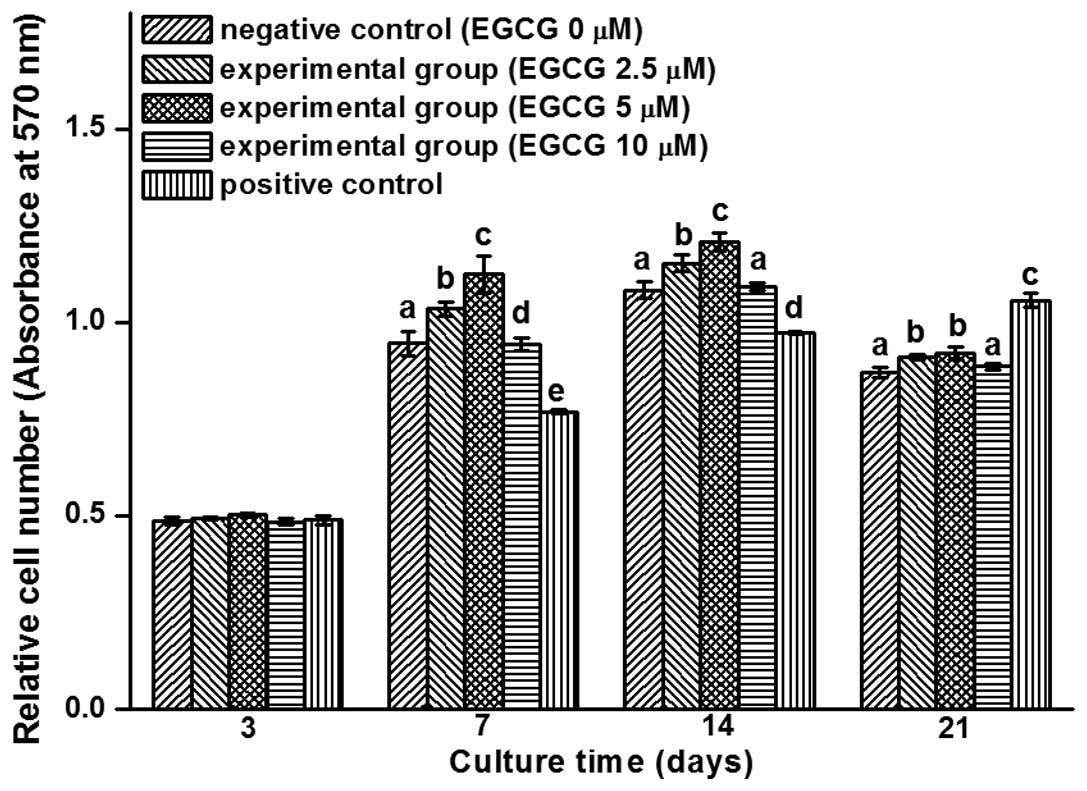
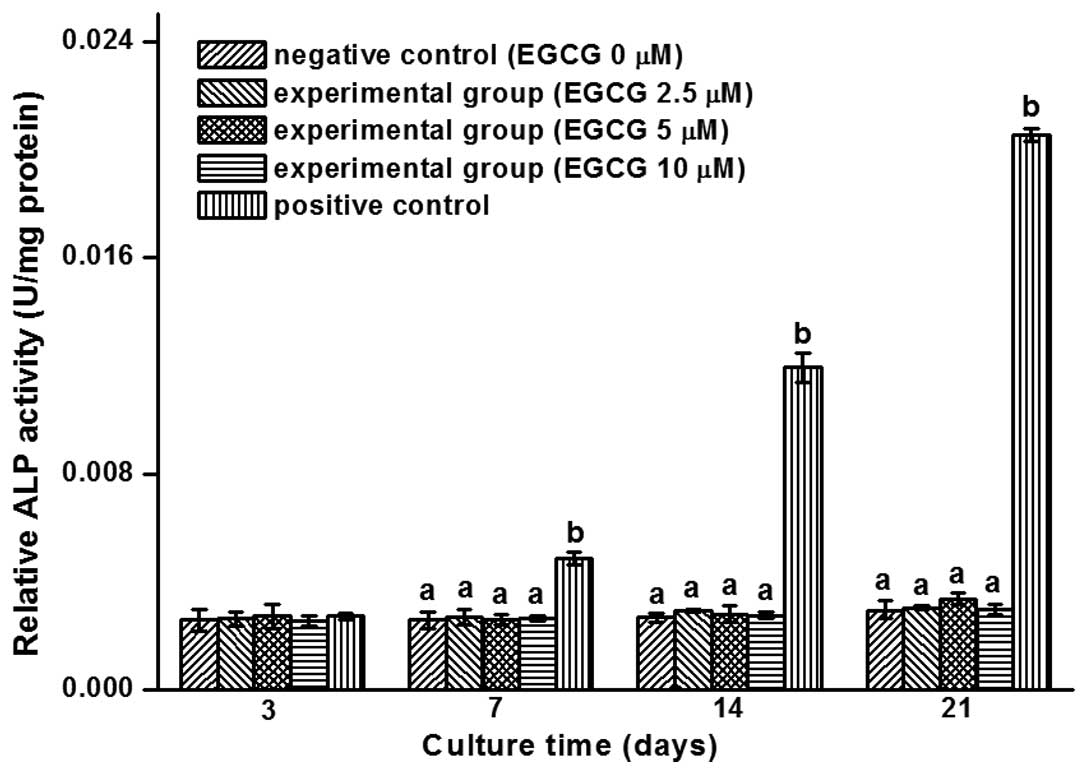
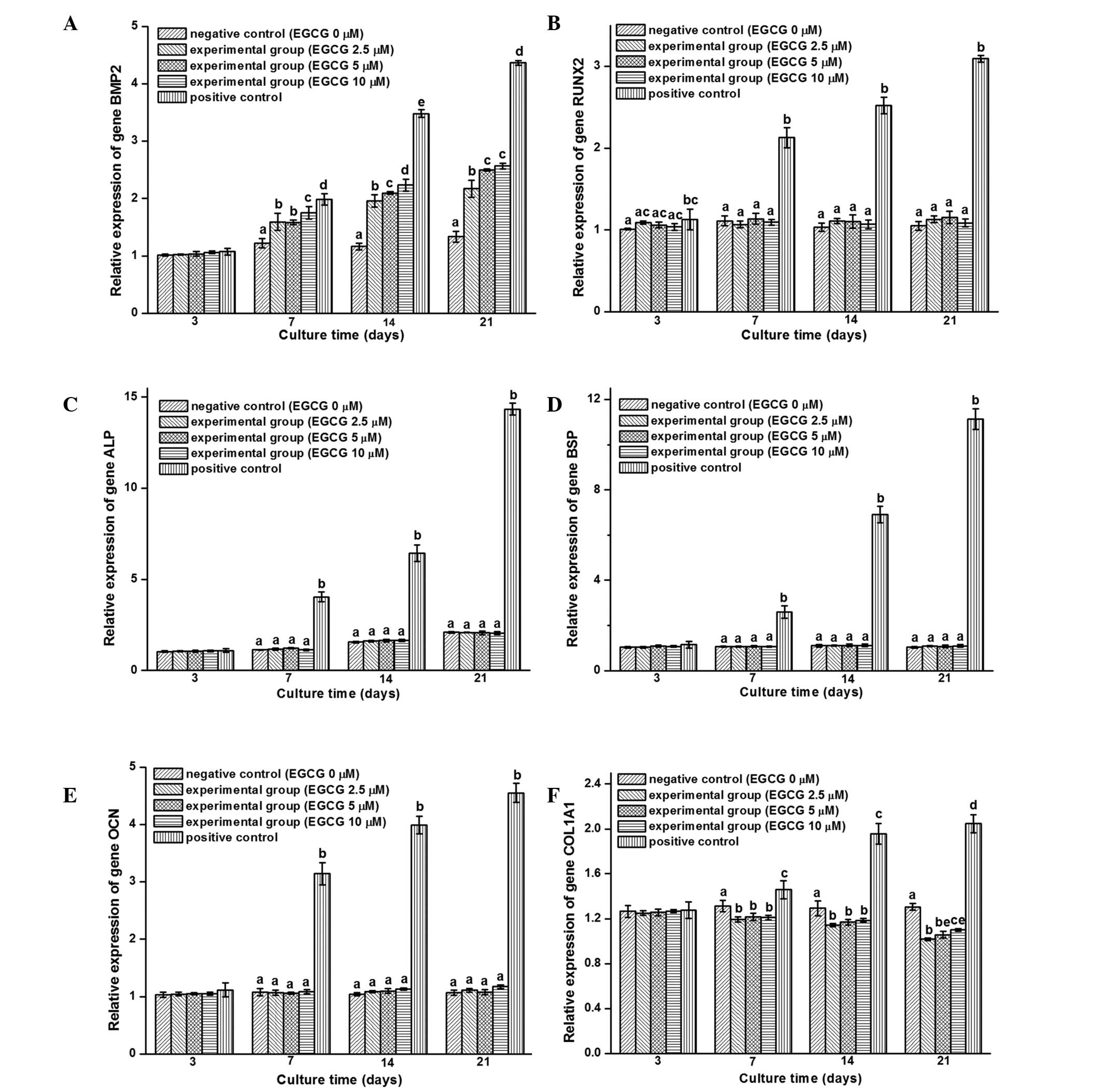
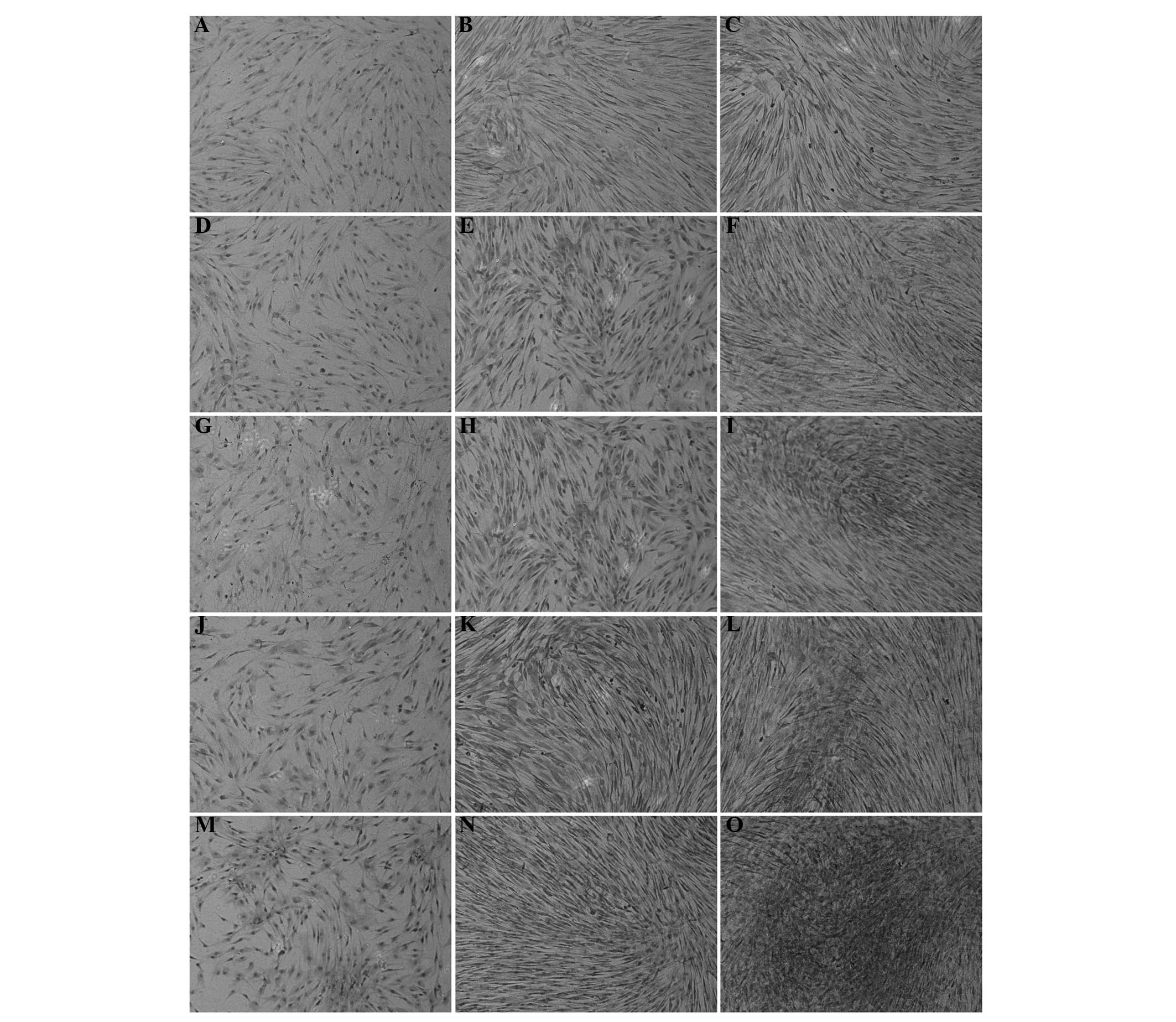
|
1
|
Hoover PA, Webber CE, Beaumont LF and
Blake JM: Postmenopausal bone mineral density: Relationship to
calcium intake, calcium absorption, residual estrogen, body
composition and physical activity. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
74:911–917. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hegarty VM, May HM and Khaw KT: Tea
drinking and bone mineral density in older women. Am J Clin Nutr.
71:1003–1007. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu CH, Yang YC, Yao WJ, et al:
