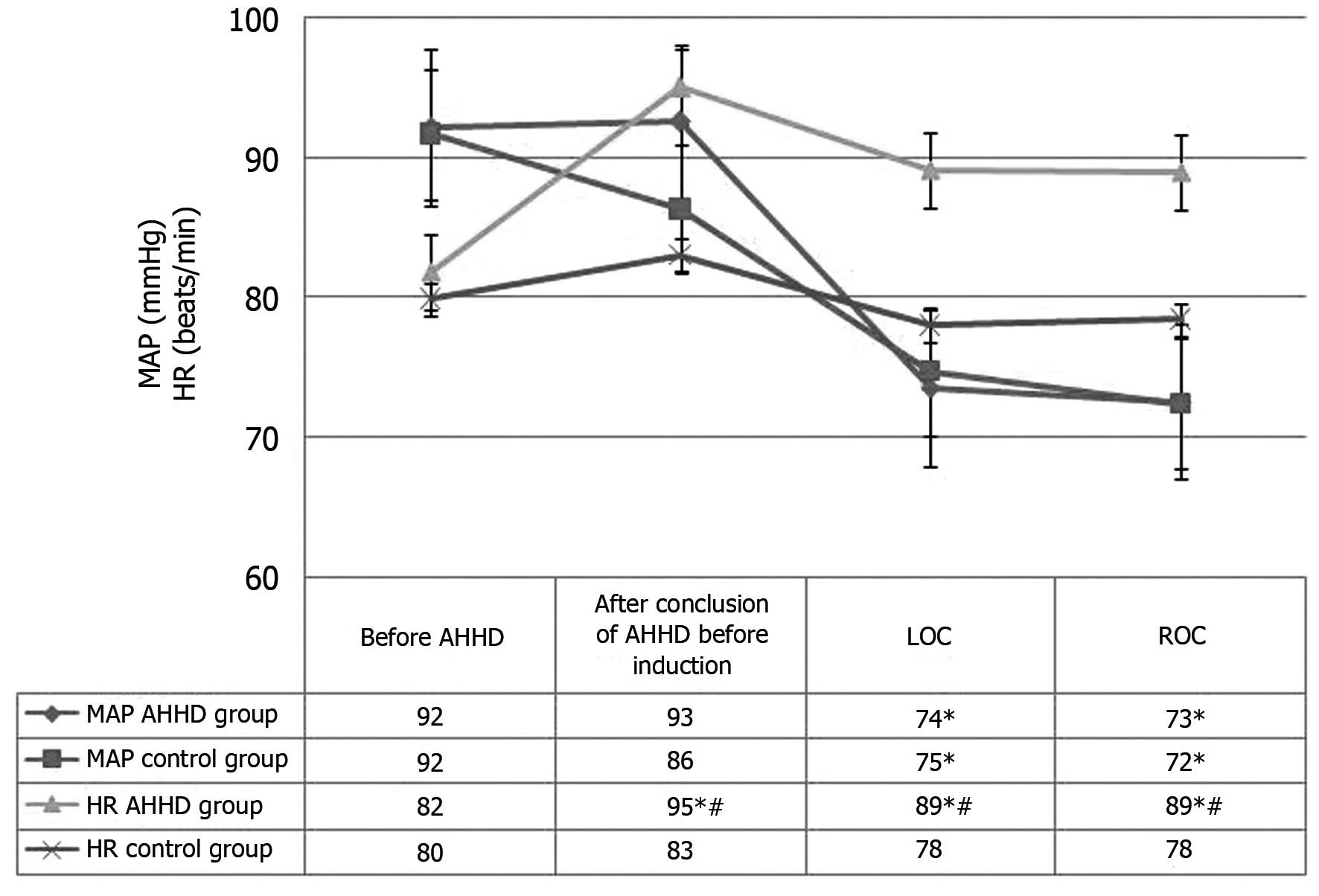
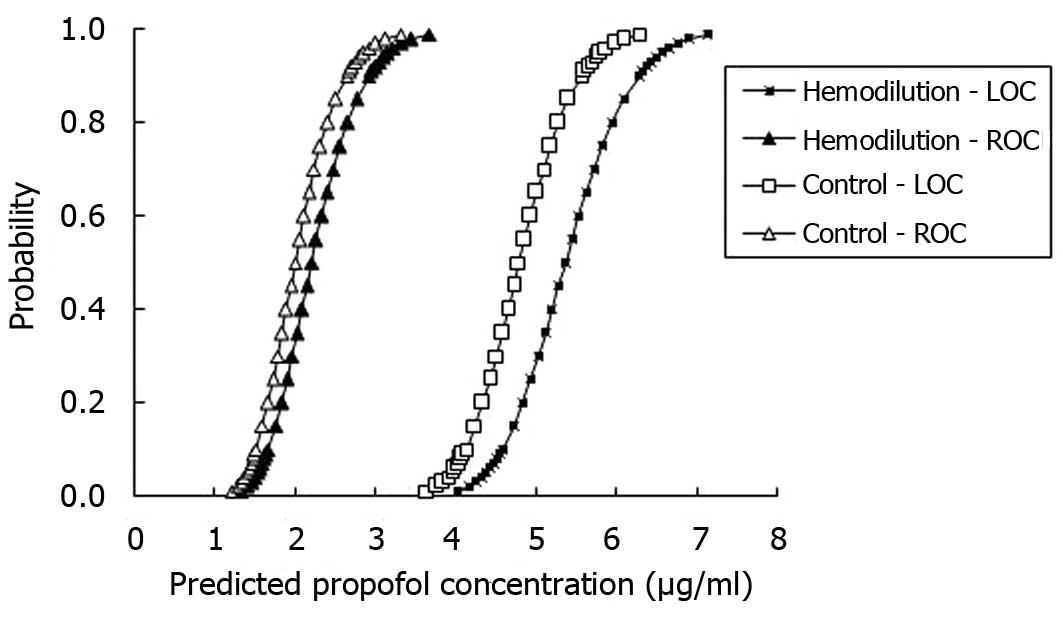
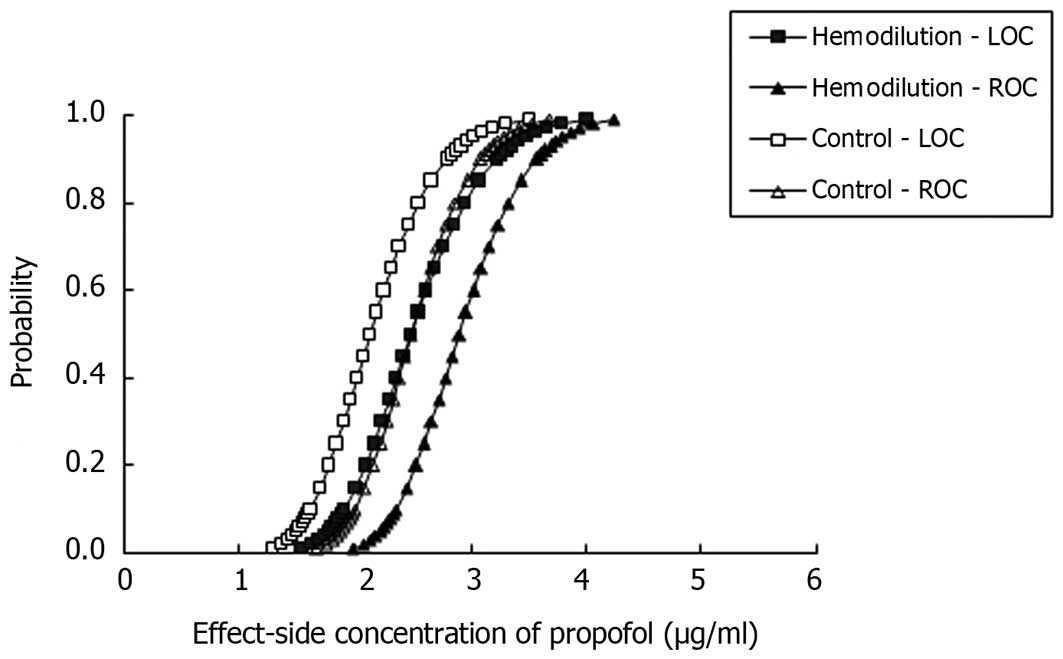
|
1
|
Mielke LL, Entholzner EK, Kling M,
Breinbauer BE, Burgkart R, Hargasser SR and Hipp RF: Preoperative
acute hypervolemic hemodilution with hydroxyethylstarch: An
alternative to acute normovolemic hemodilution? Anesth Analg.
