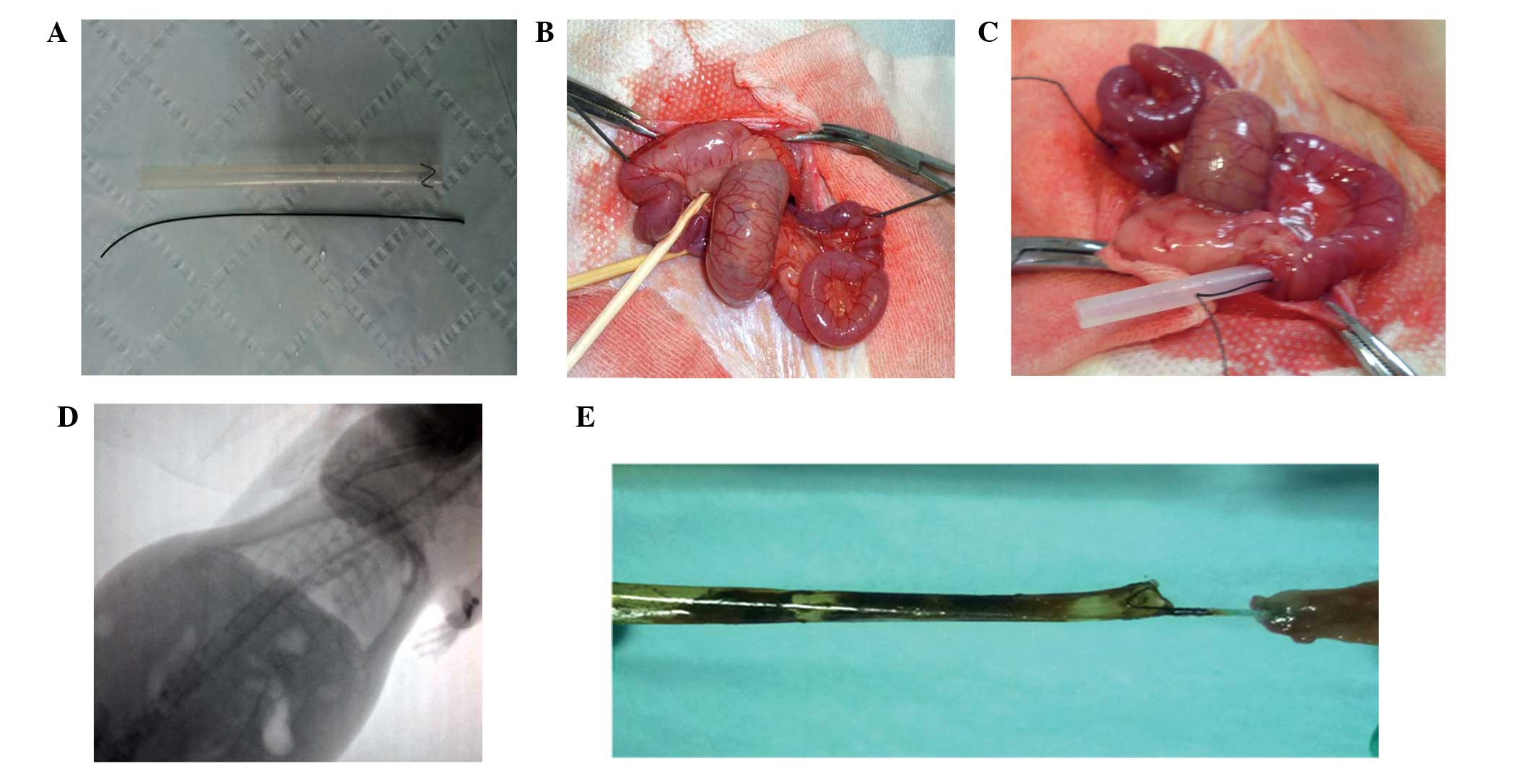
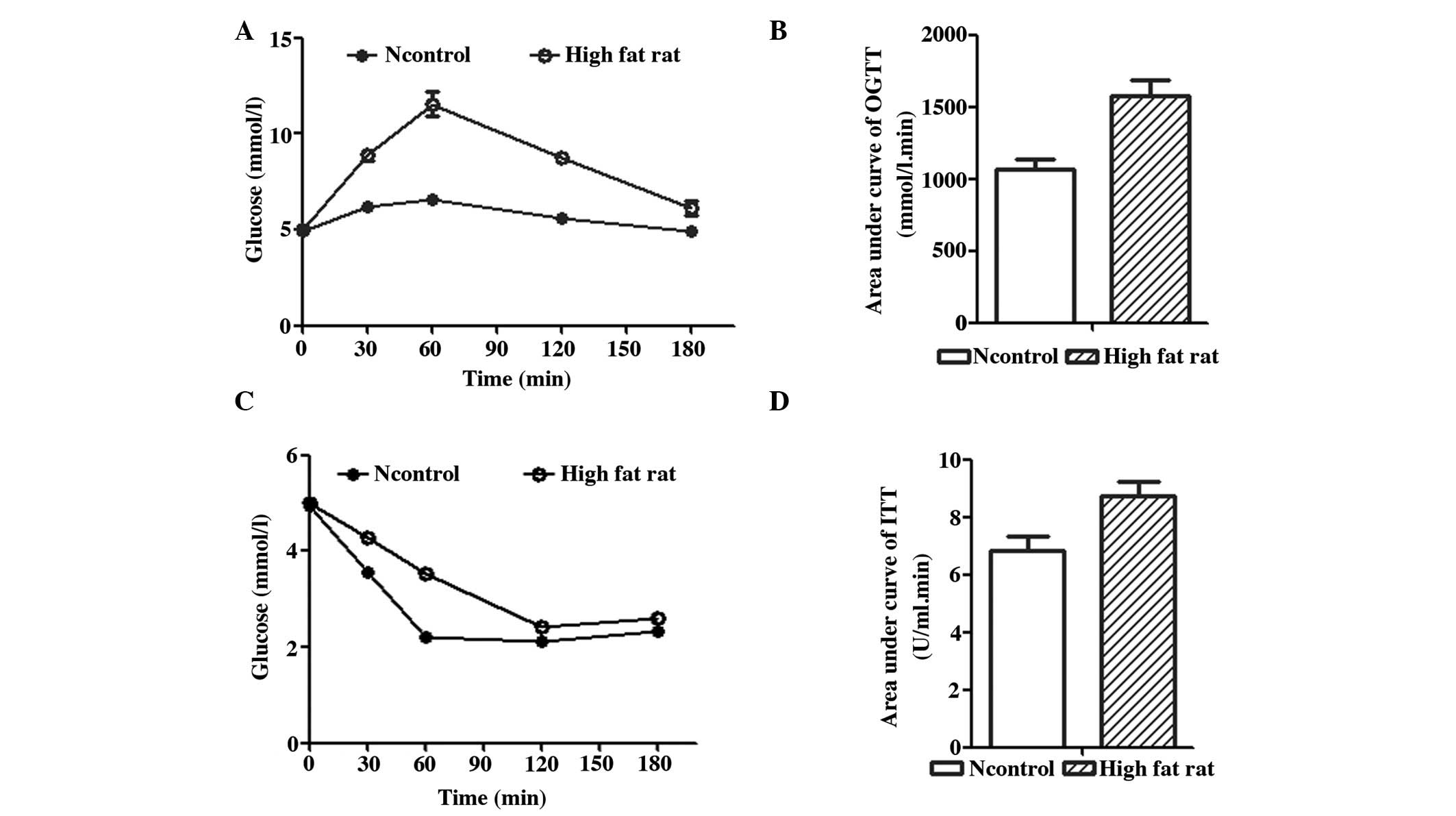
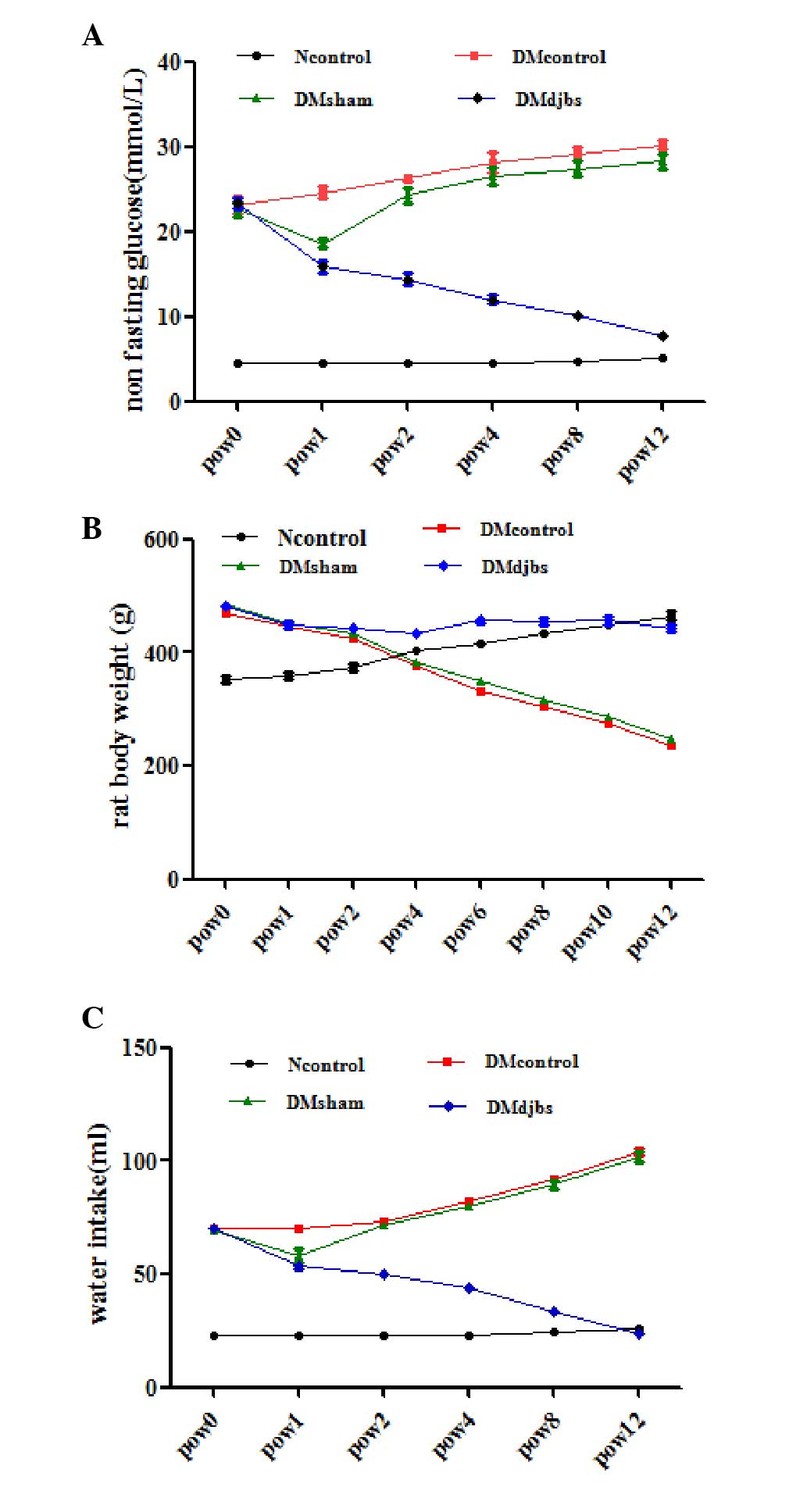
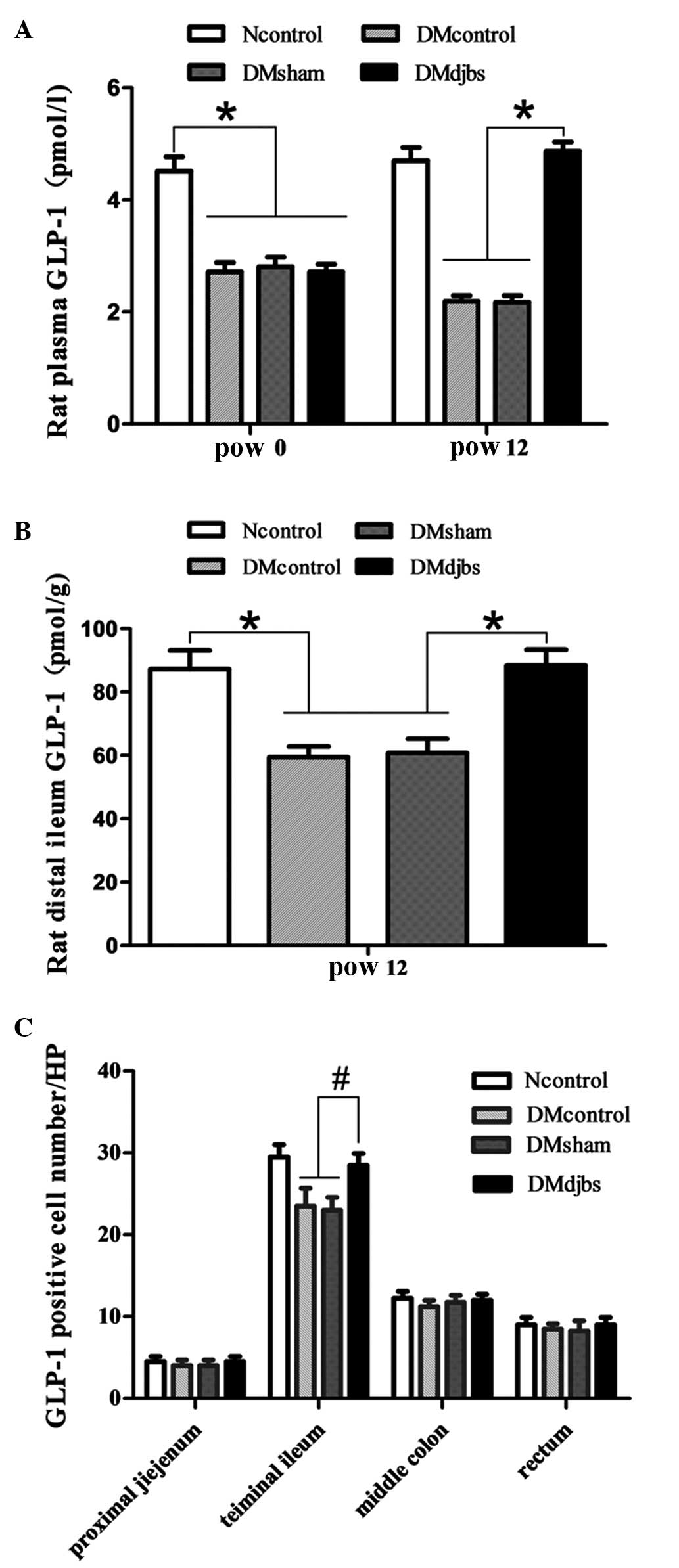
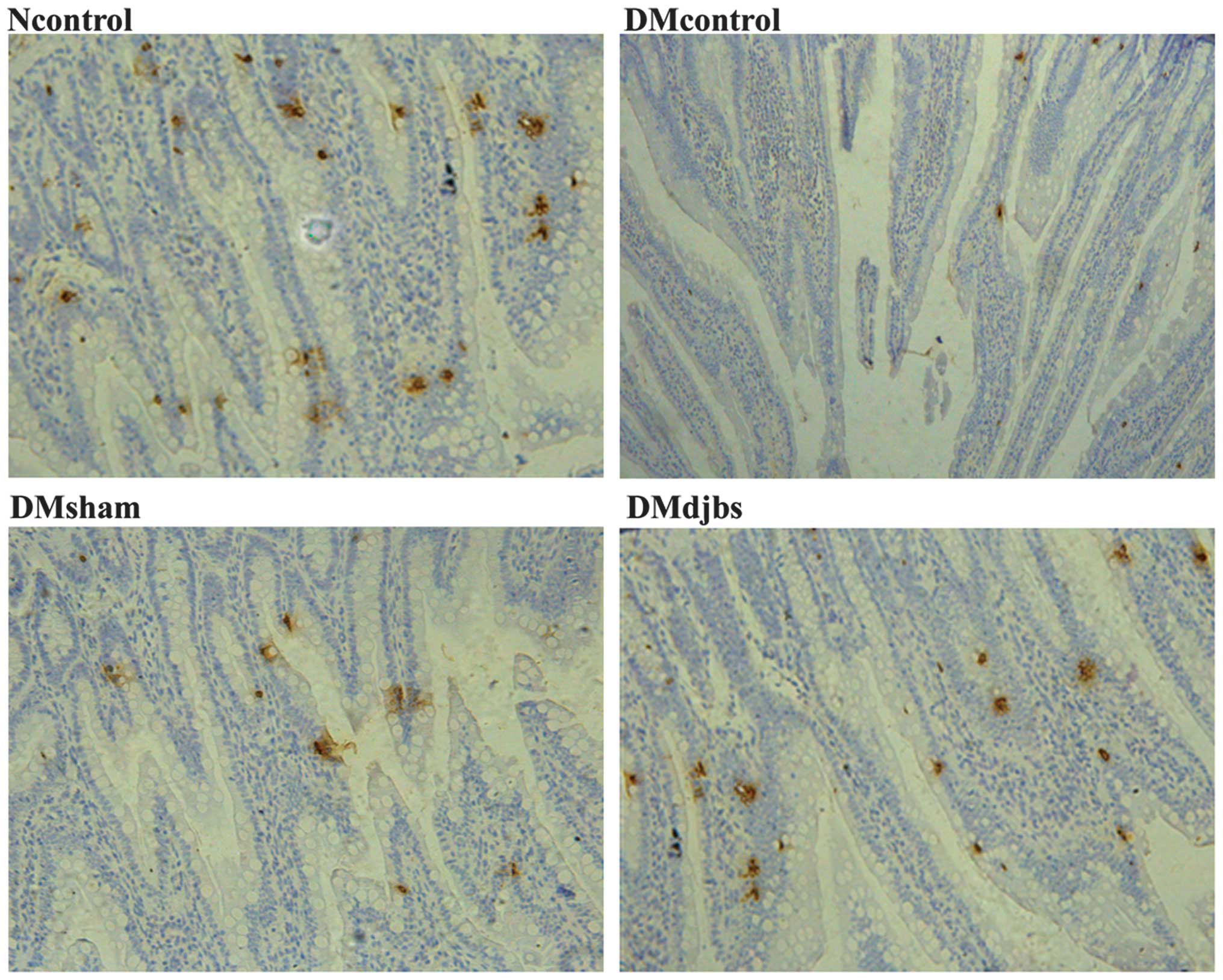
|
1
|
Shaw JE, Sicree RA and Zimmet PZ: Global
estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes
Res Clin Prac. 87:4–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J,
Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, et al: Prevalence of diabetes among
men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 362:1090–1101. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nissen SE and Wolski K: Rosiglitazone
revisited: An updated meta-analysis of risk for myocardial
infarction and cardiovascular mortality. Arch Intern Med.
170:1191–1201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loke YK, Kwok CS and Singh S: Comparative
cardiovascular effects of thiazolidinediones: Systematic review and
meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ. 342:d13092011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS)
Group, . Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or
insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of
complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet.
