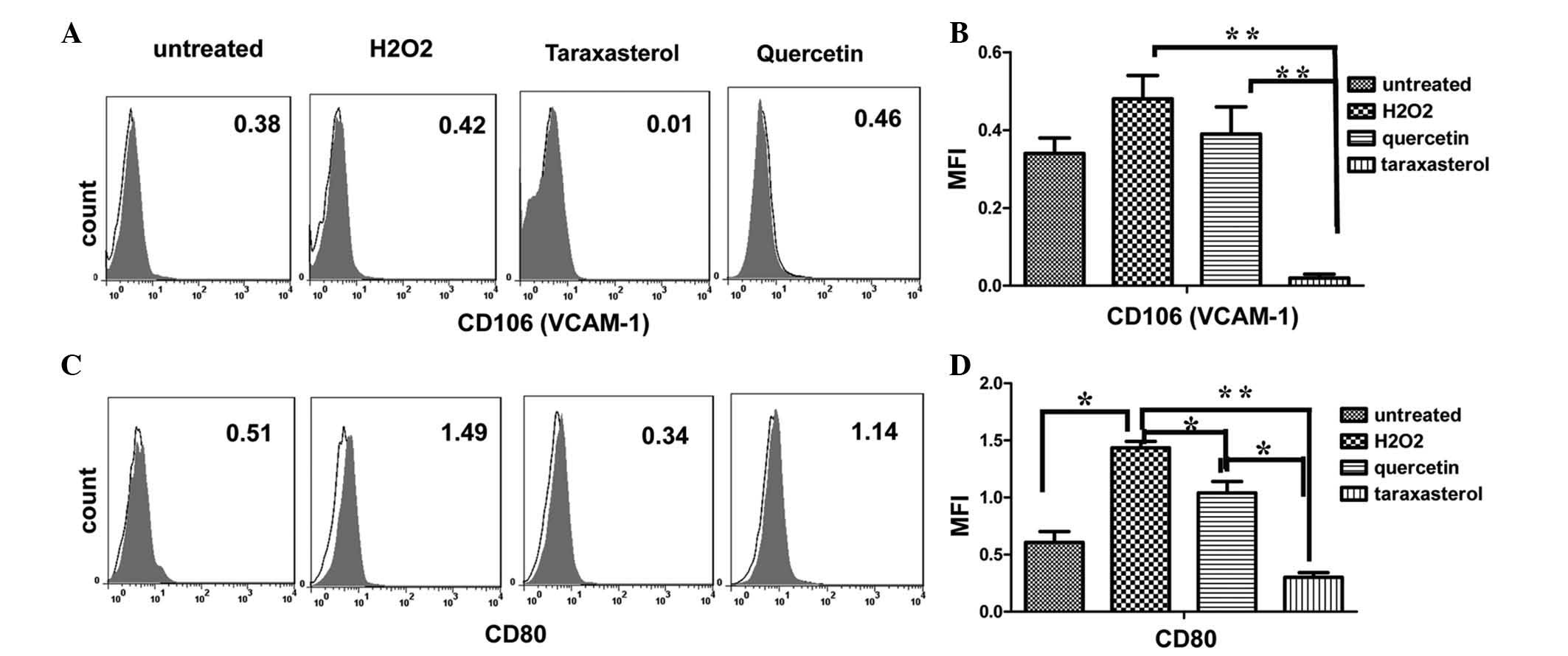
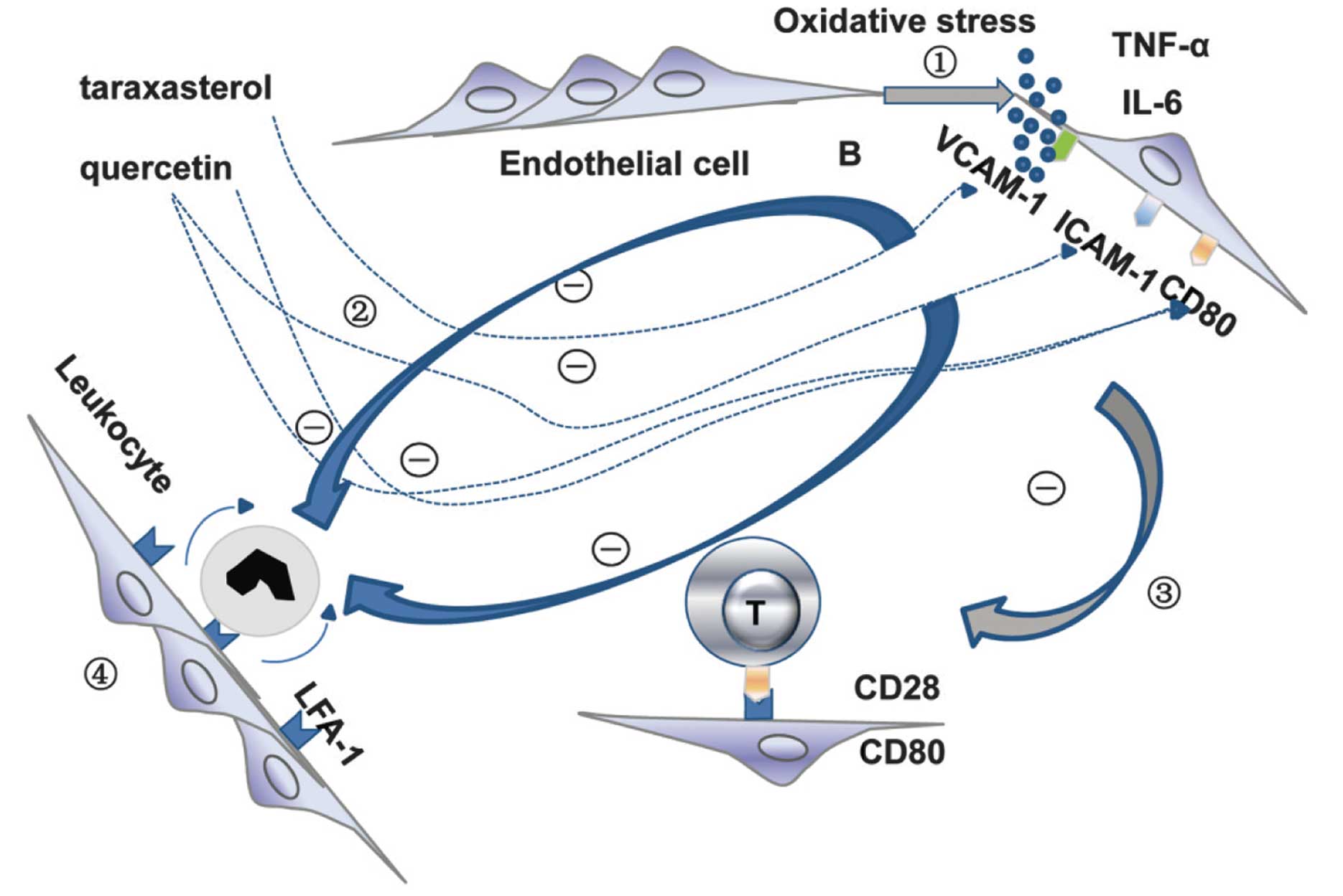
|
1
|
Versari D, Daghini E, Virdis A, Ghiadoni L
and Taddei S: Endothelial dysfunction as a target for prevention of
cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 32 Suppl. 2:S314–S321. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Savoia C, Sada L, Zezza L, et al: Vascular
inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in experimental
hypertension. Int J Hypertens. 2011:2812402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thompson AM, Zhang Y, Tong W, et al:
Association of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction with
metabolic syndrome, prediabetes and diabetes in adults from Inner
Mongolia, China. BMC Endocr Disord. 11:162011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wannamethee SG, Tchernova J, Whincup P, et
al: Plasma leptin: associations with metabolic, inflammatory and
haemostatic risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Atherosclerosis. 191:418–426. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spagnoli LG, Bonanno E, Sangiorgi G and
Mauriello A: Role of inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Nucl Med.
48:1800–1815. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lawson C and Wolf S: ICAM-1 signaling in
endothelial cells. Pharmacol Rep. 61:22–32. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hwang SJ, Ballantyne CM, Sharrett AR, et
al: Circulating adhesion molecules VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin
in carotid atherosclerosis and incident coronary heart disease
cases: the Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) study.