Epidemiological evidence of increased bone mineral density in
habitual tea drinkers. Arch Intern Med. 162:1001–1006. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen Z, Pettinger MB, Ritenbaugh C, et al:
Habitual tea consumption and risk of osteoporosis: A prospective
study in the women's health initiative observational cohort. Am J
Epidemiol. 158:772–781. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Muraki S, Yamamoto S, Ishibashi H, et al:
Diet and lifestyle associated with increased bone mineral density:
Cross-sectional study of Japanese elderly women at an osteoporosis
outpatient clinic. J Orthop Sci. 12:317–320. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Devine A, Hodgson JM, Dick IM and Prince
RL: Tea drinking is associated with benefits on bone density in
older women. Am J Clin Nutr. 86:1243–1247. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johnell O, Gullberg B, Kanis JA, et al:
Risk factors for hip fracture in European women: The MEDOS study.
Mediterranean Osteoporosis Study. J Bone Miner Res. 10:1802–1815.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kanis J, Johnell O, Gullberg B, et al:
Risk factors for hip fracture in men from southern Europe: The
MEDOS study. Mediterranean Osteoporosis Study. Osteoporos Int.
9:45–54. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harbowy ME and Balentine DA: Tea
chemistry. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 16:415–480. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen CH, Ho ML, Chang JK, et al: Green tea
catechins enhance the expression of osteoprotegerin (OPG) in
pluripotent stem cells. J Orthop Surg Taiwan. 20:178–183. 2003.
|
|
11
|
Dulloo AG, Duret C, Rohrer D, et al:
Efficacy of a green tea extract rich in catechin polyphenols and
caffeine in increasing 24-h energy expenditure and fat oxidation in
humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 70:1040–1045. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stagg GV and Millin DJ: The nutritional
and therapeutic value of tea - a review. J Sci Food Agric.
