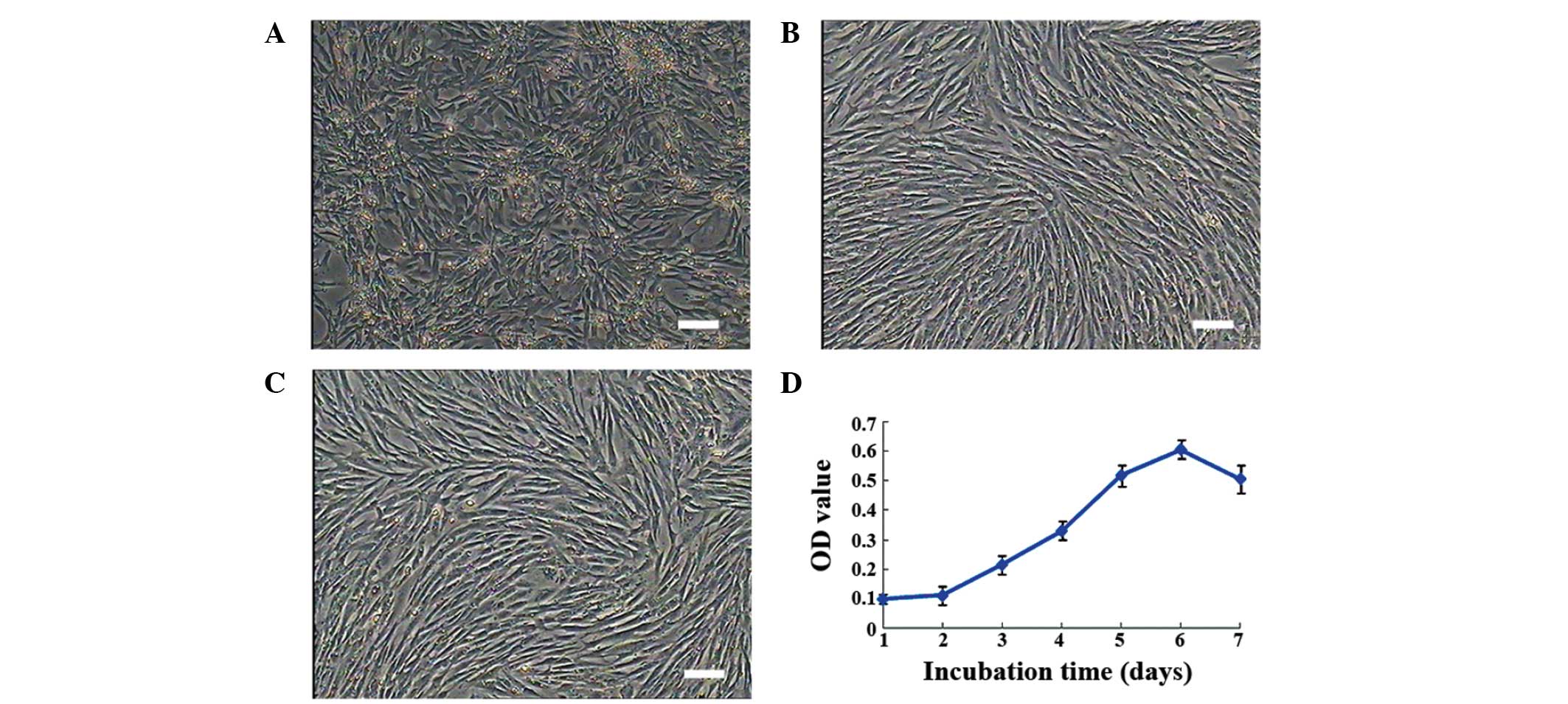
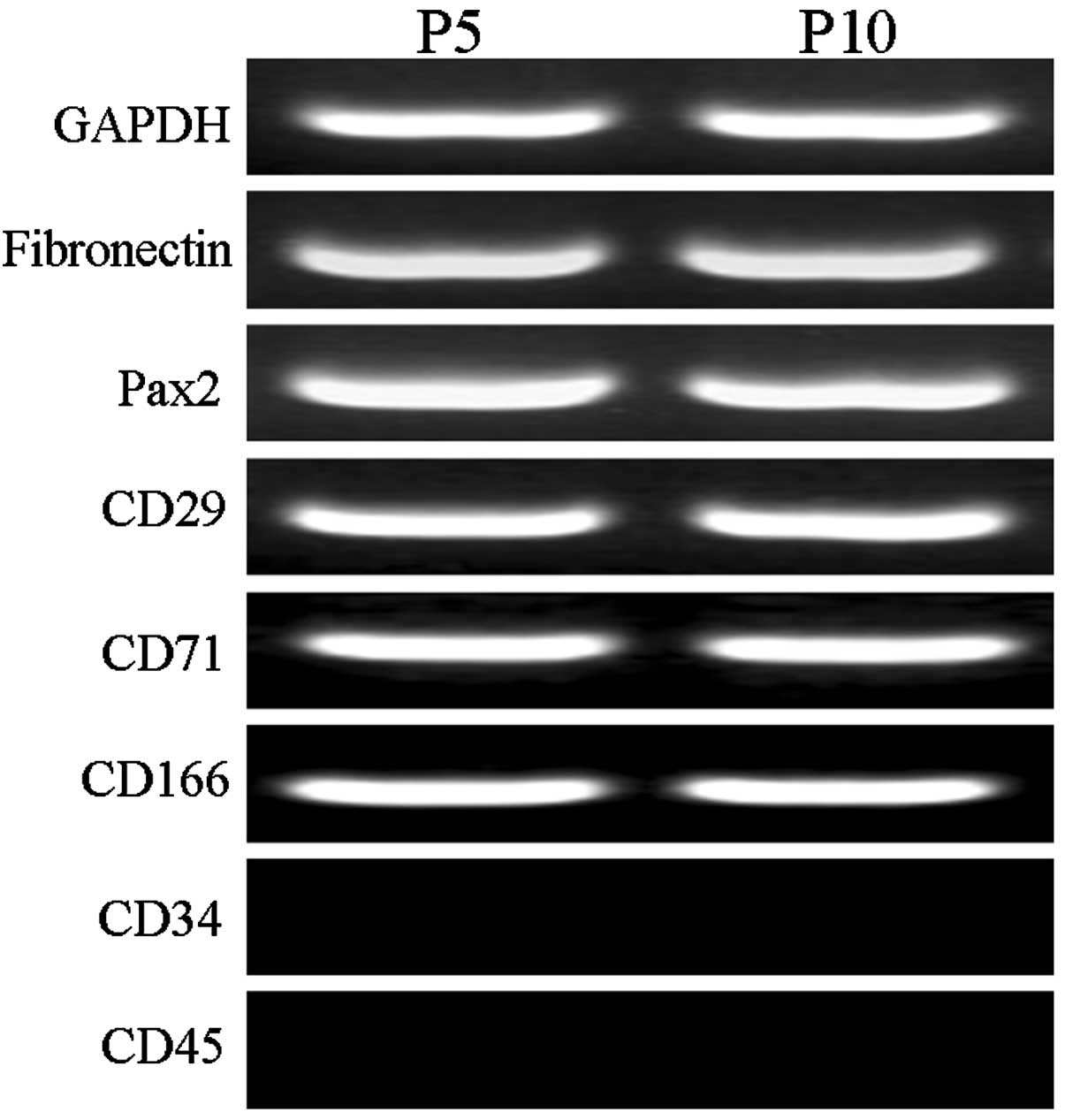
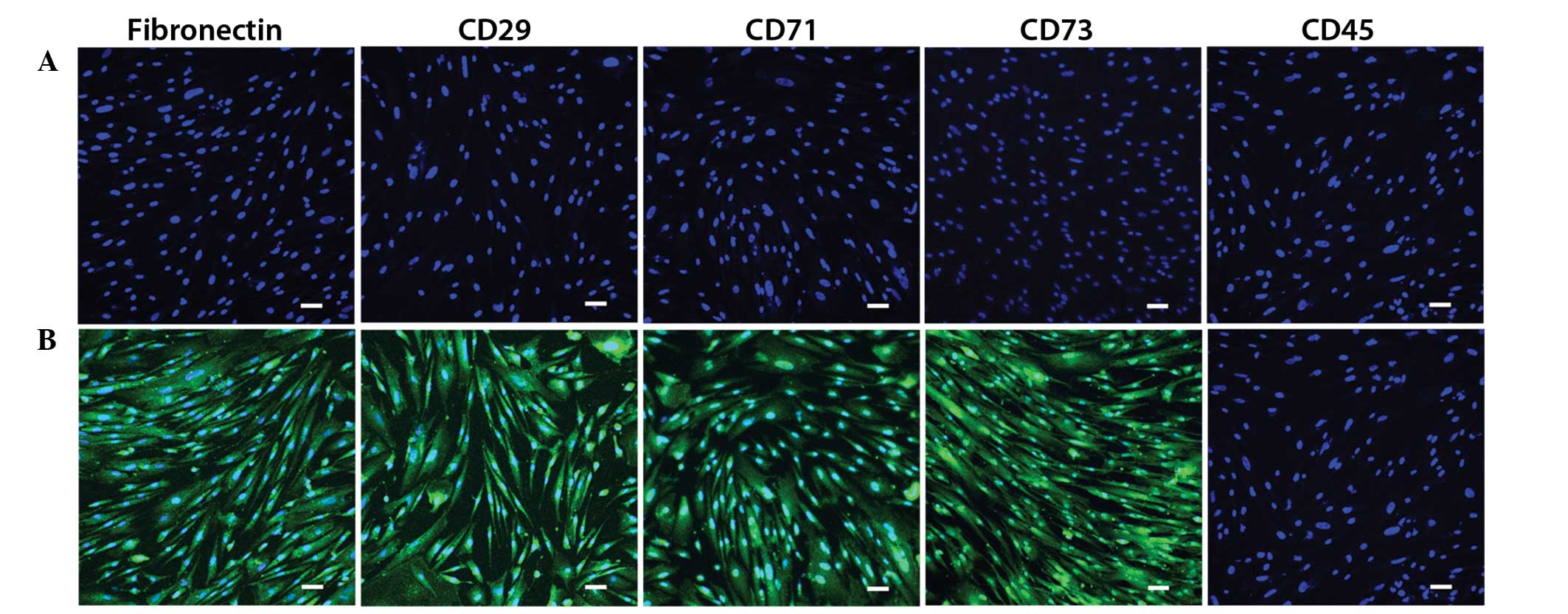
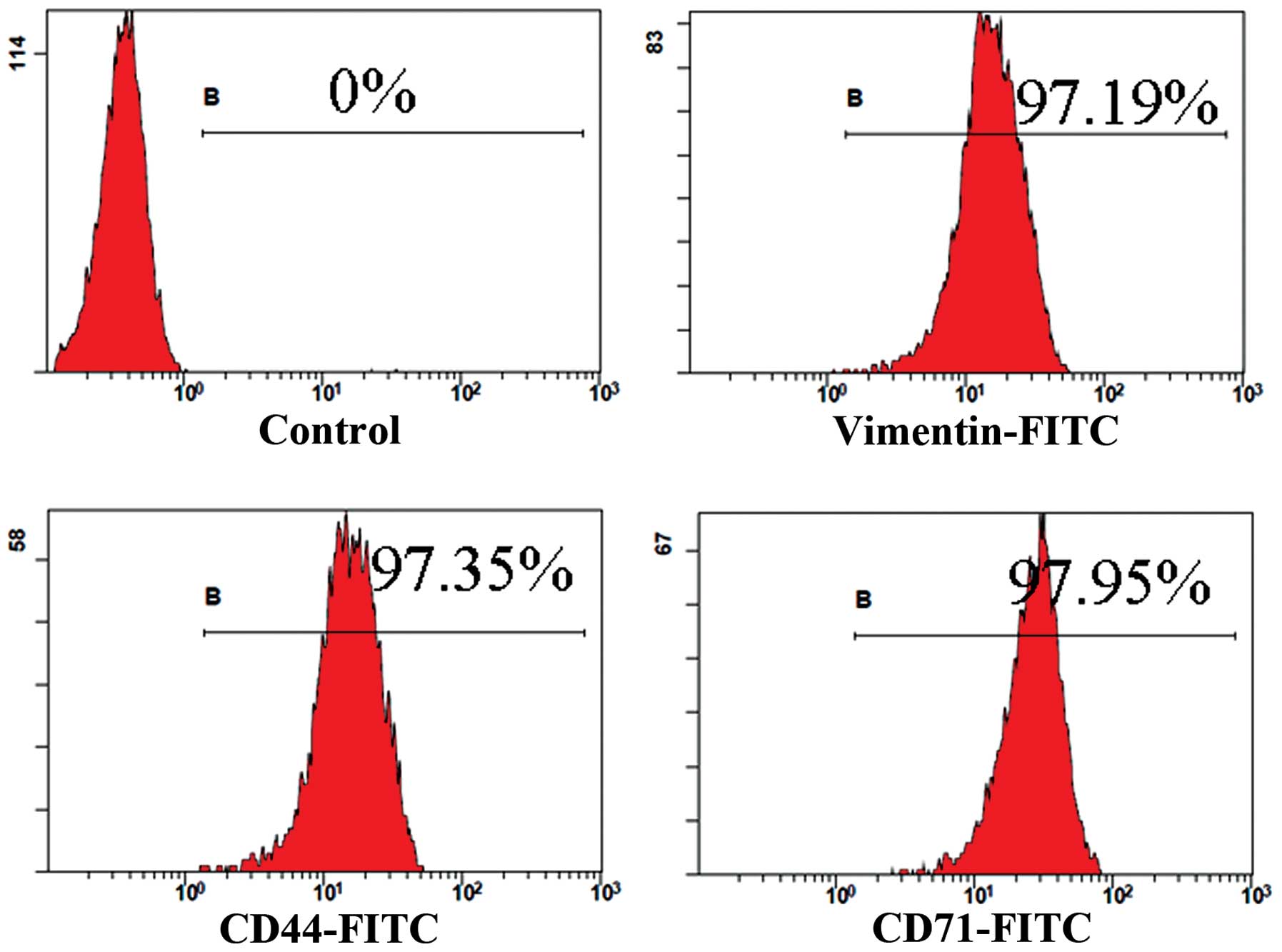
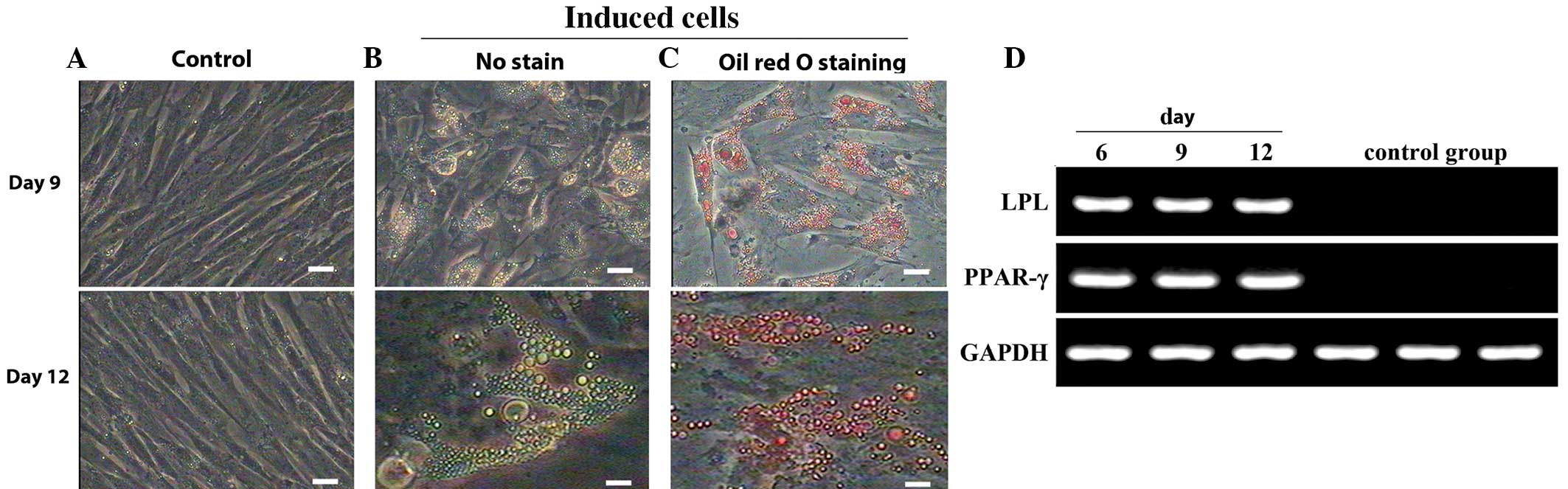
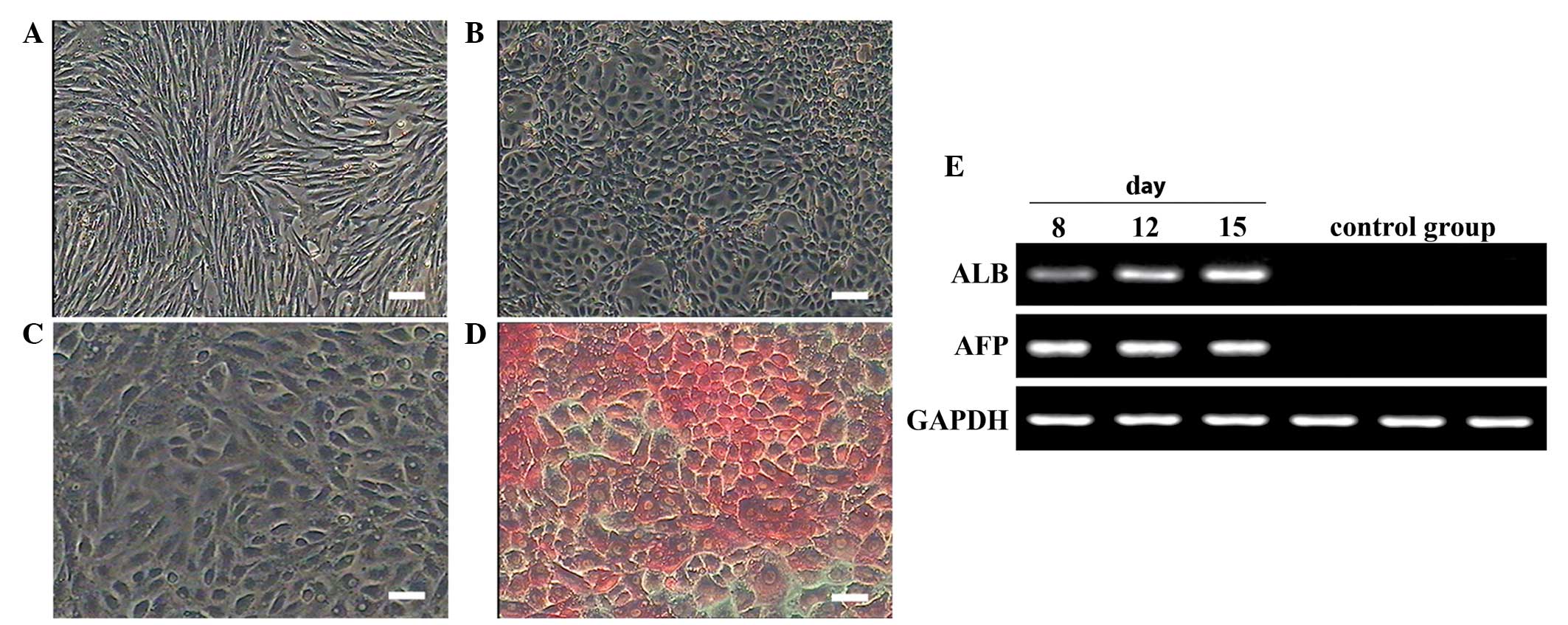
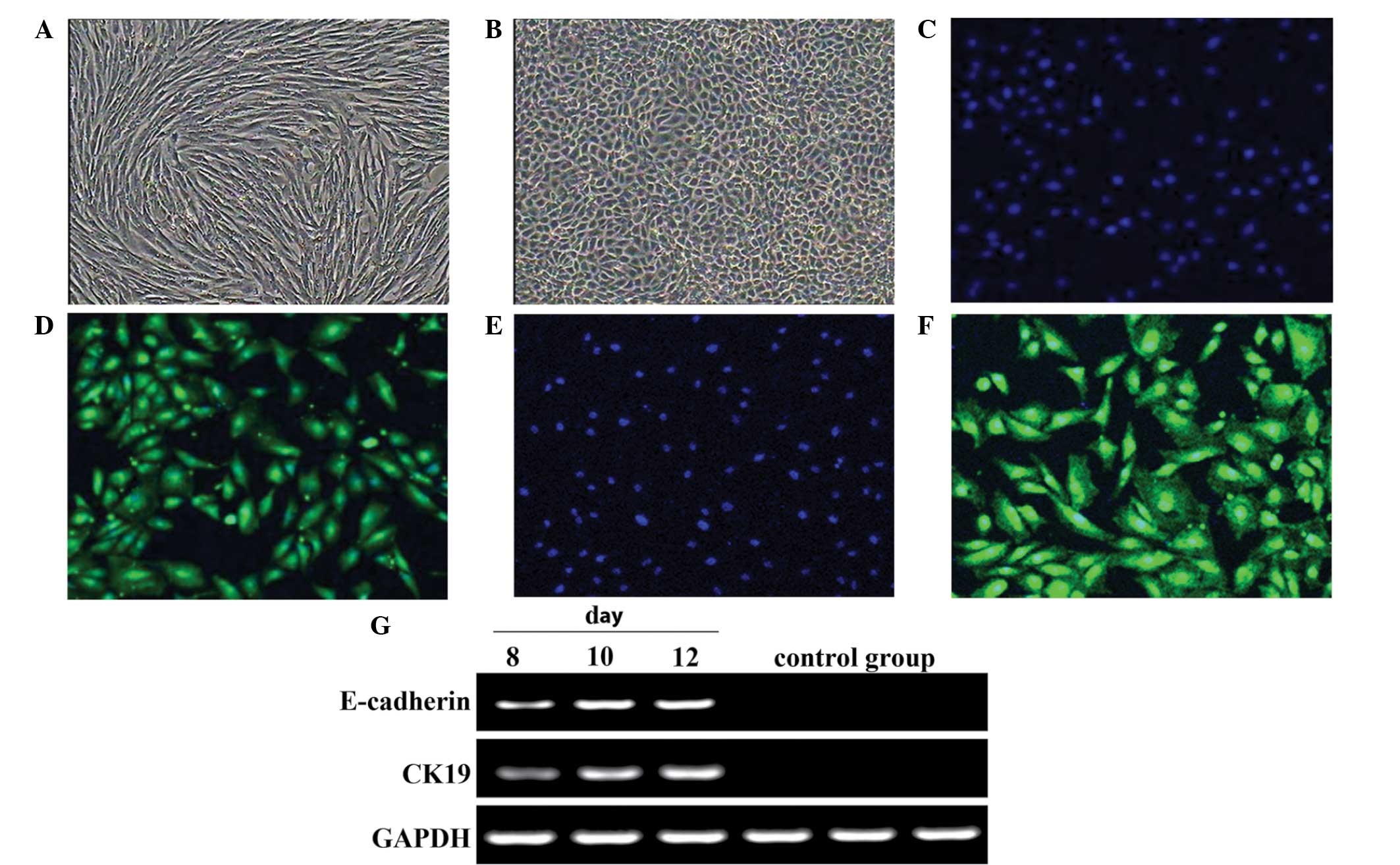
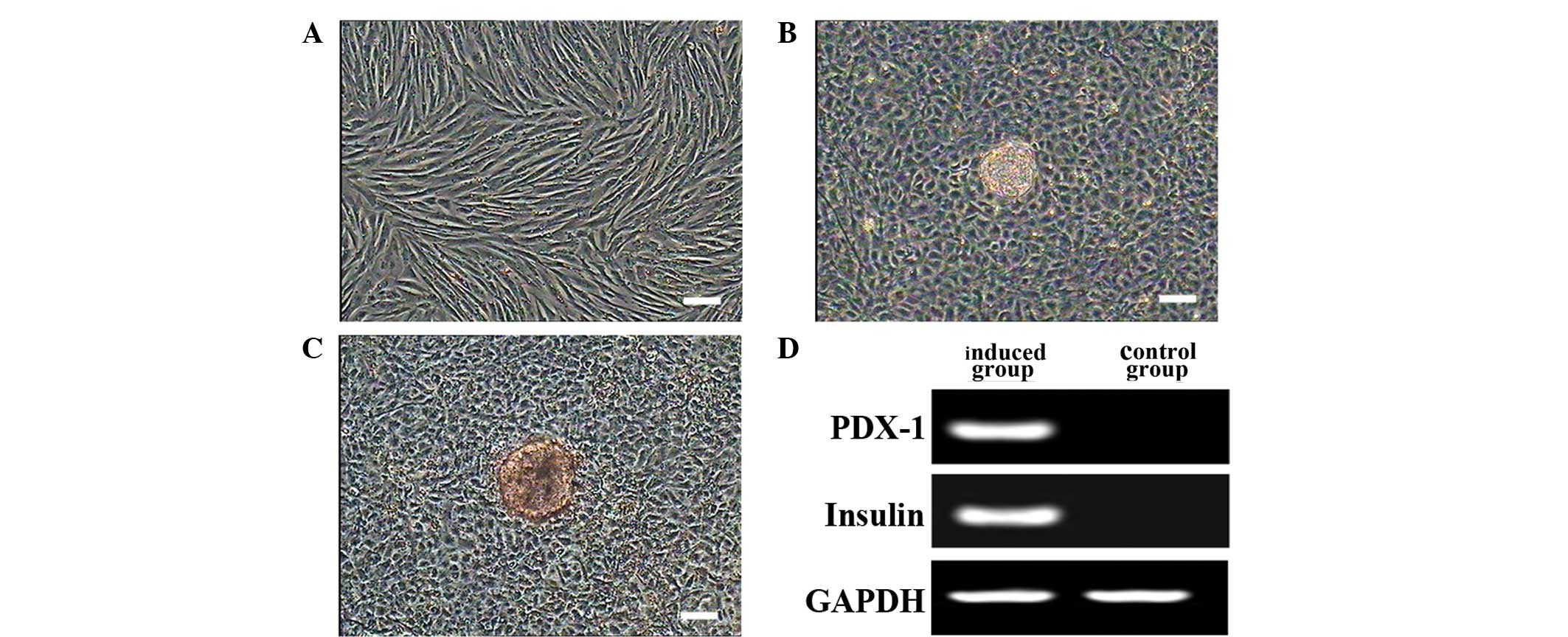
|
1
|
Salgado AJ, Oliveira JT, Pedro AJ and Reis