Circulation. 96:4219–4225. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rubio Guerra, Vargas-Robles H, Serrano AM,
et al: Correlation between the levels of circulating adhesion
molecules and atherosclerosis in hypertensive type-2 diabetic
patients. Clin Exp Hypertens. 32:308–310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ellison S, Gabunia K, Kelemen SE, et al:
Attenuation of experimental atherosclerosis by interleukin-19.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:2316–2324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McLaren JE, Michael DR, Salter RC, et al:
IL-33 reduces macrophage foam cell formation. J Immunol.
185:1222–1229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miller AM, Xu D, Asquith DL, et al: IL-33
reduces the development of atherosclerosis. J Exp Med. 205:339–346.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ridker PM, Rifai N, Clearfield M, et al:
Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study
Investigators: Measurement of C-reactive protein for the
targeting of statin therapy in the primary prevention of acute
coronary events. N Engl J Med. 344:1959–1965. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kleemann R, Verschuren L, de Rooij BJ, et
al: Evidence for anti-inflammatory activity of statins and
PPARalpha activators in human C-reactive protein transgenic mice in
vivo and in cultured human hepatocytes in vitro. Blood.
103:4188–4194. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mirjanic Azaric, Rizzo M, Sormaz L, et al:
Atorvastatin in stable angina patients lowers CCL2 and ICAM1
expression: pleiotropic evidence from plasma mRNA analyses. Clin
Biochem. 46:1526–1531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Colucci R, Fornai M, Duranti E, et al:
Rosuvastatin prevents angiotensin II-induced vascular changes by
inhibition of NAD(P)H oxidase and COX-1. Br J Pharmacol.
169:554–566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nie P, Li D, Hu L, et al: Atorvastatin
improves plaque stability in ApoE-knockout mice by regulating
chemokines and chemokine receptors. PLoS One. 9:e970092014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Berman JP, Farkouh ME and Rosenson RS:
Emerging anti-inflammatory drugs for atherosclerosis. Expert Opin
Emerg Drugs. 18:193–205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Larson AJ, Symons JD and Jalili T:
Therapeutic potential of quercetin to decrease blood pressure:
review of efficacy and mechanisms. Adv Nutr. 3:39–46. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Egert S, Bosy-Westphal A, Seiberl J, et
al: Quercetin reduces systolic blood pressure and plasma oxidised
low-density lipoprotein concentrations in overweight subjects with
a high-cardiovascular disease risk phenotype: a double-blinded,
placebo-controlled cross-over study. Br J Nutr. 102:1065–1074.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Galindo P, Rodriguez-Gómez I,
González-Manzano S, et al: Glucuronidated quercetin lowers blood
pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats via deconjugation. PLoS
One. 7:e326732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chopra M, Fitzsimons PE, Strain JJ,
Thurnham DI and Howard AN: Nonalcoholic red wine extract and
quercetin inhibit LDL oxidation without affecting plasma
antioxidant vitamin and carotenoid concentrations. Clin Chem.
46:1162–1170. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Galindo P, González-Manzano S, Zarzuelo
MJ, et al: Different cardiovascular protective effects of quercetin
administered orally or intraperitoneally in spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Food Funct. 3:643–650. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hubbard GP, Wolffram S, de Vos R, et al:
Ingestion of onion soup high in quercetin inhibits platelet
aggregation and essential components of the collagen-stimulated
platelet activation pathway in man: a pilot study. Br J Nutr.
96:482–488. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Xiong H and Liu L: Effects of
taraxasterol on inflammatory responses in
lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol.
141:206–211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu J, Xiong H, Cheng Y, et al: Effects of
taraxasterol on ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma in mice. J
Ethnopharmacol. 148:787–793. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shen HM, Dai J, Chia SE, Lim A and Ong CN:
Detection of apoptotic alterations in sperm in subfertile patients
and their correlations with sperm quality. Hum Reprod.
17:1266–1273. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kumar A, Sehgal N, Kumar P, Padi SS and
Naidu PS: Protective effect of quercetin against ICV
colchicine-induced cognitive dysfunctions and oxidative damage in
rats. Phytother Res. 22:1563–1569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ishizawa K, Yoshizumi M, Kawai Y, et al:
Pharmacology in health food: metabolism of quercetin in vivo and
its protective effect against arteriosclerosis. J Pharmacol Sci.
