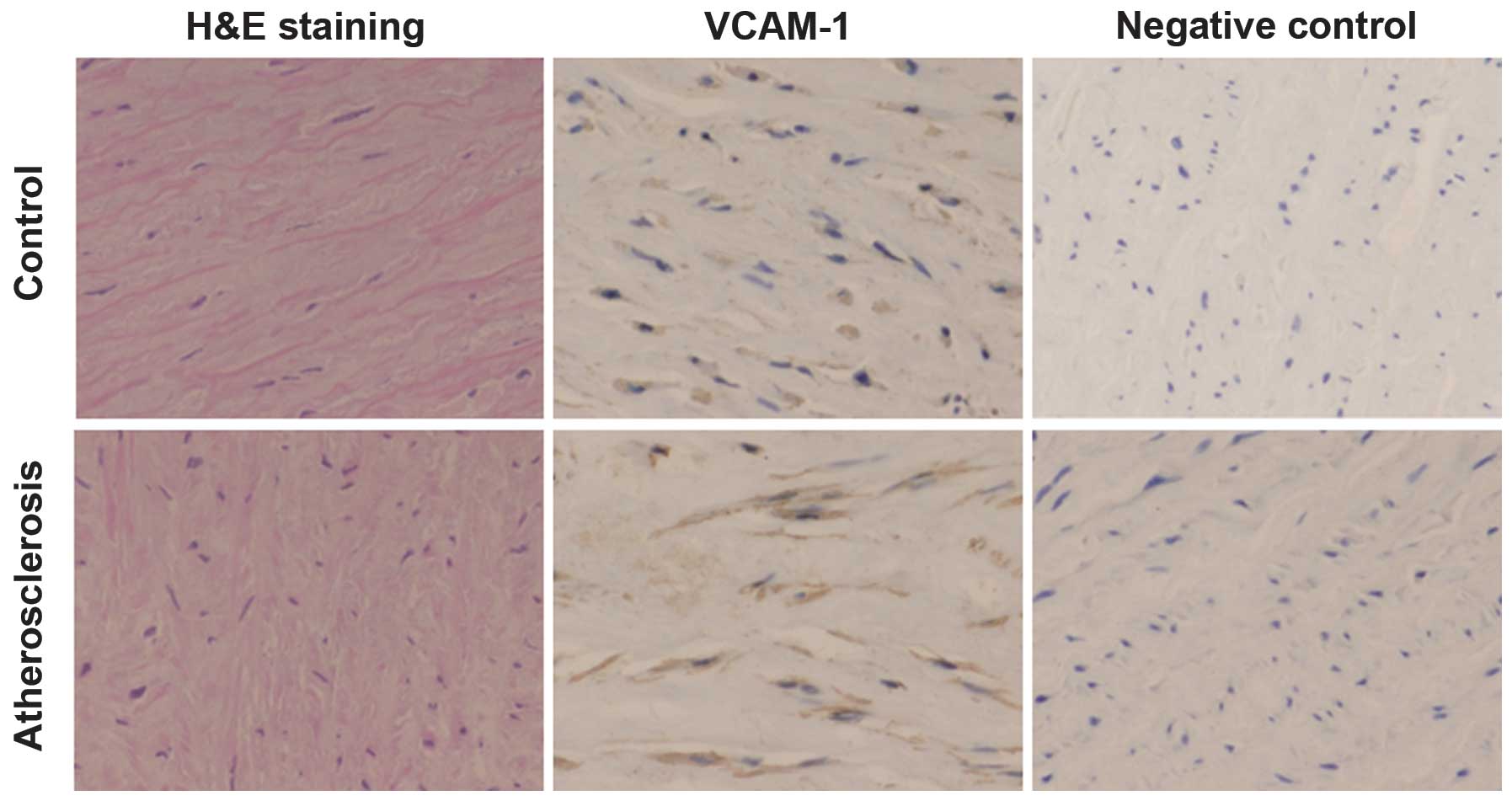
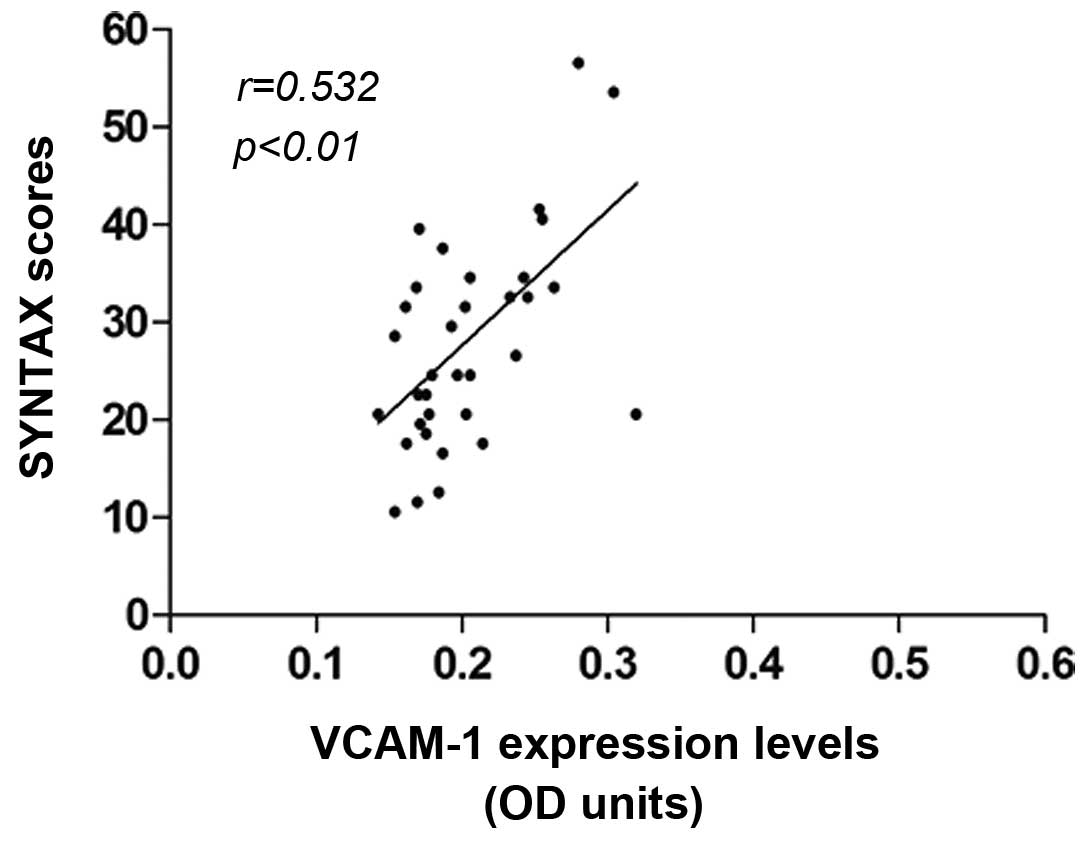
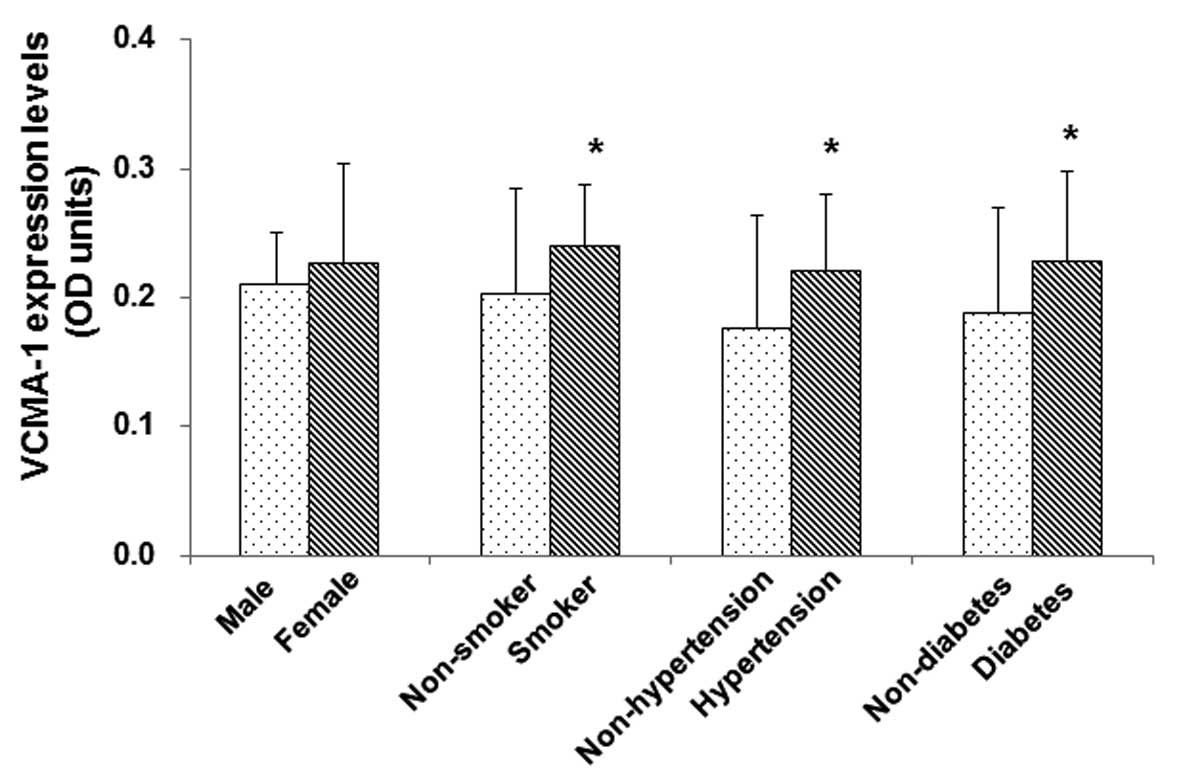
|
1
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis - an inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wolf D, Stachon P, Bode C and Zirlik A:
Inflammatory mechanisms in atherosclerosis. Hamostaseologie.
34:63–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nakashima Y, Raines EW, Plump AS, Breslow
JL and Ross R: Upregulation of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 at
atherosclerosis-prone sites on the endothelium in the
ApoE-deficient mouse. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 18:842–851.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sitia S, Tomasoni L, Atzeni F, et al: From
endothelial dysfunction to atherosclerosis. Autoimmun Rev.
9:830–834. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu B, Wang J, Cheng L and Liang J: Role
of JNK and NF-κB pathways in Porphyromonas gingivalis
LPS-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human
