|
1
|
Sakai D: Future perspectives of cell-based
therapy for intervertebral disc disease. Eur Spine J. 17(Suppl 4):
452–458. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sudo H, Yamada K, Iwasaki K, Higashi H,
Ito M, Minami A and Iwasaki N: Global identification of genes
related to nutrient deficiency in intervertebral disc cells in an
experimental nutrient deprivation model. PLoS One. 8:e588062013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Richardson SM, Walker RV, Parker S, Rhodes
NP, Hunt JA, Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA: Intervertebral disc
cell-mediated mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells.
24:707–716. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sobajima S, Vadala G, Shimer A, Kim JS,
Gilbertson LG and Kang JD: Feasibility of a stem cell therapy for
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 8:888–896. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song YQ, Karasugi T, Cheung KM, Chiba K,
Ho DW, Miyake A, Kao PY, Sze KL, Yee A, Takahashi A, et al: Lumbar
disc degeneration is linked to a carbohydrate sulfotransferase 3
variant. J Clin Invest. 123:4909–4917. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
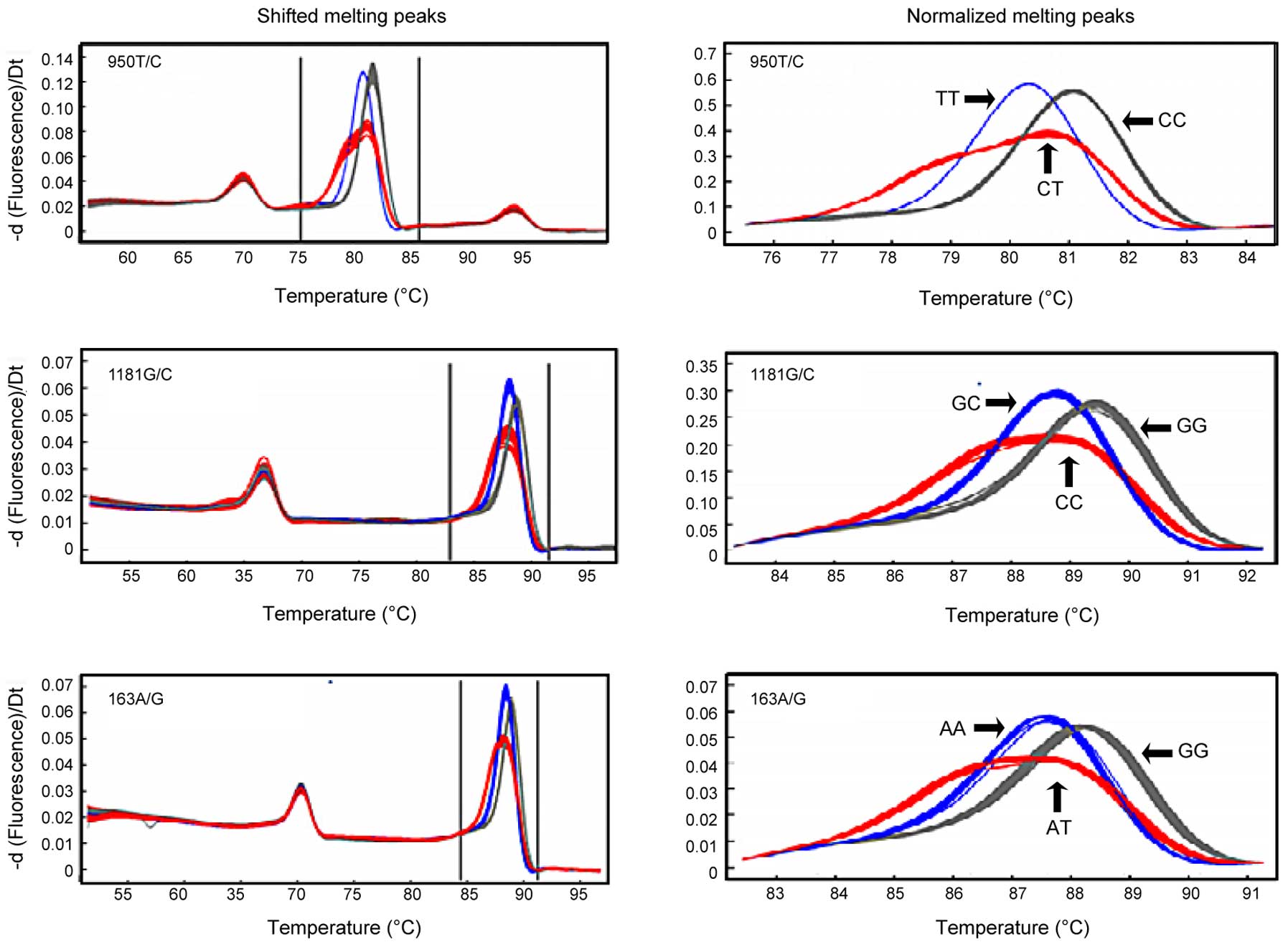
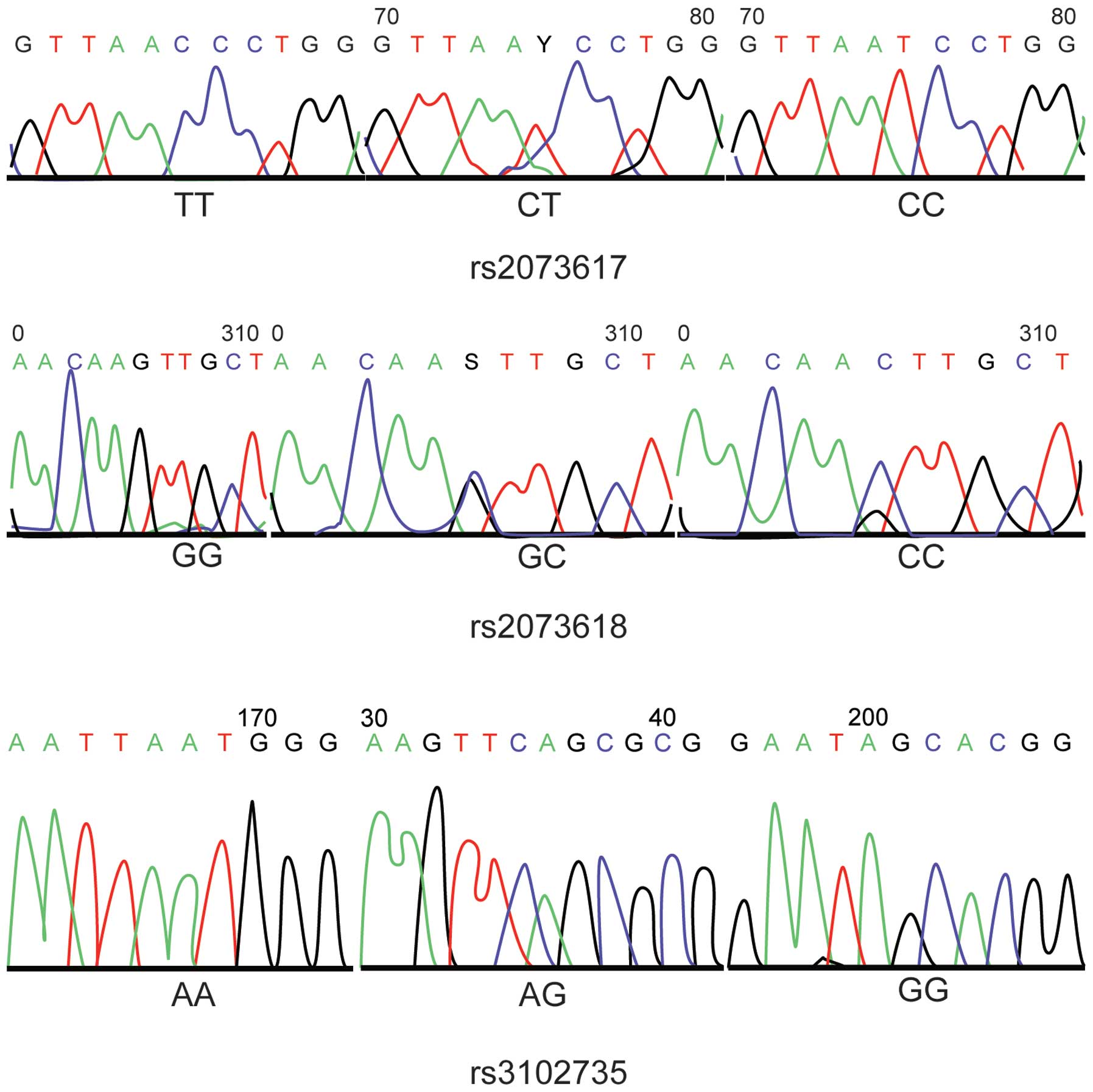
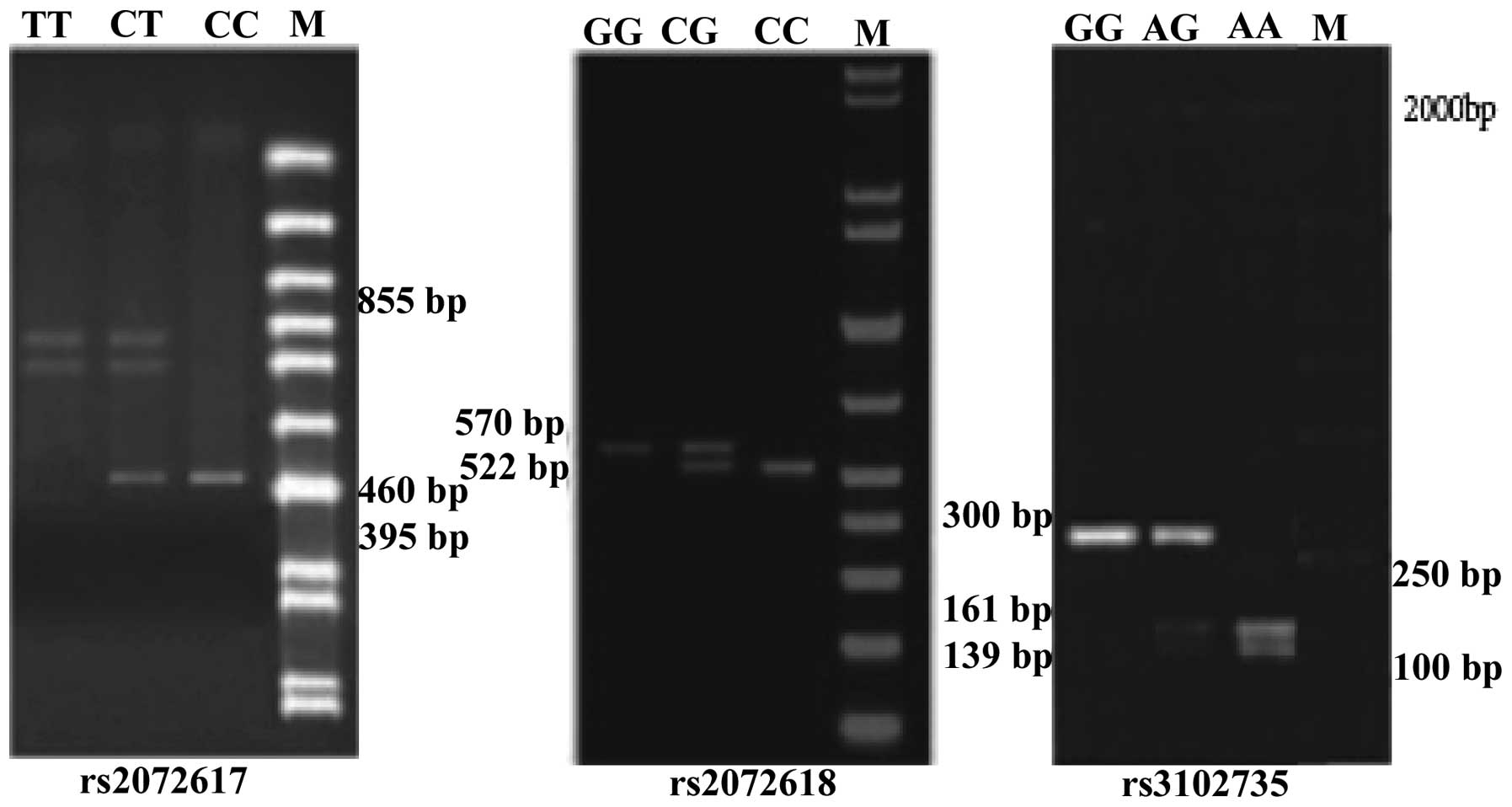
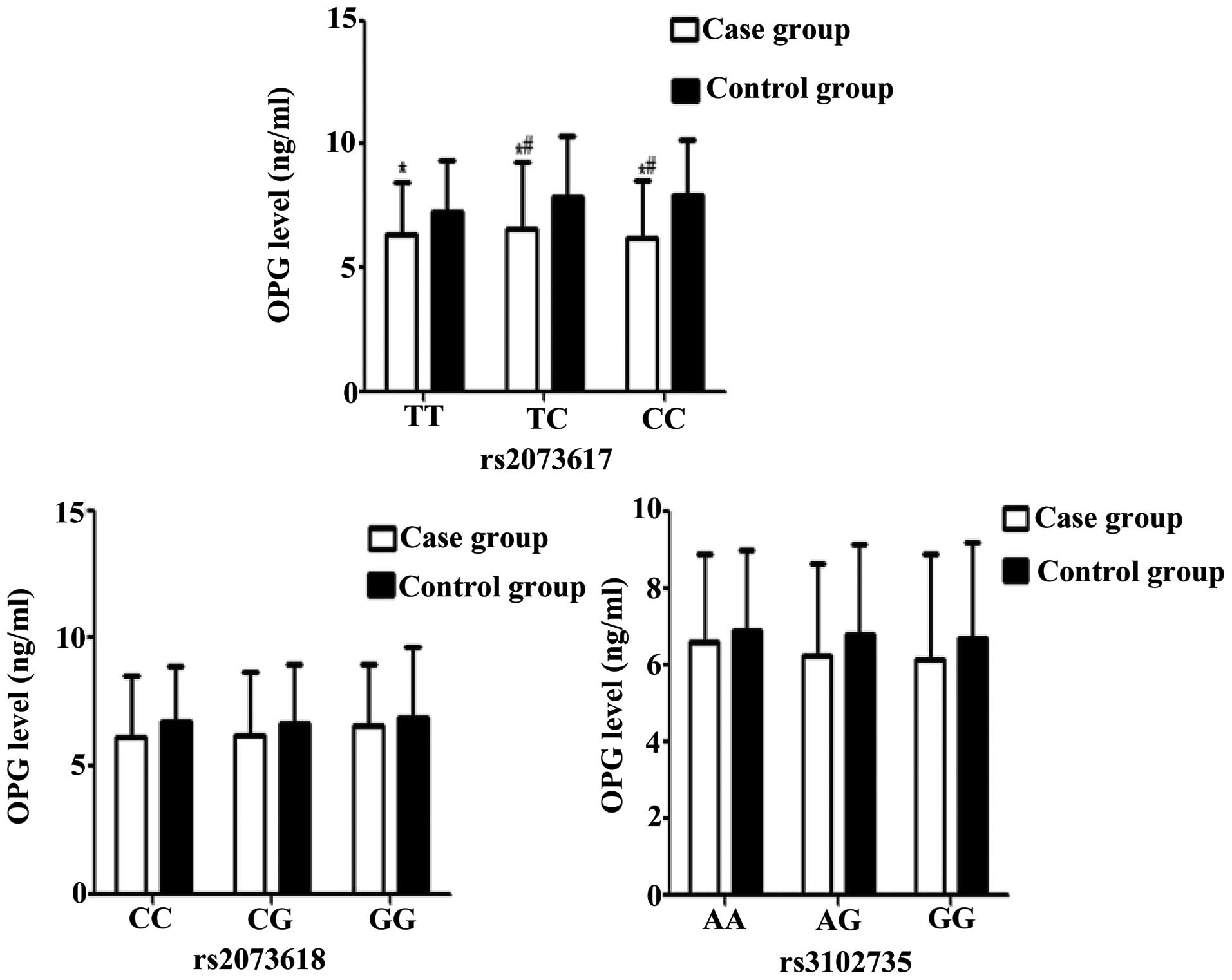
Wang YX, Griffith JF, Zeng XJ, Deng M,
Kwok AW, Leung JC, Ahuja AT, Kwok T and Leung PC: Prevalence and
sex difference of lumbar disc space narrowing in elderly chinese
men and women: Osteoporotic fractures in men (Hong Kong) and
osteoporotic fractures in women (Hong Kong) studies. Arthritis
Rheum. 65:1004–1010. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hangai M, Kaneoka K, Kuno S, Hinotsu S,
Sakane M, Mamizuka N, Sakai S and Ochiai N: Factors associated with
lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in the elderly. Spine J.