352:837–853. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buchwald H and Oien DM:
Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2008. Obes Surg.
19:1605–1611. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, Banel D,
Jensen MD, Pories WJ, Bantle JP and Sledge I: Weight and type 2
diabetes after bariatric surgery: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Am J Med. 122:248–256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A,
Guidone C, Iaconelli A, Leccesi L, Nanni G, Pomp A, Castagneto M,
Ghirlanda G and Rubino F: Bariatric surgery versus conventional
medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 366:1577–1585.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dogan K, Betzel B, Homan J, Aarts EO,
Ploeger N, de Boer H, Aufenacker TJ, van Laarhoven CJ, Janssen IM
and Berends FJ: Long-term effects of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric
bypass on diabetes mellitus, hypertension and dyslipidaemia in
morbidly obese patients. Obes Surg. 24:1835–1842. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Adams TD, Gress RE, Smith SC, Halverson
RC, Simper SC, Rosamond WD, Lamonte MJ, Stroup AM and Hunt SC:
Long-term mortality after gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med.
357:753–761. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Encinosa WE, Bernard DM, Steiner CA and
Chen CC: Use and costs of bariatric surgery and prescription
weight-loss medications. Health Aff (Millwood). 24:1039–1046. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rodriguez L, Reyes E, Fagalde P, Oltra MS,
Saba J, Aylwin CG, Prieto C, Ramos A, Galvao M, Gersin KS and Sorli
C: Pilot clinical study of an endoscopic, removable
duodenal-jejunal bypass liner for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Technol Ther. 11:725–732. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Milone L, Gagner M, Ueda K, Bardaro SJ and
Ki-Young Y: Effect of a polyethylene endoluminal duodeno-jejunal
tube (EDJT) on weight gain: A feasibility study in a porcine model.
Obes Surg. 16:620–626. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gersin KS, Keller JE, Stefanidis D, Simms
CS, Abraham DD, Deal SE, Kuwada TS and Heniford BT: Duodenal-
jejunal bypass sleeve: A totally endoscopic device for the
treatment of morbid obesity. Surg Innov. 14:275–278. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schouten R, Rijs CS, Bouvy ND, Hameeteman
W, Koek GH, Janssen IM and Greve JW: A multicenter, randomized
efficacy study of the EndoBarrier gastrointestinal liner for
presurgical weight loss prior to bariatric surgery. Ann Surg.
251:236–243. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
de Jonge C, Rensen SS, Verdam FJ, Vincent
RP, Bloom SR, Buurman WA, le Roux CW, Schaper NC, Bouvy ND and
Greve JW: Endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner rapidly improves
type 2 diabetes. Obes Surg. 23:1354–1360. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mumphrey MB, Patterson LM, Zheng H and
Berthoud HR: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery increases number but
not density of CCK-, GLP-1-, 5-HT- and neurotensin-expressing
enteroendocrine cells in rats. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
25:e70–e79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Muñoz R, Carmody JS, Stylopoulos N, Davis
P and Kaplan LM: Isolated duodenal exclusion increases energy
expenditure and improves glucose homeostasis in diet-induced obese
rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 303:R985–R993. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Holst JJ: Enteroendocrine secretion of gut
hormones in diabetes, obesity and after bariatric surgery. Curr
Opin Pharmacol. 13:983–988. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Holst JJ and Gromada J: Role of incretin
hormones in the regulation of insulin secretion in diabetic and
nondiabetic humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 287:E199–E206.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Perley MJ and Kipnis DM: Plasma insulin
responses to oral and intravenous glucose: Studies in normal and
diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 46:1954–1962. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McIntyre N, Holdsworth CD and Turner DS:
New interpretation of oral glucose tolerance. Lancet. 4:20–21.
