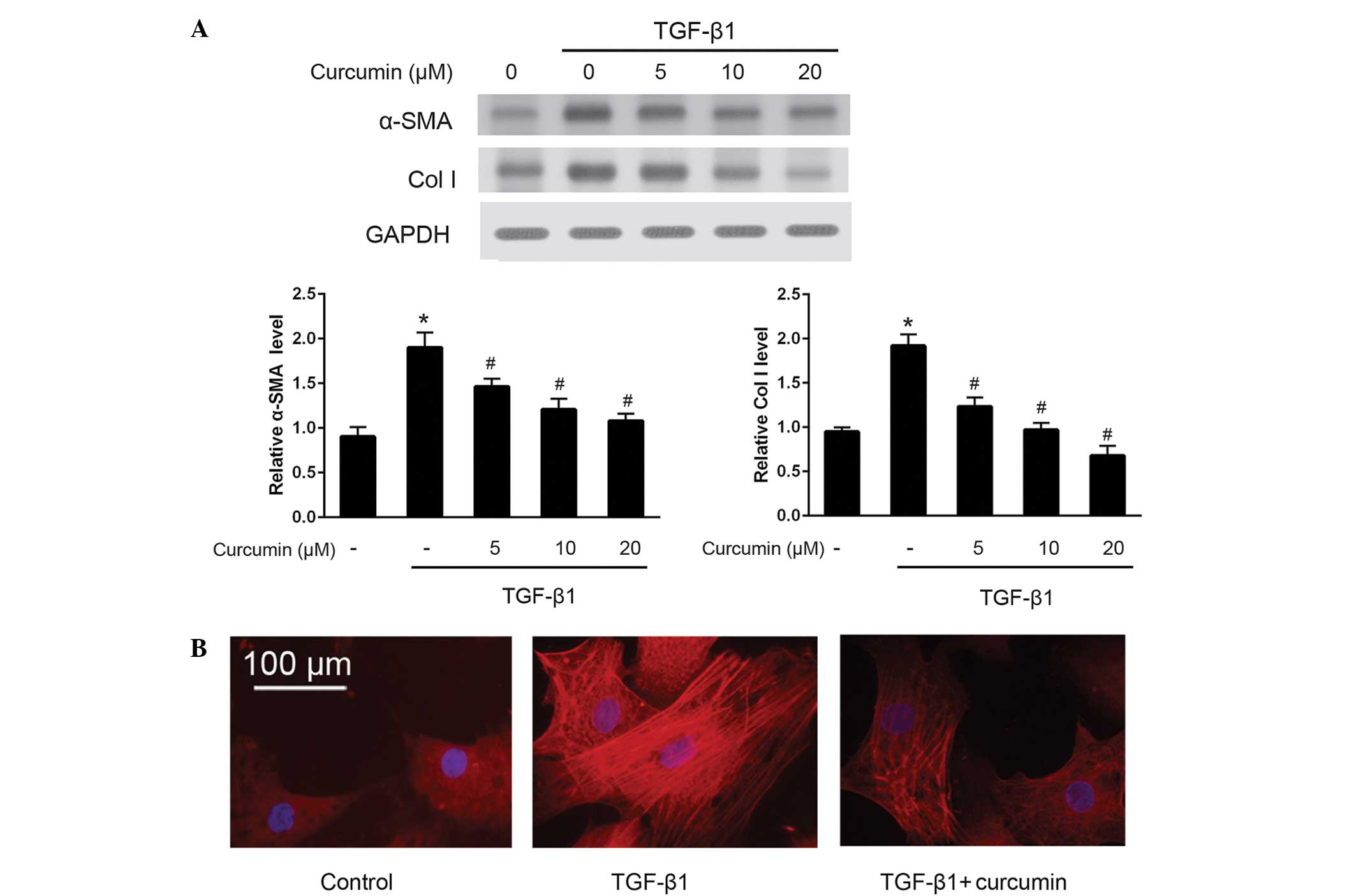
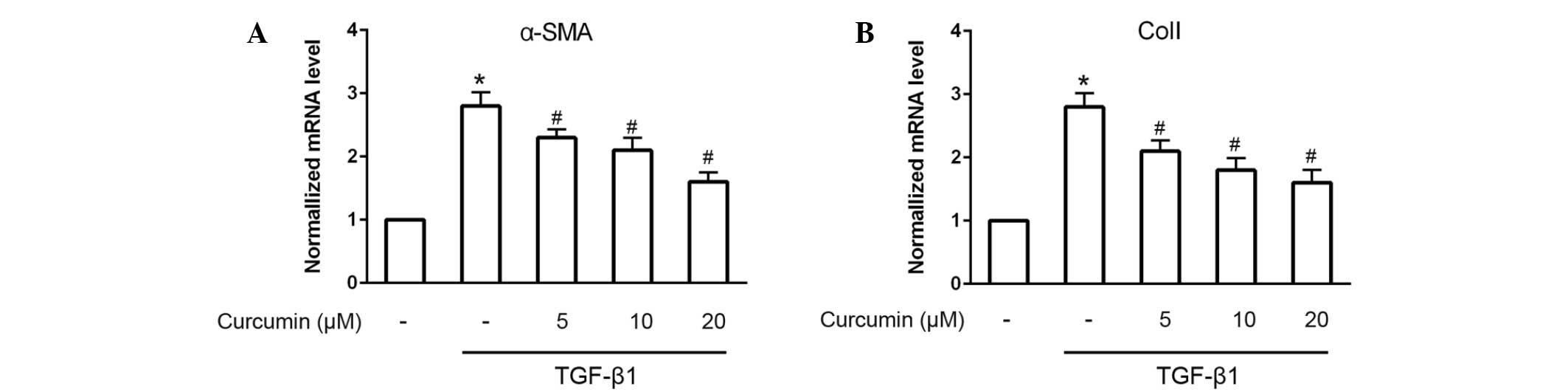
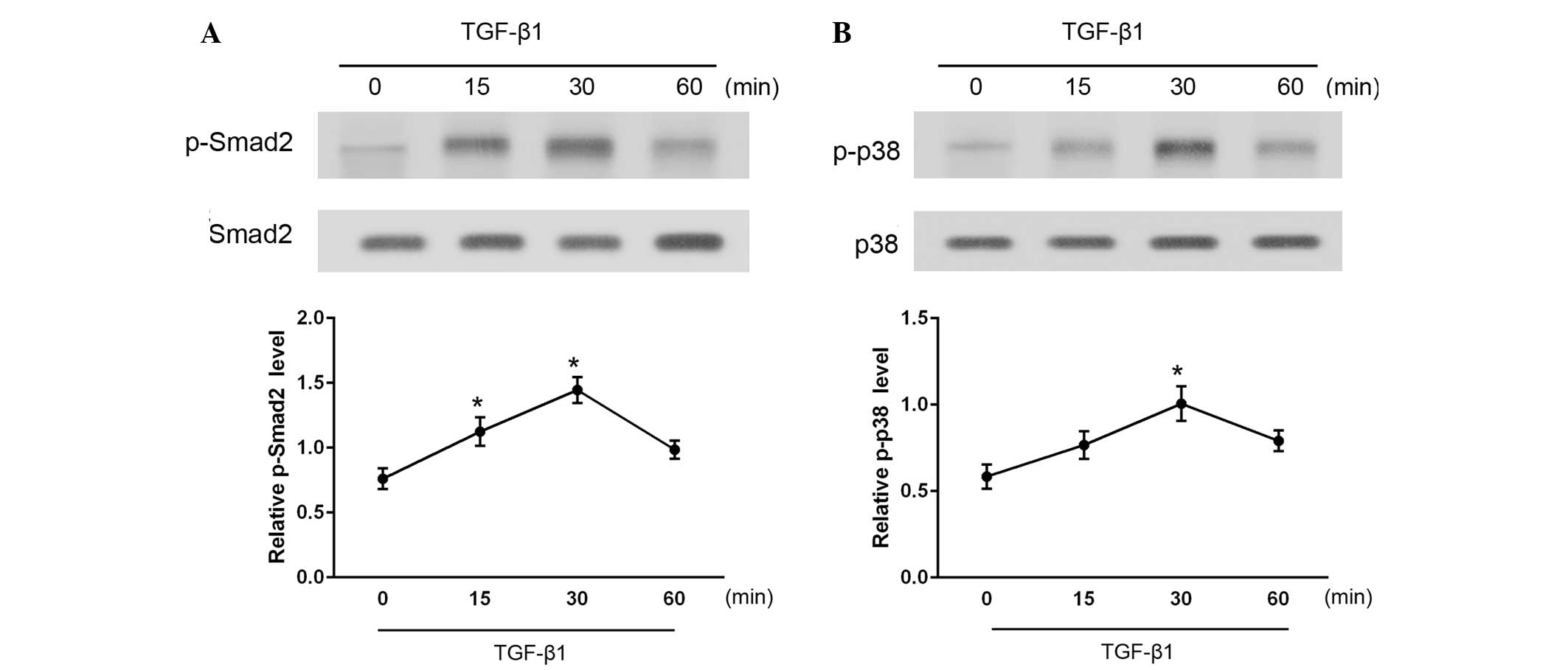
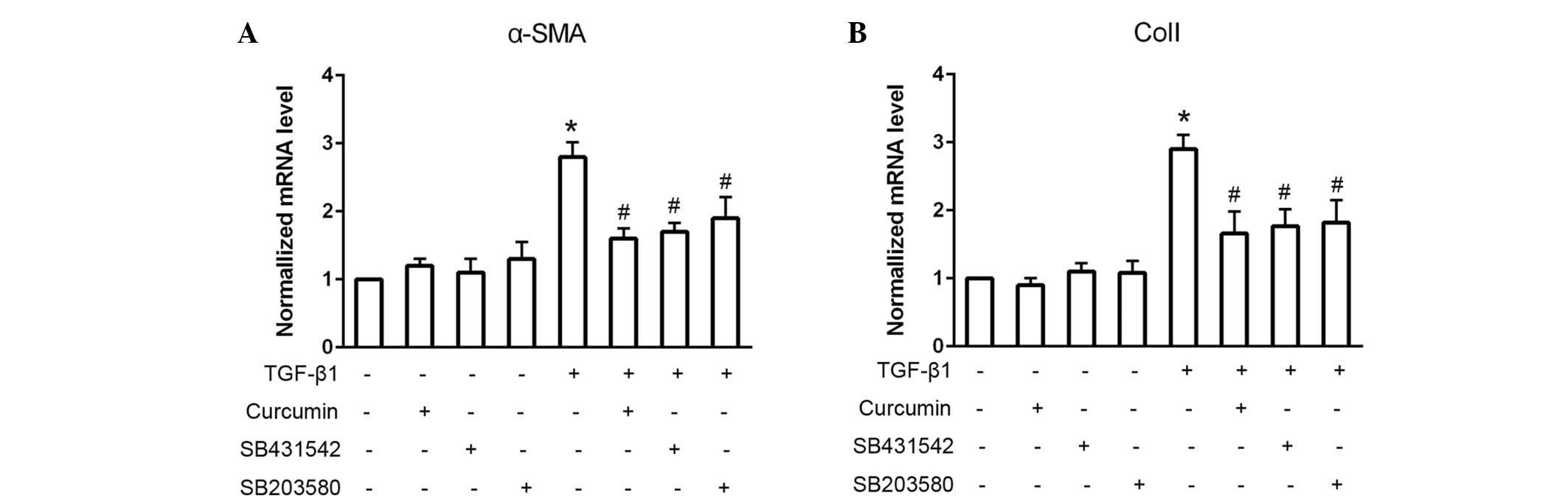
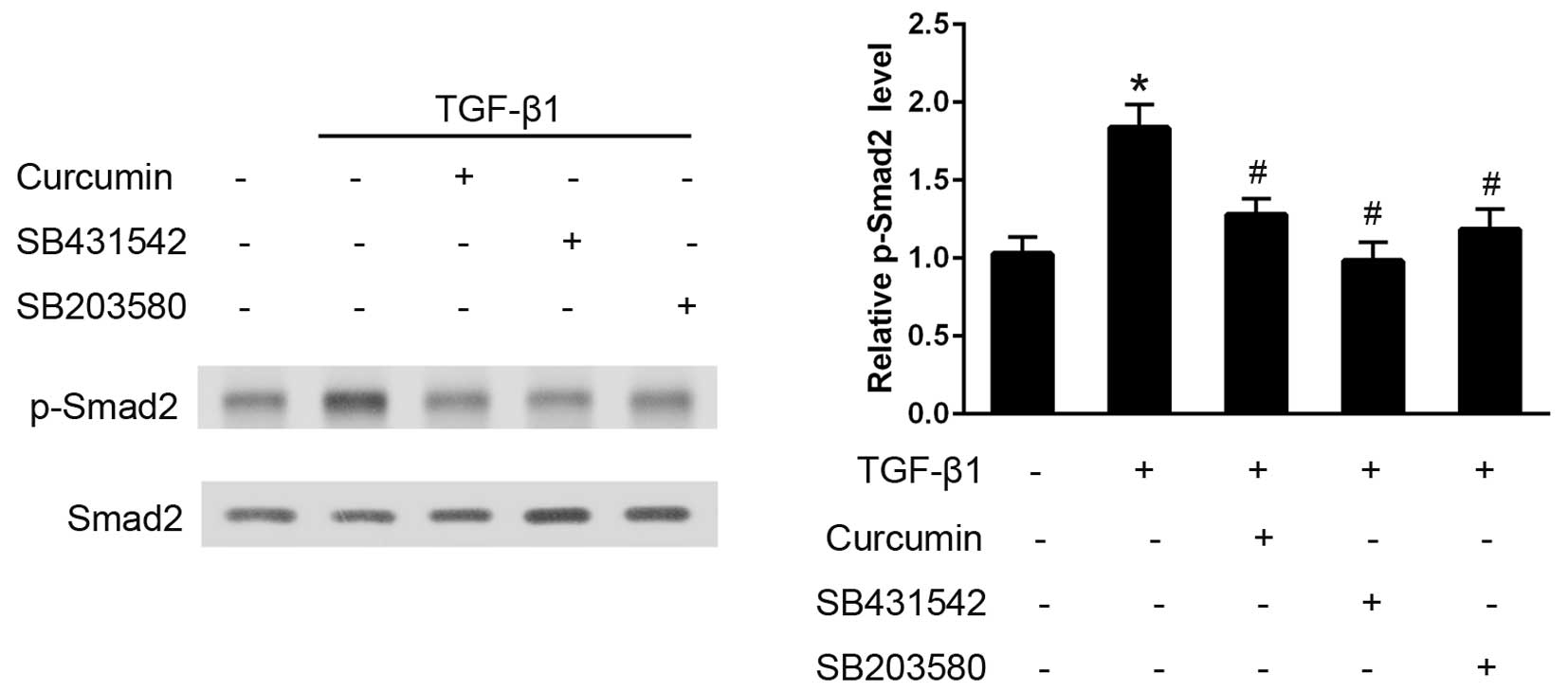
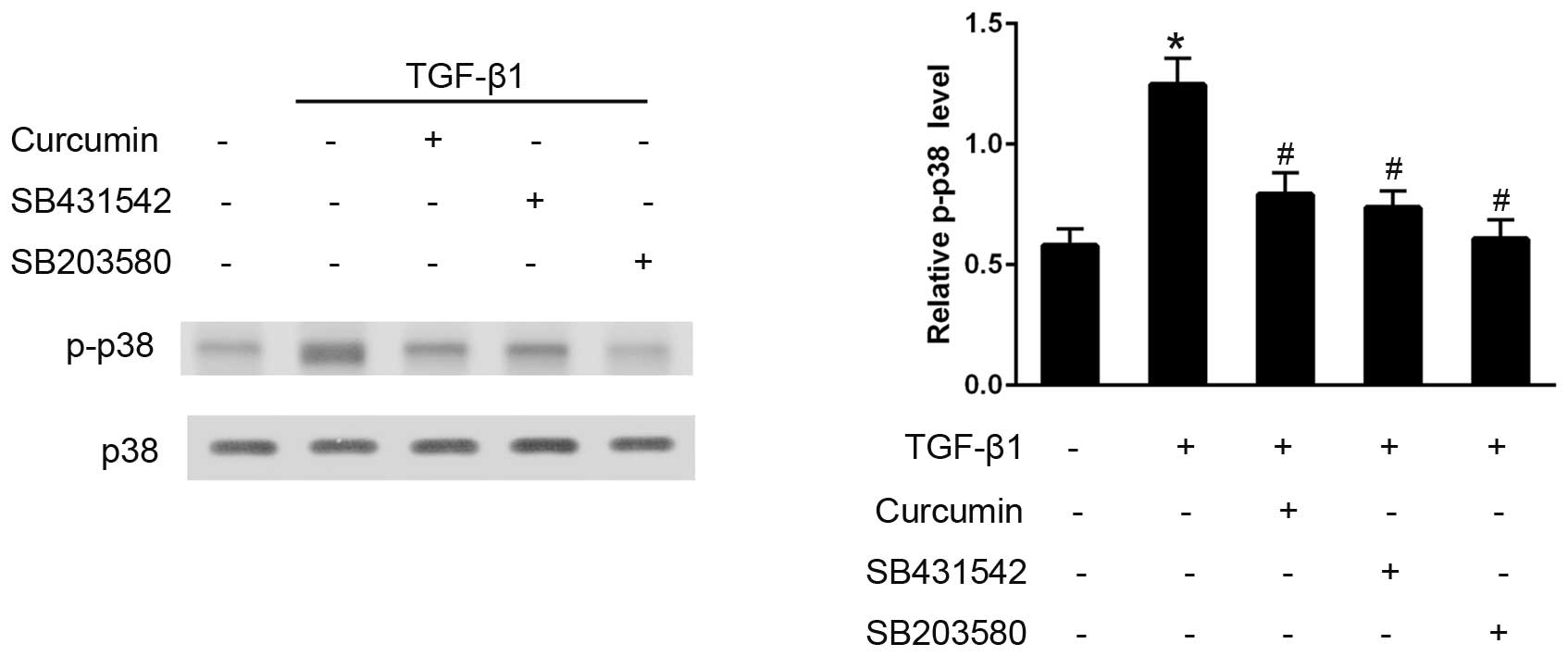
|
1
|
Daskalopoulos EP, Janssen BJ and
Blankesteijn WM: Myofibroblasts in the infarct area: Concepts and
challenges. Microsc Microanal. 18:35–49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gupta SC, Patchva S, Koh W and Aggarwal
BB: Discovery of curcumin, a component of golden spice and its
miraculous biological activities. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