8:732–740. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu G, Cao P, Chen H, Yuan W, Wang J and
Tang X: MiR-27a regulates apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells by
targeting PI3K. PLoS One. 8:e752512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kalichman L and Hunter DJ: The genetics of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Familial predisposition and
heritability estimation. Joint Bone Spine. 75:383–387. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guehring T, Wilde G, Sumner M, Grünhagen
T, Karney GB, Tirlapur UK and Urban JP: Notochordal intervertebral
disc cells: Sensitivity to nutrient deprivation. Arthritis Rheum.
60:1026–1034. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Smith LJ, Nerurkar NL, Choi KS, Harfe BD
and Elliott DM: Degeneration and regeneration of the intervertebral
disc: Lessons from development. Dis Model Mech. 4:31–41. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takatalo J, Karppinen J, Taimela S,
Niinimäki J, Laitinen J, Blanco Sequeiros R, Paananen M, Remes J,
Näyhä S, Tammelin T, et al: Body mass index is associated with
lumbar disc degeneration in young Finnish males: Subsample of
Northern Finland birth cohort study 1986. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
14:872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang YX and Griffith JF: Menopause causes
vertebral endplate degeneration and decrease in nutrient diffusion
to the intervertebral discs. Med Hypotheses. 77:18–20. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Omair A, Holden M, Lie BA, Reikeras O and
Brox JI: Treatment outcome of chronic low back pain and
radiographic lumbar disc degeneration are associated with
inflammatory and matrix degrading gene variants: A prospective
genetic association study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 14:1052013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kalb S, Martirosyan NL, Kalani MY, Broc GG
and Theodore N: Genetics of the degenerated intervertebral disc.
World Neurosurg. 77:491–501. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Purmessur D, Walter BA, Roughley PJ,
Laudier DM, Hecht AC and Iatridis J: A role for TNF-α in
intervertebral disc degeneration: A non-recoverable catabolic
shift. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 433:151–156. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liang QQ, Li XF, Zhou Q, Xing L, Cheng SD,
Ding DF, Xu LQ, Tang DZ, Bian Q, Xi ZJ, et al: The expression of
osteoprotegerin is required for maintaining the intervertebral disc
endplate of aged mice. Bone. 48:1362–1369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ciacli C and Puşchiţă M: RANKL/RANK/OPG
molecular complex-control factors in bone remodeling in psoriatic
arthritis. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 115:354–360.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chollet ME, Brouland JP, Bal Dit Sollier
C, Bauduer F, Drouet L and Bellucci S: Evidence of a colocalisation
of osteoprotegerin (OPG) with von Willebrand factor (VWF) in
platelets and megakaryocytes alpha granules. Studies from normal
and grey platelets. Br J Haematol. 148:805–807. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pobeha P, Petrasova D, Tkacova R and Joppa
P: Circulatory osteoprotegerin is related to osteoporosis of the
hip in patients with COPD. Respir Med. 108:621–627. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jayakumar P and Di Silvio L: Osteoblasts
in bone tissue engineering. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 224:1415–1440.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tousoulis D, Siasos G, Maniatis K,
Oikonomou E, Kioufis S, Zaromitidou M, Paraskevopoulos T, Michalea
S, Kollia C, Miliou A, et al: Serum osteoprotegerin and osteopontin
levels are associated with arterial stiffness and the presence and
severity of coronary artery disease. Int J Cardiol. 167:1924–1928.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Trouvin AP and Goeb V: Receptor activator
of nuclear factor-κB ligand and osteoprotegerin: Maintaining the
