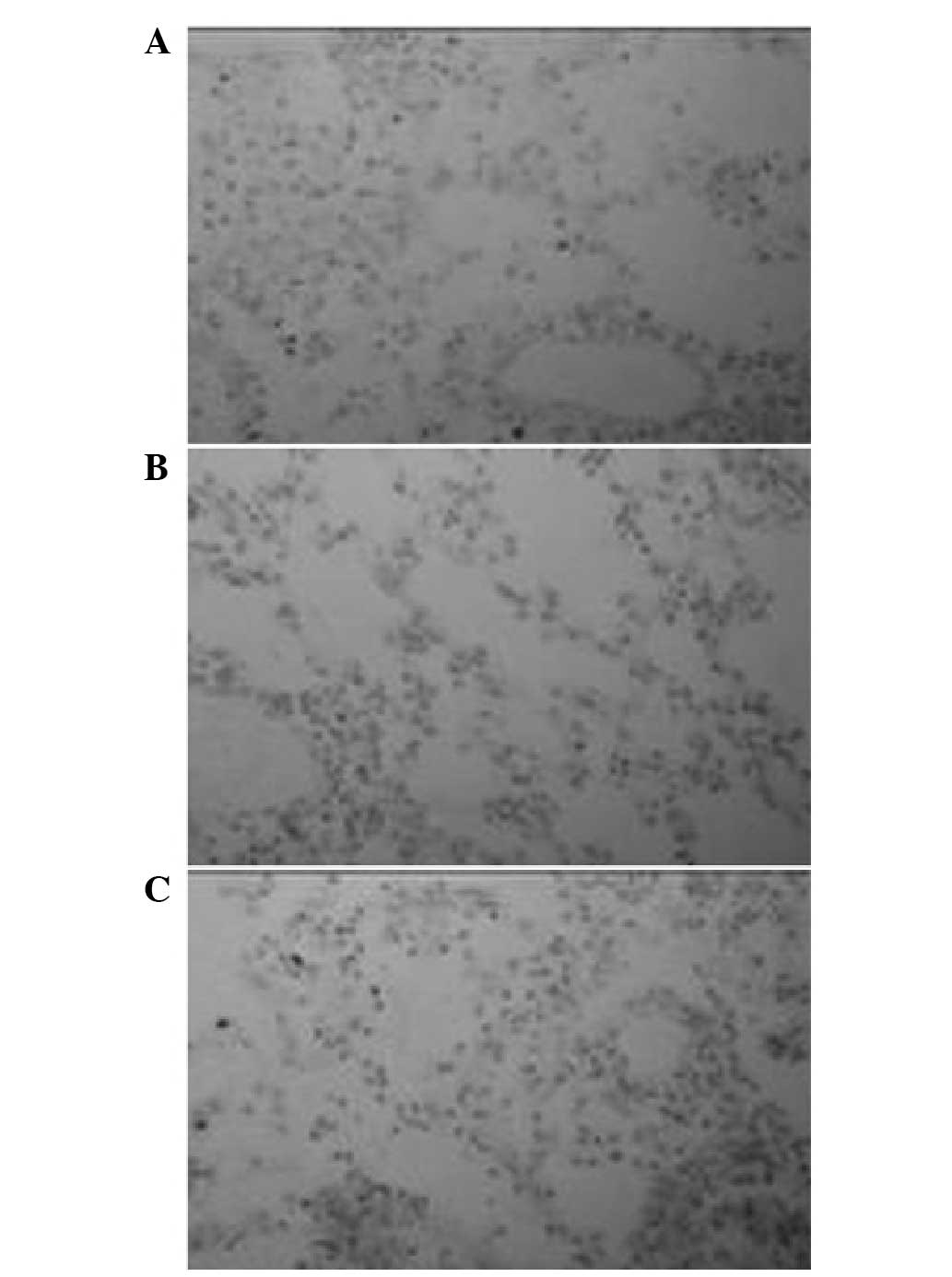
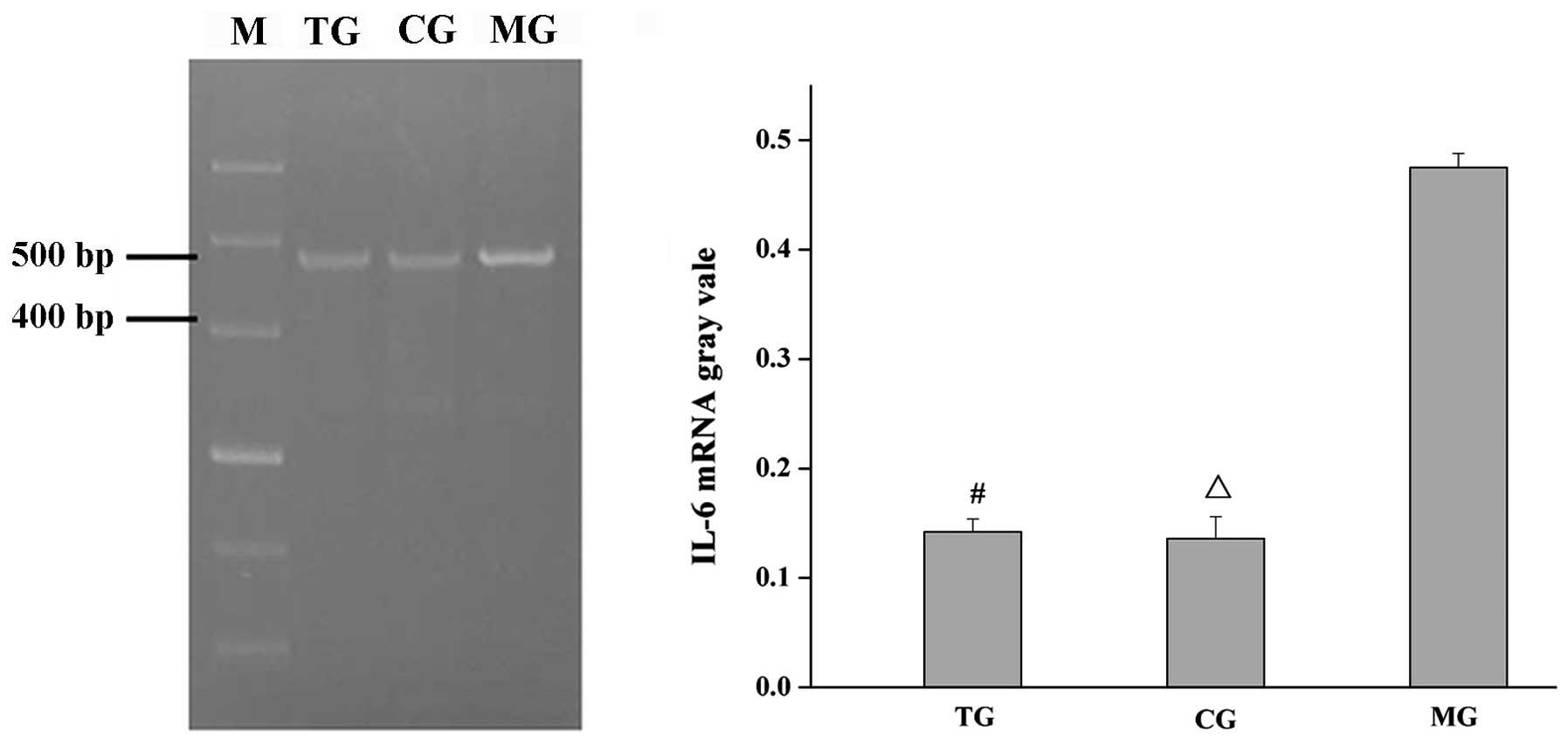
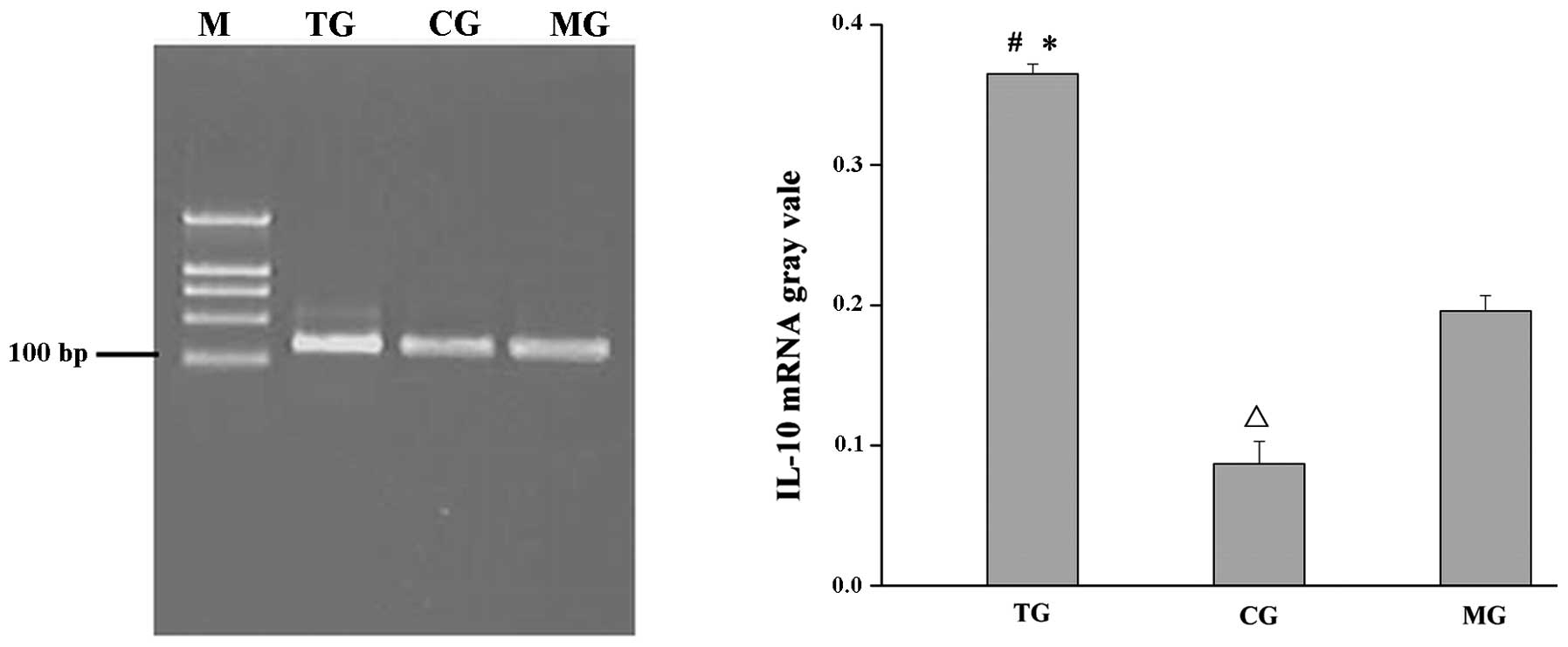
|
1
|
Liu W and Jin FG: New progress of acute
lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Chin J Lung
Dis (Electronic Edition). 1:61–64. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
2
|
Chang HM, Ji ML, Song XR, et al: Effect of
inflammatory cell adhesion molecules-1 on acute lung injury in
infant rats following meconium aspiration. Shi Yong Er Ke Lin
Chuang Za Zhi. 27:1835–1836. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Saraiva M and O’Garra A: The regulation of
IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:170–181.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rittirsch D, Flierl MA and Ward PA:
Harmful molecular mechanisms in sepsis. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:776–787.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Porter JC and Hall A: Epithelial ICAM-1
and ICAM-2 regulate the egression of human T cells across the
bronchial epithelium. FASEB J. 23:492–502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grommes J and Soehnlein O: Contribution of
neutrophils to acute lung injury. Mol Med. 17:293–307. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Orlikowsky T, Wang ZQ, Dudhane A, et al:
Two distinct pathways of human macrophage differentiation are
mediated by interferon-gamma and interleukin-10. Immunology.
