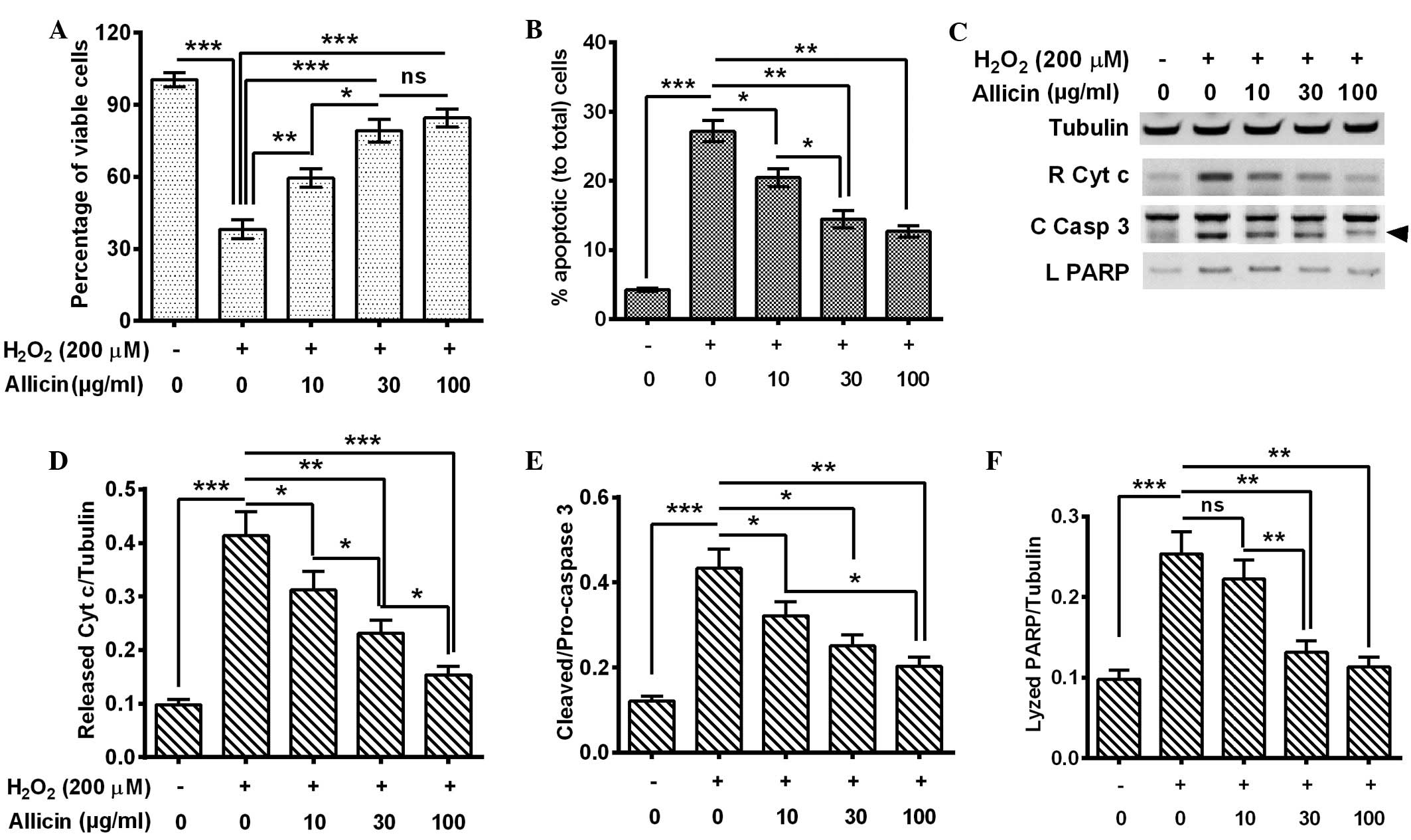
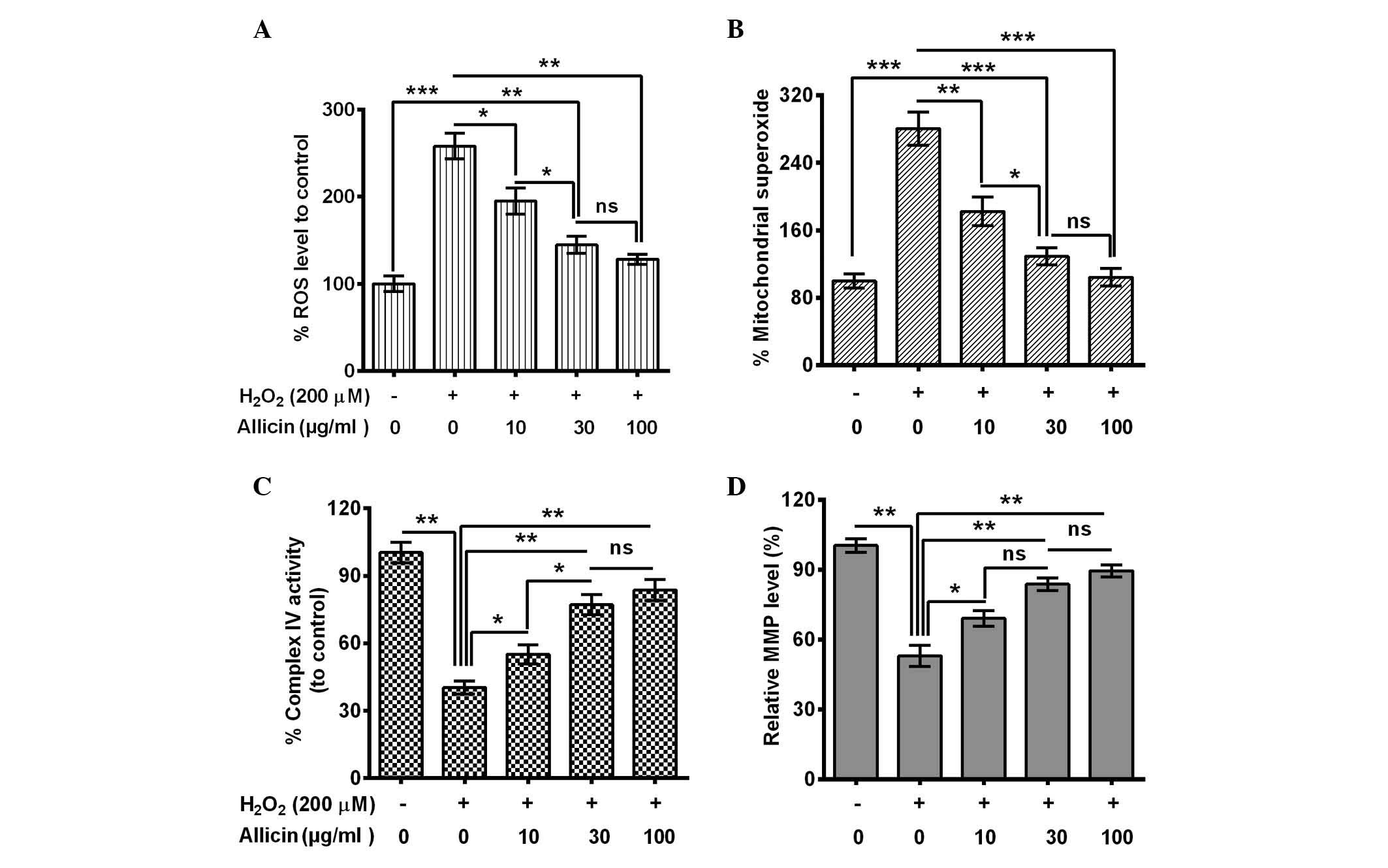
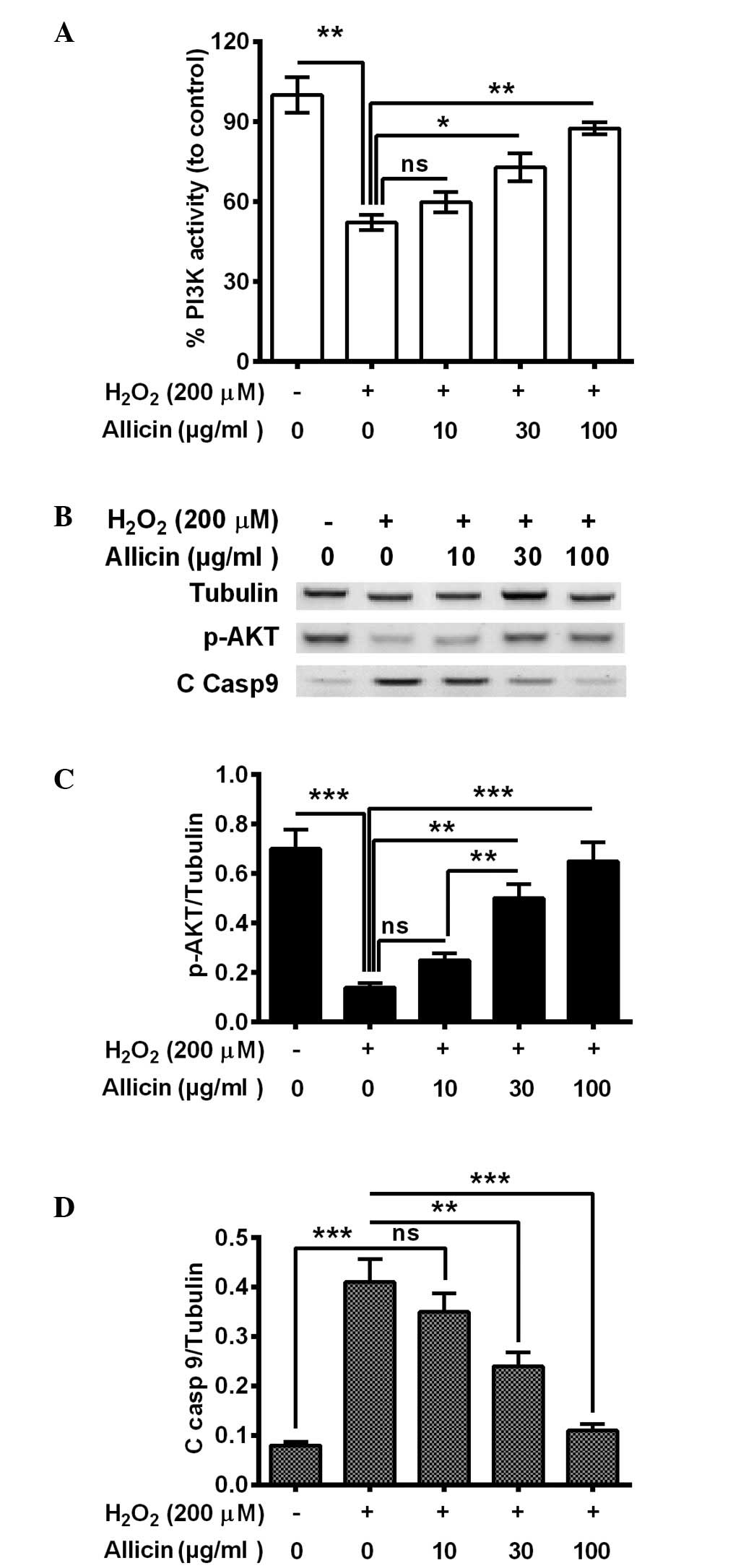
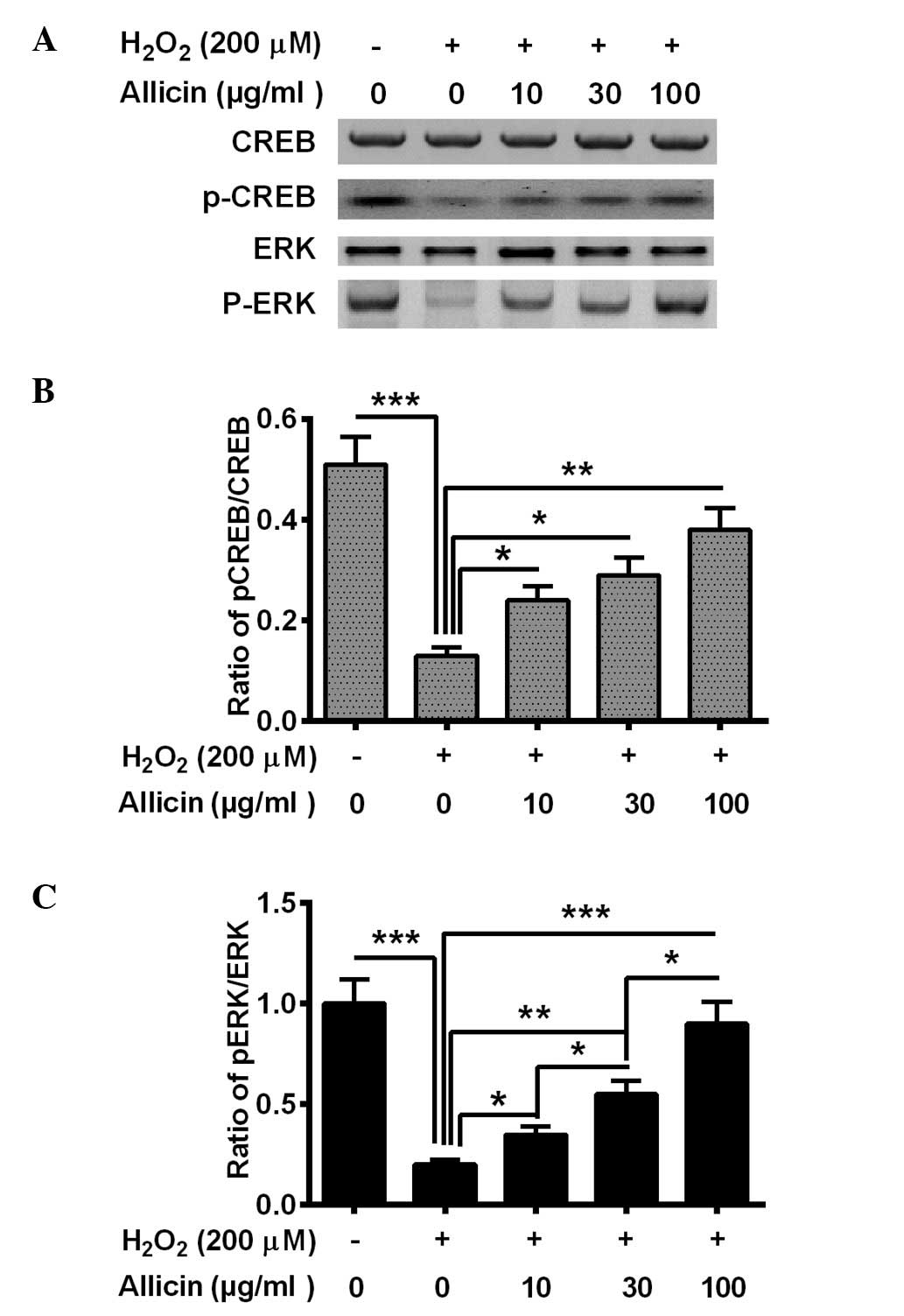
|
1
|
Graat-Verboom L, Wouters EF, Smeenk FW,
van den Borne BE, Lunde R and Spruit MA: Current status of research
on osteoporosis in COPD: A systematic review. Eur Respir J.
34:209–218. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao Y, Liu Y and Zheng Y: Osteoporosis
and related factors in older females with skeletal pain or
numbness: A retrospective study in East China. J Int Med Res.
41:859–866. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abe E, Sun L, Mechanick J, Iqbal J, Yamoah
K, Baliram R, Arabi A, Moonga BS, Davies TF and Zaidi M: Bone loss
in thyroid disease: Role of low TSH and high thyroid hormone. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 1116:383–391. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Compston JE: Risk factors for
osteoporosis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 36:223–224. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chrischilles EA, Butler CD, Davis CS and
Wallace RB: A model of lifetime osteoporosis impact. Arch Intern
Med. 151:2026–2032. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shah M, Kola B, Bataveljic A, Arnett TR,
Viollet B, Saxon L, Korbonits M and Chenu C: AMP-activated protein
kinase (AMPK) activation regulates in vitro bone formation and bone
mass. Bone. 47:309–319. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee NK, Sowa H, Hinoi E, Ferron M, Ahn JD,
Confavreux C, Dacquin R, Mee PJ, McKee MD, Jung DY, et al:
Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell.
