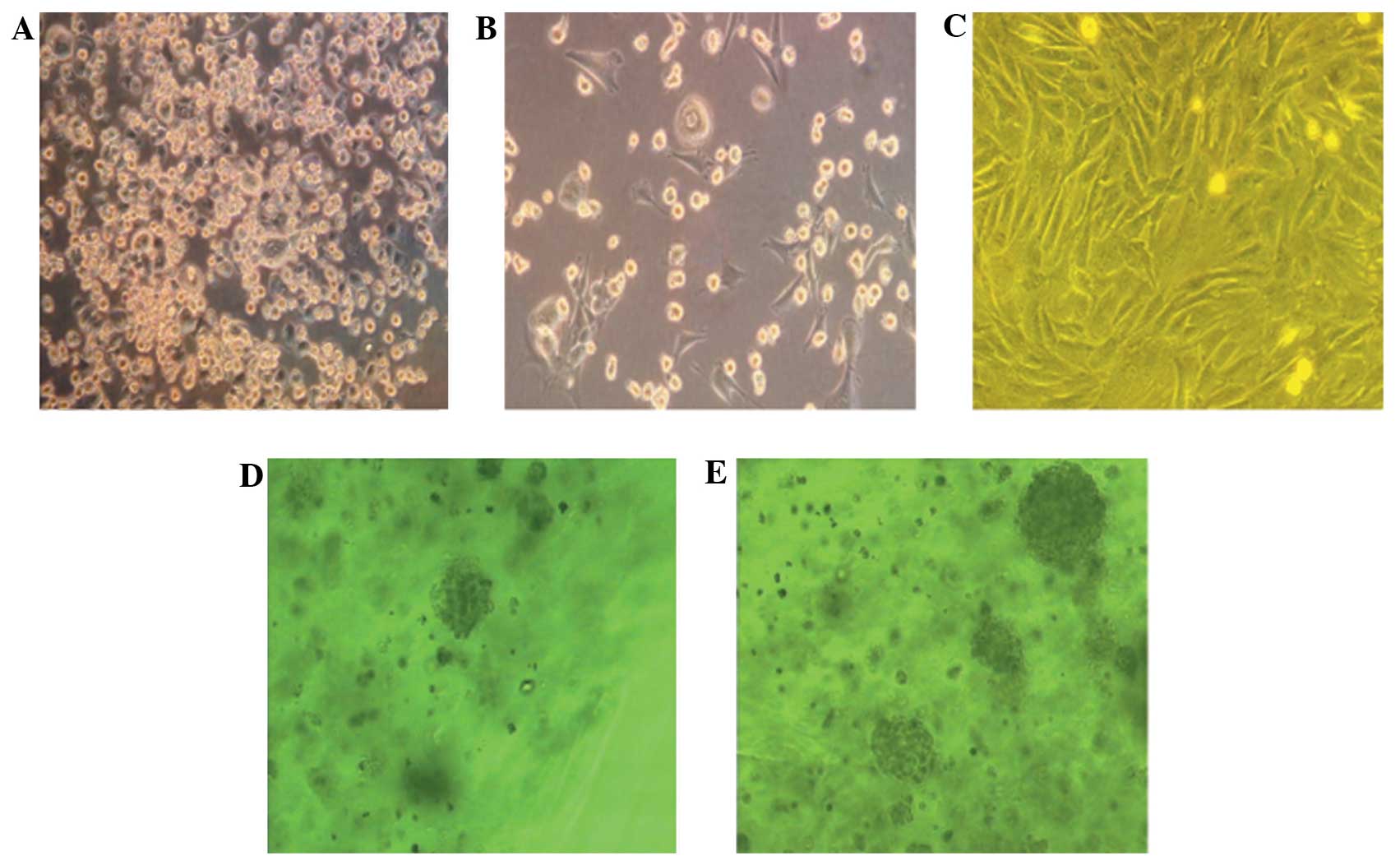
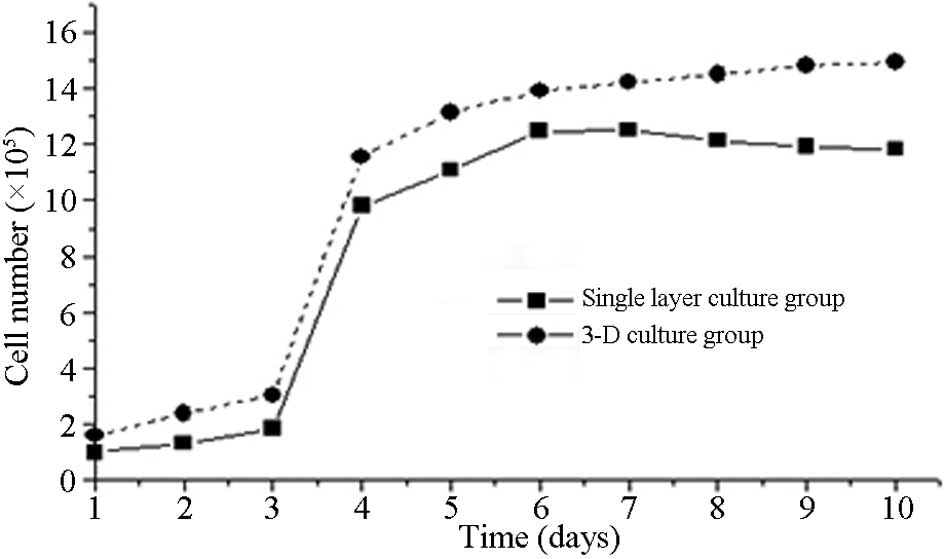
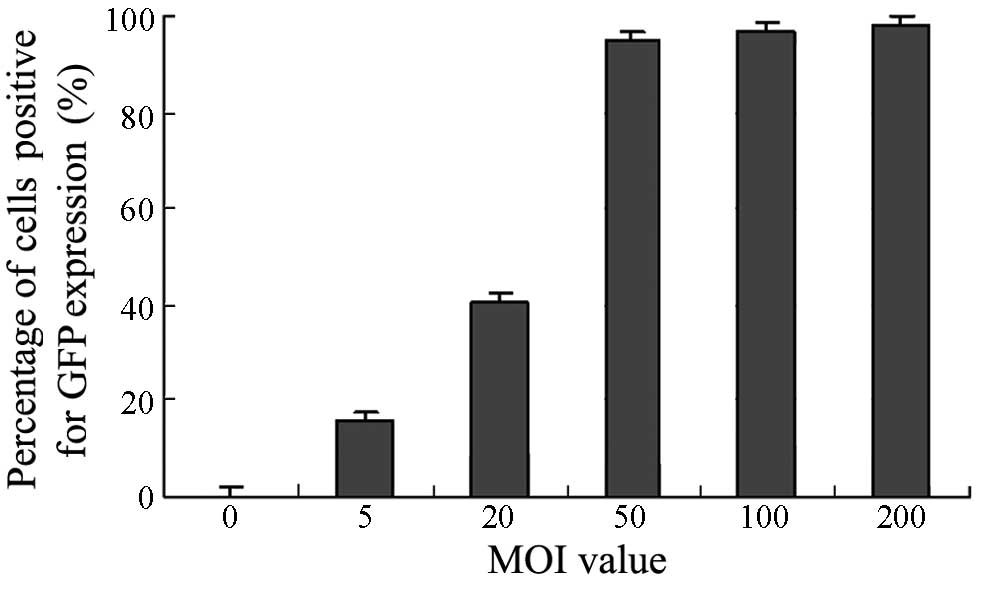
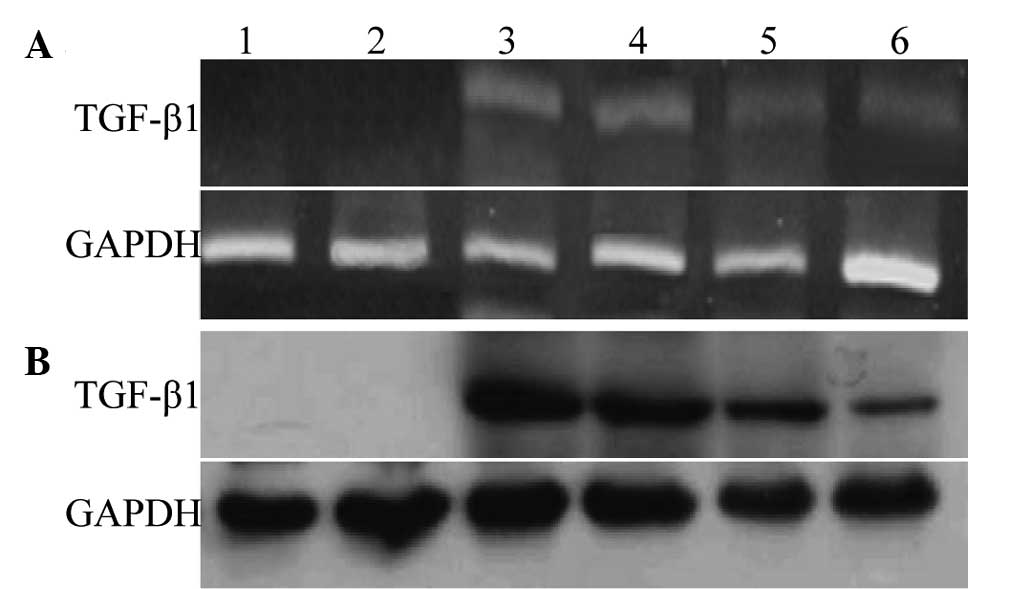
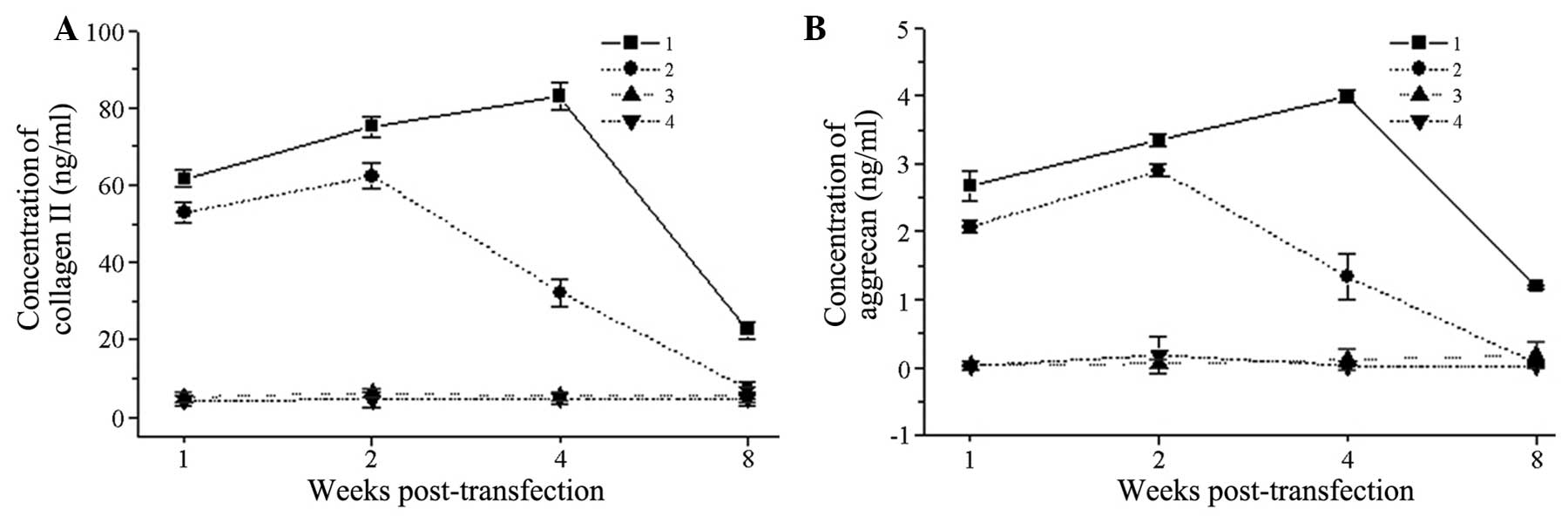
