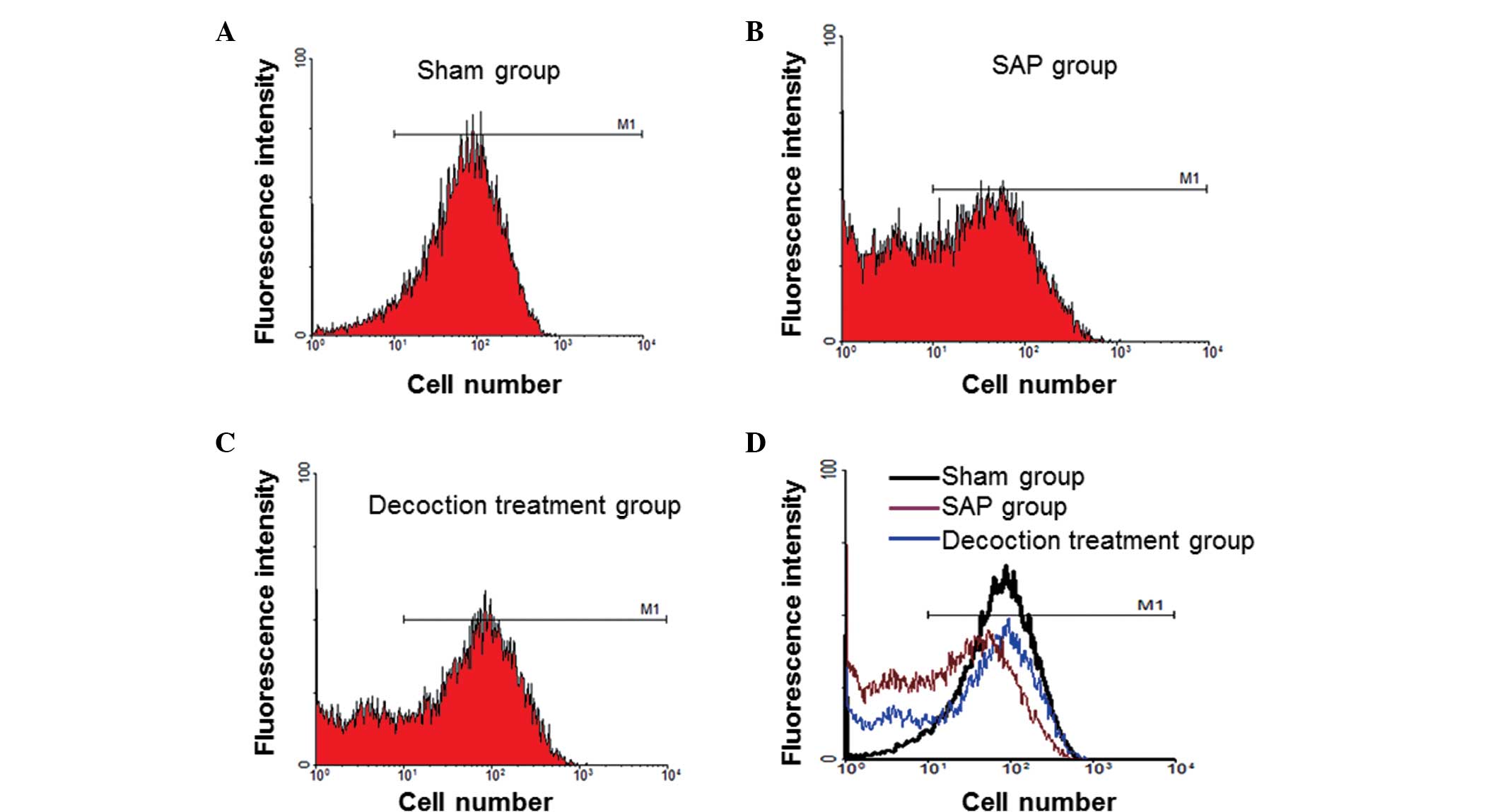
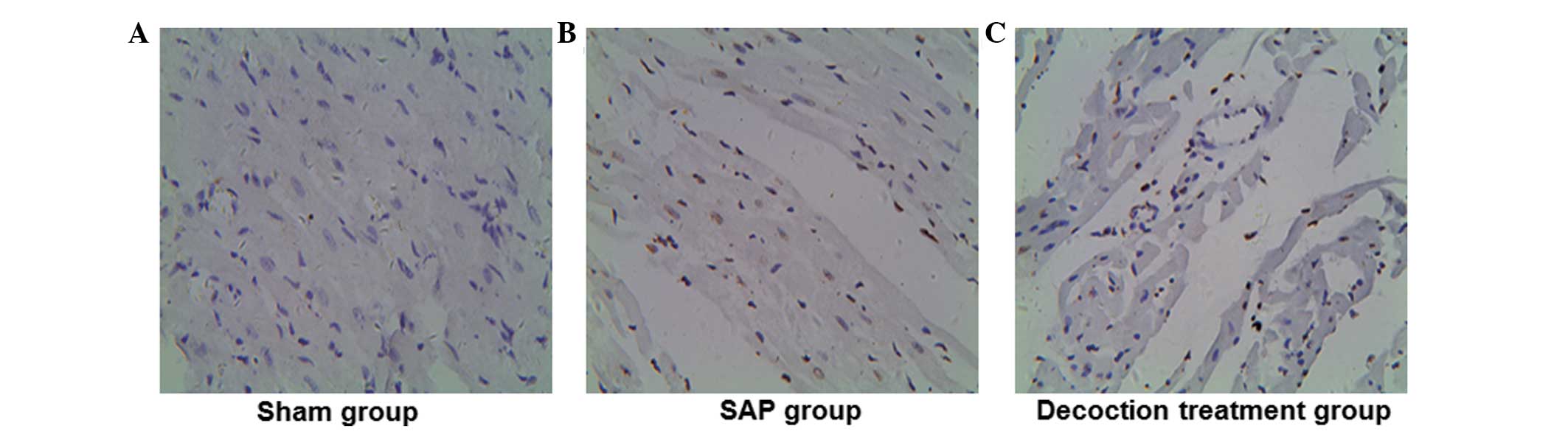
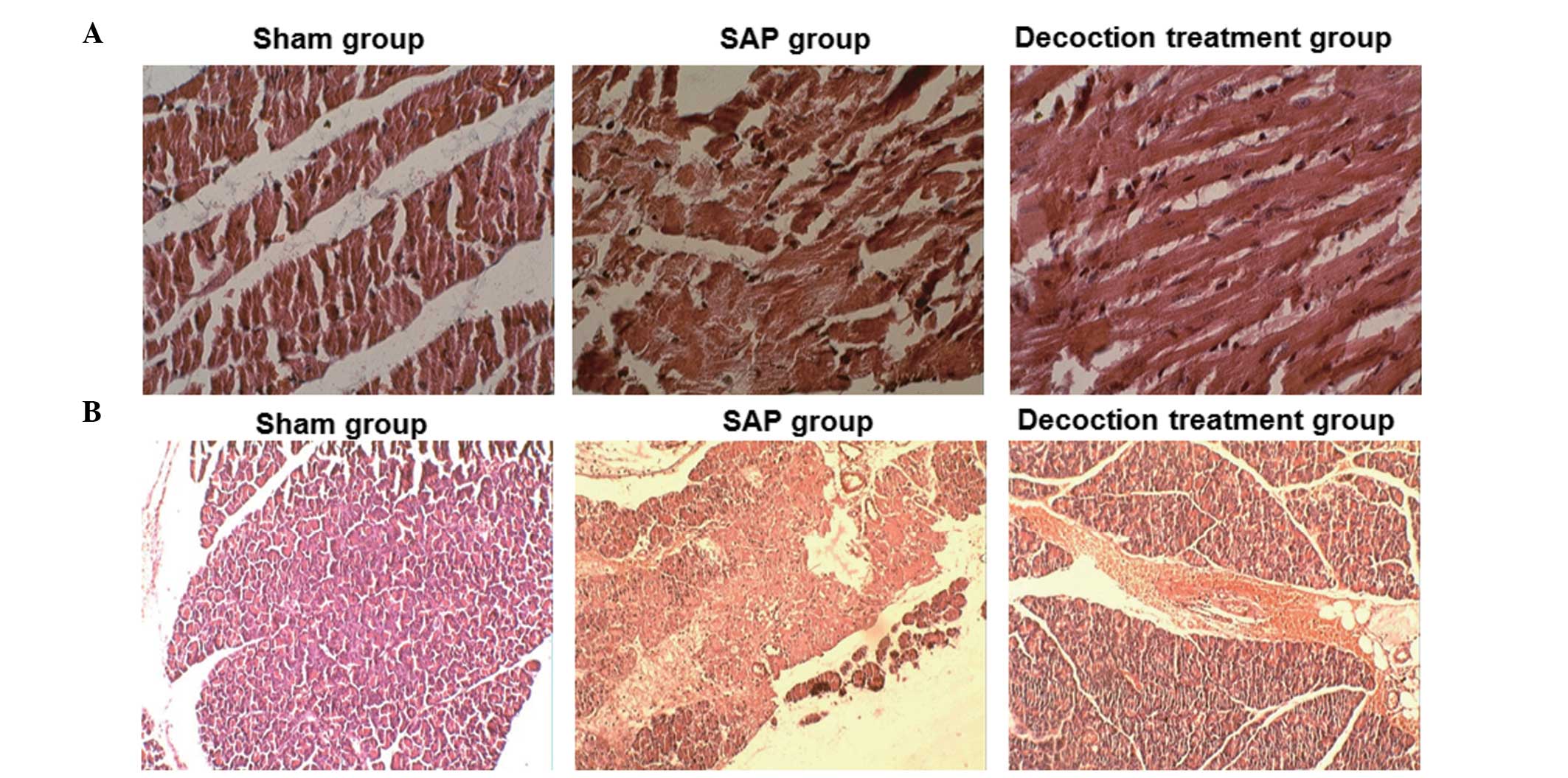
|
1
|
Harper SJ and Cheslyn-Curtis S: Acute
pancreatitis. Ann Clin Biochem. 48:23–37. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chen Y, Zak Y, Hernandez-Boussard T, Park
W and Visser BC: The epidemiology of idiopathic acute pancreatitis,
analysis of the nationwide inpatient sample from 1998 to 2007.