aortic endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 8:1594–1600. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
De Caterina R, Basta G, Lazzerini G, et
al: Soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 as a biohumoral
correlate of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
17:2646–2654. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeitler H, Ko Y, Zimmermann C, et al:
Elevated serum concentrations of soluble adhesion molecules in
coronary artery disease and acute myocardial infarction. Eur J Med
Res. 2:389–394. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee MS, Applegate B, Rao SV, Kirtane AJ,
Seto A and Stone GW: Minimizing femoral artery access complications
during percutaneous coronary intervention: A comprehensive review.
Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 84:62–69. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sianos G, Morel MA, Kappetein AP, et al:
The SYNTAX Score: An angiographic tool grading the complexity of
coronary artery disease. EuroIntervention. 1:219–227.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tan HW, Xing SS, Bi XP, et al: Felodipine
attenuates vascular inflammation in a fructose-induced rat model of
metabolic syndrome via the inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 29:1051–1059. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
DeVerse JS, Sandhu AS, Mendoza N, Edwards
CM, Sun C, Simon SI and Passerini AG: Shear stress modulates VCAM-1
expression in response to TNF-α and dietary lipids via interferon
regulatory factor-1 in cultured endothelium. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 305:H1149–H1157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fotis L, Agrogiannis G, Vlachos IS, et al:
Intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and vascular cell adhesion
molecule (VCAM)-1 at the early stages of atherosclerosis in a rat
model. In Vivo. 26:243–250. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cook-Mills JM: VCAM-1 signals during
lymphocyte migration: Role of reactive oxygen species. Mol Immunol.
