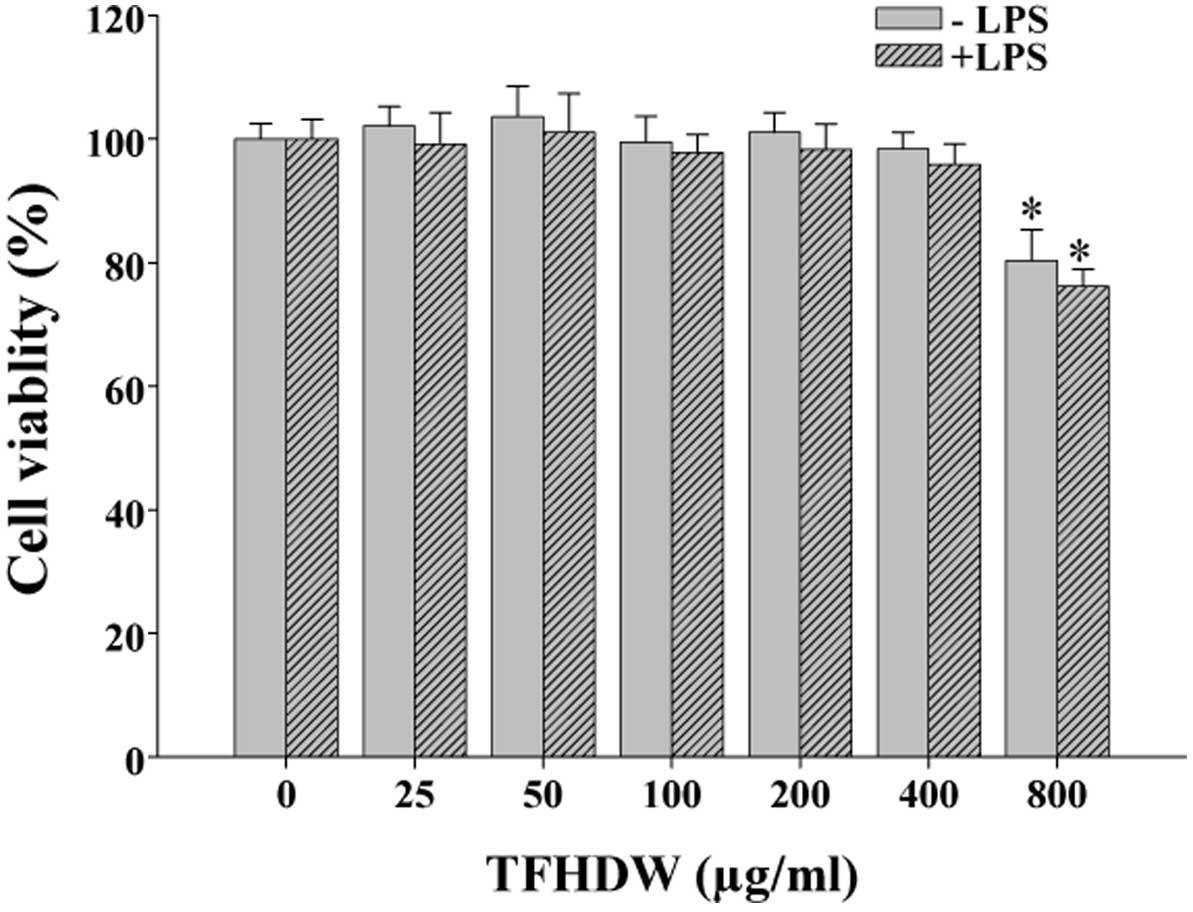
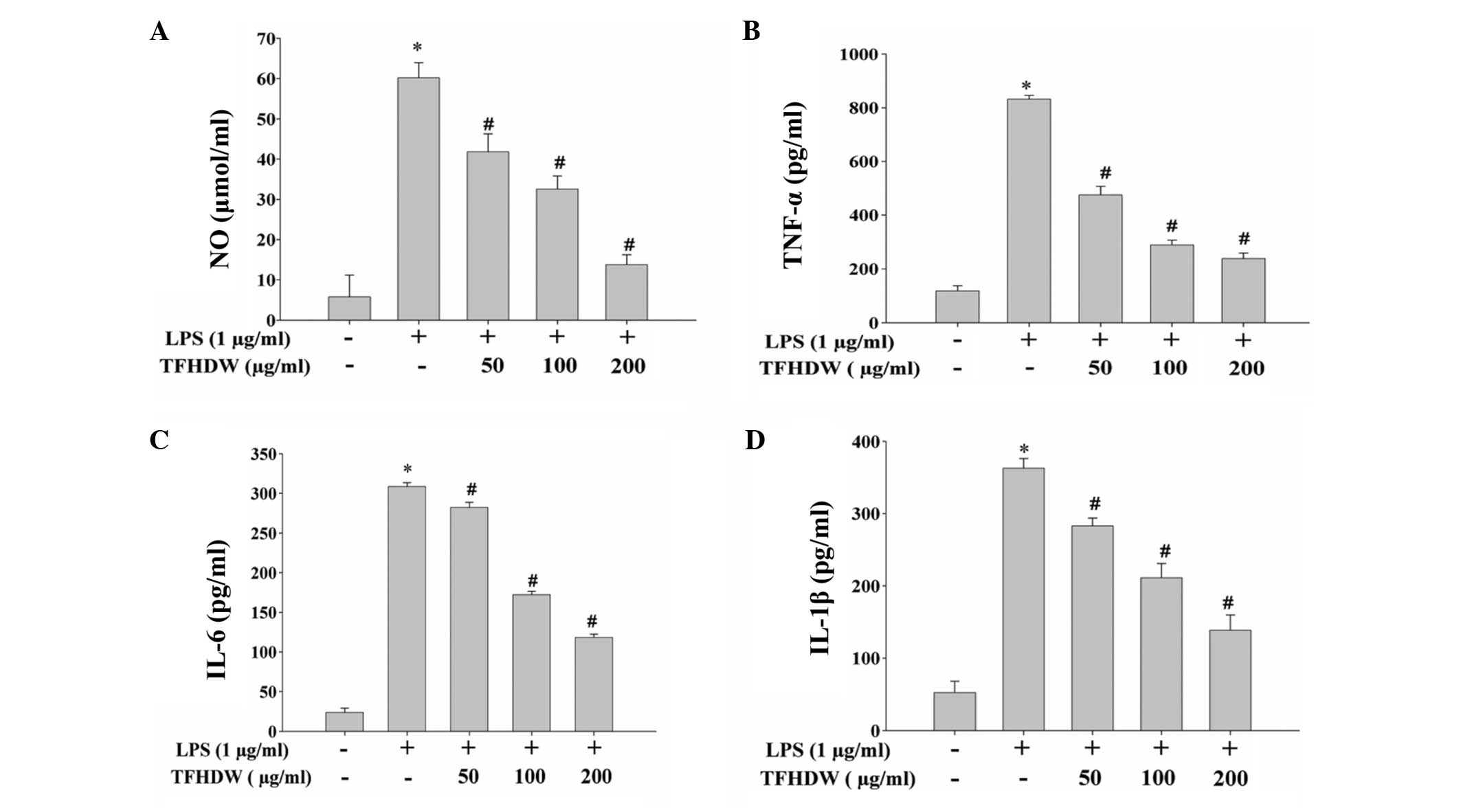
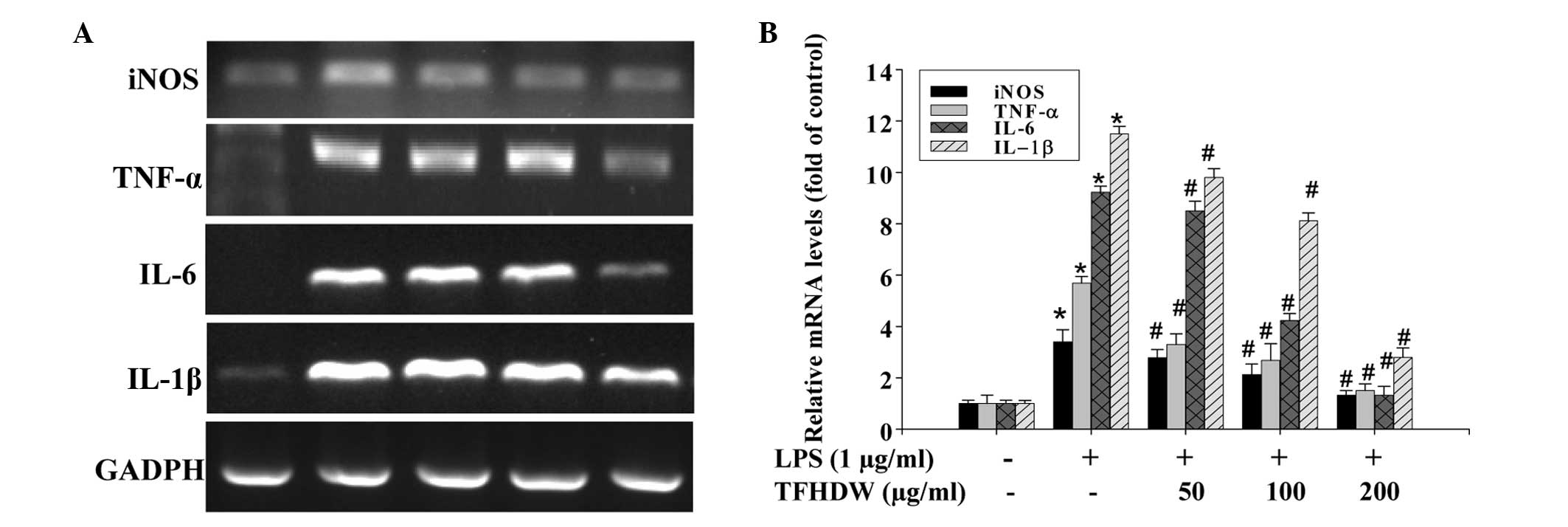
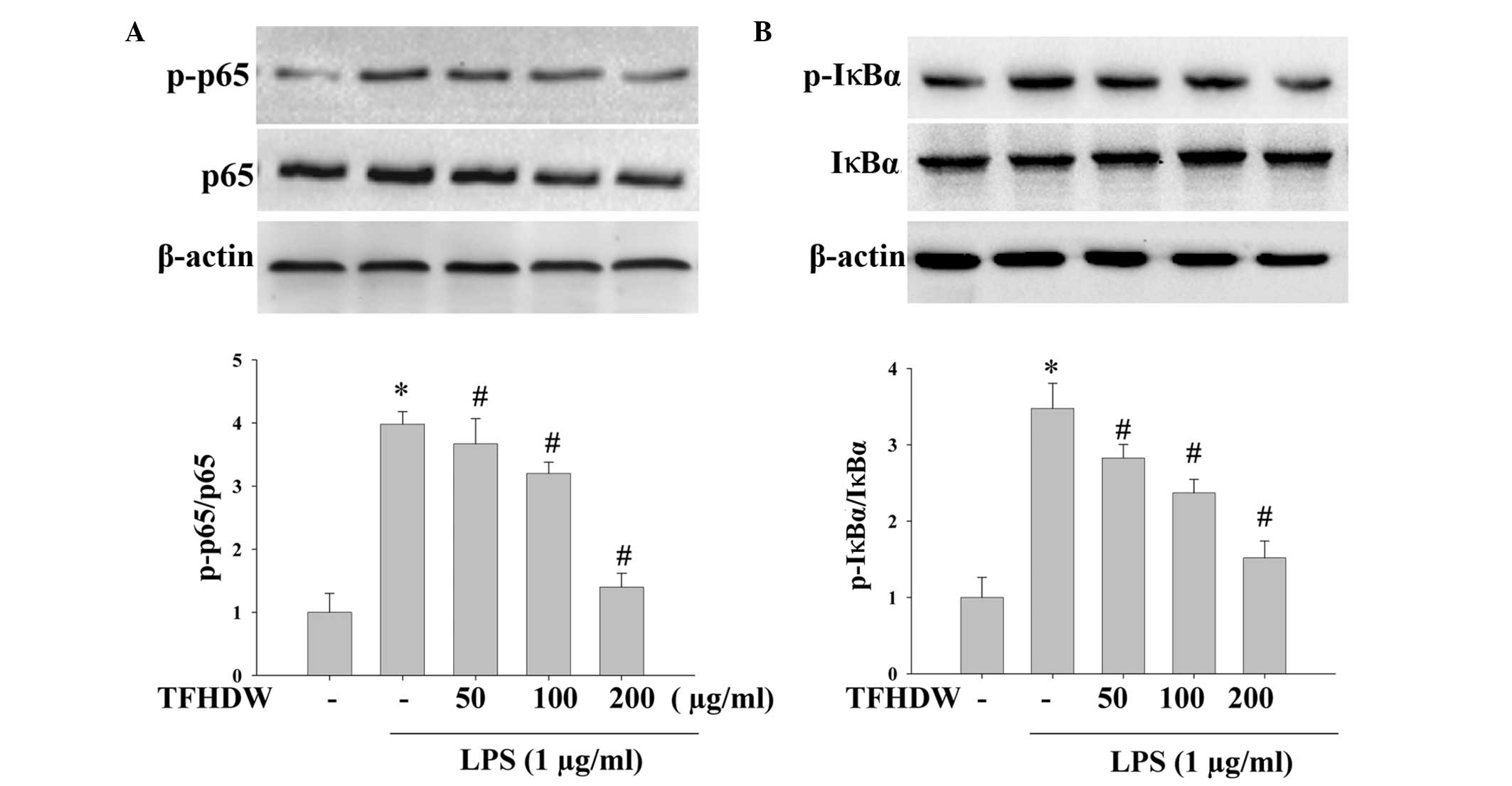
|
1
|
Dinarello CA: Proinflammatory and
anti-inflammatory cytokines as mediators in the pathogenesis of
septic shock. Chest. 112(Suppl 6): S321–S329. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Palladino MA, Bahjat FR, Theodorakis EA
and Moldawe LL: Anti-TNF-alpha therapies: The next generation. Natl
Rev Drug Discov. 2:736–746. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Pierce GF: Macrophages: Important
