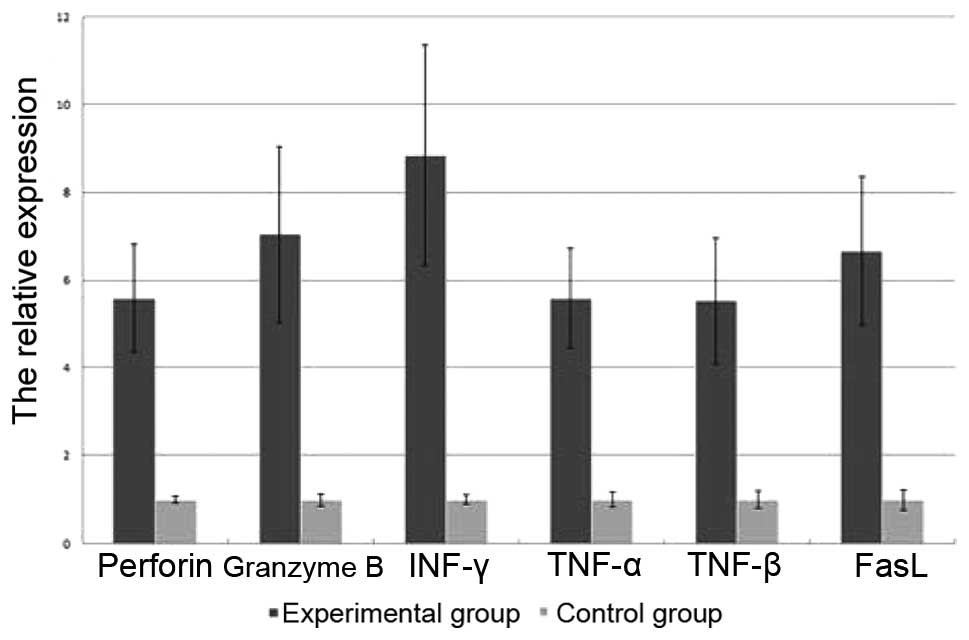
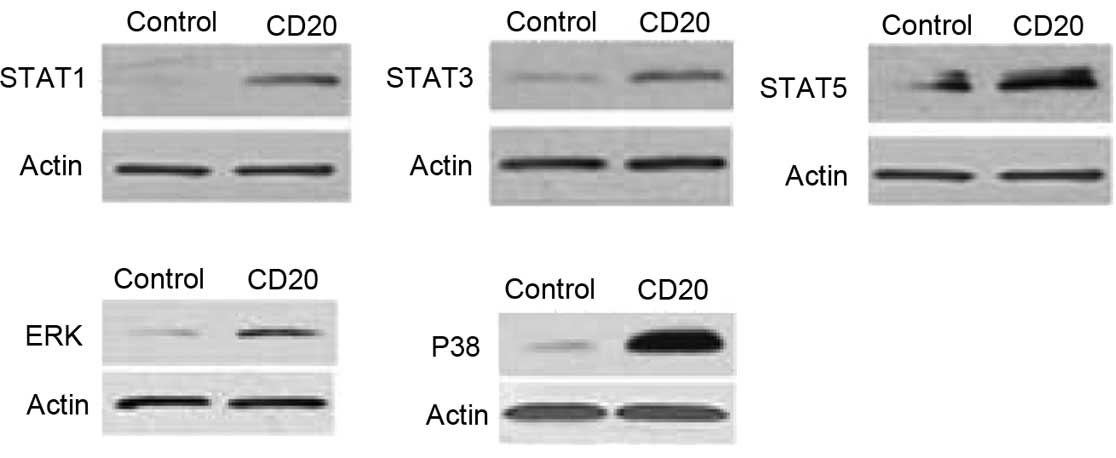
|
1
|
Dölken G: Detection of minimal residual
disease. Adv Cancer Res. 82:133–185. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Scheffold C, Brandt K, Johnston V, et al:
Potential of autologous immunologic effector cells for bone marrow
purging in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow
Transplant. 15:33–39. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nagaraj S, Ziske C and Schmidt-Wolf IG:
Human cytokine-induced killer cells have enhanced in vitro
cytolytic activity via non-viral interleukin-2 gene transfer. Genet
Vaccines Ther. 2:122004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Edinger M, Cao YA, Verneris MR, et al:
Revealing lymphoma growth and the efficacy of immune cell therapies
using in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Blood. 101:640–648. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Marin V, Dander E, Biagi E, et al:
Characterization of in vitro migratory properties of anti-CD19
chimeric receptor-redirected CIK cells for their potential use in
B-ALL immunotherapy. Exp Hematol. 34:1219–1229. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi M, Zhang B, Tang ZR, et al: Autologous
cytokine-induced killer cell therapy in clinical trial phase I is
safe in patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:1146–1151. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Introna M, Borleri G, Conti E, et al:
Repeated infusions of donor-derived cytokine-induced killer cells
in patients relapsing after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a
phase I study. Haematologica. 92:952–959. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feugier P, Van Hoof A, Sebban C, et al:
Long-term results of the R-CHOP study in the treatment of elderly
patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a study by the Groupe
d’Etude des Lymphomes de I’Adulte. J Clin Oncol. 23:4117–4126.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Habermann TM, Weller EA, Morrison VA, et
al: Rituximab-CHOP versus CHOP alone or with maintenance rituximab
in older patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol.
24:3121–3127. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pfreundschuh M, Trümper L, Osterborg A, et
al; MabThera International Trial Group. CHOP-like chemotherapy plus
rituximab versus CHOP-like chemotherapy alone in young patients
with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: a randomised
controlled trial by the MabThera International Trial (MInT) Group.
Lancet Oncol. 7:379–391. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Leemhuis T, Wells S, Scheffold C, et al: A
phase I trial of autologous cytokine-induced killer cells for the
treatment of relapsed Hodgkin disease and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 11:181–187. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Linn YC and Hui KM: Cytokine-induced
