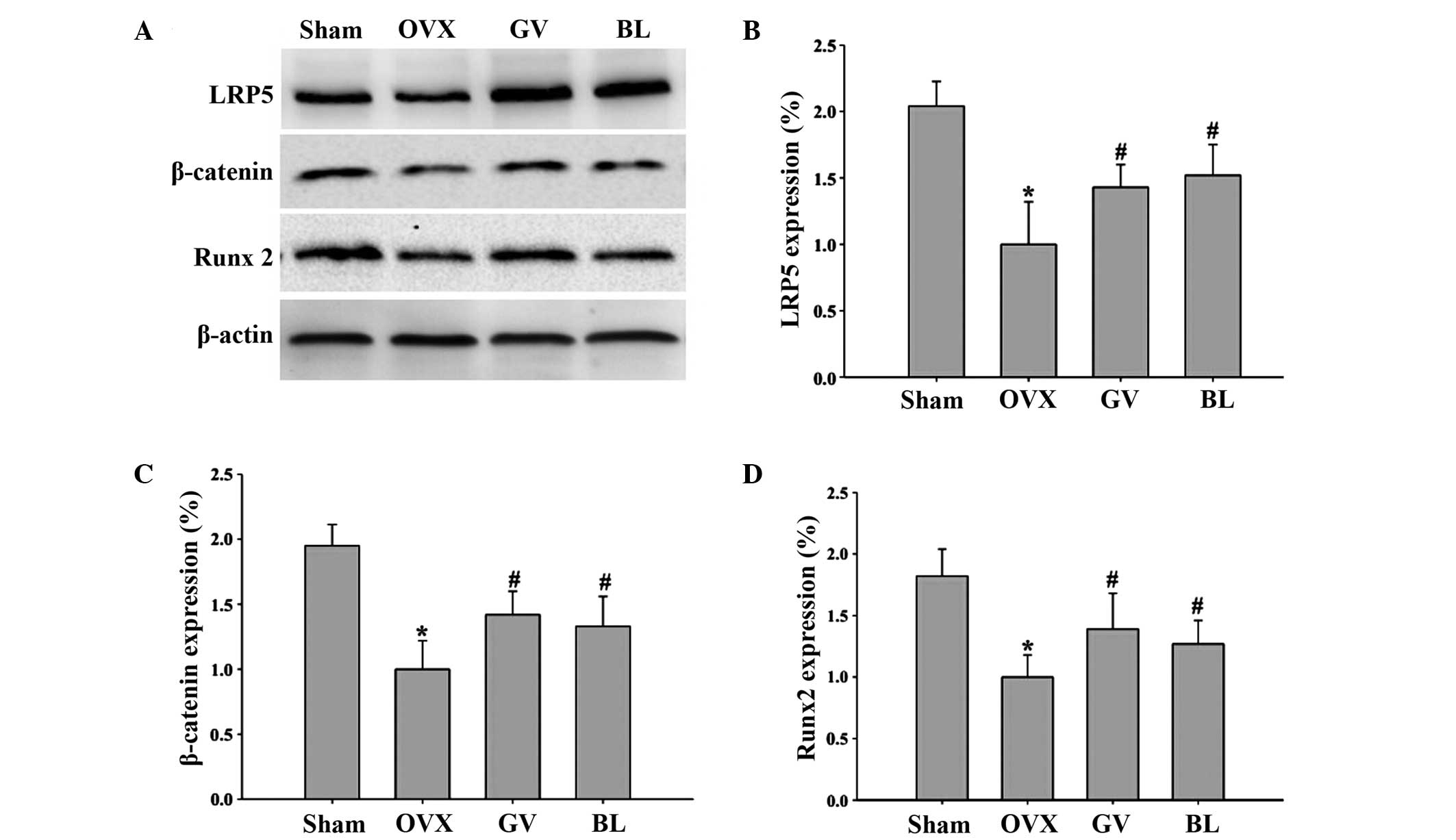
|
1
|
NIH Consensus Development Panel on
Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy, . Osteoporosis
prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. JAMA. 285:785–795. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kanis JA: Diagnosis of osteoporosis and
assessment of fracture risk. Lancet. 359:1929–1936. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meczekalski B and Czyzyk A: Selective
estrogen receptor modulators in treatment of postmenopausal
osteoporosis. Ginekol Pol. 80:213–217. 2009.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cole Z, Dennison E and Cooper C: Update on
the treatment of post-menopausal osteoporosis. Br Med Bull.