RL: Adult stem cells in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Curr
Stem Cell Res Ther. 1:345–364. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ding DC, Shyu WC and Lin SZ: Mesenchymal
stem cells. Cell Transplant. 20:5–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tocci A and Forte L: Mesenchymal stem
cell: Use and perspectives. Hematol J. 4:92–96. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cooper K and Viswanathan C: Establishment
of a mesenchymal stem cell bank. Stem Cells Int. 2011:9056212011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gao Y, Bai C, Xiong H, Li Q, Shan Z, Huang
L, Ma Y and Guan W: Isolation and characterization of chicken
dermis-derived mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells. Biomed Res Int.
2013:6262582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Duffield JS, Park KM, Hsiao LL, Kelley VR,
Scadden DT, Ichimura T and Bonventre JV: Restoration of tubular
epithelial cells during repair of the postischemic kidney occurs
independently of bone marrow-derived stem cells. J Clin Invest.
115:1743–1755. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brown WR, Hubbard SJ, Tickle C and Wilson
SA: The chicken as a model for large-scale analysis of vertebrate
gene function. Nat Rev Genet. 4:87–98. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Deans RJ and Moseley AB: Mesenchymal stem
cells: Biology and potential clinical uses. Exp Hematol.
28:875–884. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baddoo M, Hill K, Wilkinson R, Gaupp D,
Hughes C, Kopen GC and Phinney DG: Characterization of mesenchymal
stem cells isolated from murine bone marrow by negative selection.
J Cell Biochem. 89:1235–1249. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang W, Zhang F, Shi H, Tan R, Han S, Ye
G, Pan S, Sun F and Liu X: Comparisons of rabbit bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cell isolation and culture methods in
vitro. PloS One. 9:e887942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fong CY, Richards M, Manasi N, Biswas A
and Bongso A: Comparative growth behaviour and characterization of
stem cells from human Wharton's jelly. Reprod Biomed Online.