39:283–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chiu J, Khan ZA, Farhangkhoee H and
Chakrabarti S: Curcumin prevents diabetes-associated abnormalities
in the kidneys by inhibiting p300 and nuclear factor-κB. Nutrition.
25:964–972. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kolodziejczyk J, Olas B, Saluk-Juszczak J
and Wachowicz B: Antioxidative properties of curcumin in the
protection of blood platelets against oxidative stress in vitro.
Platelets. 22:270–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abe Y, Hashimoto S and Horie T: Curcumin
inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by human peripheral
blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages. Pharmacol Res. 39:41–47.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Teiten MH, Gaascht F, Cronauer M, Henry E,
Dicato M and Diederich M: Anti-proliferative potential of curcumin
in androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells occurs through
modulation of the Wingless signaling pathway. Int J Oncol.
38:603–611. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hartojo W, Silvers AL, Thomas DG, Seder
CW, Lin L, Rao H, Wang Z, Greenson JK, Giordano TJ, Orringer MB, et
al: Curcumin promotes apoptosis, increases chemosensitivity, and
inhibits nuclear factor kappaB in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Transl
Oncol. 3:99–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chanvorachote P, Pongrakhananon V,
Wannachaiyasit S, Luanpitpong S, Rojanasakul Y and Nimmannit U:
Curcumin sensitizes lung cancer cells to cisplatin-induced
apoptosis through superoxide anion-mediated Bcl-2 degradation.
Cancer Invest. 27:624–635. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghosh SS, Salloum FN, Abbate A, Krieg R,
Sica DA, Gehr TW and Kukreja RC: Curcumin prevents cardiac
remodeling secondary to chronic renal failure through deactivation
of hypertrophic signaling in rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
299:H975–H984. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li HL, Liu C, de Couto G, Ouzounian M, Sun
M, Wang AB, Huang Y, He CW, Shi Y, Chen X, et al: Curcumin prevents
and reverses murine cardiac hypertrophy. J Clin Invest.
118:879–893. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang NP, Wang ZF, Tootle S, Philip T and
Zhao ZQ: Curcumin promotes cardiac repair and ameliorates cardiac
dysfunction following myocardial infarction. Br J Pharmacol.
