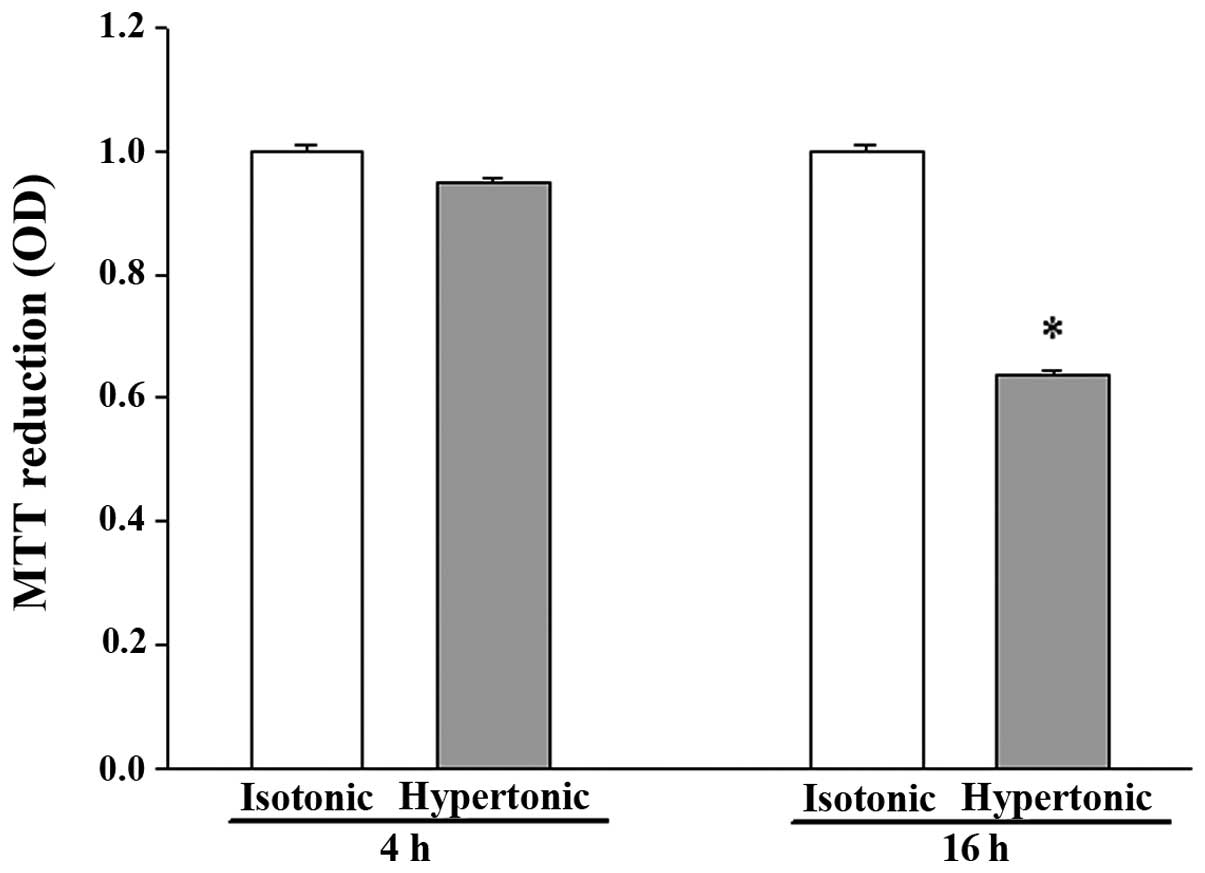
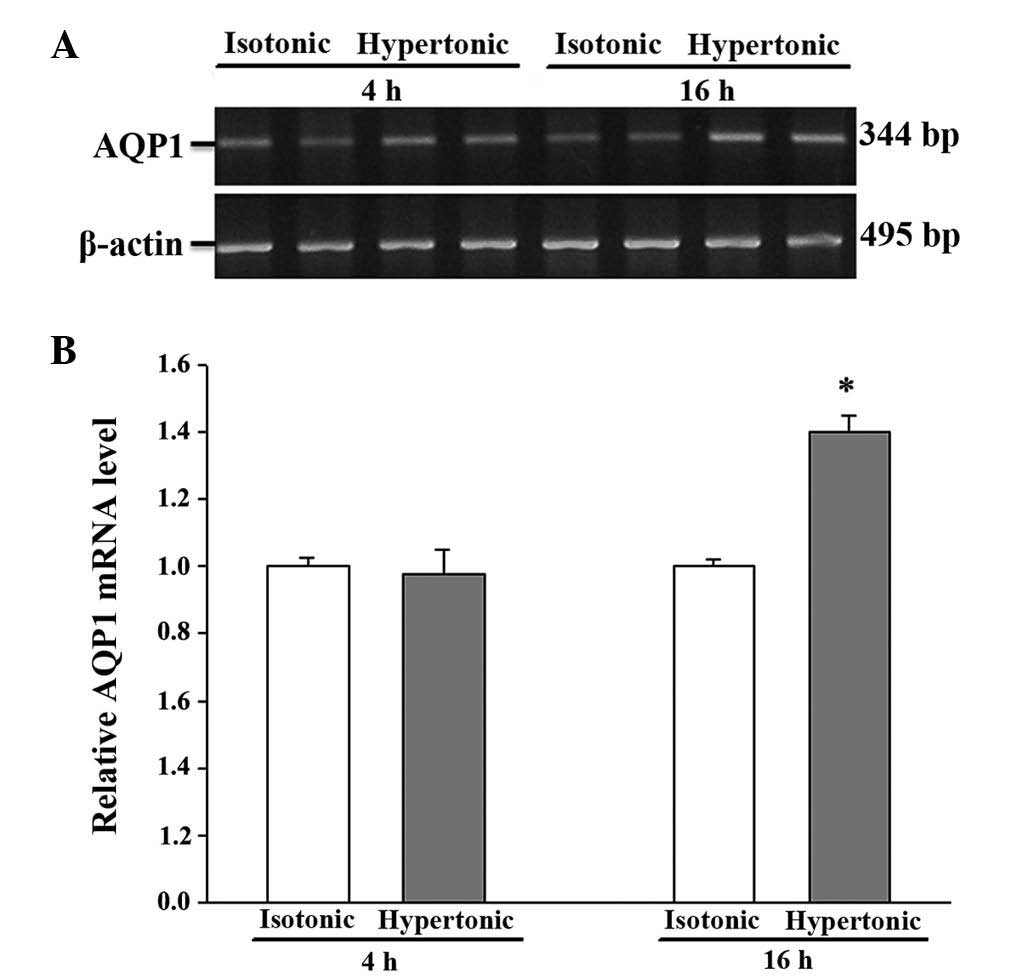
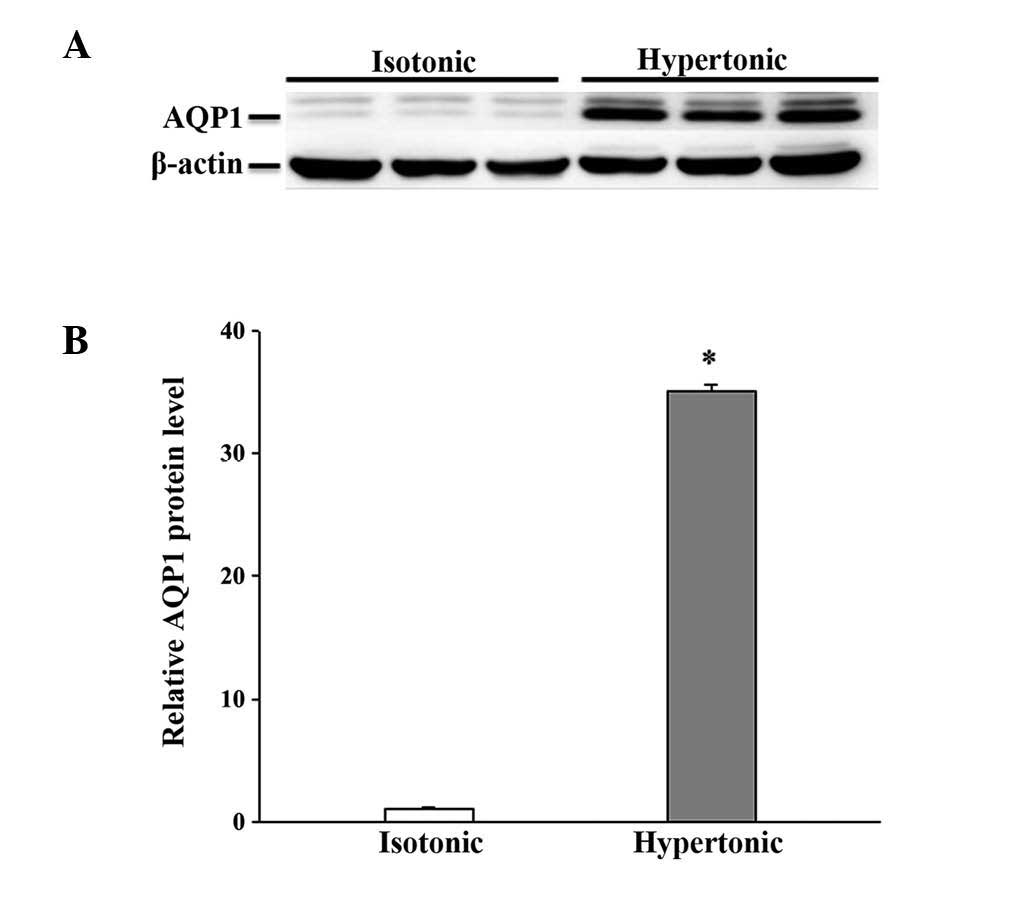
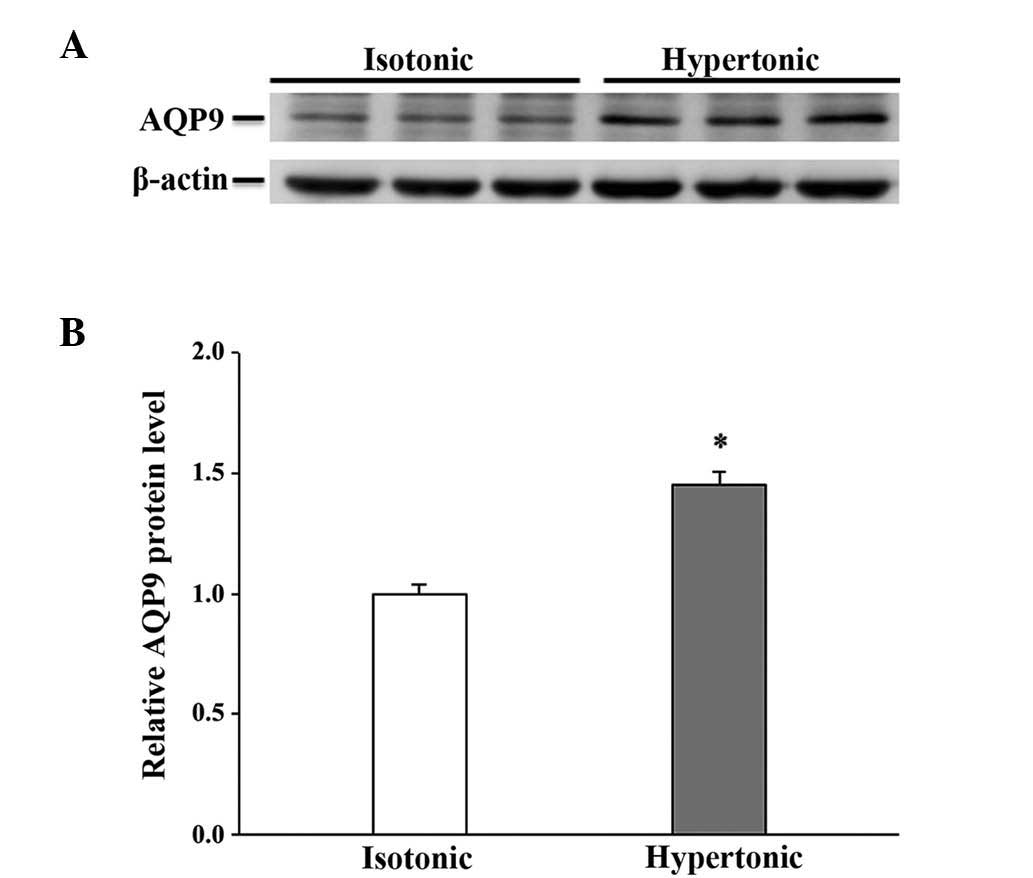
|
1
|
Loo DD, Zeuthen T, Chandy G and Wright EM:
Cotransport of water by the Na+/glucose cotransporter.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:13367–13370. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ma T and Verkman AS: Aquaporin water
channels in gastrointestinal physiology. J Physiol. 517:317–326.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Masyuk AI, Marinelli RA and LaRusso NF:
Water transport by epithelia of the digestive tract.
Gastroenterology. 122:545–562. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Agre P, King LS, Yasui M, Guggino WB,
Ottersen OP, Fujiyoshi Y, Engel A and Nielsen S: Aquaporin water
channels - from atomic structure to clinical medicine. J Physiol.
542:3–16. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nielsen J, Kwon TH, Christensen BM,
Frøkiaer J and Nielsen S: Dysregulation of renal aquaporins and
epithelial sodium channel in lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes
insipidus. Semin Nephrol. 28:227–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nielsen S, Frøkiaer J, Marples D, Kwon TH,
Agre P and Knepper MA: Aquaporins in the kidney: From molecules to
medicine. Physiol Rev. 82:205–244. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rojek A, Praetorius J, Frøkiaer J, Nielsen
S and Fenton RA: A current view of the mammalian aquaglyceroporins.