15:708–718. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Colter DC, Sekiya I and Prockop DJ:
Identification of a subpopulation of rapidly self-renewing and
multipotential adult stem cells in colonies of human marrow stromal
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:7841–7845. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bühring HJ, Battula VL, Treml S, Schewe B,
Kanz L and Vogel W: Novel markers for the prospective isolation of
human MSC. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1106:262–271. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu Y, Liao L, Wang Q, Ma L, Ma G, Jiang X
and Zhao RC: Isolation and identification of mesenchymal stem cells
from human fetal pancreas. J Lab Clin Med. 141:342–349. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu LL, Liu YJ, Yang SG, Zhao QJ, Wang X,
Gong W, Han ZB, Xu ZS, Lu YX, Liu D, et al: Isolation and
characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials.
Haematologica. 91:1017–1026. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huss R, Lange C, Weissinger EM, Kolb HJ
and Thalmeier K: Evidence of peripheral blood-derived,
plastic-adherent CD34(−/low) hematopoietic stem cell clones with
mesenchymal stem cell characteristics. Stem Cells. 18:252–260.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uppalapati D, Ohta N, Zhang Y, Kawabata A,
Pyle MM, Becker KG, Troyer D and Tamura M: Identification and
characterization of unique tumoricidal genes in rat umbilical cord
matrix stem cells. Mol Pharm. 8:1549–1558. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Păunescu V, Deak E, Herman D, Siska IR,
Tănasie G, Bunu C, Anghel S, Tatu CA, Oprea TI, Henschler R, et al:
In vitro differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to
epithelial lineage. J Cell Mol Med. 11:502–508. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thirumala S, Gimble JM and Devireddy RV:
Evaluation of methylcellulose and dimethyl sulfoxide as the
cryoprotectants in a serum-free freezing media for cryopreservation
of adipose-derived adult stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 19:513–522.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Poloni A, Maurizi G, Leoni P, Serrani F,
Mancini S, Frontini A, Zingaretti MC, Siquini W, Sarzani R and
Cinti S: Human dedifferentiated adipocytes show similar properties
to bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev.
30:965–974. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lysy PA, Smets F, Najimi M and Sokal EM:
Leukemia inhibitory factor contributes to hepatocyte-like
differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.
Differentiation. 76:1057–1067. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
DiRenzo J, Signoretti S, Nakamura N,
Rivera-Gonzalez R, Sellers W, Loda M and Brown M: Growth factor
requirements and basal phenotype of an immortalized mammary
epithelial cell line. Cancer Res. 62:89–98. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chao KC, Chao KF, Fu YS and Liu SH:
Islet-like clusters derived from mesenchymal stem cells in
Wharton's Jelly of the human umbilical cord for transplantation to
control type 1 diabetes. PloS One. 3:e14512008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rao MS and Mattson MP: Stem cells and
aging: Expanding the possibilities. Mech Ageing Dev. 122:713–734.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaufman DS, Hanson ET, Lewis RL, Auerbach
R and Thomson JA: Hematopoietic colony-forming cells derived from
human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:10716–10721.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Wei X, Ling J, Huang Y, Gong Q and
Huo Y: Identification and characterization of side population cells
from adult human dental pulp after ischemic culture. J Endod.
38:1489–1497. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lindenmair A, Hatlapatka T, Kollwig G,
Hennerbichler S, Gabriel C, Wolbank S, Redl H and Kasper C:
Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells from amnion and umbilical cord
tissue and their potential for clinical applications. Cells.
1:1061–1088. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lorenz K, Sicker M, Schmelzer E, Rupf T,
Salvetter J, Schulz-Siegmund M and Bader A: Multilineage
differentiation potential of human dermal skin-derived fibroblasts.
Exp Dermatol. 17:925–932. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pera EM, Ikeda A, Eivers E and De Robertis
EM: Integration of IGF, FGF, and anti-BMP signals via Smad1
phosphorylation in neural induction. Genes Dev. 17:3023–3028. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alkhalidi HM and Alhumaidy AA: Cystic
panfolliculoma of the scalp: Report of a very rare case and brief
review. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 56:437–439. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li HY, Chen YJ, Chen SJ, Kao CL, Tseng LM,
Lo WL, Chang CM, Yang DM, Ku HH, Twu NF, et al: Induction of
insulin-producing cells derived from endometrial mesenchymal
stem-like cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 335:817–829. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zanini C, Bruno S, Mandili G, Baci D,
Cerutti F, Cenacchi G, Izzi L, Camussi G and Forni M:
Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from pancreatic
islets and bone marrow into islet-like cellphenotype. PLoS One.
6:e281752011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|