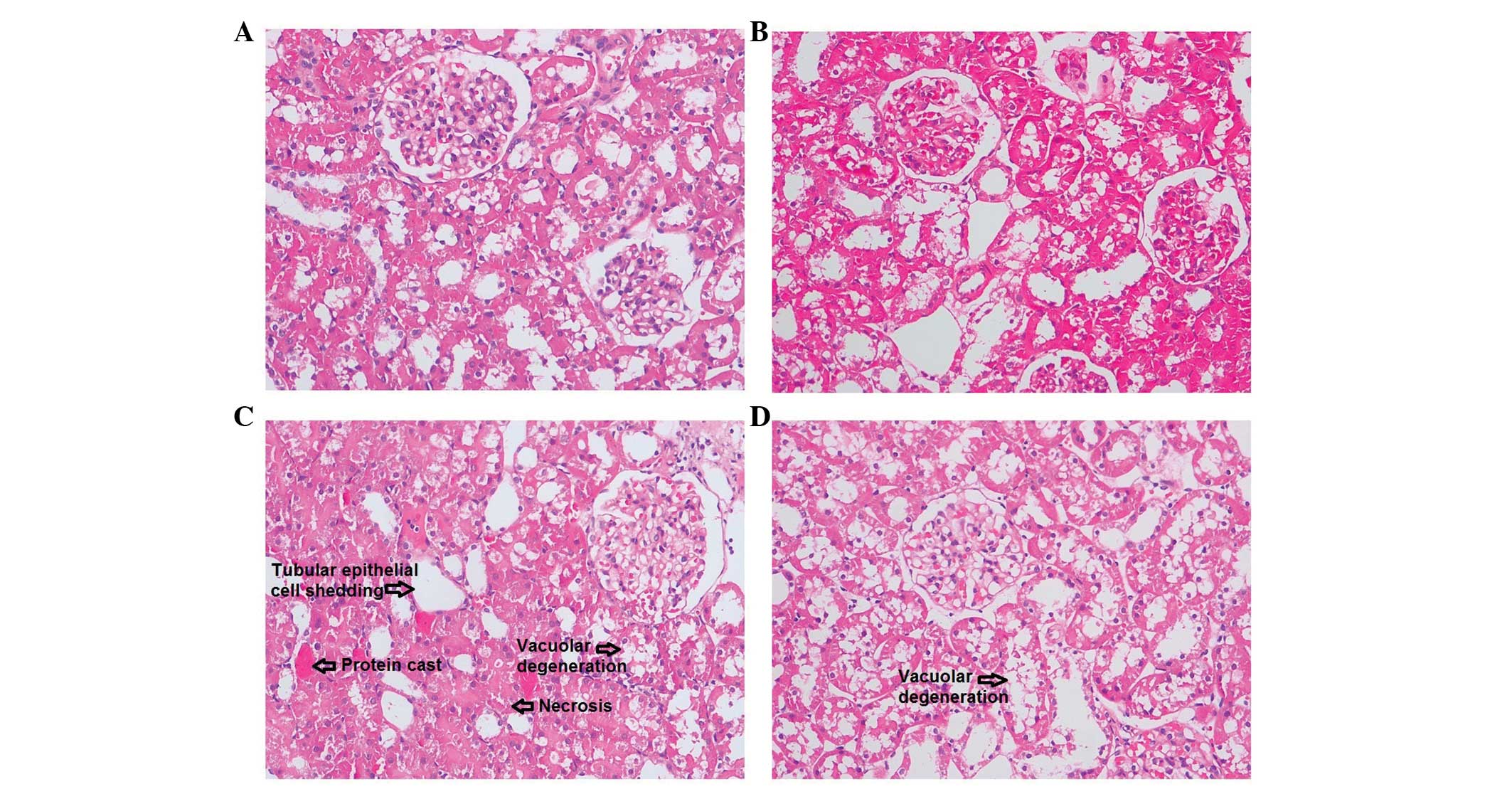
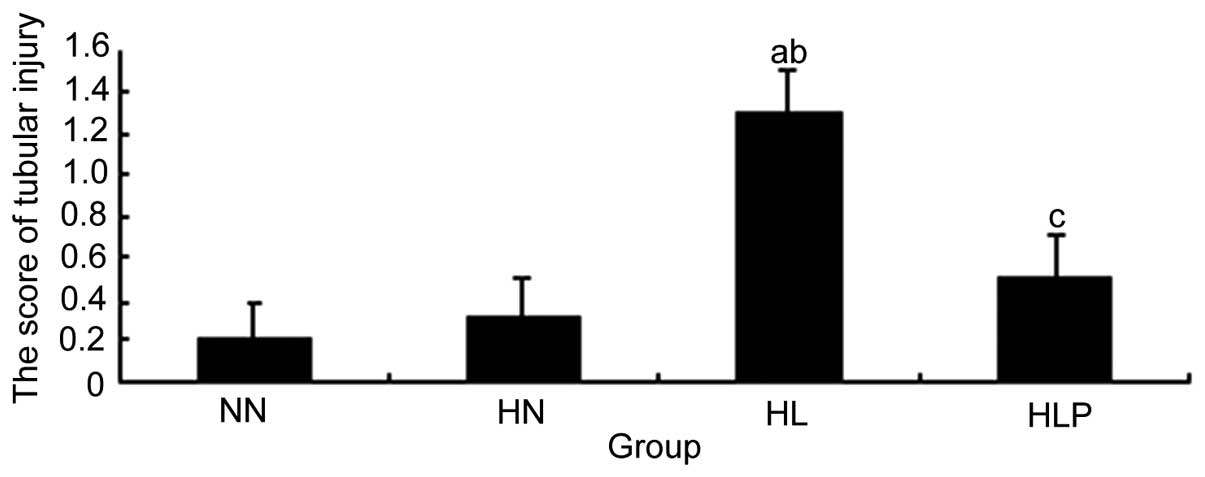
|
1
|
Itoh Y, Yano T, Sendo T and Oishi R:
Clinical and experimental evidence for prevention of acute renal
failure induced by radiographic contrast media. J Pharmacol Sci.