Annu Rev Physiol. 70:301–327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kwon TH, Nielsen J, Møller HB, Fenton RA,
Nielsen S and Frøkiær J: Aquaporins in the kidney. Aquaporins.
Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Beitz E: 190:(Berlin,
Heidelberg). Springer-Verlag. 95–132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marinelli RA, Tietz PS, Pham LD, Rueckert
L, Agre P and LaRusso NF: Secretin induces the apical insertion of
aquaporin-1 water channels in rat cholangiocytes. Am J Physiol.
276:G280–G286. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matsuzaki T, Tajika Y, Ablimit A, Aoki T,
Hagiwara H and Takata K: Aquaporins in the digestive system. Med
Electron Microsc. 37:71–80. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Laforenza U, Gastaldi G, Grazioli M, Cova
E, Tritto S, Faelli A, Calamita G and Ventura U: Expression and
immunolocalization of aquaporin-7 in rat gastrointestinal tract.
Biol Cell. 97:605–613. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hatakeyama S, Yoshida Y, Tani T, Koyama Y,
Nihei K, Ohshiro K, Kamiie JI, Yaoita E, Suda T, Hatakeyama K and
Yamamoto T: Cloning of a new aquaporin (AQP10) abundantly expressed
in duodenum and jejunum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 287:814–819.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ishibashi K, Morinaga T, Kuwahara M,
Sasaki S and Imai M: Cloning and identification of a new member of
water channel (AQP10) as an aquaglyceroporin. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1576:335–340. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Laforenza U: Water channel proteins in the
gastrointestinal tract. Mol Aspects Med. 33:642–650. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang KS, Ma T, Filiz F, Verkman AS and
Bastidas JA: Colon water transport in transgenic mice lacking
aquaporin-4 water channels. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 279:G463–G470. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang B, Song Y, Zhao D and Verkman AS:
Phenotype analysis of aquaporin-8 null mice. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 288:C1161–C1170. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kwon TH, Hager H, Nejsum LN, Andersen ML,
Frøkiaer J and Nielsen S: Physiology and pathophysiology of renal
aquaporins. Semin Nephrol. 21:231–238. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hara-Chikuma M and Verkman AS: Roles of
aquaporin-3 in the epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 128:2145–2151.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Umenishi F and Schrier RW: Identification
and characterization of a novel hypertonicity-responsive element in
the human aquaporin-1 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
292:771–775. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
García F, Kierbel A, Larocca MC, Gradilone
SA, Splinter P, LaRusso NF and Marinelli RA: The water channel
aquaporin-8 is mainly intracellular in rat hepatocytes, and its
plasma membrane insertion is stimulated by cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem.
276:12147–12152. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kültz D and Burg M: Evolution of osmotic
stress signaling via MAP kinase cascades. J Exp Biol.
201:3015–3021. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schwartz LM and Osborne BA: Programmed
cell death, apoptosis and killer genes. Immunol Today. 14:582–590.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cohen DM, Wasserman JC and Gullans SR:
Immediate early gene and HSP70 expression in hyperosmotic stress in
MDCK cells. Am J Physiol. 261:C594–C601. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Burg MB, Kwon ED and Kültz D: Osmotic
regulation of gene expression. FASEB J. 10:1598–1606.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Blomberg A: Osmoresponsive proteins and
functional assessment strategies in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Electrophoresis. 18:1429–1440. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Burg MB, Ferraris JD and Dmitrieva NI:
Cellular response to hyperosmotic stresses. Physiol Rev.
87:1441–1474. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leitch V, Agre P and King LS: Altered
ubiquitination and stability of aquaporin-1 in hypertonic stress.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:2894–2898. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsukaguchi H, Shayakul C, Berger UV,
Mackenzie B, Devidas S, Guggino WB, van Hoek AN and Hediger MA:
Molecular characterization of a broad selectivity neutral solute
channel. J Biol Chem. 273:24737–24743. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sato Y and Endo T: Alteration of brain
glycoproteins during aging. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 10(Suppl 1):
S32–S40. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Öberg F, Sjöhamn J, Fischer G, Moberg A,
Pedersen A, Neutze R and Hedfalk K: Glycosylation increases the
thermostability of human aquaporin 10 protein. J Biol Chem.
286:31915–31923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sasaki M and Joh T: Oxidative stress and
ischemia-reperfusion injury in gastrointestinal tract and
antioxidant, protective agents. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 40:1–12. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|