84:26–30. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith I, White PF, Nathanson M and
Gouldson R: Propofol: An update on its clinical use.
Anesthesiology. 81:1005–1043. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liang H, Yang CX, Li H, Liu HZ and Wang
HB: Effects of preoperative acute hypervolemic hemodilution on
hypercoagulability of patients with colon cancer. Ai Zheng.
25:1256–1260. 2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Laks J, Pilon RN, Klovekorn WP, Anderson
W, MacCallum JR and O'Connor NE: Acute hemodilution: Its effects on
hemodynamics and oxygen transport in anesthetized man. Ann Surg.
180:103–109. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van den Oever HL, Dzoljic M, Ince C,
Hollmann MW and Mokken FC: Orthogonal polarization spectral imaging
of the microcirculation during acute hypervolemic hemodilution and
epidural lidocaine injection. Anesth Analg. 103:484–487. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kurdiumova NV, Parfenov AL, Fokin MS,
Grinenko EA, Eliava ShSh, Kheĭreddin AS and Sazonov IA: Intensive
care using hypervolemic hypertensive hemodilution in the acute
period of subarachnoidal hemorrhages in patients with arterial
aneurysms. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2:48–53. 2006.(In
Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saricaoglu F, Akinci SB, Celiker V and
Aypar U: The effect of acute normovolemic hemodilution and acute
hypervolemic hemodilution on coagulation and allogeneic
transfusion. Saudi Med J. 26:792–798. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng H, Wang J, Cao X, Zuo J and Liu J:
Effect of acute hypervolemic hemodilution on the pharmacokinetics
of propofol by target-controlled infusion. Zhonghua Ma Zui Xue Za
Zhi. 24:418–421. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Tauzin-Fin P, Vinçon G, Houdek MC,
Demotes-Mainard F and Muscagorry JM: Pharmacokinetics of propofol
injected after deliberate preoperative hemodilution. Ann Fr Anesth
Reanim. 10:337–342. 1991.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takizawa E, Takizawa D, Hiraoka H, Saito S
and Goto F: Disposition and pharmacodynamics of propofol during
isovolaemic haemorrhage followed by crystalloid resuscitation in
humans. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 61:256–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He M, Gao F and Tian YK: Effect of acute
non-normovolaemic hemodilution on sedation of propofol target
controlled infusion. Lin Chuang Ma Zui Xue Za Zhi. 28:837–840.
2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Tang J, Wu G and Peng L: Pharmacokinetics
of propofol in patients undergoing total hip replacement: Effect of
acute hypervolemic hemodilution. Anaesthesist. 60:835–840. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marsh B, White M, Morton N and Kenny GN:
Pharmacokinetic model driven infusion of propofol in children. Br J
Anaesth. 67:41–48. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kumar R, Chakraborty I and Sehgal R: A
prospective randomized study comparing two techniques of
perioperative blood conservation: Isovolemic hemodilution and
hypervolemic hemodilution. Anesth Analg. 95:1154–1161. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Johnson KB, Egan TD, Kern SE, White JL,
McJames SW, Syroid N and Church T: The influence of hemorrhagic
shock on propofol: a pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis.