39:499–508. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Petersen EJ, Miyoshi T, Yuan Z, Hirohata
S, Li JZ, Shi W and Angle JF: siRNA silencing reveals role of
vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in vascular smooth muscle cell
migration. Atherosclerosis. 198:301–306. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cybulsky MI and Gimbrone MA Jr:
Endothelial expression of a mononuclear leukocyte adhesion molecule
during atherogenesis. Science. 251:788–791. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu HH, Sheng ZQ, Wang Y and Zhang L:
Levels of soluble adhesion molecules in patients with various
clinical presentations of coronary atherosclerosis. Chin Med J
(Engl). 123:3123–3126. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Karasek D, Vaverkova H, Frysak Z, Halenka
M, Jackuliakova D, Novotny D and Lukes J: Soluble intercellular
cell adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in
asymptomatic dyslipidemic subjects. Int Angiol. 30:441–450.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakai K, Itoh C, Kawazoe K, et al:
Concentration of soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1)
correlated with expression of VCAM-1 mRNA in the human
atherosclerotic aorta. Coron Artery Dis. 6:497–502. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leca G, Mansur SE and Bensussan A:
Expression of VCAM-1 (CD106) by a subset of TCR gamma delta-bearing
lymphocyte clones. Involvement of a metalloprotease in the specific
hydrolytic release of the soluble isoform. J Immunol.
154:1069–1077. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hackman A, Abe Y, Insull W Jr, et al:
Levels of soluble cell adhesion molecules in patients with
dyslipidemia. Circulation. 93:1334–1338. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saidi H, Vakilian M, Noori GH, Ghafouri HB
and Abazarian N: Alterations in circulating adhesion molecules in
acute myocardial infarction before and after thrombolysis with
streptokinase. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 5:139–141. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Steinberg D and Witztum JL: Oxidized
low-density lipoprotein and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 30:2311–2316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ross R and Harker L: Hyperlipidemia and
atherosclerosis. Science. 193:1094–1100. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feig JE, Rong JX, Shamir R, et al: HDL
promotes rapid atherosclerosis regression in mice and alters
inflammatory properties of plaque monocyte-derived cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:7166–7171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ashfaq F, Goel PK, Moorthy N, Sethi R,
Khan MI and Idris MZ: Lipoprotein(a) and SYNTAX score association
with severity of coronary artery atherosclerosis in North India.
Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 12:465–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Serruys PW, Morice MC, Kappetein AP, et
al: SYNTAX Investigators: Percutaneous coronary intervention versus
coronary-artery bypass grafting for severe coronary artery disease.
N Engl J Med. 360:961–972. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wykrzykowska JJ, Garg S, Girasis C, et al:
Value of the SYNTAX score for risk assessment in the all-comers
population of the randomized multicenter LEADERS (Limus Eluted from
A Durable versus ERodable Stent coating) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol.
56:272–277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chakravarty T, Buch MH, Naik H, et al:
Predictive accuracy of SYNTAX score for predicting long-term
outcomes of unprotected left main coronary artery
revascularization. Am J Cardiol. 107:360–366. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Edirisinghe I and Rahman I: Cigarette
smoke-mediated oxidative stress, shear stress, and endothelial
dysfunction: Role of VEGFR2. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1203:66–72. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Turnbull F, Kengne AP and MacMahon S:
Blood pressure and cardiovascular disease: Tracing the steps from
Framingham. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 53:39–44. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Opie LH: Acute myocardial infarction and
diabetes. Lancet. 370:634–635. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park JG, Ryu SY, Jung IH, et al:
Evaluation of VCAM-1 antibodies as therapeutic agent for
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.
Atherosclerosis. 226:356–63. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang W, Xing SS, Sun XL and Xing QC:
Overexpression of activated nuclear factor-kappa B in aorta of
patients with coronary atherosclerosis. Clin Cardiol. 32:E42–E47.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gong YL, Xing SS, Zhang W and Xing QC:
Relationship between Toll-like receptor 4 protein and
atherosclerosis. Shan Dong Da Xue Xue (Yi Xue Ban). 48:127–130.
2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Xing SS, Gong ZS, Mu W, Wang D, Gong YL
and Xing QC: Expression of human living aortic high mobility group
protein box1 and its relationship with the pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis. Shan Dong Da Xue Xue (Yi Xue Ban). 51:62–65.
2013.(In Chinese).
|