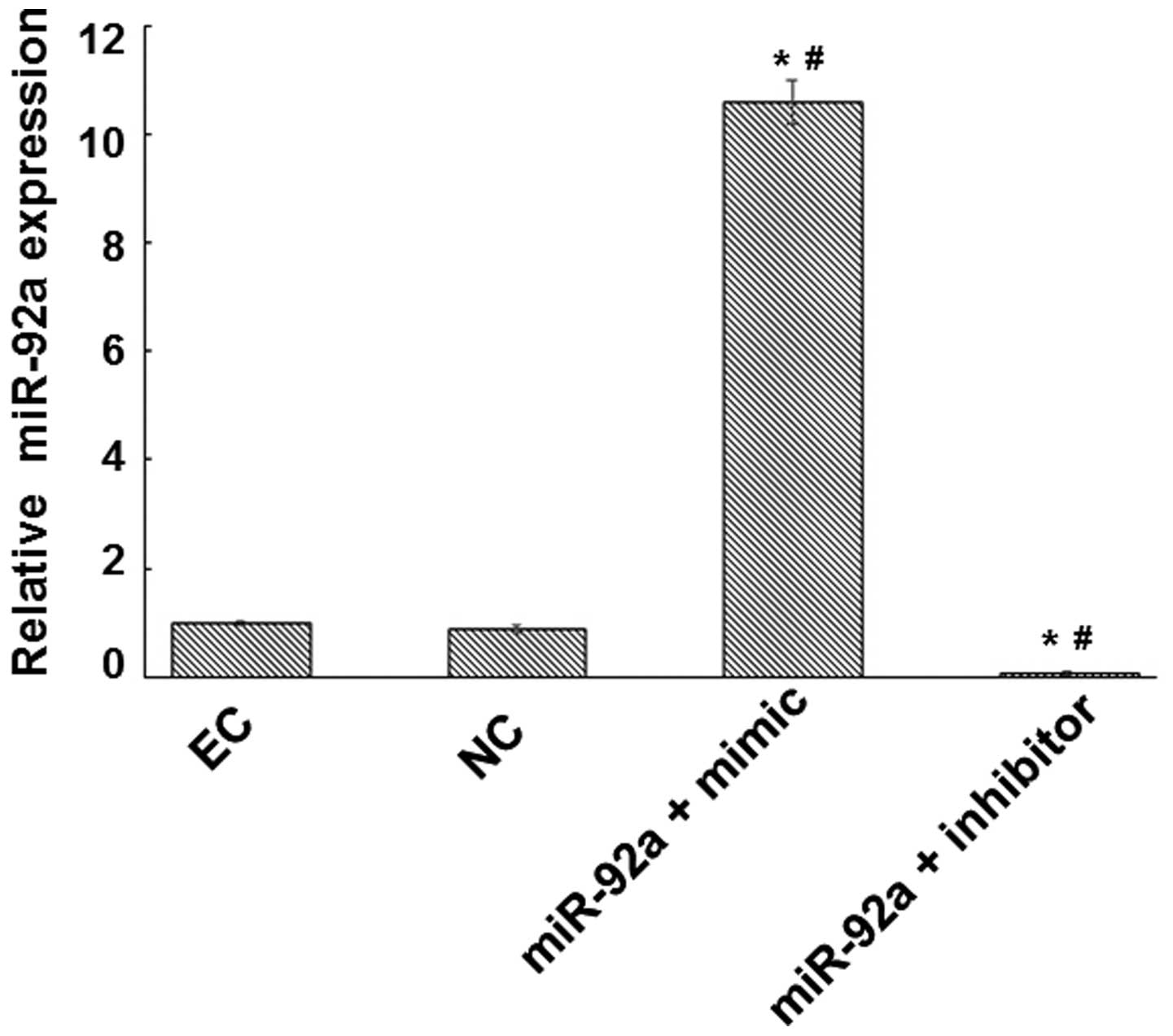