97:473–488. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aspelin P, Aubry P, Fransson SG, Strasser
R, Willenbrock R and Berg KJ: NEPHRIC Study Investigators:
Nephrotoxic effects in high-risk patients undergoing angiography. N
Engl J Med. 348:491–499. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Seeliger E, Sendeski M, Rihal CS and
Persson PB: Contrast-induced kidney injury: mechanisms, risk
factors, and prevention. Eur Heart J. 33:2007–2015. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Russo D, Minutolo R, Cianciaruso B, Memoli
B, Conte G and De Nicola L: Early effects of contrast media on
renal hemodynamics and tubular function in chronic renal failure. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 6:1451–1458. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Perianayagam MC, Liangos O, Kolyada AY, et
al: NADPH oxidase p22phox and catalase gene variants are associated
with biomarkers of oxidative stress and adverse outcomes in acute
renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:255–263. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Duan SB, Liu GL, Chen GC, Wang P, Pan P
and Xu XQ: Aged rats are susceptible to nephrotoxicity induced by
iodinated contrast media. Ren Fail. 35:150–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Duan SB, Yang SK, Zhou QY, et al:
Mitochondria-targeted peptides prevent on contrast-induced acute
kidney injury in the rats with hypercholesterolemia. Ren Fail.
35:1124–1129. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roozbeh J, Hamidian Jahromi A, Sharifian
M, Pakfetrat M and Afshariani R: Protective effect of
pentoxifylline on contrast induced nephropathy. Saudi J Kidney Dis
Transpl. 19:985–986. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nasiri-Toosi Z, Dashti-Khavidaki S,
Khalili H and Lessan-Pezeshki M: A review of the potential
protective effects of pentoxifylline against drug-induced
nephrotoxicity. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 69:1057–1073. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Firouzi A, Eshraghi A, Shakerian F, et al:
Efficacy of pentoxifylline in prevention of contrast-induced
nephropathy in angioplasty patients. Int Urol Nephrol.
44:1145–1149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yang D, Lin S, Yang D, Wei L and Shang W:
Effects of short- and long-term hypercholesterolemia on
contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Am J Nephrol. 35:80–89. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang DW, Jia RH, Yang DP, Ding GH and
Huang CX: Dietary hypercholesterolemia aggravates contrast
media-induced nephropathy. Chin Med J (Engl). 117:542–546.
2004.
|
|
13
|
Lin SL, Chiang WC, Chen YM, Lai CF, Tsai
TJ and Hsieh BS: The renoprotective potential of pentoxifylline in
chronic kidney disease. J Chin Med Assoc. 68:99–105. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Duan S, Zhou X, Liu F, et al: Comparative
cytotoxicity of high-osmolar and low-osmolar contrast media on HKCs
in vitro. J Nephrol. 19:717–724. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rudnick MR and Goldfarb S: Pathogenesis of
contrast-induced nephropathy: experimental and clinical
observations with an emphasis on the role of osmolality. Rev
Cardiovasc Med. 4(Suppl 5): S28–S33. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ahmad A, Mondello S, Di Paola R, et al:
Protective effect of apocynin, a NADPH-oxidase inhibitor, against
contrast-induced nephropathy in the diabetic rats: a comparison
with N-acetylcysteine. Eur J Pharmacol. 674:397–406. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Benko A, Fraser-Hill M, Magner P, et al:
Canadian Association of Radiologists: consensus guidelines for the
prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy. Can Assoc Radiol J.
58:79–87. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Quintavalle C, Brenca M, De Micco F, et
al: In vivo and in vitro assessment of pathways involved in
contrast media-induced renal cells apoptosis. Cell Death Dis.
2:e1552011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Samlaska CP and Winfield EA:
Pentoxifylline. J Am Acad Dermatol. 30:603–621. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dávila-Esqueda ME and Martínez-Morales F:
Pentoxifylline diminishes the oxidative damage to renal tissue
induced by streptozotocin in the rat. Exp Diabesity Res. 5:245–251.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Costantini TW, Deree J, Peterson CY, et
al: Pentoxifylline modulates p47phox activation and downregulates
neutrophil oxidative burst through PKA-dependent and -independent
mechanisms. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 32:82–91. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Savic V, Vlahovic P, Djordjevic V,
Mitic-Zlatkovic M, Avramovic V and Stefanovic V: Nephroprotective
effects of pentoxifylline in experimental myoglobinuric acute renal
failure. Pathol Biol (Paris). 50:599–607. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tyagi P, Sharma P, Sharma BC, Puri AS,
Kumar A and Sarin SK: Prevention of hepatorenal syndrome in
patients with cirrhosis and ascites: a pilot randomized control
trial between pentoxifylline and placebo. Eur J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 23:210–217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
de Moura FJ, Leal PP, de Souza Furtado R,
Muniz-Junqueira MI and Veiga JP: Pentoxifylline prevents the
meglumine antimonate-induced renal toxicity in rats, but not that
induced by the inorganic antimony pentachloride. Toxicology.
243:66–74. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|