physiologic and pathologic sources of polypeptide growth factors.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2:233–234. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee SJ, Bai SK, Lee KS, Namkoong S, Na HJ,
Ha KS, Han JA, Yim SV, Chang K, Kwon YG, et al: Astaxanthin
inhibits nitric oxide production and inflammatory gene expression
by suppressing I (kappa)B kinase dependent NF-kappaB activation.
Mol Cells. 16:97–105. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kundu JK and Surh YJ: Breaking the relay
in deregulated cellular signal transduction as a rationale for
chemo prevention with anti-inflammatory phytochemicals. Mutat Res.
591:123–146. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xie QW, Kashiwabara Y and Nathan C: Role
of transcription factor NF-kappaB/Rel in induction of nitric oxide
synthase. J Biol Chem. 269:4705–4708. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rice NR and Ernst MK: In vivo control of
NF-kappaB activation by I kappaB alpha. EMBO J. 12:4685–4695.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Makarov SS: NF-kappaB as a therapeutic
target in chronic inflammation: Recent advances. Mol Med Today.
6:441–448. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Gibson Beers T, Xu
BE, Karandikar M, Berman K and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated protein
(MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions.
Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cargnello M and Roux PP: Activation and
function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated
protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 75:50–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu YG and Song LR: Zhong Hua Ben Cao.
Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press. 1530–1533.
1998.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Cai QY, Lin JM, Wei L, Zhang L, Wang L,
Zhan Y, Zeng J, Xu W, Shen A, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis
diffusa willd inhibits colorectal cancer growth in vivo via
inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 13:6117–6128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang YY and Luo JB: Analysis of the
chemical constituents of Hedyotis diffusa. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da
Xue Xue Bao. 28:127–128. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee HZ, Bau DT, Kuo CL, Tsai RY, Chen YC
and Chang YH: Clarification of the phenotypic characteristics and
anti-tumor activity of Hedyotis diffusa. Am J Chin Med.
39:201–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang W, Li Y and Jiang J: Chemical
constituents from Hedyotis diffusa. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za
Zhi. 34:712–714. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang YL, Zhang Y, Fang M, Li QJ, Jiang Q
and Ming L: Immunomodulatory effects of total flavonoids of
Oldenlandia diffusa Willd. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Tong Bao.
21:444–447. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Luo SY, Zhong ZG and Zhou L: Experimental
study of the total flavonids of Oldenlandia diffusa on
ulcerative colitis in the rats. Zhongguo Yi Yuan Yao Xue Za Zhi.
31:437–440. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Luo SY, Le Z, Lv XH and Zhong ZG: Study on
effect of total flavonids of Oldenlandia diffusa on
ulcerative colitis and its immunological mechanism. Zhongguo Zhong
Yao Za Zhi. 39:896–900. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang YL, Zhang Y, Fang M, Li QJ, Jiang Q
and Ming L: Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects of total
flavones of Oldenlandia diffusa Willd. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue
Tong Bao. 21:348–350. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Korhonen R, Lahti A, Kankaanranta H and
Moilanen E: Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation.
Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:471–479. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS
and Girardin SE: Chronic inflammation: Importance of NOD2 and NALP3
in interleukin-1beta generation. Clin Exp Immunol. 147:227–235.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoon JH and Baek SJ: Molecular targets of
dietary polyphenols with anti-inflammatory properties. Yonsei Med
J. 46:585–596. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Robak J and Gryglewski RJ: Bioactivity of
flavonoids. Pol J Pharmacol. 48:555–564. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Russo A, Acquaviva R, Campisi A, Sorrenti
V, Di Giacomo C, Virgata G, Barcellona ML and Vanella A:
Bioflavonoids as antiradicals, antioxidants and DNA cleavage
protectors. Cell Biol Toxicol. 16:91–98. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Havsteen BH: The biochemistry and medical
significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol Ther. 96:67–202. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
de las Heras B and Hortelano S: Molecular
basis of the antiinflammatory effects of terpenoids. Inflamm
Allergy Drug Targets. 8:28–39. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Israf DA, Khaizurin TA, Syahida A, Lajis
NH and Khozirah S: Cardamonin inhibits COX and iNOS expression via
inhibition of p65NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and Ikappa-B
phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Mol Immunol.
44:673–679. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou HY, Shin EM, Guo LY, Youn UJ, Bae K,
Kang SS, Zou LB and Kim YS: Anti-inflammatory activity of
4-methoxyhonokiol is a function of the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2
expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages via NF-kappaB, JNK and p38 MAPK
inactivation. Eur J Pharmacol. 586:340–349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim HG, Yoon DH, Lee WH, Han SK, Shrestha
B, Kim CH, Lim MH, Chang W, Lim S, Choi S, et al: Phellinus
linteus inhibits inflammatory mediators by suppressing
redox-based NF-kappaB and MAPKs activation in
lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophage. J Ethnopharmacol.
114:307–315. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jung WK, Choi I, Lee DY, Yea SS, Choi YH,
Kim MM, Park SG, Seo SK, Lee SW, Lee CM, et al: Caffeic acid
phenethyl ester protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock and
inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible
nitric oxide synthase expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages via the
p38/ERK and NF-kappaB pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
40:2572–2582. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|