balance to prevent bone loss. Clin Interv Aging. 5:345–354.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ohmori R, Momiyama Y, Taniguchi H, Tanaka
N, Kato R, Nakamura H, Ohsuzu F, Nagano M and Egashira T:
Association between osteoprotegerin gene polymorphism and coronary
artery disease in Japanese men. Atherosclerosis. 187:215–217. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Granchi D, Pellacani A, Spina M, Cenni E,
Savarino LM, Baldini N and Giunti A: Serum levels of
osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB
ligand as markers of periprosthetic osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg
Am. 88:1501–1509. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vega D, Maalouf NM and Sakhaee K: CLINICAL
Review #: The role of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB
(RANK)/RANK ligand/osteoprotegerin: Clinical implications. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 92:4514–4521. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grimaud E, Soubigou L, Couillaud S,
Coipeau P, Moreau A, Passuti N, Gouin F, Redini F and Heymann D:
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand
(RANKL)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) ratio is increased in severe
osteolysis. Am J Pathol. 163:2021–2031. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Silva I and Branco JC: Rank/Rankl/opg:
Literature review. Acta Reumatol Port. 36:209–218. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakamura M, Udagawa N, Matsuura S, Mogi M,
Nakamura H, Horiuchi H, Saito N, Hiraoka BY, Kobayashi Y, Takaoka
K, et al: Osteoprotegerin regulates bone formation through a
coupling mechanism with bone resorption. Endocrinology.
144:5441–5449. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jurado S, Nogués X, Agueda L,
Garcia-Giralt N, Urreizti R, Yoskovitz G, Pérez-Edo L, Saló G,
Carreras R, Mellibovsky L, et al: Polymorphisms and haplotypes
across the osteoprotegerin gene associated with bone mineral
density and osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 21:287–296.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun T, Chen M, Lin X, Yu R, Zhao Y and
Wang J: The influence of osteoprotegerin genetic polymorphisms on
bone mineral density and osteoporosis in Chinese postmenopausal
women. Int Immunopharmacol. 22:200–203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morinaga T, Nakagawa N, Yasuda H, Tsuda E
and Higashio K: Cloning and characterization of the gene encoding
human osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor. Eur J
Biochem. 254:685–691. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
García-Unzueta MT, Riancho JA, Zarrabeitia
MT, Sañudo C, Berja A, Valero C, Pesquera C, Paule B,
González-Macías J and Amado JA: Association of the 163A/G and
1181G/C osteoprotegerin polymorphism with bone mineral density.
Horm Metab Res. 40:219–224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vidal C, Formosa R and Xuereb-Anastasi A:
Functional polymorphisms within the TNFRSF11B (osteoprotegerin)
gene increase the risk for low bone mineral density. J Mol
Endocrinol. 47:327–333. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim JG, Kim JH, Kim JY, Ku SY, Jee BC, Suh
CS, Kim SH and Choi YM: Association between osteoprotegerin (OPG),
receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (RANK) and RANK ligand
(RANKL) gene polymorphisms and circulating OPG, soluble RANKL
levels and bone mineral density in Korean postmenopausal women.
Menopause. 14:913–918. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu S, Yi Z, Ling M and Shi J: Association
between g.19163A>G and g.23298T>C genetic variants of the
osteoprotegerin gene and bone mineral density in Chinese women.
Hormones (Athens). 12:578–583. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Q, Chen Z, Huang Y, Li Q, Zhu L, Cai
X, He G, Xie Y and Liu Q: The relationship between osteoprotegerin
gene polymorphisms and bone mineral density in Chinese
postmenopausal women. Int Immunopharmacol. 17:404–407. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Battié MC, Boyd SK and Videman T:
The osseous endplates in lumbar vertebrae: Thickness, bone mineral
density and their associations with age and disk degeneration.
