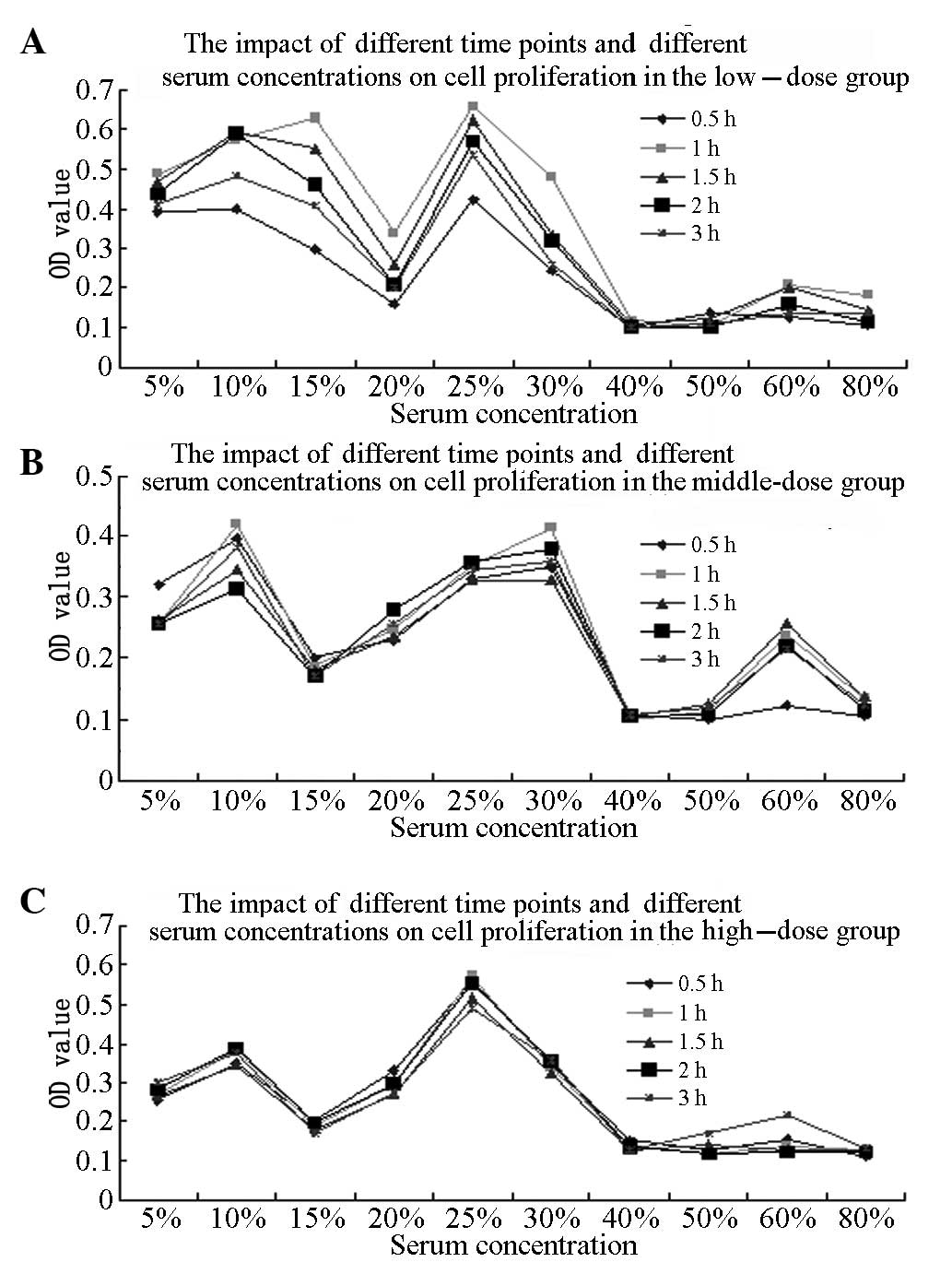
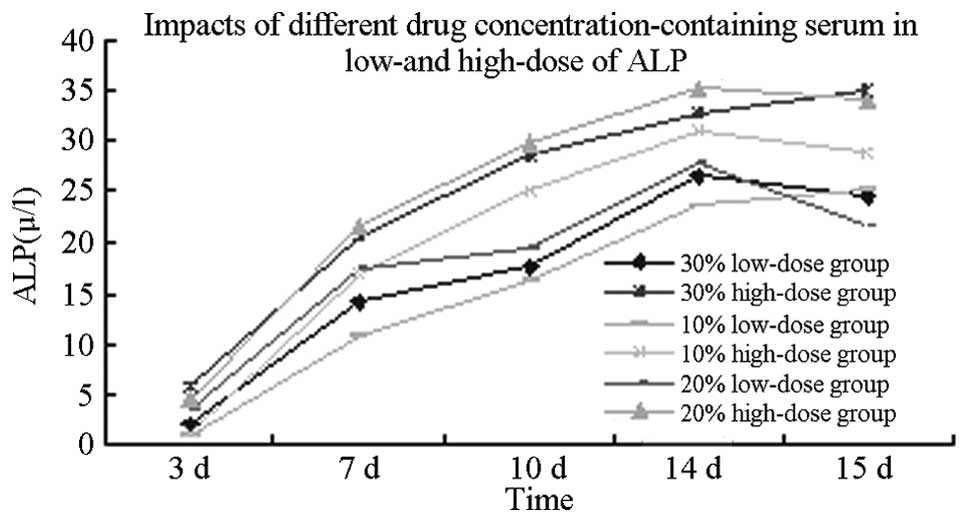
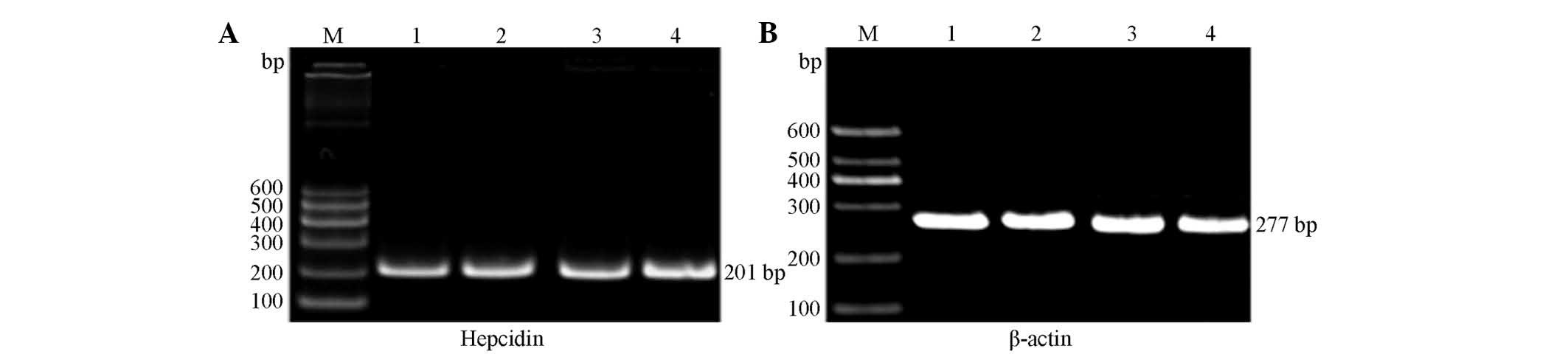
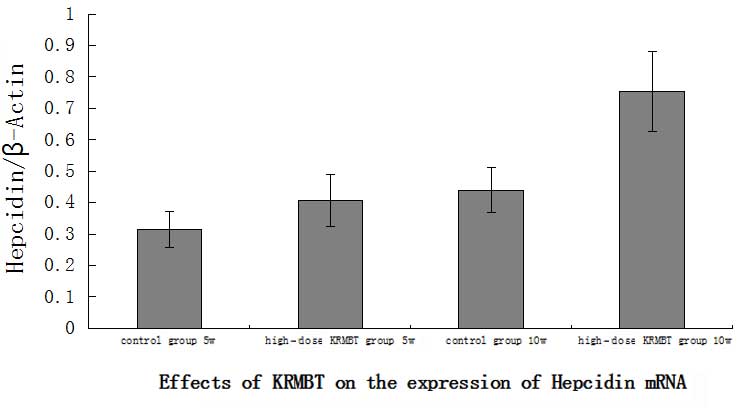
|
1
|
Liu Z, Wang YF and Liu ZH: Research
progress in the association of glucocorticoid and osteoporosis.
Zhongguo Gu Zhi Shu Song Za Zhi. 16:713–718. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
2
|
Liu GW, Gao J, Guo HJ, et al: Effect of
invigorating kidney and nourishing essence Chinese medicine
containing serum on Wnt/β-catenin osteogenic differentiation signal
pathway in BMSCs in ovariectomized mice. Zhongguo Gu Zhi Shu Song
Za Zhi. 19:324–329. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Zheng JC, Fan YG, Liu JR, et al:
Experimental study of directional differentiation of bone
mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) to osteoblasts guided by serum
containing Cistanche deserticola. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 23:606–608.