Anesthesiology. 99:409–420. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shrewsbury RP, Johnson LW and Oliver SR:
Influence of moderate haemodilution with fluosol or normal saline
on carbaryl disposition in Sprague-Dawley rats. J Pharm Pharmacol.
49:236–240. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hiraoka H, Yamamoto K, Okano N, Morita T,
Goto F and Horiuchi R: Changes in drug plasma concentrations of an
extensively bound and highly extracted drug, propofol, in response
to altered plasma binding. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 75:324–330. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wouters PF, Van de Velde MA, Marcus MA,
Deruyter HA and Van Aken H: Hemodynamic changes during induction of
anesthesia with eltanolone and propofol in dogs. Anesth Analg.
81:125–131. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leslie K, Sessler DI, Bjorksten AR and
Moayeri A: Mild hypothermia alters propofol pharmacokinetics and
increases the duration of action of atracurium. Anesth Analg.
80:1007–1014. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nollert G, Sperling J, Sakamoto T, Jaeger
BR and Jonas RA: Higher hematocrit improves liver blood flow and
metabolism during cardiopulmonary bypass in piglets. Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 49:226–230. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bhattacharya AA, Curry S and Franks NP:
Binding of the general anesthetics propofol and halothane to human
serum albumin high resolution crystal structures. J Biol Chem.
275:38731–38738. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Benet LZ and Hoener B: Changes in plasma
protein binding have little clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 71:115–121. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schuh FT: Influence of haemodilution on
the potency of neuromuscular blocking drugs. Br J Anaesth.
53:263–265. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Katz RL, Stirt J, Murray AL and Lee C:
Neuromuscular effects of atracurium in man. Anesth Analg.
61:730–734. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dahaba AA, Rinnhofer S, Wang G, Xu X, Liu
XY, Wu XM, Rehak PH and Metzler H: Influence of acute normovolaemic
haemodilution on bispectral index monitoring and propofol dose
requirements. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 52:815–820. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Upton RN, Ludbrook GL, Grant C and
Martinez AM: Cardiac output is a determinant of the initial
concentrations of propofol after short-infusion administration.
Anesth Analg. 89:545–552. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Myburgh JA, Upton RN, Grant C and Martinez
A: Epinephrine, norepinephrine and dopamine infusions decrease
propofol concentrations during continuous propofol infusion in an
ovine model. Intensive care med. 27:276–282. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kurita T, Morita K, Kazama T and Sato S:
Influence of cardiac output on plasma propofol concentrations
during constant infusion in swine. Anesthesiology. 96:1498–1503.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Glen JB: The development of ‘Diprifusor’:
A TCI system for propofol. Anesthesia. 53(Suppl 1): 13–21. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Swinhoe CF, Peacock JE, Glen JB and Reilly
CS: Evaluation of the predictive performance of a ‘Diprifusor’ TCI
system. Anaesthesia. 53(Suppl 1): 61–67. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Irwin MG, Hui TW, Milne SE and Kenny GN:
Propofol effective concentration 50 and its relationship to
bispectral index. Anaesthesia. 57:242–248. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Smith C, McEwan AI, Jhaveri R, Wilkinson
M, Goodman D, Smith LR, Canada AT and Glass PS: The interaction of
fentanyl on the Cp50 of propofol for loss of consciousness and skin
incision. Anesthesiology. 81:820–828. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
White M and Kenny GN: Intravenous propofol
anesthesia using a computerized infusion system. Anaesthesia.
45:204–209. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shafer SL and Gregg KM: Algorithms to
rapidly achieve and maintain stable drug concentrations at the site
of drug effect with a computer-controlled infusion pump. J
Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 20:147–169. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wilkes NJ, Woolf R, Mutch M, Mallett SV,
Peachey T, Stephens R and Mythen MG: The effects of balanced versus
saline-based hetastarch and crystalloid solutions on acid-base and
electrolyte status and gastric mucosal perfusion in elderly
surgical patients. Anesth Analg. 93:811–816. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|