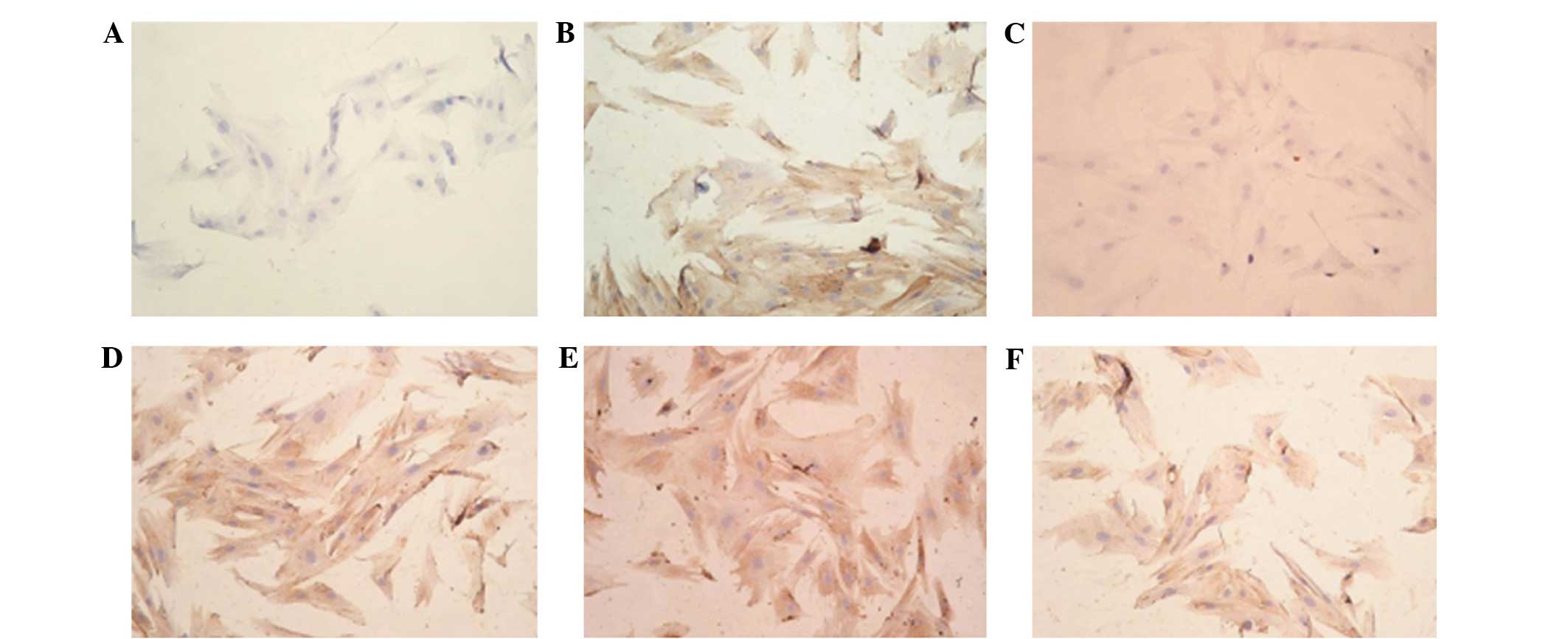
|
1
|
ODriscoll SW: The healing and regeneration
of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 80:1795–1812.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Awad HA, Butler DL, Boivin GP, Smith FN,
Malaviya P, Huibregtse B and Caplan AI: Autologous mesenchymal stem
cell-mediated repair of tendon. Tissue Eng. 5:267–277. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ostrander RV, Goomer RS, Tontz WL, Khatod
M, Harwood FL, Maris TM and Amiel D: Donor cell fate in tissue
engineering for articular cartilage repair. Clin Orthop.