91:104–108. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kylänpää L, Rakonczay Z Jr and O’Reilly
DA: The clinical course of acute pancreatitis and the inflammatory
mediators that drive it. Int J Inflam. 2012:3606852012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Favarin DC, de Oliveira JR, de Oliveira CJ
and de Rogerio AP: Potential effects of medicinal plants and
secondary metabolites on acute lung injury. Biomed Res Int.
2013:5764792013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Welty-Wolf KE, Carraway MS, Ortel TL and
Piantadosi CA: Coagulation and inflammation in acute lung injury.
Thromb Haemost. 88:17–25. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tanaka T and Kishimoto T: Targeting
interleukin-6: all the way to treat autoimmune and inflammatory
diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 8:1227–1236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Frisdal E, Lesnik P, Olivier M, et al:
Interleukin-6 protects human macrophages from cellular cholesterol
accumulation and attenuates the proinflammatory response. J Biol
Chem. 286:30926–30936. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Steiner MK, Syrkina OL, Kolliputi N, et
al: Interleukin-6 overexpression induces pulmonary hypertension.
Circ Res. 104:236–244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pedroza M, Schneider DJ, Karmouty-Quintana
H, et al: Interleukin-6 contributes to inflammation and remodeling
in a model of adenosine mediated lung injury. PLoS One.
6:e226672011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seki T, Kumagai T, Kwansa-Bentum B, et al:
Interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 suppress excessive neutrophil
infiltration and hepatocyte damage during acute murine
schistosomiasis japonica. Infect Immun. 80:159–168. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hedrich CM and Bream JH: Cell
type-specific regulation of IL-10 expression in inflammation and
disease. Immunol Res. 47:185–206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
D’Alessio FR, Tsushima K, Aggarwal NR, et
al: CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs resolve
experimental lung injury in mice and are present in humans with
acute lung injury. J Clin Invest. 119:2898–2913. 2009.
|
|
18
|
Poe SL, Arora M, Oriss TB, et al:
STAT1-regulated lung MDSC-like cells produce IL-10 and efferocytose
apoptotic neutrophils with relevance in resolution of bacterial
pneumonia. Mucosal Immunol. 6:189–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang M, Zhou M, Han Y, et al:
Identification of NF-κB inhibitors in Xuebijing injection for
sepsis treatment based on bioactivity-integrated UPLC-Q/TOF. J
Ethnopharmacol. 147:426–433. 2013.
|
|
20
|
He XD, Wang Y, Wu Q, et al: Xuebijing
protects rats from sepsis challenged with Acinetobacter
baumannii by promoting annexin A1 expression and inhibiting
proinflammatory cytokines secretion. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2013:8049402013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song XR: Regulation of breathing exercises
and experimental acute respiratory failure. Medical Function
Experiment. Chang QZ: 2nd edition. People’s Medical Publishing
House; Beijing: pp. 124–125. 2007
|
|
22
|
Yu P, Bu H, Wang H, et al: Comparative
study on image analysis and manual counting of
immunohistochemistry. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi.
20:288–290. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Jiang H, Meng F, Li W, et al: Splenectomy
ameliorates acute multiple organ damage induced by liver warm
ischemia reperfusion in rats. Surgery. 141:32–40. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smith JA: Neutrophils, host defense, and
inflammation: a double-edged sword. J Leukoc Biol. 56:672–686.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li YP, Qiao YJ, Wu ZX, et al: Effects of
Xuebijing injection on protein C and tumor necrosis factor-alpha
mRNA in rats with sepsis. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
19:488–491. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Qi F, Liang ZX, She DY, et al: A clinical
study on the effects and mechanism of xuebijing injection in severe
pneumonia patients. J Tradit Chin Med. 31:46–49. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang P, Cao SH, Cui KL, et al: The
influences of Xuebijing on the expression of human leukocyte
antigen-DR on monocytes in patients with multiple organ dysfunction
syndrome. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 9:21–23. 2002.(In
Chinese).
|