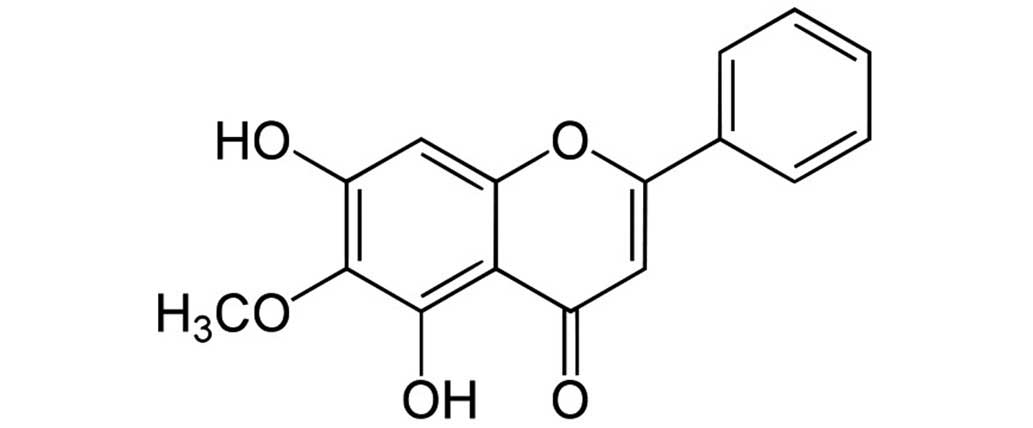
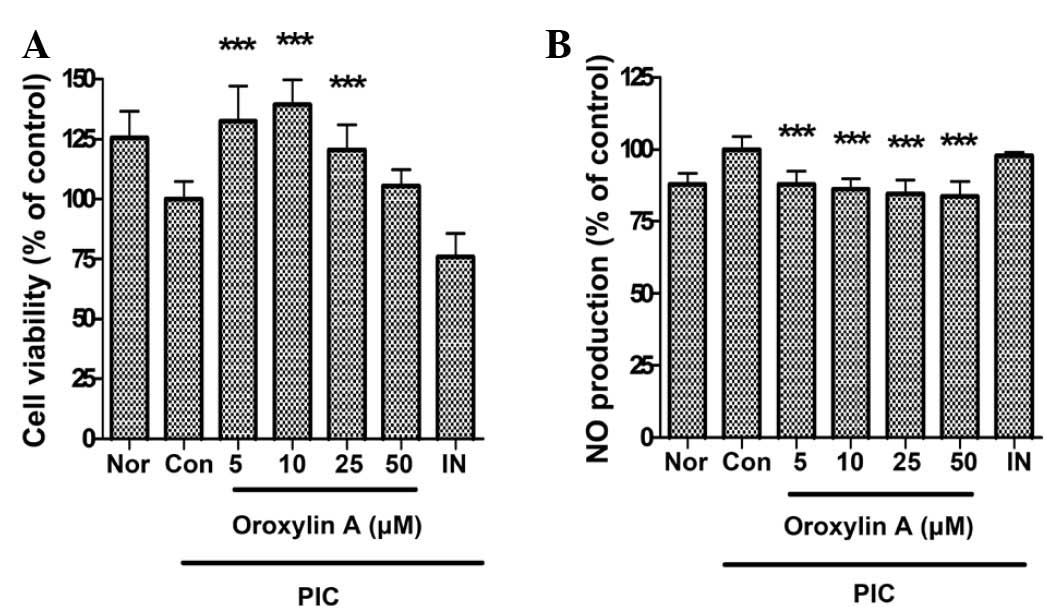
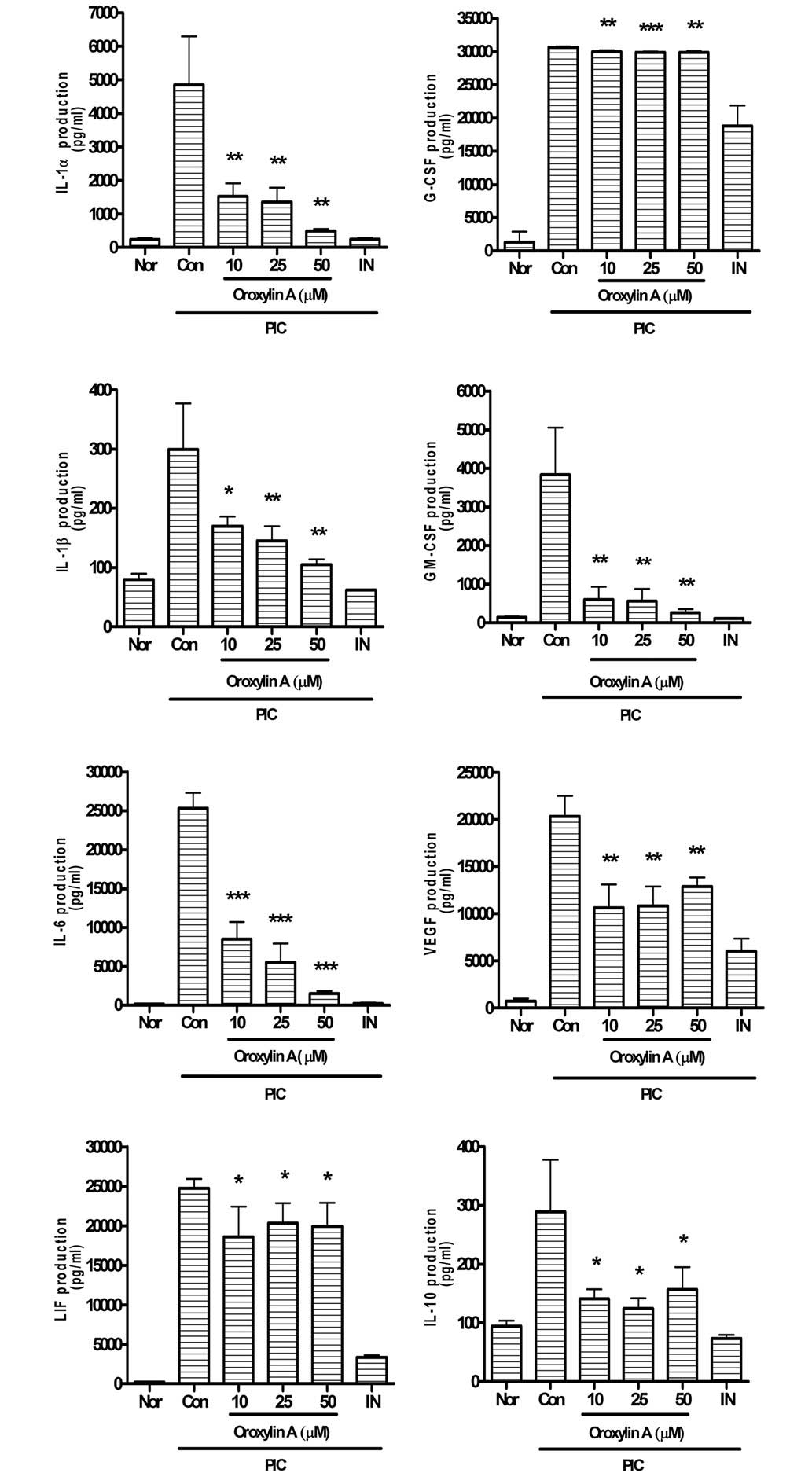
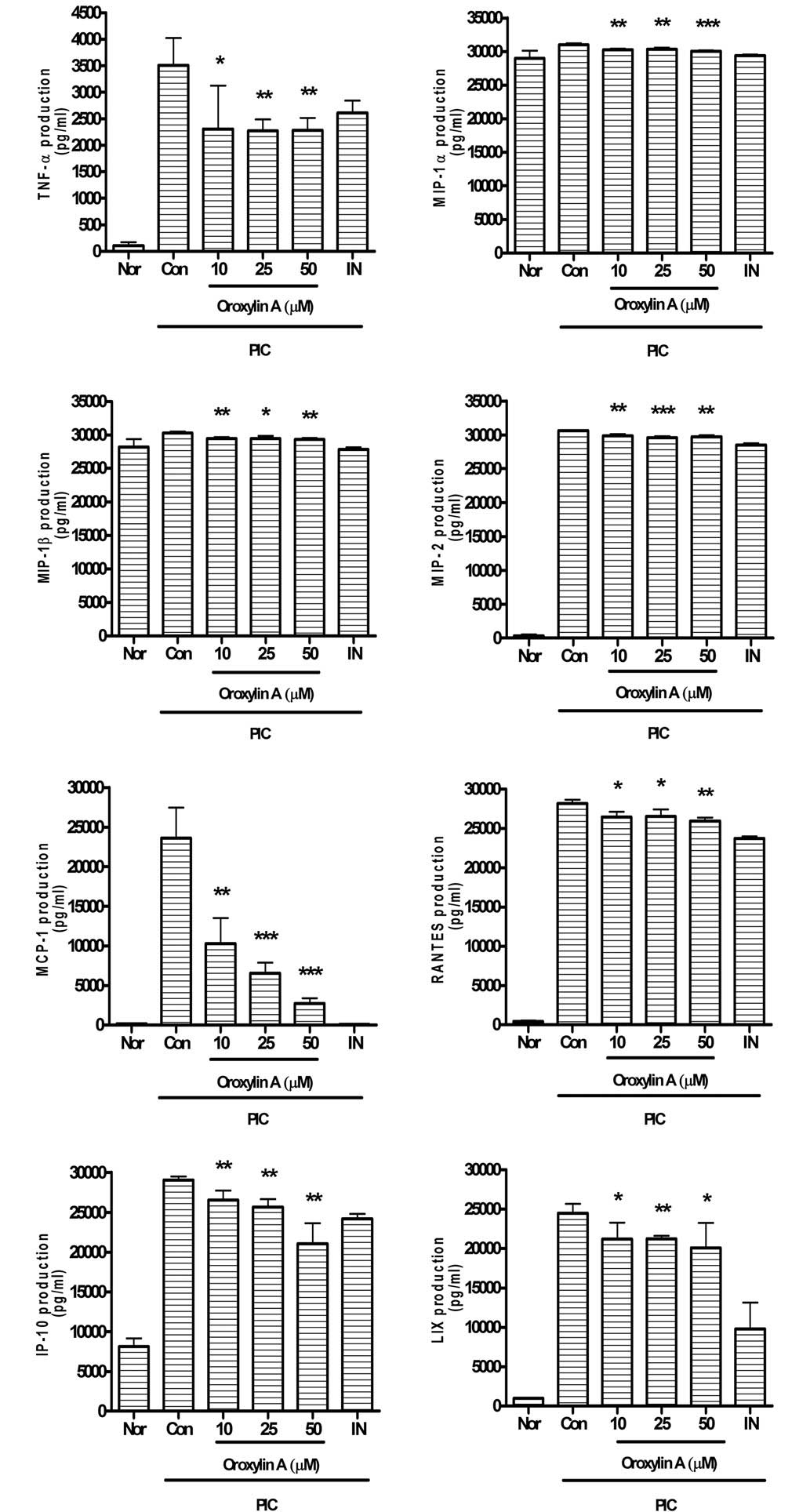
|
1
|
Gao HM and Hong JS: Why neurodegenerative
diseases are progressive: Uncontrolled inflammation drives disease
progression. Trends Immunol. 29:357–365. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee JY and Park W: Anti-inflammatory
effect of wogonin on RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages induced with
polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Molecules. 20:6888–6900. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zong Y, Sun L, Liu B, Deng YS, Zhan D,
Chen YL, He Y, Liu J, Zhang ZJ, Sun J and Lu D: Resveratrol
inhibits LPS-induced MAPKs activation via activation of the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in murine RAW 264.7
macrophage cells. PLoS One. 7:e441072012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Medina EA, Morris IR and Berton MT:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation attenuates the
TLR2-mediated macrophage proinflammatory cytokine response to
Francisella tularensis live vaccine strain. J Immunol.
185:7562–7572. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ulevitch RJ and Tobias PS:
