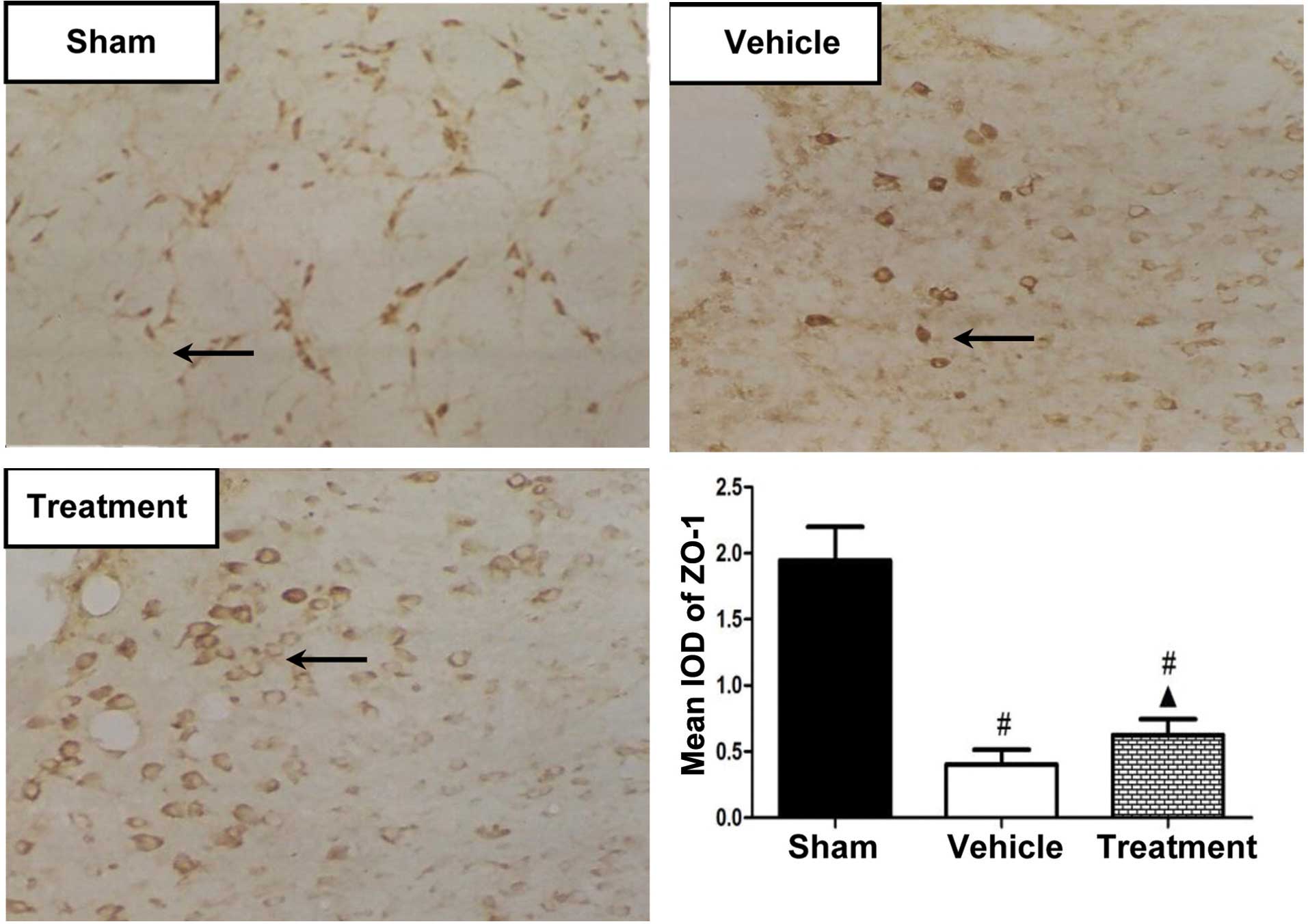
|
1
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, et al:
Heart disease and stroke statistics-2014 update: A report from the
American heart association. Circulation. 129:e28–e292. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rincon F and Mayer SA: The epidemiology of
intracerebral hemorrhage in the United States from 1979 to 2008.
Neurocrit Care. 19:95–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsai CF, Thomas B and Sudlow CL:
Epidemiology of stroke and its subtypes in Chinese vs white
populations A systematic review. Neurology. 81:264–272. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei JW, Huang Y, Wang JG, Liu M, Wong LK,
Huang Q, Wu L, Heeley EL, Arima H and Anderson CS: ChinaQUEST
Investigators: Current management of intracerebral haemorrhage in
China: A national, multi-centre, hospital register study. BMC
Neurol. 11:162011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu X, Chen-Roetling J and Regan RF:
Systemic hemin therapy attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption
after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurobiol Dis. 70:245–251. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou QB, Jin YL, Jia Q, Zhang Y, Li LY,
Liu P and Liu YT: Baicalin attenuates brain edema in a rat model of
intracerebral hemorrhage. Inflammation. 37:107–115. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zazulia AR, Diringer MN, Derdeyn CP and
Powers WJ: Progression of mass effect after intracerebral
hemorrhage. Stroke. 30:1167–1173. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Balami JS and Buchan AM: Complications of
intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 11:101–118. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE,
Yusof SR and Begley DJ: Structure and function of the blood-brain
barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 37:13–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang Y and Rosenberg GA: Blood-brain
barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease.
