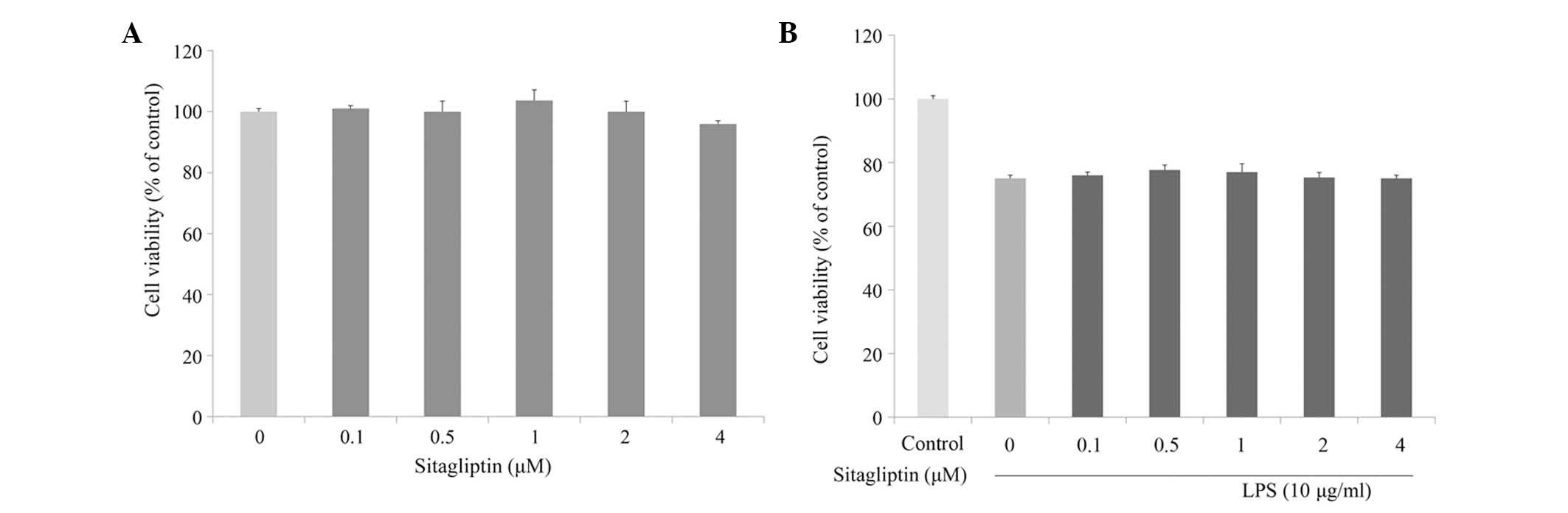
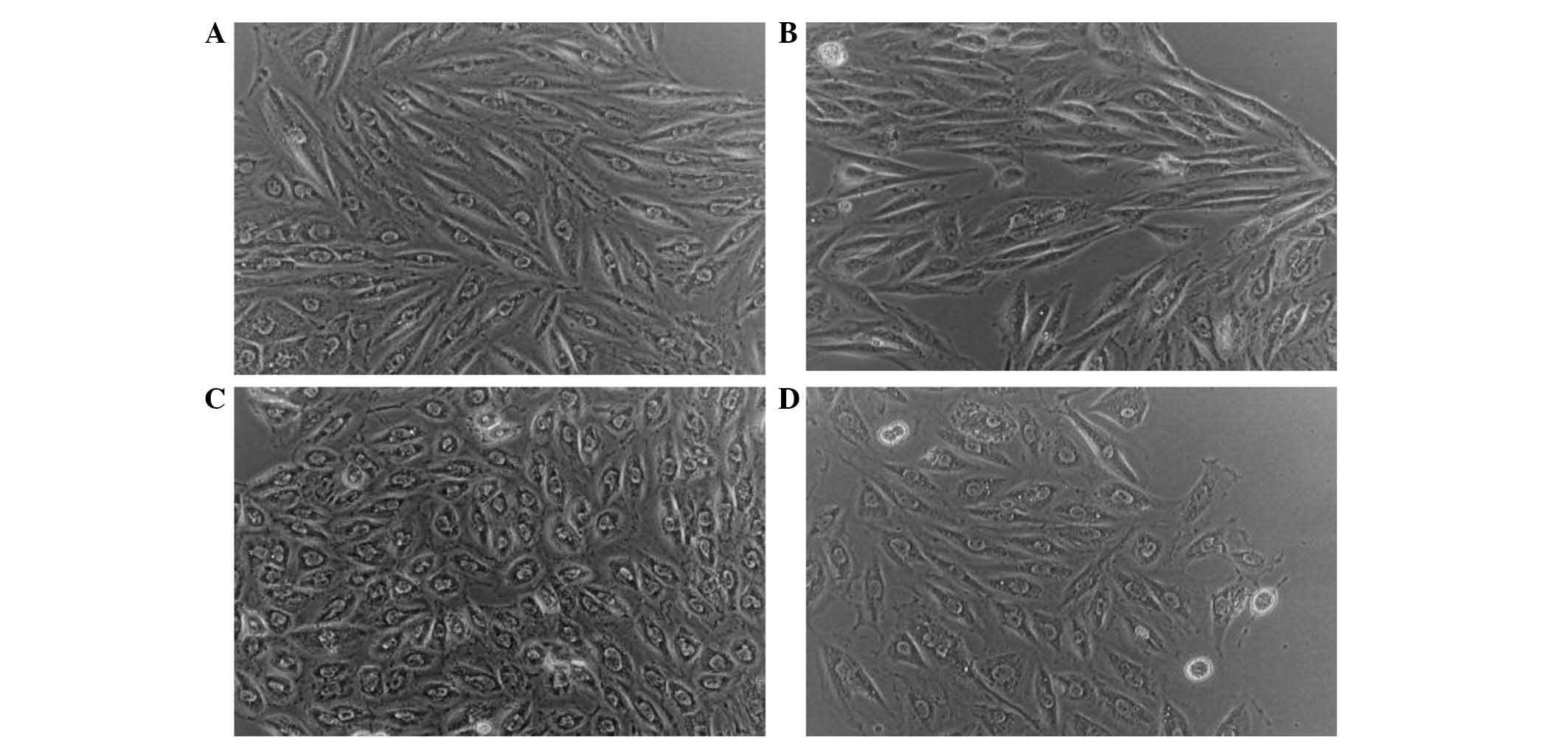
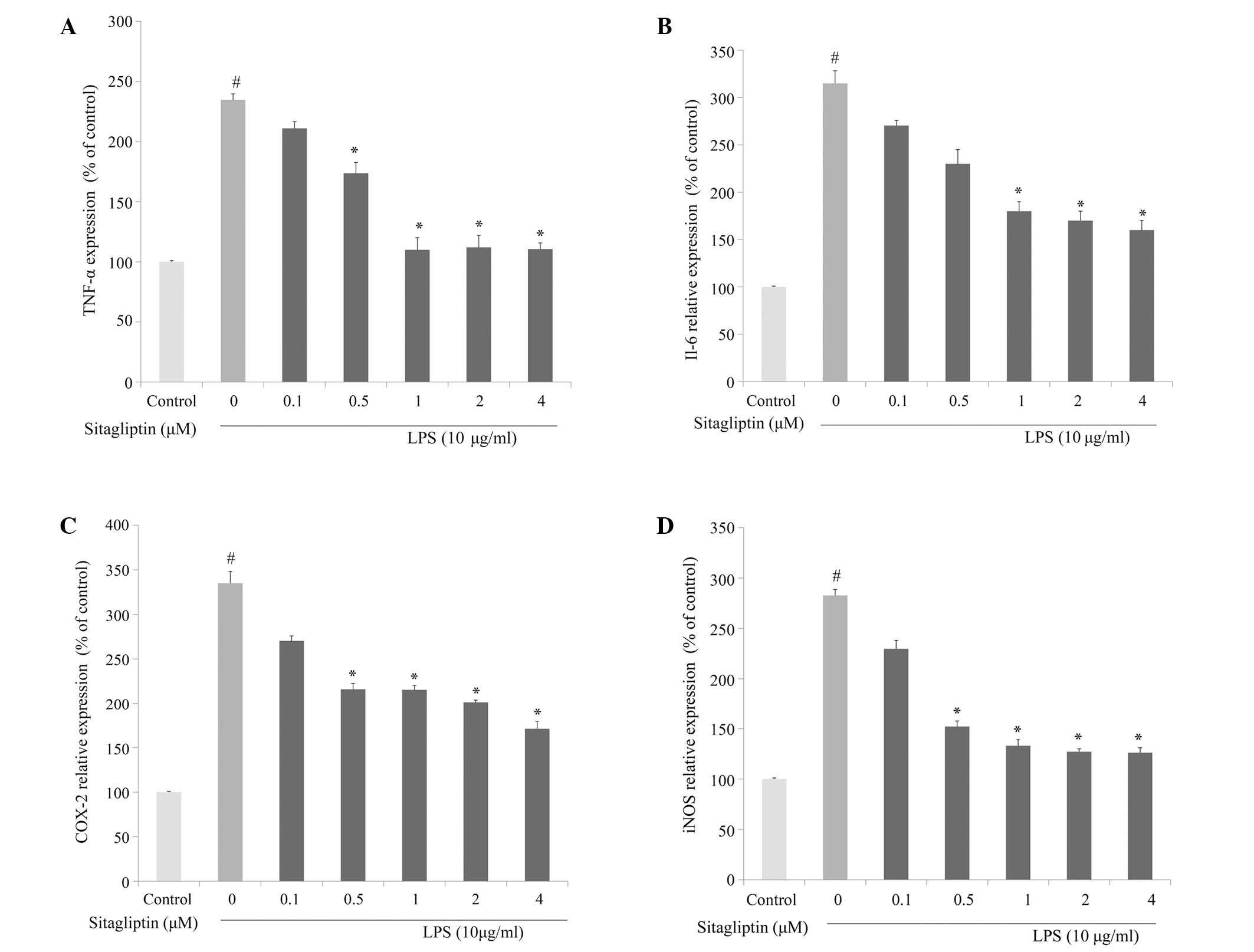
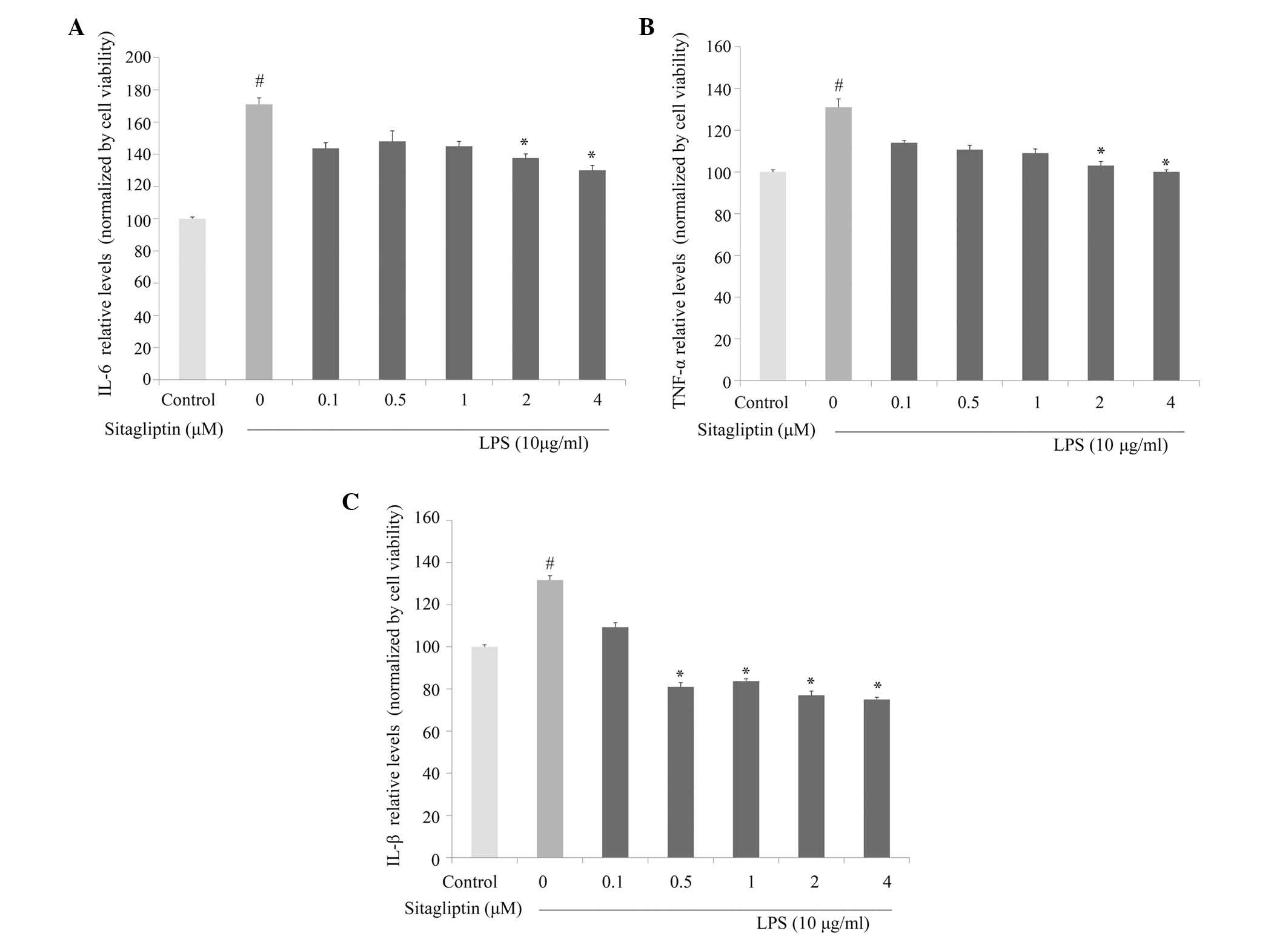
|
1
|
Jirik FR, Podor TJ, Hirano T, Kishimoto T,
Loskutoff DJ, Carson DA and Lotz M: Bacterial lipopolysaccharide
and inflammatory mediators augment IL-6 secretion by human
endothelial cells. J Immunol. 142:144–147. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fallach R, Shainberg A, Avlas O, Fainblut
M, Chepurko Y, Porat E and Hochhauser E: Cardiomyocyte toll-like
receptor 4 is involvedin heart dysfunction following septic shock
or myocardial ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:1236–1244. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu YC, Yeh WC and Ohashi PS: LPS/TLR4
signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 42:145–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Du J, An J, Wei N, Guan T, Pritchard KA Jr
and Shi Y: Increased resistance to LPS-induced myocardial
dysfunction in the Brown Norway rats versus Dahl S rats: Roles of
inflammatory cytokines and nuclear factor kappaB pathway. Shock.
