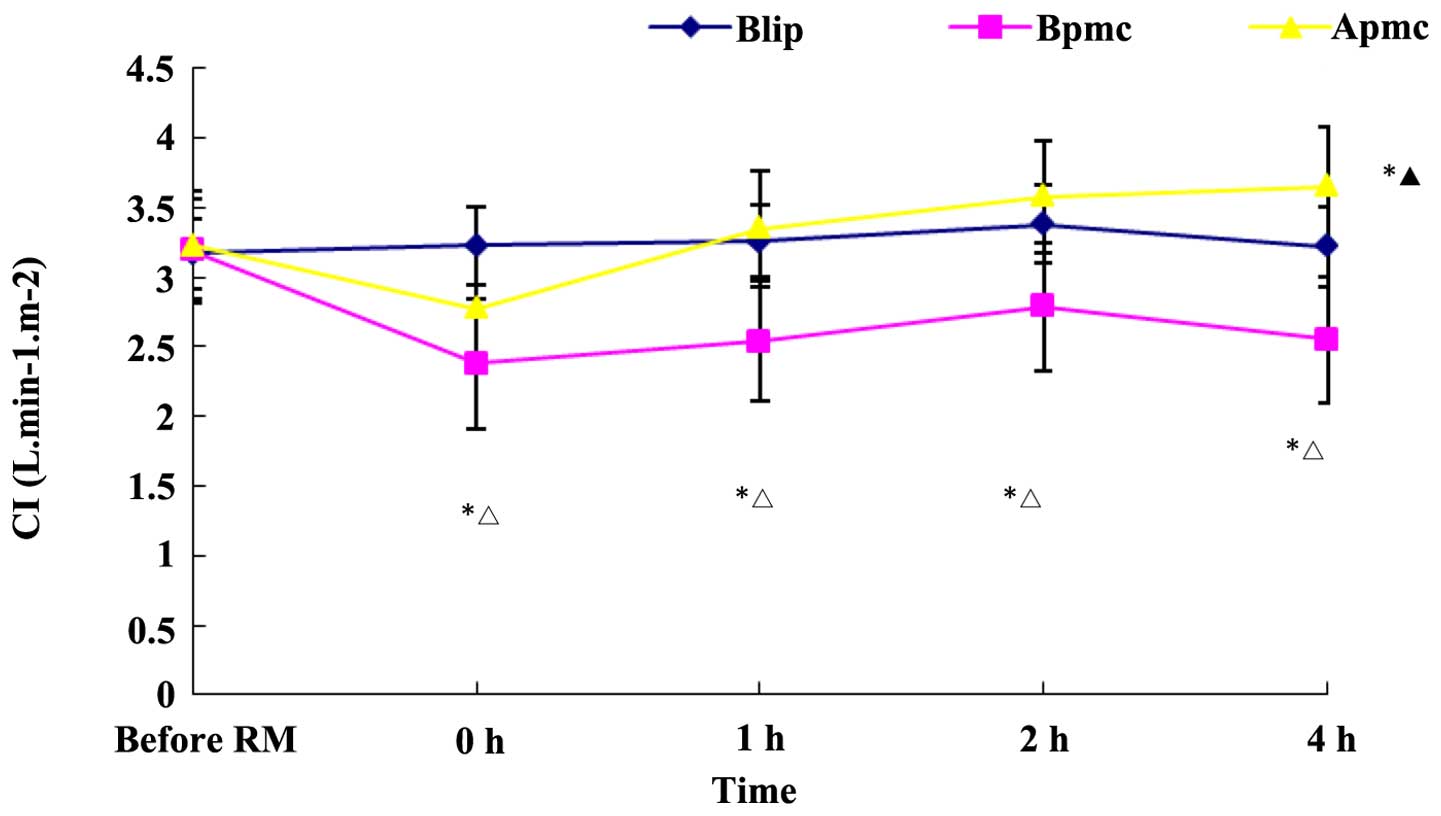
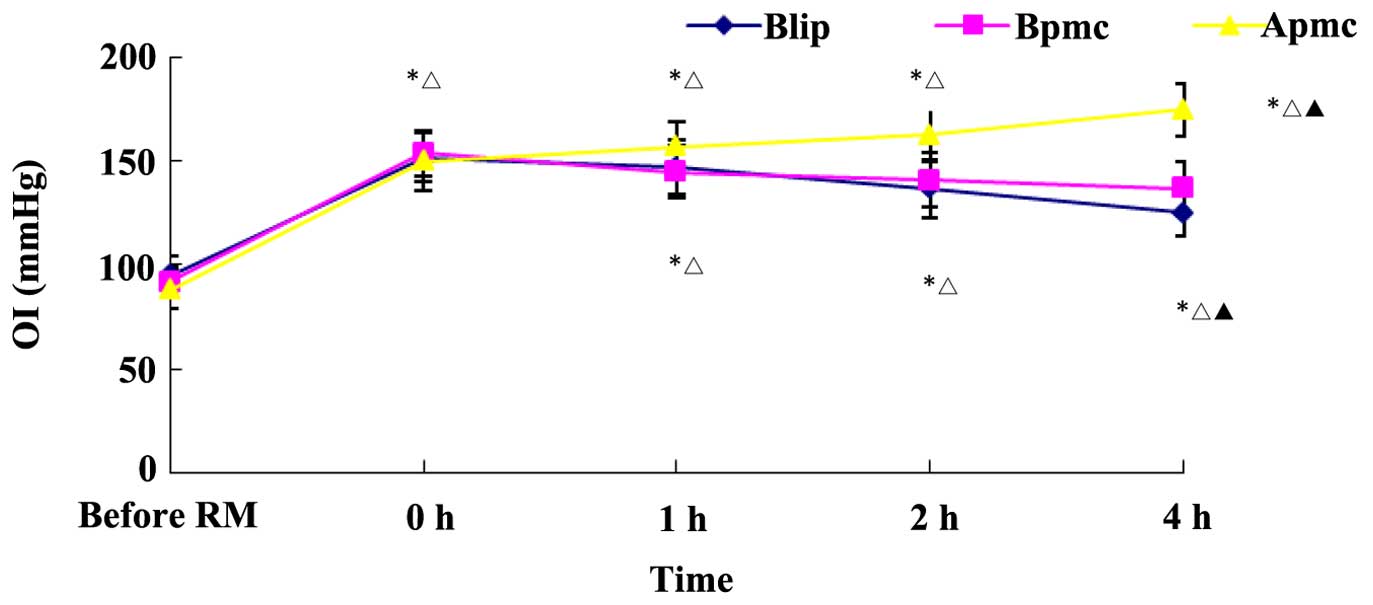
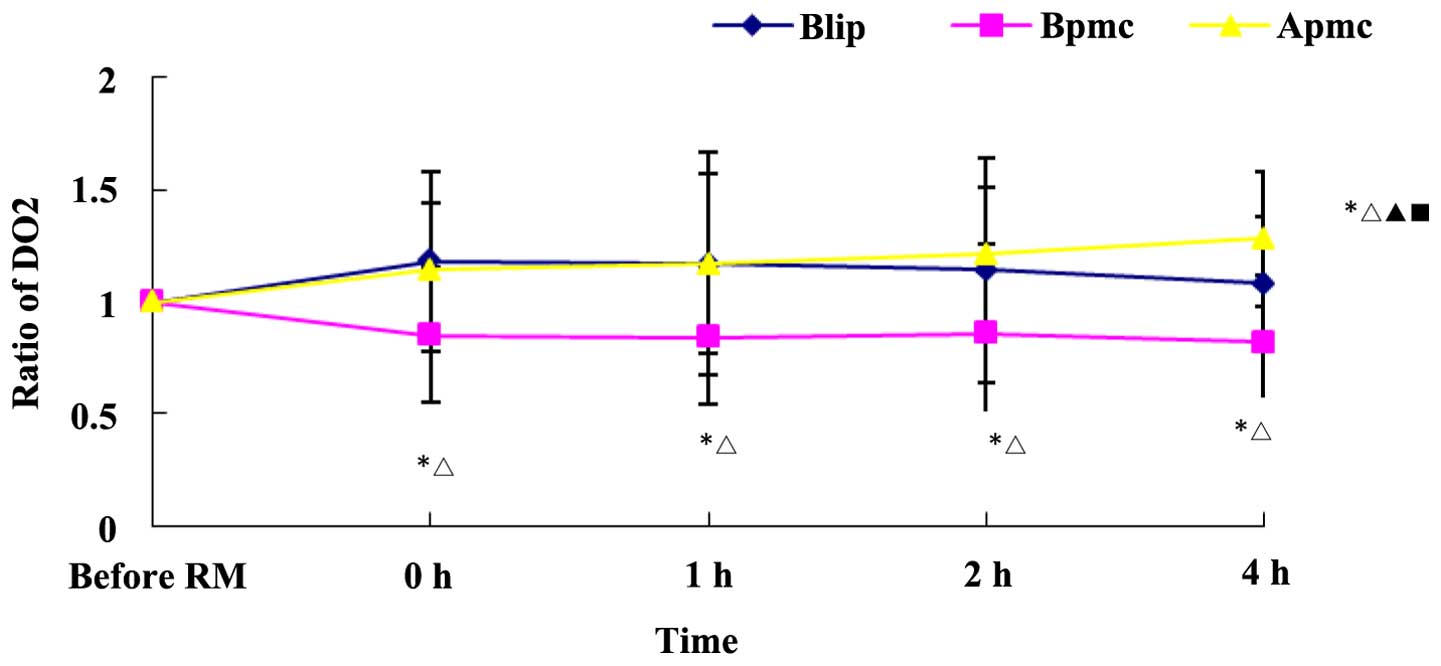
|
1
|
Richard JC, Maggiore SM, Jonson B, Mancebo
J, Lemaire F and Brochard L: Influence of tidal volume on alveolar
recruitment. Respective role of PEEP and a recruitment maneuver. Am
J Respir Crit Care Med. 163:1609–1613. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cakar N, der Kloot TV, Youngblood M, Adams
A and Nahum A: Oxygenation response to a recruitment maneuver
during supine and prone positions in an oleic acid-induced lung
injury model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 161:1949–1956. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grasso S, Mascia L, Del Turco M, Malacarne
P, Giunta F, Brochard L, Slutsky AS and Marco Ranieri V: Effects of
recruiting maneuvers in patients with acute respiratory distress
syndrome ventilated with protective ventilatory strategy.