389:228–237. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Colther DC, Sekiya I and Prockop DJ:
Identification of a subpopulation of rapidly self-renewing and
multipotential adult stem cells in colonies of human marrow stromal
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:7841–7845. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang JI, Zuk PA, Jones NF, Zhu M, Lorenz
HP, Hedrick MH and Benhaim P: Chondrogenic potential of
multipotential cells from human adipose tissue. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 113:585–594. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meirelles Lda S, Fontes AM, Covas DT and
Caplan AI: Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic properties of
mesenchymal stem cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 20:419–427.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boo L, Selvaratnam L, Tai CC, Ahmad TS and
Kamarul T: Expansion and preservation of multipotentiality of
rabbit bone-marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells in dextran-based
microcarrier spin culture. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 22:1343–1356.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seong JM, Kim BC, Park JH, et al: Stem
cells in bone tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 5:0620012010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Augello A, Kurth TB and De Bari C:
Mesenchymal stem cells: A perspective from in vitro cultures to in
vivo migration and niches. Eur Cell Mater. 20:121–133.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Worster AA, Nixon AJ, Brower-Toland BD and
Williams J: Effect of transforming growth factor betal on
chondrogenic differentiation of cultured equine mesenchymal stem
cells. Am J Vet Res. 61:1003–1010. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoo JU, Barthel TS, Nishimura K, et al:
The chondrogenic potential of human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal
progenitor cells. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 80:1745–1757.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakahara H, Dennis JE, Bruder SP,
Haynesworth SE, Lennon DP and Caplan AI: In vitro differentiation
of bone and hypertrophic cartilage from periosteal-derived cells.
Exp Cell Res. 195:492–503. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bruder SP, Fink DJ and Caplan AI:
Mesenchymal stem cells in bone development, bone repair and
skeletal regeneration therapy. J Cell Biochem. 56:283–294. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mostafa NZ, Uludağ H, Varkey M, Dederich
DN, Doschak MR and El-Bialy TH: In vitro osteogenic induction of
human gingival fibroblasts for bone regeneration. Open Dent J.
5:139–145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lisignoli G, Remiddi G, Cattinil L, et al:
An elevated number of differentiated osteoblast clonies can be
obtained from rat bone marrow stromal cells using a gradient
isolation procedure. Connect Tissue Res. 42:49–58. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qiu Q, Ducheyne P, Gao H and Ayyaswamy P:
Formation and differentiation of three-dimensional rat marrow
stromal cell culture on microcarriers in a rotating-wall vessel.
Tissue Eng. 4:19–34. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Glowacki J, Mizuno S and Greenberger JS:
Perfusion enhances functions of bone marrow stromal cells in
three-dimensional culture. Cell Transplant. 7:319–326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Angele P, Kujat R, Nerlich M, Yoo J,
Goldberg V and Johnstone B: Engineering of osteochondral tissue
with bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells in a derivatized
hyaluronan-gelatin composite sponge. Tissue Eng. 5:545–554. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ponticiello MS, Schinagl RM, Kadiyala S
and Barry FP: Gelatin-based resorbable sponge as a carrier matrix
for human mesenchymal stem cells in cartilage regeneration therapy.
J Biomed Mater Res. 52:246–255. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Majumdar MK, Banks V, Peluso DP and Morris
EA: Isolation, characterization and chondrogenic potential of human
bone marrow-derived multipotential stromal cells. J Cell Physiol.
185:98–106. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Diduch DR, Jordan LC, Mierisch CM and
Balian G: Marrow stromal cells embedded in alginate for repair of
osteochondral defects. Arthroscopy. 16:571–577. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma HL, Hung SC, Lin SY, Chen YL and Lo WH:
Chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in
alginate beads. J Biomed Mater Res A. 64:273–281. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hwang NS, Im SG, Wu PB, et al:
Chondrogenic priming adipose-mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage
tissue regeneration. Pharm Res. 28:1395–1405. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Taipaleenmäki H, Harkness L, Chen L, et
al: The crosstalk between transforming growth factor-β 1 and delta
like-1 mediates early chondrogenesis during embryonic endochondral
ossification. Stem Cells. 30:304–313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|