86:129–143. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McNamara LM: Perspective on
post-menopausal osteoporosis: Establishing an interdisciplinary
understanding of the sequence of events from the molecular level to
whole bone fractures. J R Soc Interface. 7:353–372. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nelson HD: Menopause. Lancet. 371:760–770.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rossouw JE, Anderson GL, Prentice RL, et
al Writing Group for the Women's Health Initiative Investigators:
Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy
postmenopausal women: Principal results from The Women's Health
Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 288:321–333. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han JS: Acupuncture: Neuropeptide release
produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends
Neurosci. 26:17–22. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mason S, Tovey P and Long AF: Evaluating
complementary medicine: Methodological challenges of randomised
controlled trials. BMJ. 325:832–834. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sunay D, Ozdiken M, Arslan H, Seven A and
Aral Y: The effect of acupuncture on postmenopausal symptoms and
reproductive hormones: A sham controlled clinical trial. Acupunct
Med. 29:27–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou ZH, Wang NQ, Pan FF, Wu ZH and Dai
XY: Clinical observation on combined acupuncture and medication for
osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. J Acupunct Tuina Sci.
9:370–375. 2011.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
He J, Yang L, Qing Y and He C: Effects of
electroacupuncture on bone mineral density, oestradiol level and
osteoprotegerin ligand expression in ovariectomised rabbits.
Acupunct Med. 32:37–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Feng Y, Lin H, Zhang Y, Li L, Wu X, Wang
T, Liu Y and Tan Y: Electroacupuncture promotes insulin-like growth
factors system in ovariectomized osteoporosis rats. Am J Chin Med.
36:889–897. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei YF, Liu YL, Zhang SH, Wang ZO, et al:
Effect of electroacupuncture on plasma estrin and bone mineral
density in ovariectomized rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 32:38–41. 2007.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, et al: OPGL
is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development
and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 397:315–323. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hofbauer LC and Schoppet M: Clinical
implications of the osteoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK system for bone and
vascular diseases. JAMA. 292:490–495. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hartmann C: A Wnt canon orchestrating
osteoblastogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 16:151–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim W, Kim M and Jho EH: Wnt/β-catenin
signalling: From plasma membrane to nucleus. Biochem J. 450:9–21.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bodine PV and Komm BS: Wnt signaling and
osteoblastogenesis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 7:33–39. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
The Ministry of Science and Technology of
the People's Republic of China, . Guidance Suggestions for the Care
and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006
|
|
21
|
Vincent CA and Richardson PH: The
evaluation of therapeutic acupuncture: Concepts and methods. Pain.
24:1–13. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin JG and Chen WL: Acupuncture analgesia:
A review of its mechanisms of actions. Am J Chin Med. 36:635–645.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao Y, Liu KJ, Li JH, Cai XJ and Yang JH:
Bone mineral content and kidney asthenia. Chinese J Osteoporosis.
2:19–21. 1996.(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Xie L, Yao GH and Guo ZQ: Preliminary
study on treatment of osteoporosis with spleen-strengthening and
stomach-nourishing method. Hunan Zhongyiyao Xueyuan Xuebao. 41:7–9.
1996.
|
|
25
|
Xu M, Liu BX and Huang CG: The progress of
acupuncture treatment on postmenopausal osteoporosis. Zhejiang
Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao. 2:301–302. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Frolik CA, Bryant HU, Black EC, Magee DE
and Chandrasekhar S: Time-dependent changes in biochemical bone
markers and serum cholesterol in ovariectomized rats: Effects of
raloxifene HCl, tamoxifen, estrogen, and alendronate. Bone.
18:621–627. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sato M, Bryant HU, Iversen P, et al:
Advantages of raloxifene over alendronate or estrogen on
nonreproductive and reproductive tissues in the long-term dosing of
ovariectomized rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 279:298–305.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, et al:
Identity of osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (OCIF) and
osteoprotegerin (OPG): A mechanism by which OPG/OCIF inhibits
osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Endocrinology. 139:1329–1337.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bord S, Ireland DC, Beavan SR and Compston
JE: The effects of estrogen on osteoprotegerin, RANKL, and estrogen
receptor expression in human osteoblasts. Bone. 32:136–141. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, et al:
Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast
differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou J, He H, Yang L, Chen S, Guo H, Xia
L, Liu H, Qin Y, Liu C, Wei X, Zhou Y and He C: Effects of pulsed
electromagnetic fields on bone mass and Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in ovariectomized rats. Arch Med Res. 43:274–282. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|