130:456–469. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pei L and Tontonoz P: Fat's loss is bone's
gain. J Clin Invest. 113:805–806. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rosen CJ and Bouxsein ML: Mechanisms of
disease: Is osteoporosis the obesity of bone? Nat Clin Pract
Rheumatol. 2:35–43. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Slemmer JE, Shacka JJ, Sweeney MI and
Weber JT: Antioxidants and free radical scavengers for the
treatment of stroke, traumatic brain injury and aging. Curr Med
Chem. 15:404–414. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lopes JP, Oliveira SM and Soares FJ:
Oxidative stress and its effects on insulin resistance and
pancreatic beta-cells dysfunction: Relationship with type 2
diabetes mellitus complications. Acta Med Port. 21:293–302.
2008.(In Portuguese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kingwell BA: Nitric oxide-mediated
metabolic regulation during exercise: Effects of training in health
and cardiovascular disease. Faseb J. 14:1685–1696. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maharjan BR, Jha JC, Adhikari D Akila,
Risal S, Alurkar VM and Singh PP: Oxidative stress, antioxidant
status and lipid profile in ischemic heart disease patients from
western region of Nepal. Nepal Med Coll J. 10:20–24.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sendur OF, Turan Y, Tastaban E and Serter
M: Antioxidant status in patients with osteoporosis: A controlled
study. Joint Bone Spine. 76:514–518. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sánchez-Rodríguez MA, Ruiz-Ramos M,
Correa-Muñoz E and Mendoza-Núñez VM: Oxidative stress as a risk
factor for osteoporosis in elderly Mexicans as characterized by
antioxidant enzymes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 8:1242007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ozgocmen S, Kaya H, Fadillioglu E, Aydogan
R and Yilmaz Z: Role of antioxidant systems, lipid peroxidation,
and nitric oxide in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Mol Cell Biochem.
295:45–52. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Basu S, Michaëlsson K, Olofsson H,
Johansson S and Melhus H: Association between oxidative stress and
bone mineral density. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 288:275–279.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in Health
and Disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morgan MJ and Liu ZG: Reactive oxygen
species in TNFalpha-induced signaling and cell death. Mol Cells.
30:1–12. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Freitas I, Griffini P, Bertone V, Bertone
R, Fenoglio C, Milliery R and Vairetti M: In situ detection of
reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide production in normal and
pathological tissues: Improvement by differential interference
contrast. Exp Gerontol. 37:591–602. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tan S, Sagara Y, Liu Y, Maher P and
Schubert D: The regulation of reactive oxygen species production
during programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 141:1423–1432. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kirkland RA, Windelborn JA, Kasprzak JM
and Franklin JL: A Bax-induced pro-oxidant state is critical for
cytochrome c release during programmed neuronal death. J Neurosci.
22:6480–6490. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Zheng L, Zhao Z, Shi J, Wang X
and Huang J: Grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit
H2O2-induced osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cell
apoptosis via ameliorating H2O2-induced mitochondrial dysfunction.
J Toxicol Sci. 39:803–813. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chan SW: Panax ginseng, Rhodiola
rosea and Schisandra chinensis. Int J Food Sci Nutr.
63(Suppl 1): S75–S81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Borlinghaus J, Albrecht F, Gruhlke MC,
Nwachukwu ID and Slusarenko AJ: Allicin: Chemistry and biological
properties. Molecules. 19:12591–12618. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kita T, Kume N, Minami M, Hayashida K,
Murayama T, Sano H, Moriwaki H, Kataoka H, Nishi E, Horiuchi H, et
al: Role of oxidized LDL in atherosclerosis. Ann NY Acad Sci.
947:199–206. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Arzanlou M, Bohlooli S, Jannati E and
Mirzanejad-Asl H: Allicin from garlic neutralizes the hemolytic
activity of intra- and extra-cellular pneumolysin O in vitro.
