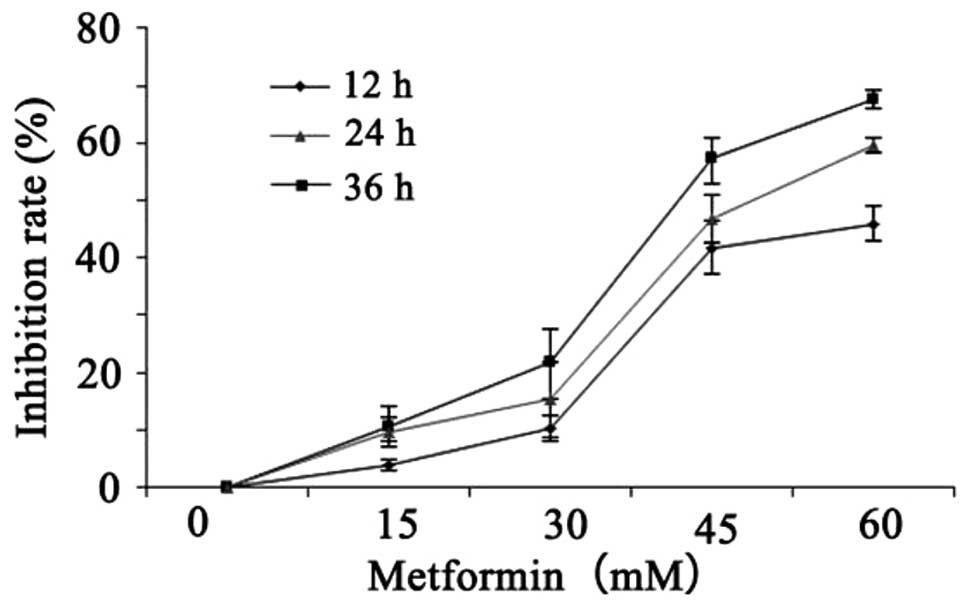
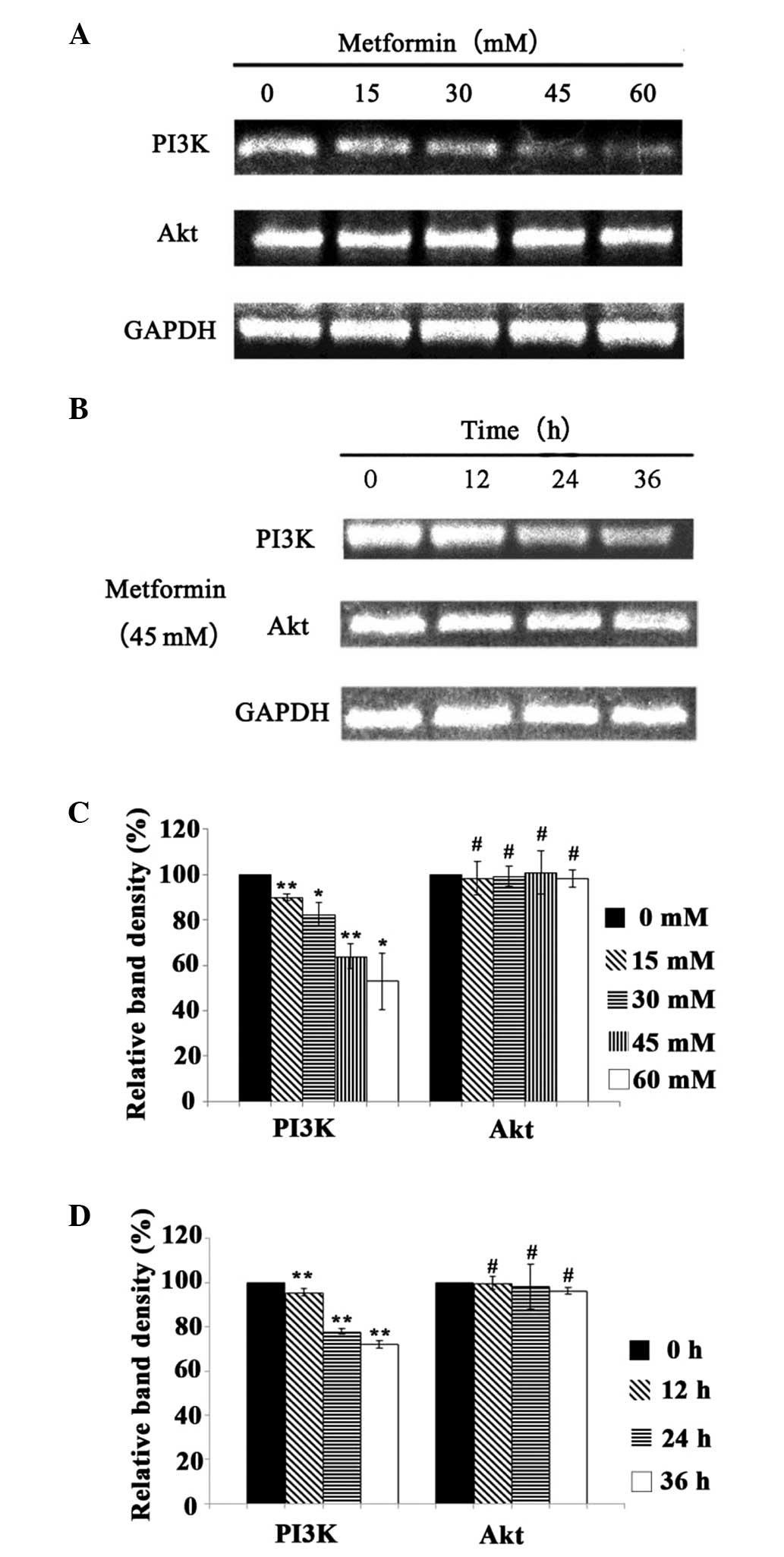
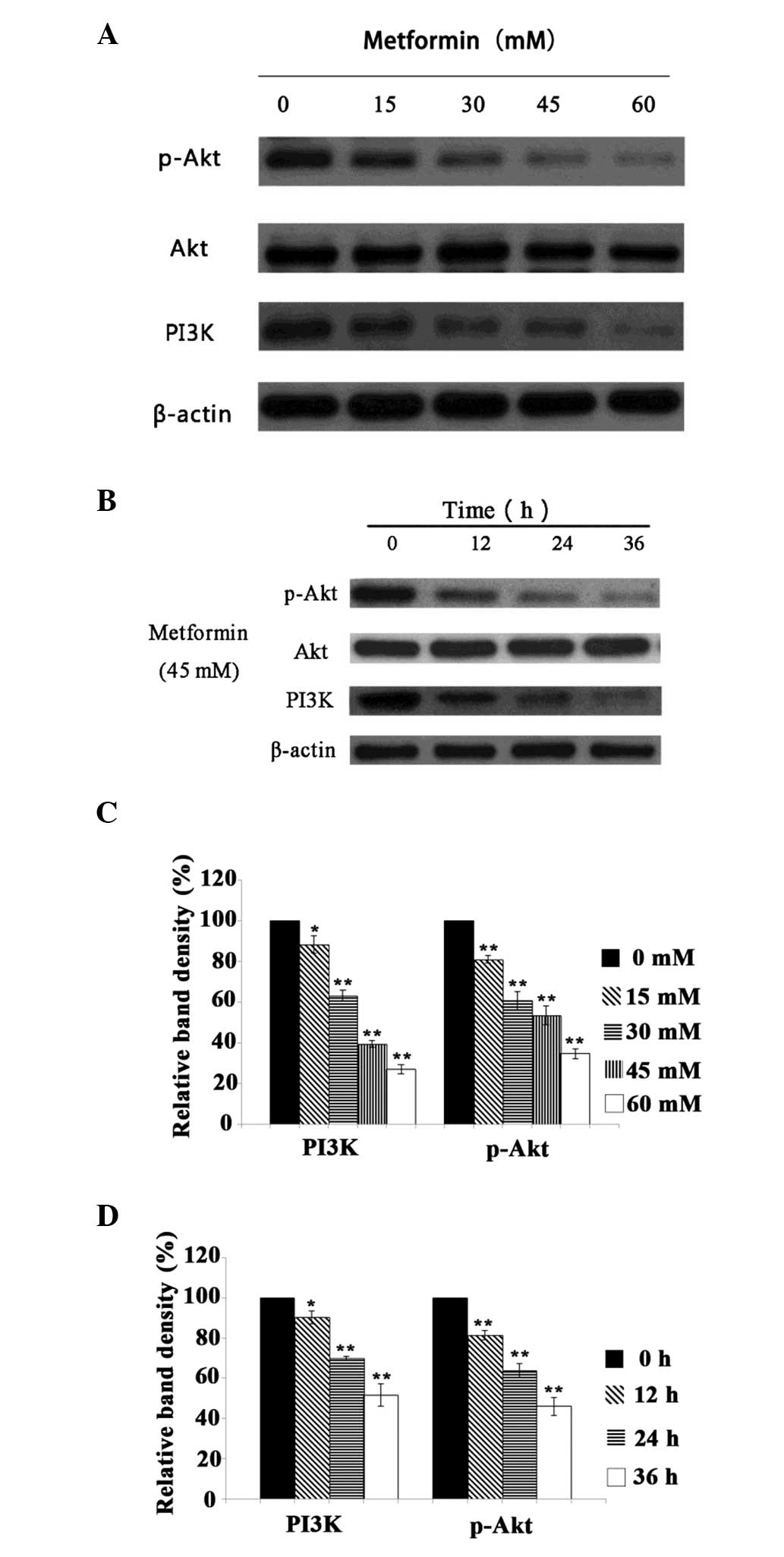
|
1
|
Samarasinghe V, Madan V and Lear JT:
Management of high-risk squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Expert
Rev Anticancer Ther. 11:763–769. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Macbeth AE, Grindlay DJ and Williams HC:
What’s new in skin cancer? An analysis of guidelines and systematic
reviews published in 2008–2009. Clin Exp Dermatol. 36:453–458.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van der Geer S, Siemerink M, Reijers HA,
Verhaegh ME, Ostertag JU, Neumann HA and Krekels GA: The incidence
of skin cancer in dermatology. Clin Exp Dermatol. 38:724–729.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nguyen TH and Ho DQ: Nonmelanoma skin
cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 3:193–203. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Samarasinghe V and Madan V: Nonmelanoma
skin cancer. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 5:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
American Diabetes Association. Standards
of medical care in diabetes - 2013. Diabetes Care. 36(Suppl 1):
S11–S66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM,
Alessi DR and Morris AD: Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in
diabetic patients. BMJ. 330:1304–1305. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Decensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, Cazzaniga
M, Gennari A, Bonanni B and Gandini S: Metformin and cancer risk in
diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 3:1451–1461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Currie CJ, Poole CD, Jenkins-Jones S, Gale