26:1439–1459. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shen CL, Wang P, Guerrieri J, et al:
Protective effect of green tea polyphenols on bone loss in
middle-aged female rats. Osteoporos Int. 19:979–990. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shen CL, Yeh JK, Stoecker BJ, et al: Green
tea polyphenols mitigate deterioration of bone microarchitecture in
middle-aged female rats. Bone. 44:684–690. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen CL, Yeh JK, Cao JJ, et al: Green tea
polyphenols mitigate bone loss of female rats in a chronic
inflammation-induced bone loss model. J Nutr Biochem. 21:968–974.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shen CL, Yeh JK, Samathanam C, et al:
Green tea polyphenols attenuate deterioration of bone
microarchitecture in female rats with systemic chronic
inflammation. Osteoporos Int. 22:327–337. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shen CL, Cao JJ, Dagda RY, et al:
Supplementation with green tea polyphenols improves bone
microstructure and quality in aged, orchidectomized rats. Calcif
Tissue Int. 88:455–463. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rodriguez R, Kondo H, Nyan M, et al:
Implantation of green tea catechin α-tricalcium phosphate
combination enhances bone repair in rat skull defects. J Biomed
Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 98:263–271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vali B, Rao LG and El-Sohemy A:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate increases the formation of mineralized
bone nodules by human osteoblast-like cells. J Nutr Biochem.
18:341–347. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen CH, Ho ML, Chang JK, et al: Green tea
catechin enhances osteogenesis in a bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cell line. Osteoporos Int. 16:2039–2045. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakagawa H, Wachi M, Woo JT, et al: Fenton
reaction is primarily involved in a mechanism of
(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate to induce osteoclastic cell death.
Biochem Bioph Res Commun. 292:94–101. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yun JH, Pang EK, Kim CS, et al: Inhibitory
effects of green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin gallate on the
expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and on the formation of
osteoclasts. J Periodontal Res. 39:300–307. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jin P, Wu H, Xu G, et al:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) as a pro-osteogenic agent to
enhance osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from
human bone marrow: An in vitro study. Cell Tissue Res. 356:381–390.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Na K, Sun BK, Woo DG, et al: Osteogenic
differentiation of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells in
thermo-reversible hydrogel constructs containing hydroxyapatite and
bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP-2). Biomaterials. 28:2631–2637.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Harris SE, Bonewald LF, Harris MA, et al:
Effects of transforming growth factor beta on bone nodule formation
and expression of bone morphogenetic protein 2, osteocalcin,
osteopontin, alkaline phosphatase and type I collagen mRNA in
long-term cultures of fetal rat calvarial osteoblasts. J Bone Miner
Res. 9:855–863. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hogan BL: Bone morphogenetic proteins:
Multifunctional regulators of vertebrate development. Genes Dev.
10:1580–1594. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reddi AH: Bone and cartilage
differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 4:737–744. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wozney JM, Rosen V, Celeste AJ, et al:
Novel regulators of bone formation: Molecular clones and
activities. Science. 242:1528–1534. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wozney JM: The bone morphogenetic protein
family and osteogenesis. Mol Reprod Dev. 32:160–167. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yamaguchi A, Katagiri T, Ikeda T, et al:
Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates
osteoblastic maturation and inhibits myogenic differentiation in
vitro. J Cell Biol. 113:681–687. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Harborne JB and Williams CA: Advances in
flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry. 55:481–504. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kamon M, Zhao R and Sakamoto K: Green tea
polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin gallate suppressed the
differentiation of murine osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Cell Biol
Int. 34:109–116. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang CH, Lin CY, Yang JH, et al:
Supplementary catechins attenuate cooking-oil-fumes-induced
oxidative stress in rat lung. Chin J Physiol. 52:151–159. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yagi H, Tan J and Tuan RS: Polyphenols
suppress hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human
bone-marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem.
114:1163–1173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hanai J, Chen LF, Kanno T, et al:
Interaction and functional cooperation of PEBP2/CBF with Smads.
Synergistic induction of the immunoglobulin germline C-alpha
promoter. J Biol Chem. 274:31577–31582. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Javed A, Barnes GL, Jasanya BO, et al:
Runt homology domain transcription factors (Runx, Cbfa and AML)
mediate repression of the bone sialoprotein promoter: Evidence for
promoter context-dependent activity of Cbfa proteins. Mol Cell
Biol. 21:2891–2905. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nishimura R, Hata K, Harris SE, et al:
Core-binding factor alpha 1 (Cbfa1) induces osteoblastic
differentiation of C2C12 cells without interactions with Smad1 and
Smad5. Bone. 31:303–312. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|