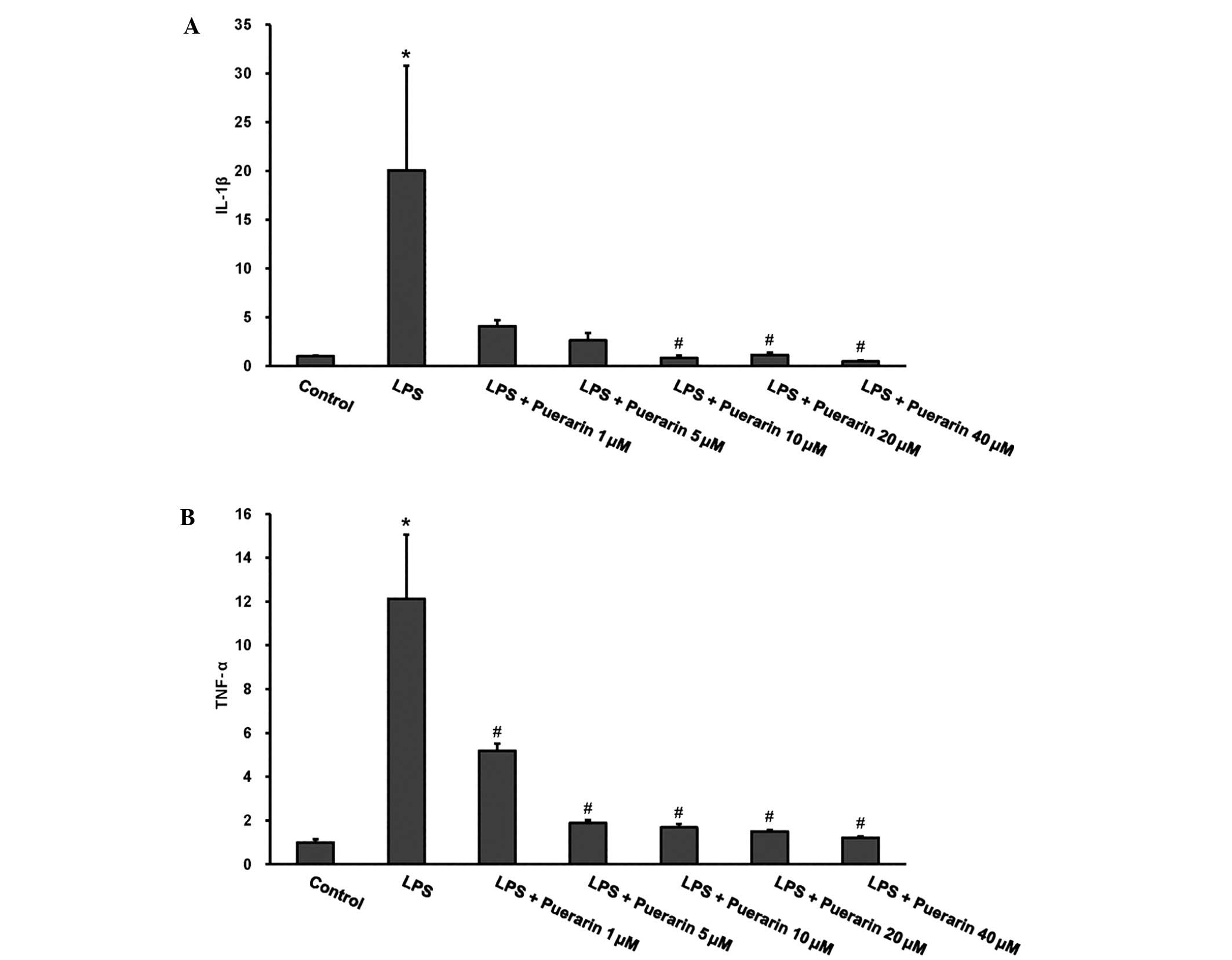
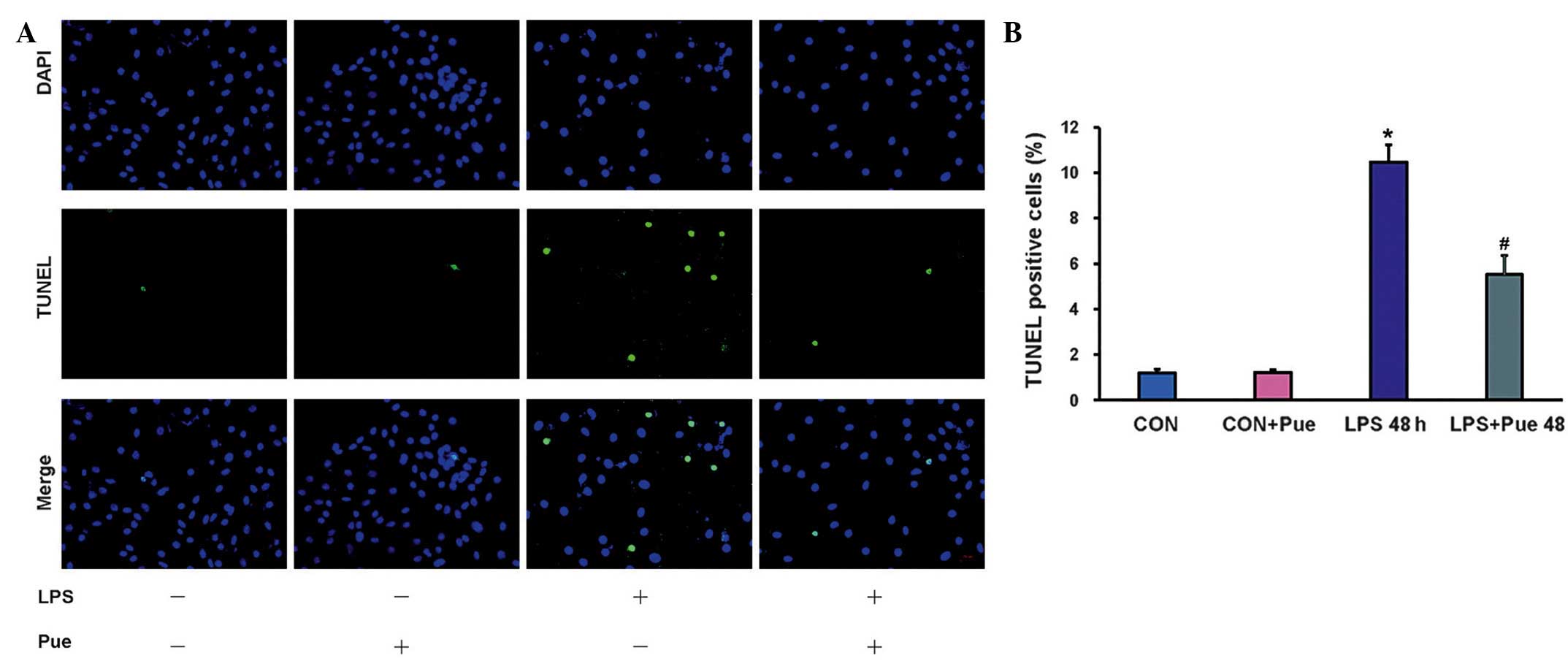
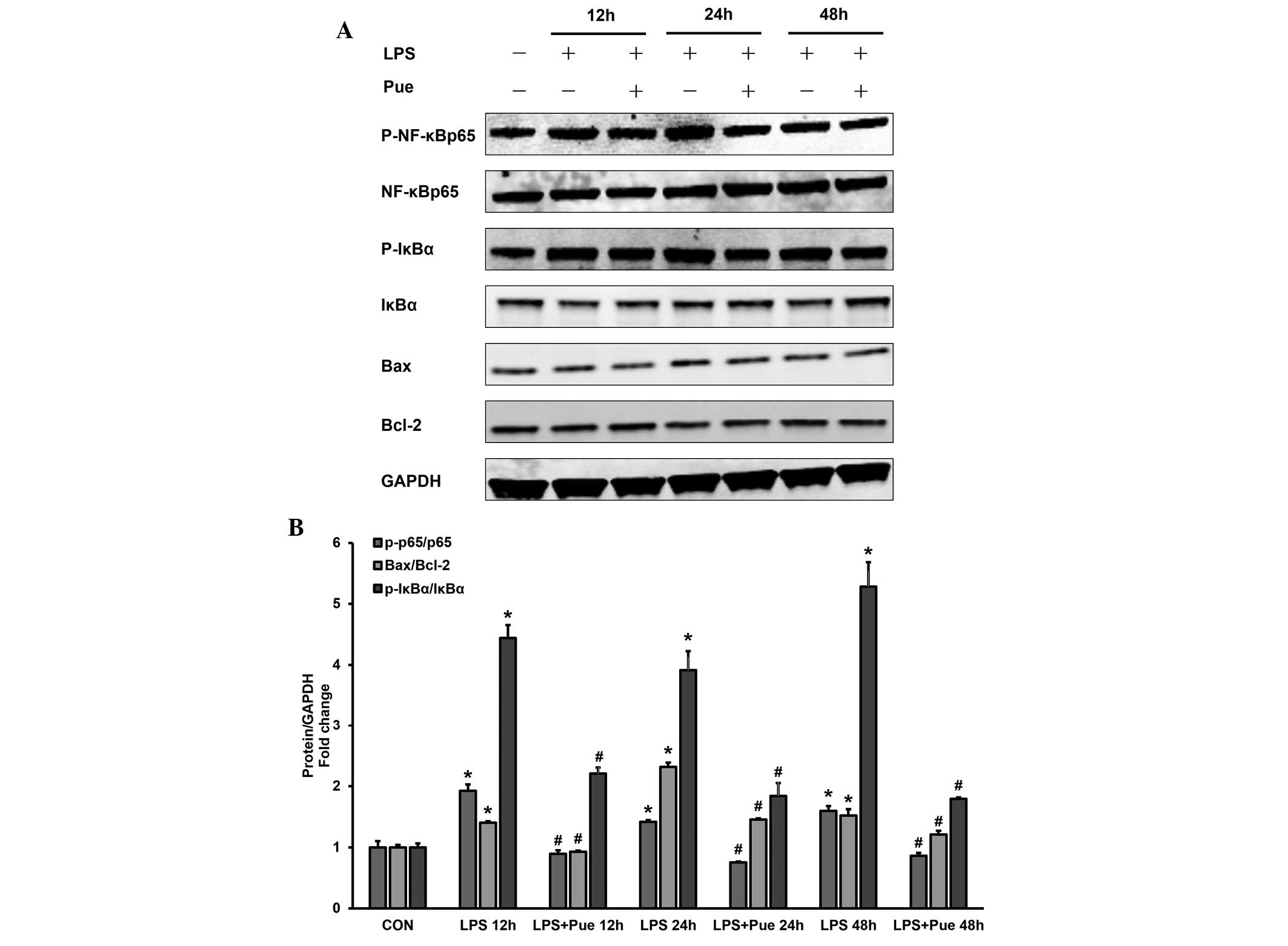
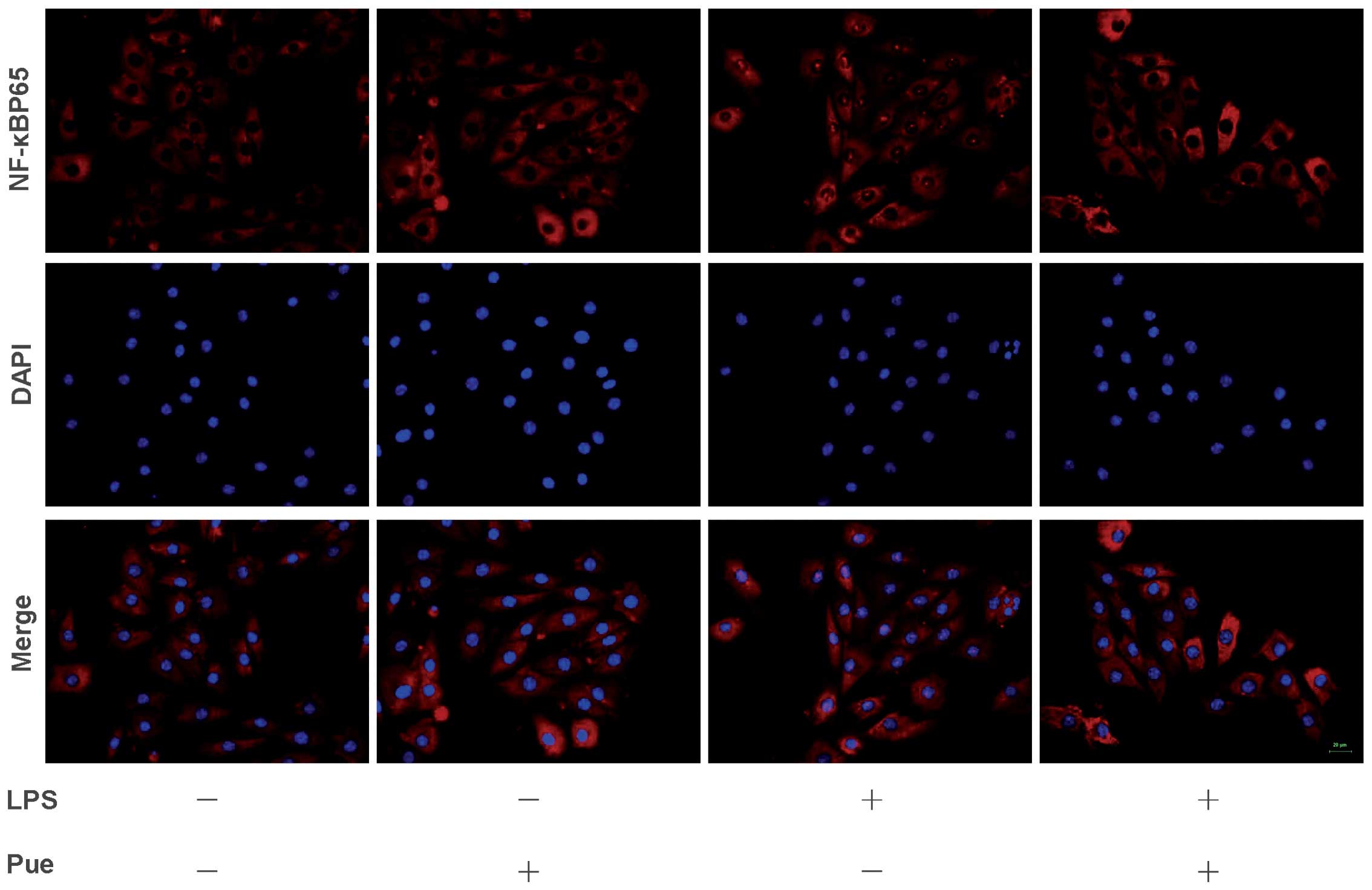
|
1
|
Murray CJ, Atkinson C, Bhalla K, Birbeck
G, Burstein R, Chou D, Dellavalle R, Danaei G, Ezzati M, Fahimi A,
et al: The state of US health, 1990-2010: Burden of diseases,
injuries, and risk factors. JAMA. 310:591–608. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S and Moss M:
The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through
2000. N Engl J Med. 348:1546–1554. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tupchong K, Koyfman A and Foran M: Sepsis,
severe sepsis, and septic shock, A review of the literature.
African J Emerg Med. 5:127–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Romero-Bermejo FJ, Ruiz-Bailen M,
Gil-Cebrian J and Huertos-Ranchal MJ: Sepsis-induced
cardiomyopathy. Curr Cardiol Rev. 7:163–183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rudiger A and Singer M: The heart in
sepsis: From basic mechanisms to clinical management. Curr Vasc
Pharmacol. 11:187–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seymour CW and Rosengart MR: Septic Shock:
Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA. 314:708–717. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Plociennikowska A, Hromada-Judycka A,
Borzecka K and Kwiatkowska K: Co-operation of TLR4 and raft
proteins in LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 72:557–581. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Charalambous BM, Stephens RC, Feavers IM
and Montgomery HE: Role of bacterial endotoxin in chronic heart
failure, The gut of the matter. Shock. 28:15–23. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Frazier WJ, Xue J, Luce WA and Liu Y: MAPK
signaling drives inflammation in LPS-stimulated cardiomyocytes, The
route of crosstalk to G-protein-coupled receptors. PLoS One.