EA, Johnson JA and Morgan CL: Mortality after incident cancer in
people with and without type 2 diabetes: Impact of metformin on
survival. Diabetes Care. 35:299–304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh S, Singh H, Singh PP, Murad MH and
Limburg PJ: Antidiabetic medications and the risk of colorectal
cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 22:2258–2268.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gallagher EJ and LeRoith D: Diabetes,
antihyperglycemic medications and cancer risk: Smoke or fire. Curr
Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 20:485–494. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wright JL and Stanford JL: Metformin use
and prostate cancer in Caucasian men: Results from a
population-based case-control study. Cancer Causes Control.
20:1617–1622. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A,
Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Colosetti P, Auberger P, Tanti JF, Le
Marchand-Brustel Y and Bost F: The antidiabetic drug metformin
exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a
decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene. 27:3576–3586. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG,
Sonenberg N and Pollak M: Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent
growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:10269–10273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yung MM, Chan DW, et al: Activation of
AMPK inhibits cervical cancer cell growth through AKT/FOXO3a/FOXM1
signaling cascade. BMC Cancer. 13:3272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rattan R, Giri S, Hartmann LC and Shridhar
V: Metformin attenuates ovarian cancer cell growth in an AMP-kinase
dispensable manner. J Cell Mol Med. 15:166–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, et al: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bodmer M, Meier C, Krähenbühl S, Jick SS
and Meier CR: Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased
risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care. 33:1304–1308. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Byekova YA, Herrmann JL, Xu J, Elmets CA
and Athar M: Liver kinase B1 (LKB1) in the pathogenesis of
UVB-induced murine basal cell carcinoma. Arch Biochem Biophys.
508:204–211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karnevi E, Said K, Andersson R and
Rosendahl AH: Metformin-mediated growth inhibition involves
suppression of the IGF-I receptor signalling pathway in human
pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 13:2352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei W, Jin J, Schlisio S, Harper JW and
Kaelin WG Jr: The v-Jun point mutation allows c-Jun to escape
GSK3-dependent recognition and destruction by the Fbw7 ubiquitin
ligase. Cancer Cell. 8:25–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Welcker M, Singer J, Loeb KR, Grim J,
Bloecher A, Gurien-West M, Clurman BE and Roberts JM: Multisite
phosphorylation by Cdk2 and GSK3 controls cyclin E degradation. Mol
Cell. 12:381–392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mamane Y, Petroulakis E, Rong L, Yoshida
K, Ler LW and Sonenberg N: eIF4E - from translation to
transformation. Oncogene. 23:3172–3179. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
King FW, Skeen J, Hay N and Shtivelman E:
Inhibition of Chk1 by activated PKB/Akt. Cell Cycle. 3:634–637.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|