killer cells: NK-like T cells with cytotolytic specificity against
leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 44:1457–1462. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Verneris MR, Ito M, Baker J, et al:
Engineering hematopoietic grafts: purified allogeneic hematopoietic
stem cells plus expanded CD8+ NK-T cells in the treatment of
lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 7:532–542. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Verneris MR, Karami M, Baker J, et al:
Role of NKG2D signaling in the cytotoxicity of activated and
expanded CD8+ T cells. Blood. 103:3065–3072. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Alvarnas JC, Linn YC, Hope EG and Negrin
RS: Expansion of cytotoxic CD3+ CD56+ cells from peripheral blood
progenitor cells of patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic
cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 7:216–222.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pievani A, Belussi C, Klein C, et al:
Enhanced killing of human B-cell lymphoma targets by combined use
of cytokine-induced killer cell (CIK) cultures and anti-CD20
antibodies. Blood. 117:510–518. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
David M: Signal transduction by type I
interferons. Biotechniques Suppl. 58–65. 2002.
|
|
18
|
Moro H, Otero DC, Tanabe Y and David M: T
cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic contributions of the IFNAR/STAT1-axis
to thymocyte survival. PLoS One. 6:e249722011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zeng R, Spolski R, Casas E, et al: The
molecular basis of IL-21-mediated proliferation. Blood.
109:4135–4142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eckelhart E, Warsch W, Zebedin E, et al: A
novel Ncr1-Cre mouse reveals the essential role of STAT5 for
NK-cell survival and development. Blood. 117:1565–1573. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hand TW, Cui W, Jung YW, et al:
Differential effects of STAT5 and PI3K/AKT signaling on effector
and memory CD8 T-cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:16601–16606. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Santen RJ, Song RX, McPherson R, et al:
The role of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in breast
cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 80:239–256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Frigo DE, Tang Y, Beckman BS, et al:
Mechanism of AP-1-mediated gene expression by select
organochlorines through the p38 MAPK pathway. Carcinogenesis.
25:249–261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Antoon JW, Nitzchke AM, Martin EC, et al:
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase alters microRNA
expression and reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Int J
Oncol. 42:1139–1150. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|