Bone. 48:804–809. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Salo S, Leinonen V, Rikkonen T, Vainio P,
Marttila J, Honkanen R, Tuppurainen M, Kröger H and Sirola J:
Association between bone mineral density and lumbar disc
degeneration. Maturitas. 79:449–455. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
World Medical Association: World Medical
Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim NK, Shin DA, Han IB, Yoo EH, Kim SH
and Chung SS: The association of aggrecan gene polymorphism with
the risk of intervertebral disc degeneration. Acta Neurochir
(Wien). 153:129–133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mwale F, Iatridis JC and Antoniou J:
Quantitative MRI as a diagnostic tool of intervertebral disc matrix
composition and integrity. Eur Spine J. 17(Suppl 4): 432–440. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hashemi M, Ebrahimi M, Amininia S, Naderi
M, Eskandari-Nasab E and Taheri M: Evaluation of rs3102735 and
rs2073617 Osteoprotegerin Gene Polymorphisms and the Risk of
Childhood Acute lymphoblastic Leukemia in Zahedan Southeast Iran.
Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 8:39–44. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Stephens M and Scheet P: Accounting for
decay of linkage disequilibrium in haplotype inference and
missing-data imputation. Am J Hum Genet. 76:449–462. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Risbud MV and Shapiro IM: Role of
cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc
content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:44–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shamji MF, Setton LA, Jarvis W, So S, Chen
J, Jing L, Bullock R, Isaacs RE, Brown C and Richardson WJ:
Proinflammatory cytokine expression profile in degenerated and
herniated human intervertebral disc tissues. Arthritis Rheum.
62:1974–1982. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li WF, Hou SX, Yu B, Li MM, Férec C and
Chen JM: Genetics of osteoporosis: Accelerating pace in gene
identification and validation. Hum Genet. 127:249–285. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zupan J, Mencej-Bedrac S, Jurković-Mlakar
S, Prezelj J and Marc J: Gene-gene interactions in RANK/RANKL/OPG
system influence bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 118:102–106. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shimizu S, Asou Y, Itoh S, Chung UI,
Kawaguchi H, Shinomiya K and Muneta T: Prevention of cartilage
destruction with intraarticular osteoclastogenesis inhibitory
factor/osteoprotegerin in a murine model of osteoarthritis.
Arthritis Rheum. 56:3358–3365. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kadri A, Ea HK, Bazille C, Hannouche D,
Lioté F and Cohen-Solal ME: Osteoprotegerin inhibits cartilage
degradation through an effect on trabecular bone in murine
experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 58:2379–2386. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Styrkarsdottir U, Halldorsson BV,
Gretarsdottir S, Gudbjartsson DF, Walters GB, Ingvarsson T,
Jonsdottir T, Saemundsdottir J, Center JR, Nguyen TV, et al:
Multiple genetic loci for bone mineral density and fractures. N
Engl J Med. 358:2355–2365. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee YH, Woo JH, Choi SJ, Ji JD and Song
GG: Associations between osteoprotegerin polymorphisms and bone
mineral density: A meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 37:227–234. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Stolina M, Schett G, Dwyer D, Vonderfecht
S, Middleton S, Duryea D, Pacheco E, Van G, Bolon B, Feige U, et
al: RANKL inhibition by osteoprotegerin prevents bone loss without
affecting local or systemic inflammation parameters in two rat
arthritis models: Comparison with anti-TNFalpha or anti-IL-1
therapies. Arthritis Res Ther. 11:R1872009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kepler CK, Ponnappan RK, Tannoury CA,
Risbud MV and Anderson DG: The molecular basis of intervertebral
disc degeneration. Spine J. 13:318–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Raj PP: Intervertebral disc:
Anatomy-physiology-pathophysiology-treatment. Pain Pract. 8:18–44.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Matzko ME, Bowen TR and Smith WR:
Orthogenomics: An update. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 20:536–546. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Biscetti F, Porreca CF, Bertucci F,
Straface G, Santoliquido A, Tondi P, Angelini F, Pitocco D, Santoro
L, Gasbarrini A, et al: TNFRSF11B gene polymorphisms increased risk
of peripheral arterial occlusive disease and critical limb ischemia
in patients with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 51:1025–1032.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Straface G, Biscetti F, Pitocco D,
Bertoletti G, Misuraca M, Vincenzoni C, Snider F, Arena V,
Stigliano E, Angelini F, et al: Assessment of the genetic effects
of polymorphisms in the osteoprotegerin gene, TNFRSF11B, on serum
osteoprotegerin levels and carotid plaque vulnerability. Stroke.
42:3022–3028. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|