167:1550–1562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Morimoto T, Sunagawa Y, Kawamura T, Takaya
T, Wada H, Nagasawa A, Komeda M, Fujita M, Shimatsu A, Kita T and
Hasegawa K: The dietary compound curcumin inhibits p300 histone
acetyltransferase activity and prevents heart failure in rats. J
Clin Invest. 118:868–878. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Soetikno V, Sari FR, Sukumaran V,
Lakshmanan AP, Mito S, Harima M, Thandavarayan RA, Suzuki K, Nagata
M, Takagi R and Watanabe K: Curcumin prevents diabetic
cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Possible
involvement of PKC-MAPK signaling pathway. Eur J Pharm Sci.
47:604–614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Biernacka A, Dobaczewski M and
Frangogiannis NG: TGF-β signaling in fibrosis. Growth factors.
29:196–202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cucoranu I, Clempus R, Dikalova A, Phelan
PJ, Ariyan S, Dikalov S and Sorescu D: NAD (P) H oxidase 4 mediates
transforming growth factor-β1-induced differentiation of cardiac
fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. Circ Res. 97:900–907. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dobaczewski M, Bujak M, Li N,
Gonzalez-Quesada C, Mendoza LH, Wang XF and Frangogiannis NG: Smad3
signaling critically regulates fibroblast phenotype and function in
healing myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 107:418–428. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deaton RA, Su C, Valencia TG and Grant SR:
Transforming growth factor-β1-induced expression of smooth muscle
marker genes involves activation of PKN and p38 MAPK. J Biol Chem.
280:31172–31181. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan-Hong F, Hui D, Qing P, Lei S,
Hai-Chang W, Wei Z and Yan-Jie C: Effects of arginine vasopressin
on differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 55:489–495. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Porter KE and Turner NA: Cardiac
fibroblasts: at the heart of myocardial remodeling. Pharmacol Ther.
123:255–278. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van den Borne SW, Diez J, Blankesteijn WM,
Verjans J, Hofstra L and Narula J: Myocardial remodeling after
infarction: the role of myofibroblasts. Nat Rev Cardiol. 7:30–37.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sabbah HN, Sharov VG, Lesch M and
Goldstein S: Progression of heart failure: A role for interstitial
fibrosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 147:29–34. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McDowell KS, Arevalo HJ, Maleckar MM and
Trayanova NA: Susceptibility to arrhythmia in the infarcted heart
depends on myofibroblast density. Biophys J. 101:1307–1315. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rohr S: Myofibroblasts in diseased hearts:
new players in cardiac arrhythmias? Heart Rhythm. 6:848–856. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Leask A: Potential therapeutic targets for
cardiac fibrosis TGFβ, angiotensin, endothelin, CCN2 and PDGF,
partners in fibroblast activation. Circ Res. 106:1675–1680. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chapman D, Weber KT and Eghbali M:
Regulation of fibrillar collagen types I and III and basement
membrane type IV collagen gene expression in pressure overloaded
rat myocardium. Circ Res. 67:787–794. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cleutjens JP, Verluyten MJ, Smiths JF and
Daemen MJ: Collagen remodeling after myocardial infarction in the
rat heart. Am J Pathol. 147:325–338. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meng Z, Yu Xh, Chen J, Li L and Li S:
Curcumin attenuates cardiac fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensive
rats through PPAR-γ activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:1247–1256.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bujak M and Frangogiannis NG: The role of
TGF-β signaling in myocardial infarction and cardiac remodeling.
Cardiovasc Res. 74:184–195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leask A: TGFbeta, cardiac fibroblasts and
the fibrotic response. Cardiovasc Res. 74:207–212. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Carthy JM, Garmaroudi FS, Luo Z and
McManus BM: Wnt3a induces myofibroblast differentiation by
upregulating TGF-β signaling through SMAD2 in a β-catenin-dependent
manner. PloS one. 6:e198092011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Horowitz JC, Rogers DS, Sharma V, Vittal
R, White ES, Cui Z and Thannickal VJ: Combinatorial activation of
FAK and AKT by transforming growth factor-beta1 confers an
anoikis-resistant phenotype to myofibroblasts. Cell Signal.
19:761–771. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|