33:332–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Knuefermann P, Nemoto S, Baumgarten G,
Misra A, Sivasubramanian N, Carabello BA and Vallejo JG: Cardiac
inflammation and innate immunity in septic shock: Is there a role
for toll-like receptors? Chest. 121:1329–1336. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Panaro MA, Acquafredda A, Cavallo P,
Cianciulli A, Saponaro C and Mitolo V: Inflammatory responses in
embryonal cardiomyocytesexposed to LPS challenge: An in vitro model
of deciphering the effects of LPS on the heart. Curr Pharm Des.
16:754–765. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grandel U, Hopf M, Buerke M, Hattar K,
Heep M, Fink L, Bohle RM, Morath S, Hartung T, Pullamsetti S, et
al: Mechanisms of cardiac depression caused by lipoteichoic acids
from staphylococcus aureus in isolated rat hearts. Circulation.
112:691–698. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reddy AB, Srivastava SK and Ramana KV:
Anti-inflammatory effect of aldose reductase inhibition in murine
polymicrobial sepsis. Cytokine. 48:170–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
von Rosenstiel N, von Rosenstiel I and
Adam D: Management of sepsis and septic shock in infants and
children. Paediatr Drugs. 3:9–27. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cariou B: Pleiotropic effects of insulin
and GLP-1 receptor agonists: Potential benefits of the association.
Diabetes Metab. 41:6S28–6S35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ceriello A, Novials A, Ortega E, Canivell
S, La Sala L, Pujadas G, Esposito K, Giugliano D and Genovese S:
Glucagon-like peptide 1 reduces endothelial dysfunction,
inflammation and oxidative stress induced by both hyperglycemia and
hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 36:2346–2350. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shiraki A, Oyama J, Komoda H, Asaka M,
Komatsu A, Sakuma M, Kodama K, Sakamoto Y, Kotooka N, Hirase T and
Node K: The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces
TNF-α-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial
cells. Atherosclerosis. 221:375–382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee TI, Kao YH, Chen YC, Huang JH, Hsu MI
and Chen YJ: The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor-sitagliptin
modulates calcium dysregulation, inflammation and PPARs in
hypertensive cardiomyocytes. Int J Cardiol. 168:5390–5395. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chinda K, Palee S, Surinkaew S,
Phornphutkul M, Chattipakorn S and Chattipakorn N: Cardioprotective
effect of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor during
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 167:451–457. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang XM, Yang YJ and Wu YJ: The emerging
role of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in cardiovascular
protection: Current position and perspectives. Cardiovasc Drugs
Ther. 27:297–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu L, Liu J, Wong WT, Tian XY, Lau CW,
Wang YX, Xu G, Pu Y, Zhu Z, Xu A, et al: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4
inhibitor sitagliptin protects endothelial function in hypertension
through a glucagon-like peptide 1-dependent mechanism.