Receptor-dependent mechanisms of cell stimulation by bacterial
endotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol. 13:437–457. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carrithers MD: Innate immune viral
recognition: Relevance to CNS infections. Handb Clin Neurol.
123:215–223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim DH, Kim S, Jeon SJ, Son KH, Lee S,
Yoon BH, Cheong JH, Ko KH and Ryu JH: The effects of acute and
repeated oroxylin A treatments on abeta (25-35)-induced memory
impairment in mice. Neuropharmacology. 55:639–647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li HN, Nie FF, Liu W, Dai QS, Lu N, Qi Q,
Li ZY, You QD and Guo QL: Apoptosis induction of oroxylin A in
human cervical cancer HeLa cell line in vitro and in vivo.
Toxicology. 257:80–85. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tran TV, Malainer C, Schwaiger S, Hung T,
Atanasov AG, Heiss EH, Dirsch VM and Stuppner H: Screening of
vietnamese medicinal plants for NF-kB signaling inhibitors:
Assessing the activity of flavonoids from the stem bark of
Oroxylum indicum. J Ethnopharmacol. 159:36–42. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh J and Kakkar P: Oroxylin A, a
constituent of Oroxylum indicum inhibits adipogenesis and
induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1 cells. Phytomedicine. 21:1733–1741.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Akinyi M, Gao XM, Li YH, Wang BY, Liu EW,
Chai LJ, JawoBah A and Fan GW: Vascular relaxation induced by
Eucommiae ulmoides oliv. and its compounds oroxylin A and
wogonin: Implications on their cytoprotection action. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 7:3164–3180. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JY and Park W: Anti-inflammatory
effect of myristicin on RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with
polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Molecules. 16:7132–7142. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoon SB, Lee YJ, Park SK, Kim HC, Bae H,
Kim HM, Ko SG, Choi HY, Oh MS and Park W: Anti-inflammatory effects
of Scutellaria baicalensis water extract on LPS-activated
RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol. 125:286–290. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuk SS, Lim EM, Lee JY, Lee YJ, Kim YS,
Lee TH, Park SK, Bae H, Kim HM, Ko SG, et al: Antiinflammatory
effects of Epimedium brevicornum water extract on
lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW264.7 macrophages. Phytother Res.