1964. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Morgan LM: The role of the entero-insular
axis in insulin secretion. Biochem Soc Trans. 18:101–102. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Eissele R, Göke R, Willemer S, Harthus HP,
Vermeer H, Arnold R and Göke B: Glucagon-like peptide-1 cells in
the gastrointestinal-tract and pancreas of rat, pig and man. Eur J
Clin Invest. 22:283–291. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hansen CF, Bueter M, Theis N, Lutz T,
Paulsen S, Dalbøge LS, Vrang N and Jelsing J: Hypertrophy dependent
doubling of L-cells in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass operated rats. PLoS
One. 8:656962013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Aguirre V, Stylopoulos N, Grinbaum R and
Kaplan LM: An endoluminal sleeve induces substantial weight loss
and normalizes glucose homeostasis in rats with diet-induced
obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 16:2585–2592. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL
and Ramarao P: Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose
streptozotocin-treated rat: A model for type 2 diabetes and
pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 52:313–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu SZ, Deng YX, Chen B, Zhang XJ, Shi QZ
and Qiu XM: Antihyperglycemic effect of the traditional Chinese
scutellaria-coptis herb couple and its main components in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
145:490–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tolhurst G, Reimann F and Gribble FM:
Nutritional regulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. J
Physiol. 587:Pt 127–32. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gautier JF, Choukem SP and Girard J:
Physiology of incretins (GIP and GLP-1) and abnormalities in type 2
diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 34 (Suppl 2):S65–S72. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vilsbøll T, Krarup T, Deacon CF, Madsbad S
and Holst JJ: Reduced postprandial concentrations of intact
biologically active glucagon like peptide 1 in type 2 diabetes
patients. Diabetes. 50:609–613. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
ToftNielsen MB, Damholt MB, Madsbad S,
Hilsted LM, Hughes TE, Michelsen BK and Holst JJ: Determinants of
the impaired secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 in type 2
diabetes patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86:3717–3723. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dar MS, Chapman WH III, Pender JR, Drake
AJ III, O'Brien K, Tanenberg RJ, Dohm GL and Pories WJ: GLP-1
response to a mixed meal: What happens 10 years after Roux-en-Y
gastric bypass (RYGB)? Obes Surg. 22:1077–1083. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chaikomin R, Doran S, Jones KL,
FeinleBisset C, O'Donovan D, Rayner CK and Horowitz M: Initially
more rapid small intestinal glucose delivery increases plasma
insulin, GIP and GLP-1 but does not improve overall glycemia in
healthy subjects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 289:E504–E507.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pilichiewicz AN, Chaikomin R, Brennan IM,
Wishart JM, Rayner CK, Jones KL, Smout AJ, Horowitz M and
Feinle-Bisset C: Load-dependent effects of duodenal glucose on
glycemia, gastrointestinal hormones, antropyloroduodenal motility
and energy intake in healthy men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
293:E743–E753. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chaikomin R, Wu KL, Doran S, Jones KL,
Smout AJ, Renooij W, Holloway RH, Meyer JH, Horowitz M and Rayner
CK: Concurrent duodenal manometric and impedance recording to
evaluate the effects of hyoscine on motility and flow events,
glucose absorption and incretin release. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 292:G1099–G1104. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Little TJ, Doran S, Meyer JH, Smout AJ,
O'Donovan DG, Wu KL, Jones KL, Wishart J, Rayner CK, Horowitz M and
Feinle-Bisset C: The release of GLP-1 and ghrelin, but not GIP and
CCK, by glucose is dependent upon the length of small intestine
exposed. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 291:E647–E655. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gentilcore D, Bryant B, Wishart JM, Morris
HA, Horowitz M and Jones KL: Acarbose attenuates the hypotensive
response to sucrose and slows gastric emptying in the elderly. Am J
Med. 118:12892005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qualmann C, Nauck MA, Holst JJ, Orskov C
and Creutzfeldt W: Glucagon-like peptide 1 (7–36 amide) secretion
in response to luminal sucrose from the upper and lower gut. A
study using alpha-glucosidase inhibition (acarbose). Scand J
Gastroenterol. 30:892–896. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|