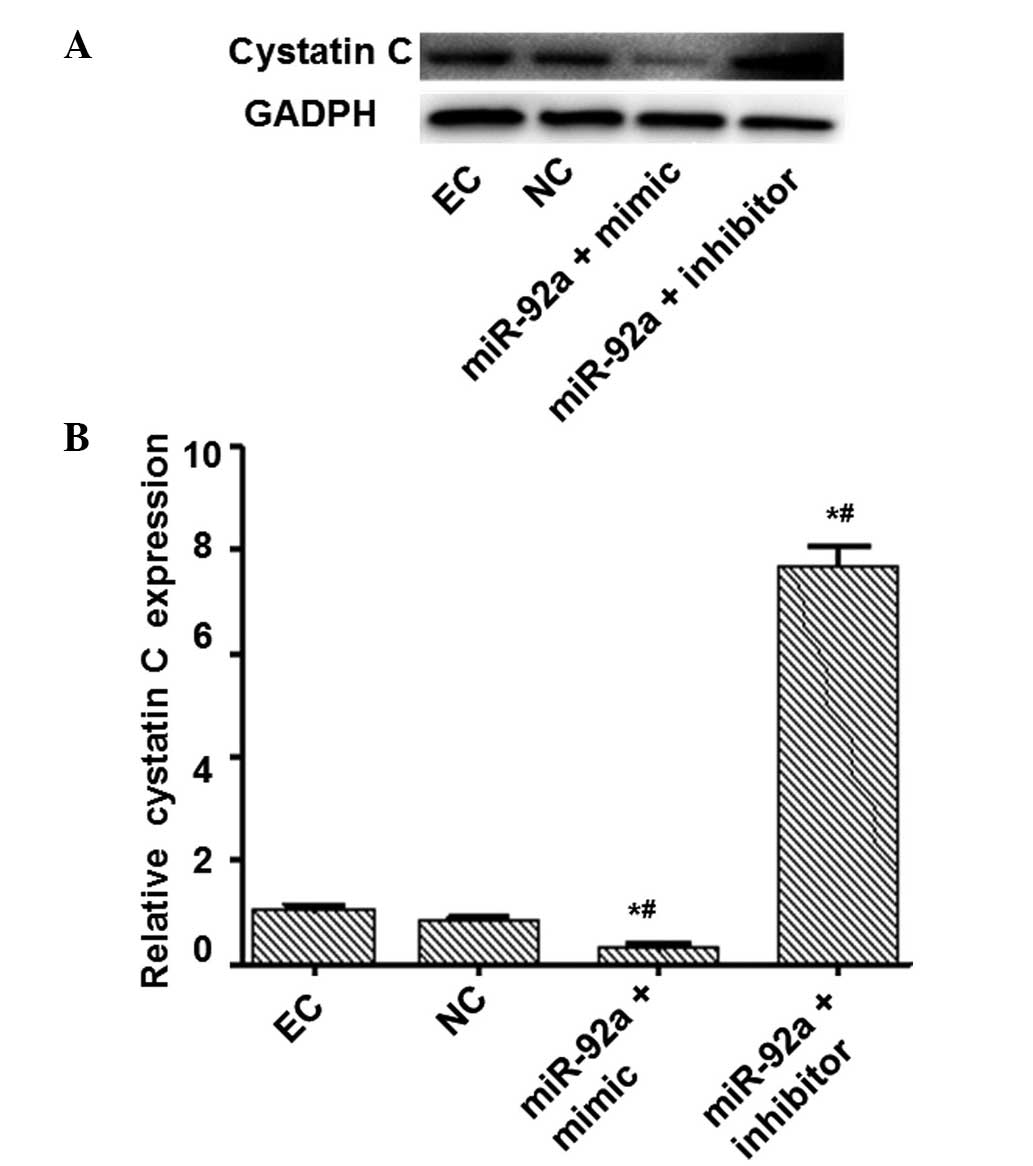
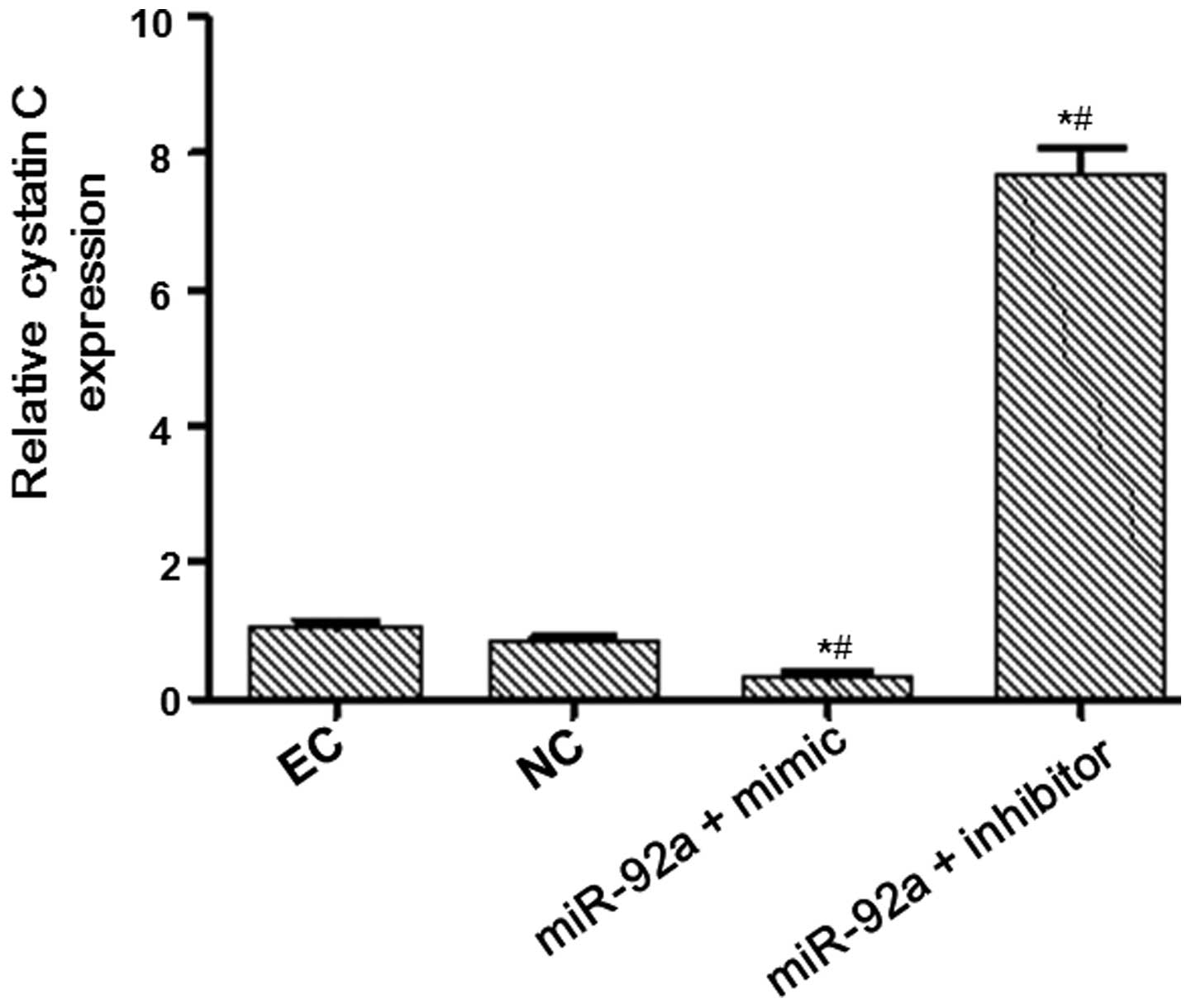