24:1781–1787. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Flagella M, Bui S, Zheng Z, Nguyen CT,
Zhang A, Pastor L, Ma Y, Yang W, Crawford KL, McMaster GK, et al: A
multiplex branched DNA assay for parallel quantitative gene
expression profiling. Anal Biochem. 352:50–60. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qiao C, Wei L, Dai Q, Zhou Y, Yin Q, Li Z,
Xiao Y, Guo Q and Lu N: UCP2-related mitochondrial pathway
participates in oroxylin A-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer
cells. J Cell Physiol. 230:1054–1063. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye M, Wang Q, Zhang W, Li Z, Wang Y and Hu
R: Oroxylin A exerts anti-inflammatory activity on
lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse macrophage via Nrf2/ARE
activation. Biochem Cell Biol. 92:337–348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou DG, Diao BZ, Zhou W and Feng JL:
Oroxylin A Inhibits Allergic Airway Inflammation in Ovalbumin
(OVA)-Induced Asthma Murine Model. Inflammation. 39:867–872. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hui H, Yang H, Dai Q, Wang Q, Yao J, Zhao
K, Guo Q and Lu N: Oroxylin A inhibits ATRA-induced IL-6 expression
involved in retinoic acid syndrome by down-regulating CHOP. Gene.
551:230–235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, Miao H, Li W, Yao J, Sun Y, Li Z,
Zhao L and Guo Q: CXCL12/CXCR4 axis confers adriamycin resistance
to human chronic myelogenous leukemia and oroxylin A improves the
sensitivity of K562/ADM cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 90:212–225. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Canna SW, de Jesus AA, Gouni S, Brooks SR,
Marrero B, Liu Y, DiMattia MA, Zaal KJ, Sanchez GA, Kim H, et al:
An activating NLRC4 inflammasome mutation causes autoinflammation
with recurrent macrophage activation syndrome. Nat Genet.
46:1140–1146. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Spite M, Norling LV, Summers L, Yang R,
Cooper D, Petasis NA, Flower RJ, Perretti M and Serhan CN: Resolvin
D2 is a potent regulator of leukocytes and controls microbial
sepsis. Nature. 461:1287–1291. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ulloa L and Tracey KJ: The ‘cytokine
profile’: A code for sepsis. Trends Mol Med. 11:56–63. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Riedemann NC, Neff TA, Guo RF, Bernacki
KD, Laudes IJ, Sarma JV, Lambris JD and Ward PA: Protective effects
of IL-6 blockade in sepsis are linked to reduced C5a receptor
expression. J Immunol. 170:503–507. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Srivastava M, Jung S, Wilhelm J, Fink L,
Bühling F, Welte T, Bohle RM, Seeger W, Lohmeyer J and Maus UA: The
inflammatory versus constitutive trafficking of mononuclear
phagocytes into the alveolar space of mice is associated with
drastic changes in their gene expression profiles. J Immunol.
175:1884–1893. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wareing MD, Lyon AB, Lu B, Gerard C and
Sarawar SR: Chemokine expression during the development and
resolution of a pulmonary leukocyte response to influenza A virus
infection in mice. J Leukoc Biol. 76:886–895. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sakaguchi S and Wing K: Immunology.
damping by depletion. Science. 332:542–543. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ballara S, Taylor PC, Reusch P, Marmé D,
Feldmann M, Maini RN and Paleolog EM: Raised serum vascular
endothelial growth factor levels are associated with destructive
change in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 44:2055–2064.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ruddy MJ, Shen F, Smith JB, Sharma A and
Gaffen SL: Interleukin-17 regulates expression of the CXC chemokine
LIX/CXCL5 in osteoblasts: Implications for inflammation and
neutrophil recruitment. J Leukoc Biol. 76:135–144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schön MP and Boehncke WH: Psoriasis. N
Engl J Med. 352:1899–1912. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dace DS, Khan AA, Stark JL, Kelly J, Cross
AH and Apte RS: Interleukin-10 overexpression promotes
Fas-ligand-dependent chronic macrophage-mediated demyelinating
polyneuropathy. PLoS One. 4:e71212009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cuschieri J and Maier RV: Oxidative
stress, lipid rafts, and macrophage reprogramming. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 9:1485–1497. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Timmins JM, Ozcan L, Seimon TA, Li G,
Malagelada C, Backs J, Backs T, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN, Anderson
ME and Tabas I: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
links ER stress with Fas and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. J
Clin Invest. 119:2925–2941. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|