Hypertension. 60:833–841. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matsubara J, Sugiyama S, Akiyama E,
Iwashita S, Kurokawa H, Ohba K, Maeda H, Fujisue K, Yamamoto E,
Kaikita K, et al: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4inhibitor, sitagliptin,
improves endothelial dysfunction in association with its
anti-inflammatory effects in patients with coronary artery disease
and uncontrolled diabetes. Circ J. 77:1337–1344. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Panaro MA, Pricci M, Meziani F, Ragot T,
Andriantsitohaina R, Mitolo V and Tesse A: Cyclooxygenase-2-derived
prostacyclin protective role on endotoxin-induced mouse
cardiomyocyte mortality. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 11:347–356. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lobo SM and Lobo FR: Markers and mediators
of inflammatory response in infection and sepsis. Rev Bras Ter
Intensiva. 19:210–215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ashare A, Powers LS, Butler NS, Doerschug
KC, Monick MM and Hunninghake GW: Anti-inflammatory response is
associated with mortality and severity of infection in sepsis. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 288:L633–L640. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tavener SA and Kubes P: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms underlying LPS-associated myocyte impairment.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 290:H800–H806. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jatta K, Wågsäter D, Norgren L, Stenberg B
and Sirsjö A: Lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine and chemokine
expression in human carotid lesions. J Vasc Res. 42:266–271. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nemoto S, Vallejo JG, Knuefermann P, Misra
A, Defreitas G, Carabello BA and Mann DL: Escherichia coli
LPS-induced LV dysfunction: Role of toll-like receptor-4 in the
adult heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 282:H2316–H2323.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Panaro MA, Gagliardi N, Saponaro C,
Calvello R, Mitolo V and Cianciulli A: Toll-like receptor 4
mediates LPS-induced release of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha by embryonal cardiomyocytes: Biological significance
and clinical implications in human pathology. Curr Pharm Des.
16:766–774. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kodera R, Shikata K, Takatsuka T, Oda K,
Miyamoto S, Kajitani N, Hirota D, Ono T, Usui HK and Makino H:
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor ameliorates early renal injury
through its anti-inflammatory action in a rat model of type 1
diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 443:828–833. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
DeNicola M, Du J, Wang Z, Yano N, Zhang L,
Wang Y, Qin G, Zhuang S and Zhao TC: Stimulation of glucagon-like
peptide-1 receptor through exendin-4 preserves myocardial
performance and prevents cardiac remodeling in infarcted
myocardium. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 307:E630–E643. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang WJ, Chang CH, Sun MF, Hsu SF and Weng
CS: DPP-4 inhibitor attenuates toxic effects of indoxyl sulfate on
kidney tubular cells. PLoS One. 9:e934472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vona-Davis L, Zhu X, Yu AK and McFadden
DW: Modulation of interleukin-6 in cardiac myoblasts during
endotoxemia. J Surg Res. 112:91–96. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Makdissi A, Ghanim H, Vora M, Green K,
Abuaysheh S, Chaudhuri A, Dhindsa S and Dandona P: Sitagliptin
exerts an antinflammatory action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
97:3333–3341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zeng Y, Li C, Guan M, Zheng Z, Li J, Xu W,
Wang L, He F and Xue Y: The DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin attenuates
the progress of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein-E-knockout mice
via AMPK-and MAPK-dependent mechanisms. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
13:322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Frazier WJ, Xue J, Luce WA and Liu Y: MAPK
signaling drives inflammation in LPS-stimulated cardiomyocytes: The
route of crosstalk to G-protein-coupled receptors. PLoS One.
7:e500712012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Baumgarten G, Knuefermann P, Schuhmacher
G, Vervölgyi V, von Rappard J, Dreiner U, Fink K, Djoufack C, Hoeft
A, Grohé C, et al: Toll-like receptor 4, nitric oxide, and
myocardial depression in endotoxemia. Shock. 25:43–49. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee CC, Lin NT, Hsu YH and Chen HI:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition potentiates multiple
organ dysfunction induced by endotoxin in consciousrats. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 45:396–403. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu H, Shan L, Schiller PW, Mai A and Peng
T: Histone deacetylase-3 activation promotes tumor necrosis
factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) expression in cardiomyocytes during
lipopolysaccharide stimulation. J Biol Chem. 285:9429–9436. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wright G, Singh IS, Hasday JD, Farrance
IK, Hall G, Cross AS and Rogers TB: Endotoxin stress-response in
cardiomyocytes: NF-kappaB activation and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
282:H872–H879. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|