Toxicon. 57:540–545. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Hesabgar HA, Owlia
MB, Hadinedoushan H, Barzegar K and Fllahzadeh MH: The effect of
garlic tablet on pro-inflammatory cytokines in postmenopausal
osteoporotic women: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J Diet
Suppl. 9:262–271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Padiya R, Chowdhury D, Borkar R, Srinivas
R, Bhadra Pal M and Banerjee SK: Garlic attenuates cardiac
oxidative stress via activation of PI3K/AKT/Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in
fructose-fed diabetic rat. PLoS One. 9:e942282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Umoh NA, Walker RK, Al-Rubaiee M, Jeffress
MA and Haddad GE: Acute alcohol modulates cardiac function as
PI3K/Akt regulates oxidative stress. Alcohol Clin Exp Res.
38:1847–1864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang L and Jope RS: Oxidative stress
differentially modulates phosphorylation of ERK, p38 and CREB
induced by NGF or EGF in PC12 cells. Neurobiol Aging. 20:271–278.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chomyn A and Attardi G: MtDNA mutations in
aging and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 304:519–529. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Balaban RS, Nemoto S and Finkel T:
Mitochondria, oxidants and aging. Cell. 120:483–495. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Choi EM: Magnolol protects osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells against antimycin A-induced cytotoxicity through
activation of mitochondrial function. Inflammation. 35:1204–1212.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chan JY, Tsui HT, Chung IY, Chan RY, Kwan
YW and Chan SW: Allicin protects rat cardiomyoblasts (H9c2 cells)
from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative injury through inhibiting
the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Int J Food
Sci Nutr. 65:868–873. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saavedra A, García-Martínez JM, Xifró X,
Giralt A, Torres-Peraza JF, Canals JM, Díaz-Hernández M, Lucas JJ,
Alberch J and Pérez-Navarro E: PH domain leucine-rich repeat
protein phosphatase 1 contributes to maintain the activation of the
PI3K/Akt pro-survival pathway in Huntington's disease striatum.
Cell Death Differ. 17:324–335. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bhattacharya D, Singh MK and Chaudhuri S,
Acharya S, Basu AK and Chaudhuri S: T11TS impedes glioma
angiogenesis by inhibiting VEGF signaling and pro-survival
PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway with concomitant upregulation of PTEN in
brain endothelial cells. J Neurooncol. 113:13–25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hsu HH, Cheng LH, Ho TJ, Kuo WW, Lin YM,
Chen MC, Lee NH, Tsai FJ, Tsai KH and Huang CY: Apicidin-resistant
HA22T hepatocellular carcinoma cells massively promote pro-survival
capability via IGF-IR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation. Tumour
Biol. 35:303–313. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Das S, Tosaki A, Bagchi D, Maulik N and
Das DK: Potentiation of a survival signal in the ischemic heart by
resveratrol through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/mitogen-
and stress-activated protein kinase 1/cAMP response element-binding
protein signaling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 317:980–988. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dworkin S, Malaterre J, Hollande F, Darcy
PK, Ramsay RG and Mantamadiotis T: cAMP response element binding
protein is required for mouse neural progenitor cell survival and
expansion. Stem Cells. 27:1347–1357. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sato M, Bagchi D, Tosaki A and Das DK:
Grape seed proanthocyanidin reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis by
inhibiting ischemia/reperfusion-induced activation of JNK-1 and
C-JUN. Free Radic Biol Med. 31:729–737. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Carpio L, Gladu J, Goltzman D and Rabbani
SA: Induction of osteoblast differentiation indexes by PTHrP in
MG-63 cells involves multiple signaling pathways. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 281:E489–E499. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Matsuo N, Tanaka S, Gordon MK, Koch M,
Yoshioka H and Ramirez F: CREB-AP1 protein complexes regulate
transcription of the collagen XXIV gene (Col24a1) in osteoblasts. J
Biol Chem. 281:5445–5452. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
De Rasmo D, Signorile A, Roca E and Papa
S: cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) is imported into
mitochondria and promotes protein synthesis. FEBS J. 276:4325–4333.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Boucher MJ, Morisset J, Vachon PH, Reed
JC, Lainé J and Rivard N: MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates the
expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L) and Mcl-1 and promotes survival of
human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 79:355–369. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chan SL and Yu VC: Proteins of the bcl-2
family in apoptosis signalling: From mechanistic insights to
therapeutic opportunities. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 31:119–128.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|