7:e500712012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou YX, Zhang H and Peng C: Puerarin: A
review of pharmacological effects. Phytother Res. 28:961–975. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen R, Xue J and Xie M: Puerarin prevents
isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in mice by reduction of
myocardial TGF-β1 expression. J Nutr Biochem. 23:1080–1085. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu G, Wang X, Wu S, Li X and Li Q:
Neuroprotective effects of puerarin on
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine induced Parkinson's
disease model in mice. Phytother Res. 28:179–186. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang JW, Wang HD, Cong ZX, Zhou XM, Xu JG,
Jia Y and Ding Y: Puerarin ameliorates oxidative stress in a rodent
model of traumatic brain injury. J Surg Res. 186:328–337. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh AK, Jiang Y, Gupta S, Younus M and
Ramzan M: Anti-inflammatory potency of nano-formulated puerarin and
curcumin in rats subjected to the lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammation. J Med Food. 16:899–911. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kapoor S: Anti-neoplastic effects of
puerarin in systemic malignancies besides colon carcinomas. Int J
Pharm. 443:3062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu K, Liang T, Duan X, Xu L, Zhang K and
Li R: Anti-diabetic effects of puerarin, isolated from Pueraria
lobata (Willd.), on streptozotocin-diabetogenic mice through
promoting insulin expression and ameliorating metabolic function.
Food Chem Toxicol. 60:341–347. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuan Y, Zong J, Zhou H, Bian ZY, Deng W,
Dai J, Gan HW, Yang Z, Li H and Tang QZ: Puerarin attenuates
pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy. J Cardiol. 63:73–81.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu X, Jia B, Wang F, Lv X, Peng X, Wang Y,
Li H, Wang Y, Lu D and Wang H: α1 Adrenoceptor activation by
norepinephrine inhibits LPS-induced cardiomyocyte TNF-α production
via modulating ERK1/2 and NF-kappaB pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
18:263–273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Beraud AS, Guillamet CV, Hammes JL, Meng
L, Nicolls MR and Hsu JL: Efficacy of transthoracic
echocardiography for diagnosing heart failure in septic shock. Am J
Med Sci. 347:295–298. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lemarie J, Blet A, Bouazza Y,
Boisrame-Helms J, Meziani F and Levy B: Dexamethasone and
recombinant human activated protein C improve myocardial function
and efficiency during experimental septic shock. Shock. 41:522–527.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ha T, Xia Y, Liu X, Lu C, Liu L, Kelley J,
Kalbfleisch J, Kao RL, Williams DL and Li C: Glucan phosphate
attenuates myocardial HMGB1 translocation in severe sepsis through
inhibiting NF-κB activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
301:H848–H855. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ceylan-Isik AF, Zhao P, Zhang B, Xiao X,
Su G and Ren J: Cardiac overexpression of metallothionein rescues
cardiac contractile dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress
but not autophagy in sepsis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:367–378. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fallach R, Shainberg A, Avlas O, Fainblut
M, Chepurko Y, Porat E and Hochhauser E: Cardiomyocyte Toll-like
receptor 4 is involved in heart dysfunction following septic shock
or myocardial ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:1236–1244. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li X, Luo R, Jiang R, Meng X, Wu X, Zhang
S and Hua W: The role of the Hsp90/Akt pathway in myocardial
calpain-induced caspase-3 activation and apoptosis during sepsis.
BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 13:82013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alladi PA, Roy T, Singh N and Wadhwa S:
Prenatal auditory enrichment with species-specific calls and sitar
music modulates expression of Bcl-2 and Bax to alter programmed
cell death in developing chick auditory nuclei. Int J Dev Neurosci.
23:363–373. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tichý A: Apoptotic machinery: T he Bcl-2
family proteins in the role of inspectors and superintendents. Acta
Medica (Hradec Kralove). 49:13–18. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen G, Zhao J, Yin Y, Wang B, Liu Q, Li
P, Zhao L and Zhou H: C-type natriuretic peptide attenuates
LPS-induced endothelial activation, Involvement of p38, Akt and
NF-kappaB pathways. Amino Acids. 46:2653–2663. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Walley KR: Deeper understanding of
mechanisms contributing to sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction.
Crit Care. 18:1372014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baeuerle PA and Baltimore D: I kappaB: A
specific inhibitor of the NF-kappaB transcription factor. Science.
242:540–546. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grilli M, Chiu JJ and Lenardo MJ:
NF-kappaB and Rel, Participants in a multiform transcriptional
regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 143:1–62. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Muller JM, Ziegler-Heitbrock HW and
Baeuerle PA: Nuclear factor kappaB, a mediator of
lipopolysaccharide effects. Immunobiology. 187:233–256. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|