Stroke. 42:3323–3328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krafft PR, Caner B, Klebe D, Rolland WB,
Tang J and Zhang JH: PHA-543613 preserves blood-brain barrier
integrity after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Stroke.
44:1743–1747. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rosenberg GA: Neurological diseases in
relation to the blood-brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
32:1139–1151. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qiu LB, Zhou Y, Wang Q, Yang LL, Liu HQ,
Xu SL, Qi YH, Ding GR and Guo GZ: Synthetic gelatinases inhibitor
attenuates electromagnetic pulse-induced blood-brain barrier
disruption by inhibiting gelatinases-mediated ZO-1 degradation in
rats. Toxicology. 285:31–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Petty MA and Wettstein JG: Elements of
cerebral microvascular ischaemia. Brain Res Brain Res Rev.
36:23–34. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun H, Tang Y, Guan X, Li L and Wang D:
Effects of selective hypothermia on blood-brain barrier integrity
and tight junction protein expression levels after intracerebral
hemorrhage in rats. Biol Chem. 394:1317–1324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zahuranec DB, Lisabeth LD, Sánchez BN,
Smith MA, Brown DL, Garcia NM, Skolarus LE, Meurer WJ, Burke JF,
Adelman EE and Morgenstern LB: Intracerebral hemorrhage mortality
is not changing despite declining incidence. Neurology.
82:2180–2186. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
van Asch CJ, Luitse MJ, Rinkel GJ, van der
Tweel I, Algra A and Klijn CJ: Incidence, case fatality, and
functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time,
according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 9:167–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao L, Zhao H, Liu Q, Song J, Xu C, Liu P,
Gong W, Wang R, Liu KJ and Luo Y: Improvement of hematoma
absorption and neurological function in patients with acute
intracerebral hemorrhage treated with Xueshuantong. J Neurol Sci.
323:236–240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Huang X, Liang QH, Fan R, Qin F,
Guo Y, Yan KP, Liu W, Luo JK, Li YH, et al: A strategy for
detecting absorbed bioactive compounds for quality control in the
water extract of rhubarb by ultra performance liquid chromatography
with photodiode array detector. Chin J Integr Med. 18:690–698.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gu J, Zhang X, Fei Z, Wen A, Qin S, Yi S,
Chen Y and Li X: Rhubarb extracts in treating complications of
severe cerebral injury. Chin Med J (Engl). 113:529–531. 2000.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Collins RA: A ten-year audit of
traditional Chinese medicine and other natural product research
published in the Chinese Medical Journal (2000–2009). Chin Med J
(Engl). 124:1401–1408. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pharmacopoeia Commission: Pharmacopoeia of
the People's Republic of China 2010 (9th). Chemical Industry Press.
Beijing: 222010.
|
|
23
|
Wei SY, Yao WX, Ji WY, Wei JQ and Peng SQ:
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of anthraquinones in rhubarbs
by high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector
and mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 141:1710–1715. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang YP, Cai DF and Liu J: Research on
acting mechanism of rhubarb on aquaporin-4 in rats with blood-brain
barrier injury after acute cerebral hemorrhage. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi
Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 26:152–156. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Yong-Jun F, Yi Z, Zun-Hua K, Zhen-Guo Z,
Feng Z and Lu-Ning B: Effects of rhubarb powder on serum complement
3, complement 4, and hs-CRP in patients with intracerebral
hemorrhage. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 33:168–171.
2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Zhou X, Wang L, Wang M, Xu L, Yu L, Fang T
and Wu M: Emodin-induced microglial apoptosis is associated with
TRB3 induction. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 33:594–602. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang YS and Chen FQ: The influence of ten
decoction methods on active components in rhubarb decoction. Zhong
Cheng Yao. 12:5–7. 1990.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Rosenberg GA, Mun-Bryce S, Wesley M and
Kornfeld M: Collagenase induced intracerebral hemorrhage in rats.
Stroke. 21:801–807. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park HK, Lee SH, Chu K and Roh JK: Effects
of celecoxib on volumes of hematoma and edema in patients with
primary intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurol Sci. 279:43–46. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bangsow T, Baumann E, Bangsow C, Jaeger
MH, Pelzer B, Gruhn P, Wolf S, von Melchner H and Stanimirovic DB:
The epithelial membrane protein 1 is a novel tight junction protein
of the blood-brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 28:1249–1260.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Keep RF, Zhou N, Xiang J, Andjelkovic AV,
Hua Y and Xi G: Vascular disruption and blood-brain barrier
dysfunction in intracerebral hemorrhage. Fluids Barriers CNS.
11:182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brott T, Broderick J, Kothari R, Barsan W,
Tomsick T, Sauerbeck L, Spilker J, Duldner J and Khoury J: Early
hemorrhage growth in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage.
Stroke. 28:1–5. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pardridge WM: Targeting neurotherapeutic
agents through the blood-brain barrier. Arch Neurol. 59:35–40.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liebner S, Czupalla CJ and Wolburg H:
Current concepts of blood-brain barrier development. Int J Dev
Biol. 55:467–476. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nusrat A, Parkos CA, Verkade P, Foley CS,
Liang TW, Innis-Whitehouse W, Eastburn KK and Madara JL: Tight
junctions are membrane microdomains. J Cell Sci. 113:1771–1781.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fischer S, Wobben M, Marti HH, Renz D and
Schaper W: Hypoxia-induced hyperpermeability in brain microvessel
endothelial cells involves VEGF-mediated changes in the expression
of zonula occludens-1. Microvasc Res. 63:70–80. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|