2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Kerachian MA, Séguin C and Harvey EJ:
Glucocorticoids in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a new
understanding of the mechanisms of action. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 114:121–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Inoue S, Horii M, Asano T, et al: Risk
factors for nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head after
renal transplantation. J Orthop Sci. 8:751–756. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cui QJ, Wang GJ, Su CC and Balian G; The
Otto Aufranc Award. Lovastatin prevents steroid induced
adipogenesis and osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 344:8–19.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Schilling T, Nöth U, Klein-Hitpass L, et
al: Plasticity in adipgenesis and osteogenesis of human mesenchymal
stem cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 271:1–17. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kazama T, Fujie M, Endo T and Kano K:
Mature adipocyte-derived dedifferentiated fat cells can
transdifferentiate into skeletal myocytes in vitro. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 377:780–785. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang XX, Zhang YL and Huang QF: Discussion
on the main pathogenesis in traditional Chinese medicine and
etiology about primary osteoporosis. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao.
8:1119–1123. 2010.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fujita T, Ohue T, Fujii Y, Miyauchi A and
Takagi Y: Heated oyster shell-seaweed calcium (AAA Ca) on
osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 58:226–230. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anić B and Grazio S: Current osteoporosis
treatment: reasons for adding vitamin D to alendronate. Reumatizam.
53:63–65. 2006.(In Croatian).
|
|
12
|
Ji JX, Qian J, Huang FJ, et al: Study on
the active principles and pharmacological actions of hairy antler.
Zhongguo Sheng Hua Yao Wu Za Zhi. 30:141–143. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Kim KH, Kim KS, Choi BJ, et al: Anti-bone
resorption activity of deer antler aqua-acupunture, the pilose
antler of Cervus korean TEMMINCK var. mantchuricus Swinhoe
(Nokyong) in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
96:497–506. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Qian G, Zhang X, Lu L, Wu X, Li S and Meng
J: Regulation of Cbfa1 expression by total flavonoids of Herba
epimedii. Endocr J. 53:87–94. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen KM, Ge BF, Ma HP, et al: Effects of
icariin on the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow
mysenchymal stem cells in vitro. Zhongguo Gu Zhi Shu Song Za Zhi.
14:642–645. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Meng FH, Li YB, Xiong ZL, Jiang ZM and Li
FM: Osteoblastic proliferative activity of Epimedium brevicornum
Maxim. Phytomedicine. 12:189–193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo X, Song M and Liu Y: Development of
the experimental research of the effects of the drug serum in herba
epimendii on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Zhongguo
Gu Zhi Shu Song Za Zhi. 14:818–822. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Grainger DJ, Percival J, Chiano M and
Spector TD: The role of serum TGF-beta isoforms as potential
markers of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 9:398–404. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nesti LJ, Caterson EJ, Li WJ, Chang R,
McCann TD, Hoek JB and Tuan RS: TGF-beta1 calcium signaling in
osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 101:348–359. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Arnott JA, Zhang X, Sanjay A, et al:
Molecular requirements for induction of CTGF expression by
TGF-beta1 in primary osteoblasts. Bone. 42:871–885. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shin MK, Kim MK, Bae YS, et al: A novel
collagen-binding peptide promotes ostegenic differentiation via
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II/ERK/AP-1
signaling pathway in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. Cell Singal. 20:613–624. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Ozmen B, Kirmaz C, Aydin K, Kafesciler SO,
Guclu F and Hekimsoy Z: Influence of the selective oestrogen
receptor modulator (raloxifene hydrochloride) on IL-6, TNF-alpha,
TGF-beta1 and bone turnover markers in the treatment of
postmenopausal osteoporosis. Eur Cytokine Netw. 18:148–153.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Houtkooper LB, Stanford VA, Metcalfe LL,
Lohman TG and Going SB: Preventing osteoporosis the bone estrogen
strength training way. ACSMS Health Fit J. 11:21–27. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Park CH, Valore EV, Waring AJ and Ganz T:
Hepcidin, a urinary antimicrobial peptide synthesized in the liver.
J Biol Chem. 276:7806–7810. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pigeon C, Ilyin G, Courselaud B, Leroyer
P, Turlin B, Brissot P and Loréal O: A new mouse liver-specific
gene, encoding a protein homologous to human antimicrobial peptide
hepcidin, is overexpressed during iron overload. J Biol Chem.
276:7811–7819. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|