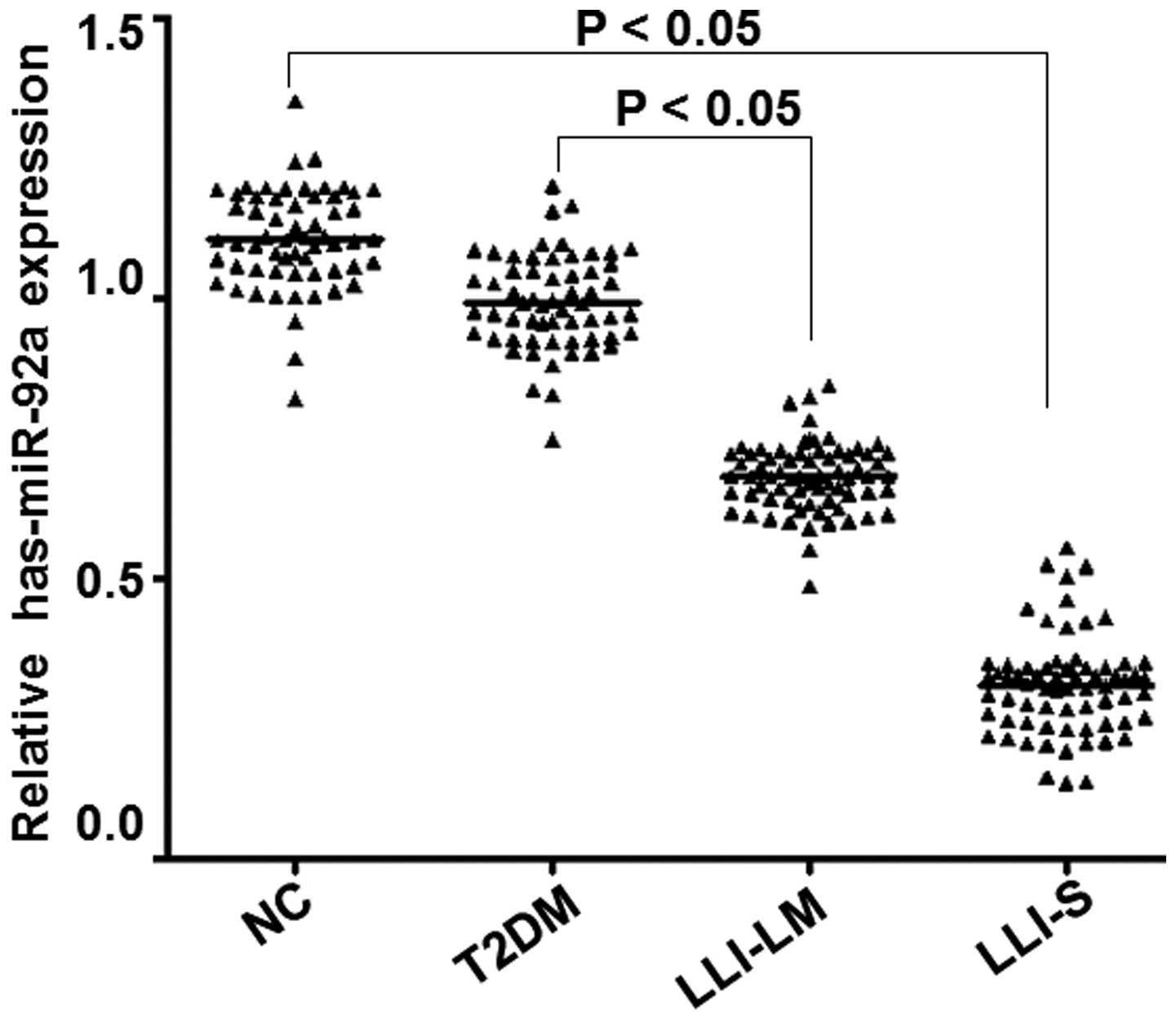
|
1
|
Ouriel K: Peripheral arterial disease.