115:466–470. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nabavi SF, Nabavi SM, Mirzaei M and
Moghaddam AH: Protective effect of quercetin against sodium
fluoride induced oxidative stress in rat's heart. Food Funct.
3:437–441. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matouk AI, Taye A, Heeba GH and El-Moselhy
MA: Quercetin augments the protective effect of losartan against
chronic doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in rats. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 36:443–450. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chi Z and Melendez AJ: Role of cell
adhesion molecules and immune-cell migration in the initiation,
onset and development of atherosclerosis. Cell Adh Migr. 1:171–175.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Buono C, Pang H, Uchida Y, et al:
B7-1/B7-2 costimulation regulates plaque antigen-specific T-cell
responses and atherogenesis in low-density lipoprotein
receptor-deficient mice. Circulation. 109:2009–2015. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Prasad V, Lorenz JN, Miller ML, et al:
Loss of NHE1 activity leads to reduced oxidative stress in heart
and mitigates high-fat diet-induced myocardial stress. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 65:33–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cooper MP: Interplay of mitochondrial
biogenesis and oxidative stress in heart failure. Circulation.
127:1932–1934. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paravicini TM and Touyz RM: NADPH
oxidases, reactive oxygen species, and hypertension: clinical
implications and therapeutic possibilities. Diabetes Care 31 Suppl.
2:S170–S180. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Moukdar F, Robidoux J, Lyght O, et al:
Reduced antioxidant capacity and diet-induced atherosclerosis in
uncoupling protein-2-deficient mice. J Lipid Res. 50:59–70. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Watanabe T, Pakala R, Katagiri T and
Benedict CR: Oxidized low-density lipoproteins potentiate the
mitogenic effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine on vascular smooth muscle
cells. Jpn Heart J. 43:35–42. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Takasaki M, Konoshima T, Tokuda H, et al:
Anti-carcinogenic activity of Taraxacum plant I. Biol Pharm Bull.
22:602–605. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kook D, Wolf AH, Yu AL, et al: The
protective effect of quercetin against oxidative stress in the
human RPE in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 49:1712–1720. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu CL, Xie LX, Li M, et al: Salvianolic
acid B inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced endothelial cell
apoptosis through regulating PI3K/Akt signaling. PLoS One.
2:e13212007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qian J, Jiang F, Wang B, et al:
Ophiopogonin D prevents H2O2-induced injury
in primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 128:438–445. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Alvarez A, Cerdá-Nicolas M, Naim Abu Nabah
Y, et al: Direct evidence of leukocyte adhesion in arterioles by
angiotensin II. Blood. 104:402–408. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Davies MJ, Gordon JL, Gearing AJ, et al:
The expression of the adhesion molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1, PECAM, and
E-selectin in human atherosclerosis. J Pathol. 171:223–229. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rendig SV, Symons JD, Longhurst JC and
Amsterdam EA: Effects of red wine, alcohol, and quercetin on
coronary resistance and conductance arteries. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 38:219–227. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ovesná Z, Vachálková A and Horváthová K:
Taraxasterol and beta-sitosterol: new naturally compounds with
chemoprotective/chemopreventive effects. Neoplasma. 51:407–414.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Villarreal ML, Alvarez L, Alonso D, et al:
Cytotoxic and antimicrobial screening of selected terpenoids from
Asteraceae species. J Ethnopharmacol. 42:25–29. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
He W, Han H, Wang W and Gao B:
Anti-influenza virus effect of aqueous extracts from dandelion.
Virol J. 8:5382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Han H, He W, Wang W and Gao B: Inhibitory
effect of aqueous Dandelion extract on HIV-1 replication and
reverse transcriptase activity. BMC Complement Altern Med.
11:1122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lakshminarayanan V, Beno DW, Costa RH and
Roebuck KA: Differential regulation of interleukin-8 and
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 by H2O2 and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha in endothelial and epithelial cells. J Biol Chem.
272:32910–32918. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
McCoy KD and Le Gros G: The role of CTLA-4
in the regulation of T cell immune responses. Immunol Cell Biol.
77:1–10. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kadono T, Venturi GM, Steeber DA and
Tedder TF: Leukocyte rolling velocities and migration are optimized
by cooperative L-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1
functions. J Immunol. 169:4542–4550. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|