Anesthesiology. 96:795–802. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hickling KG: Reinterpreting the
pressure-volume curve in patients with acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care. 8:32–38. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu Y, Lei Z and Niu S: Respiratory
pressure-volume curve in open lung strategy in dog with acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Chin J Respir Crit Monit. 3:198–203.
2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Gang L, Sun XY, Xu JQ, Zhang XL, Kou LX,
Jiang ZH and Zhang L: A comparative study between inflation and
deflation pressure-volume curve in determining the optimal positive
end-expiratory pressure. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
24:74–77. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Demirkol D, Karabocuoglu M and Citak A:
Airway pressure release ventilation: an alternative ventilation
mode for pediatric acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Indian J
Pediatr. 77:1322–1325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kallet RH: Patient-ventilator interaction
during acute lung injury, and the role of spontaneous breathing:
part 2: airway pressure release ventilation. Respir Care.
56:190–203; discussion 203–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hamdy HA, Gaber R and Gehan HA: Study of
cardiac and hemodynamic changes with airway pressure release
ventilation and pressure control ventilation in children with acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Eur Respir J. 40:46392012.
|
|
10
|
Grasso S, Terragni P, Mascia L, Fanelli V,
Quintel M, Herrmann P, Hedenstierna G, Slutsky AS and Ranieri VM:
Airway pressure-time curve profile (stress index) detects tidal
recruitment/hyperinflation in experimental acute lung injury. Crit
Care Med. 32:1018–1027. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lim SC, Adams AB, Simonson DA, Dries DJ,
Broccard AF, Hotchkiss JR and Marini JJ: Intercomparison of
recruitment maneuver efficacy in three models of acute lung injury.
Crit Care Med. 32:2371–2377. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Frank JA, McAuley DF, Gutierrez JA, Daniel
BM, Dobbs L and Matthay MA: Differential effects of sustained
inflation recruitment maneuvers on alveolar epithelial and lung
endothelial injury. Crit Care Med. 33:181–188; discussion 254–255.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hartland BL, Newell TJ and Damico N:
Alveolar recruitment maneuvers under general anesthesia: a
systematic review of the literature. Respir Care. 60:609–620. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu L, Wang SP, Zhang NX and Qin YZ:
Effects of different levels of positive end expiratory pressure on
lung recruitment and hemodynamics after sustained inflation in
acute respiratory distress syndrome in sheep. Zhongguo Wei Zhong
Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 17:679–682. 2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qiu HB, Xu HY, Yang Y, Zhou SX, Chen YM
and Sun HM: Effects of positive end-expiratory pressure on lung
recruited volume and oxygenation in patients with acute respiratory
distress syndrome. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
16:399–402. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pintado MC, de Pablo R, Trascasa M,
Milicua JM, Rogero S, Daguerre M, Cambronero JA, Arribas I and
Sánchez-García M: Individualized PEEP setting in subjects with
ARDS: arandomized controlled pilot study. Respir Care.
58:1416–1423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Spieth PM and de Gama Abreu M: Lung
recruitment in ARDS: We are still confused, but on a higher PEEP
level. Crit Care. 16:1082012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Crotti S, Mascheroni D, Caironi P, Pelosi
P, Ronzoni G, Mondino M, Marini JJ and Gattinoni L: Recruitment and
derecruitment during acute respiratory failure: a clinical study.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 164:131–140. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Daoud EG, Farag HL and Chatburn RL: Airway
pressure release ventilation: what do we know? Respir Care.
57:282–292. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|