Lancet. 358:1257–1264. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beckman JA, Creager MA and Libby P:
Diabetes and atherosclerosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology and
management. JAMA. 287:2570–2581. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy
RP and Hennekens CH: Plasma concentration of C-reactive protein and
risk of developing peripheral vascular disease. Circulation.
97:425–428. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arain FA and Cooper Jr LT: Peripheral
arterial disease: Diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc.
83:944–949. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abrahamson M, Olafsson I, Palsdottir A,
Ulvsbäck M, Lundwall A, Jensson O and Grubb A: Structure and
expression of the human cystatin C gene. Biochem J. 268:287–294.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koenig W, Twardella D, Brenner H and
Rothenbacher D: Plasma concentrations of cystatin C in patients
with coronary heart disease and risk for secondary cardiovascular
events: More than simply a marker of glomerular filtration rate.
Clin Chem. 5l:321–327. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Watanabe S, Okura T, Liu J, Miyoshi K, et
al: Serum cystatin C level is a marker of end-organ damage in
patients with essential hypertension. Hypertens Res. 26:895–899.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arpegård J, Ostergren J, de Faire U,
Hansson LO and Svensson P: Cystatin C - A marker of peripheral
atherosclerotic disease? Atherosclerosis. 199:397–401. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Groot M, Anderson R, Freedland KE,
Clouse RE and Lustman PJ: Association of depression and diabetes
complications: A meta-analysis. Psychosom Med. 63:619–630. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu F, Shen J, Zhao J, et al: Cystatin C:
A strong marker for lower limb ischemia in Chinese type 2 diabetic
patients? PloS One. 8:e669072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Berezikov E, Cuppen E and Plasterk RH:
Approaches to microRNA discovery. Nat Genet. 38:(Suppl). S2–S7.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stuwe E, Tóth KF and Aravin AA: Small but
sturdy: Small RNAs in cellular memory and epigenetics. Genes Dev.
28:423–431. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu D, Tao T, Xu B, et al: MiR-361-5p acts
as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer by targeting signal
transducer and activator of transcription-6 (STAT6). Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 445:151–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Loyer X, Potteaux S, Vion AC, et al:
Inhibition of microRNA-92a prevents endothelial dysfunction and
atherosclerosis in mice. Circ Res. 114:434–443. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun X, Belkin N and Feinberg MW:
Endothelial microRNAs and atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep.
15:3722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vickers KC, Rye KA and Tabet F: MicroRNAs
in the onset and development of cardiovascular disease. Clin Sci
(Lond). 126:183–194. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Creemers EE, Tijsen AJ and Pinto YM:
Circulating microRNAs: Novel biomarkers and extracellular
communicators in cardiovascular disease? Circ Res. 110:483–495.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huo Y, Schober A, Forlow SB, et al:
Circulating activated platelets exacerbate atherosclerosis in mice
deficient in apolipoprotein E. Nat Med. 9:61–67. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wilcox JN, Smith KM, Williams LT, Schwartz
SM and Gordon D: Platelet-derived growth factor mRNA detection in
human atherosclerotic plaques by in situ hybridization. J Clin
Invest. 82:1134–1143. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huo Y and Ley KF: Role of platelets in the
development of atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 14:18–22.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nomura S, Suzuki M, Katsura K, et al:
Platelet-derived microparticles may influence the development of
atherosclerosis in diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis. 116:235–240.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi GP, Sukhova GK, Grubb A, et al:
Cystatin C deficiency in human atherosclerosis and aortic
aneurysms. J Clin Invest. 104:1191–1197. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taglieri N, Koenig W and Kaski JC:
Cystatin C and cardiovascular risk. Clin Chem. 55:1932–1943. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Watanabe S, Okura T, Liu J, Miyoshi K,
Fukuoka T, Hiwada K and Higaki J: Serum cystatin C level is a
marker of end-organ damage in patients with essential hypertension.
Hypertens Res. 26:895–899. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|