Pancreas. 42:1–5. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Suzuki M, Sai JK and Shimizu T: Acute
pancreatitis in children and adolescents. World J Gastrointest
Pathophysiol. 5:416–426. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zerem E: Treatment of severe acute
pancreatitis and its complications. World J Gastroenterol.
20:13879–13892. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Foitzik T, Eibl G, Hotz HG, Faulhaber J,
Kirchengast M and Buhr HJ: Endothelin receptor blockade in severe
acute pancreatitis leads to systemic enhancement of
microcirculation, stabilization of capillary permeability and
improved survival rates. Surgery. 128:399–407. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Menger MD, Plusczyk T and Vollmar B:
Microcirculatory derangements in acute pancreatitis. J
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 8:187–194. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Klar E, Messmer K, Warshaw AL and Herfarth
C: Pancreatic ischaemia in experimental acute pancreatitis:
mechanism, significance and therapy. Br J Surg. 77:1205–1210. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abreu-Martin MT and Targan SR: Regulation
of immune responses of the intestinal mucosa. Crit Rev Immunol.
16:277–309. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rychter JW, van Minnen LP, Verheem A, et
al: Pretreatment but not treatment with probiotics abolishes mouse
intestinal barrier dysfunction in acute pancreatitis. Surgery.
145:157–167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi C, Zhao X, Lagergren A, Sigvardsson M,
et al: Immune status and inflammatory response differ locally and
systemically in severe acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol.
41:472–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cuthbertson CM and Christophi C:
Disturbances of the microcirculation in acute pancreatitis. Br J
Surg. 93:518–530. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lehocky P and Sarr MG: Early enteral
feeding in severe acute pancreatitis: can it prevent secondary
pancreatic (super) infection? Dig Surg. 17:571–577. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen H, Li F, Jia JG, Diao YP, Li ZX and
Sun JB: Effects of traditional Chinese medicine on intestinal
mucosal permeability in early phase of severe acute pancreatitis.
Chin Med J (Engl). 123:1537–1542. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Yu JN, Kou L and Wang J: Therapeutic
effect of Lai Fu Cheng Qi Decoction on severe acute pancreatitis
associated lung injury patients. Guo Ji Hu Xi Za Zhi. 11:859–862.
2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Sarkar PK: A quick assay for
Na+-K+-ATPase specific activity. Z
Naturforsch C. 57:562–564. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vague P, Dufayet D, Coste T, Moriscot C,
Jannot MF and Raccah D: Association of diabetic neuropathy with
Na/K ATPase gene polymorphism. Diabetologia. 40:506–511. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu YC, Li ZS, Tu ZX, Shi XG, Wang LZ, Gong
YF, Man XH and Jin J: Role of MCP-1/JE in pathogenesis of severe
acute pancreatitis. Yi Xian Bing Xue. 4:94–97. 2004.(In
Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Yu M, Yang YZ, Shen XD, Shu XH and Pan WM:
Evaluation of the cardiac function by high frequency
echocardiography in viral myocarditis mice. Zhonghua Chao Sheng
Ying Xiang Xue Za Zhi. 10:54–56. 2001.(In Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Lv B: Application of Chinese medicine in
the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Zhonghua Xiao Hua Za
Zhi. 33:743–745. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Xia Q, Jiang JM, Gong X, Chen GY, Li L and
Huang ZW: Experimental study of Tong Xia purgative method in
ameliorating lung injury in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. World J
Gastroenterol. 6:115–118. 2000.
|
|
21
|
Jia P, Zhang Z, Zhou Z and Jiang J: Impact
of WPY on pancreatic microcirculation of acute pancreatitis in
mice. Hua Xi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 32:92–95. 2001.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Di H and You SY: Effect of Lai-Fu-Qi-Cheng
treatment on acute pancreatitis associated with intestinal
paralysis in 30 cases. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Wai Ke Za Zhi.
15:128–129. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Di H and You SY: Effect of Lai-Fu-Qi-Cheng
treatment on acute pancreatitis associated with intestinal
paralysis in 30 cases. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Wai Ke Za Zhi.
15:128–129. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Dahlin LG, Kågedal B, Nylander E, et al:
Early identification of permanent myocardial damage after coronary
surgery is aided by repeated measurements of CK-MB. Scand
Cardiovasc J. 36:35–40. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dai JZ and Fan H: Protective effects of
Danhong injection against heart injury in rats with severe acute
pancreatitis. Shi Jie Hua Ren Xiao Hua Za Zhi. 10:969–975. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Fraser JA and Huang CL: A quantitative
analysis of cell volume and resting potential determination and
regulation in excitable cells. J Physiol. 559:459–478. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huigsloot M, Tijdens IB, Mulder GJ and van
de Water B: Differential regulation of doxorubicin-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis by Bcl-2 in mammary
adenocarcinoma (MTLn3) cells. J Biol Chem. 277:35869–35879. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|