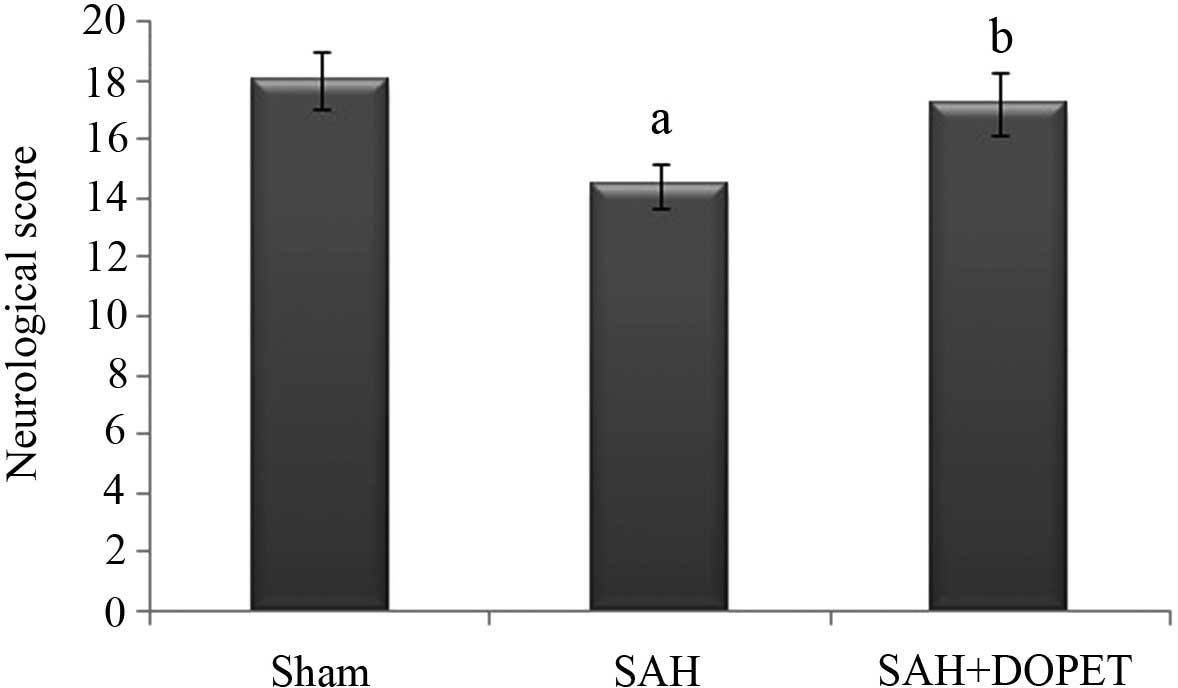
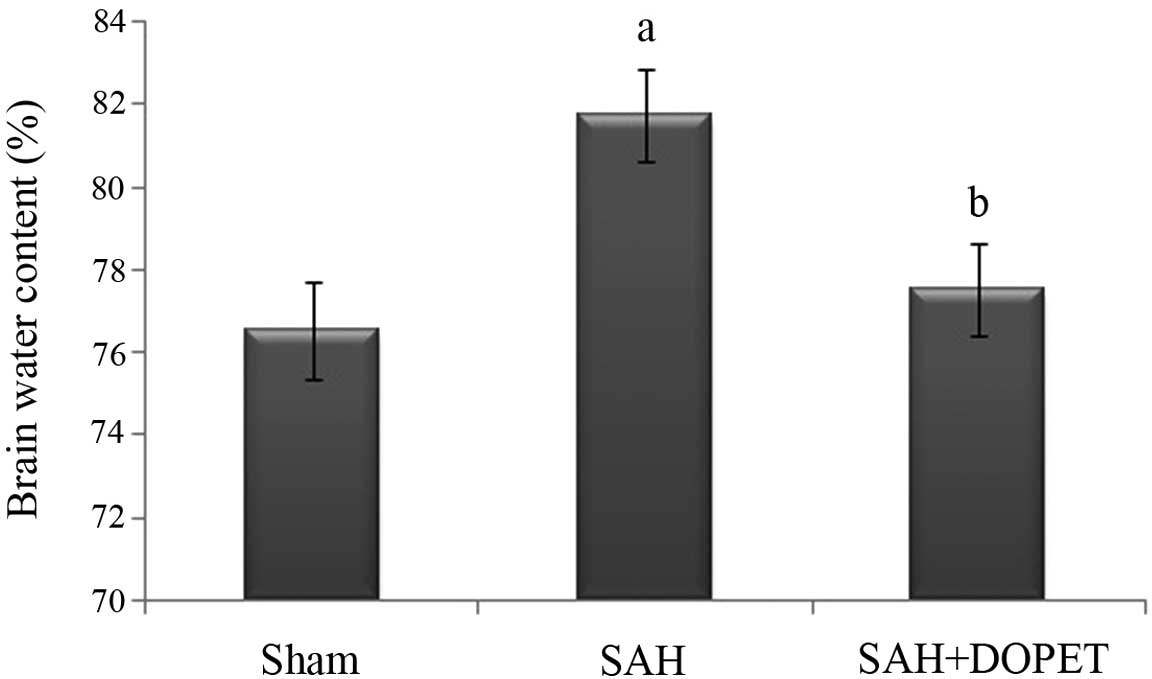
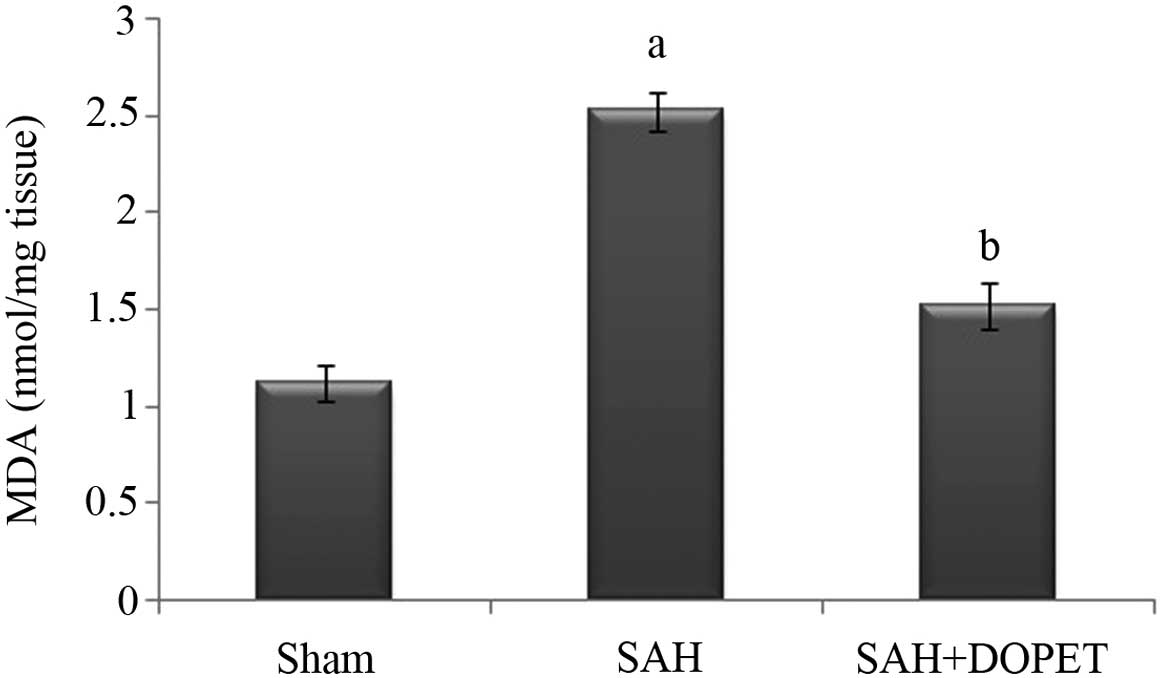
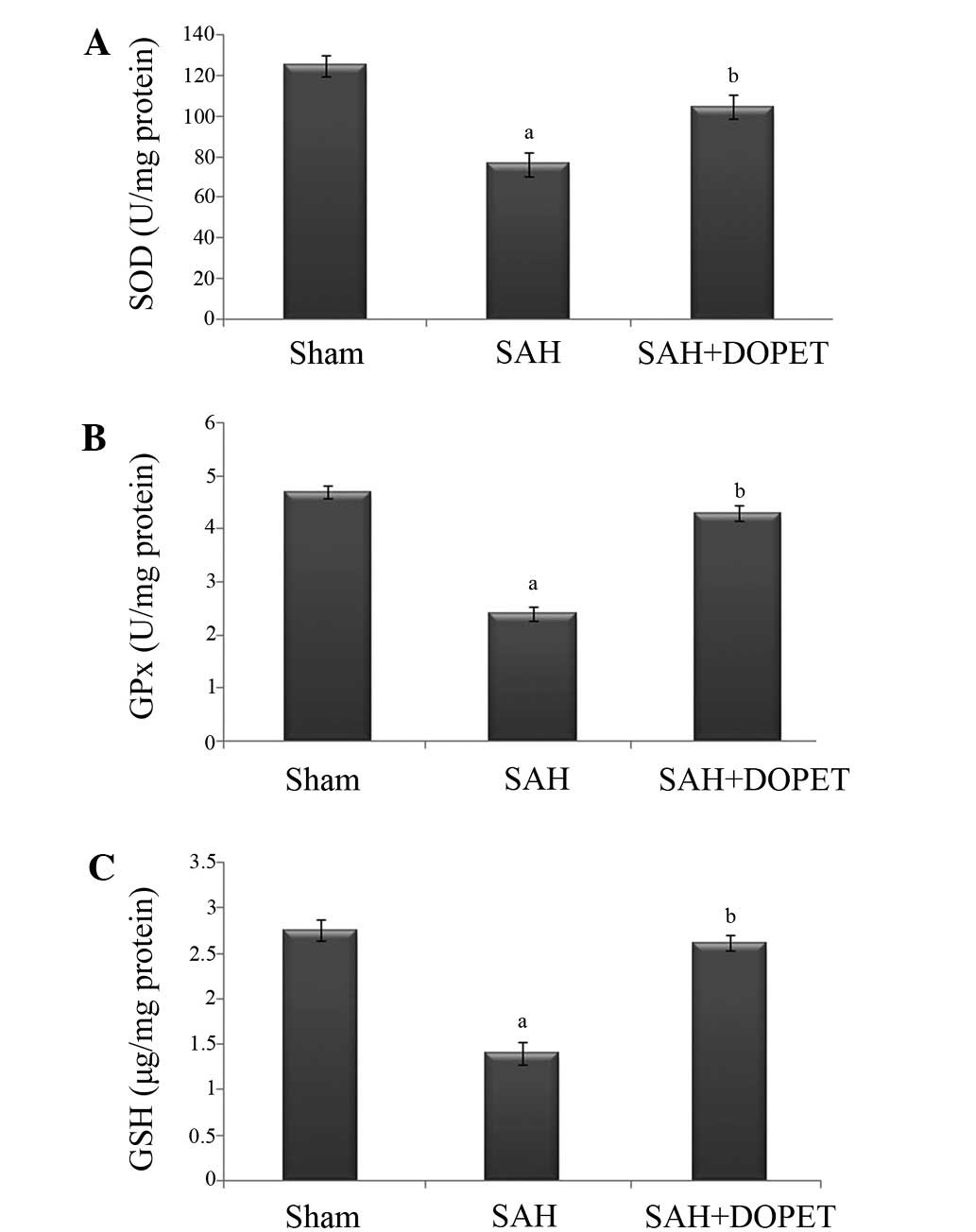
|
1
|
Ansar S, Maddahi A and Edvinsson L:
Inhibition of cerebrovascular raf activation attenuates cerebral
blood flow and prevents upregulation of contractile receptors after
subarachnoid hemorrhage. BMC Neurosci. 12:1072011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lantigua H, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Schmidt
JM, Lee K, Badjatia N, Agarwal S, Claassen J, Connolly ES and
Stephan A: Mayercorresponding author. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Who
dies, and why? Crit Care. 19:3092015.
|
|
3
|
Schievink WI, Riedinger M, Jhutty TK and
Simon P: Racial disparities in subarachnoid hemorrhage mortality:
Los Angeles county, california, 1985–1998. Neuroepidemiology.
23:299–305. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van Gijn J and Rinkel GJ: Subarachnoid
haemorrhage: Diagnosis, causes and management. Brain. 124:249–278.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hop JW, Rinkel GJ, Algra A and van Gijn J:
Changes in functional outcome and quality of life in patients and
caregivers after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg.
95:957–963. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen S, Feng H, Sherchan P, Klebe D, Zhao
G, Sun X, Zhang J, Tang J and Zhang JH: Controversies and evolving
new mechanisms in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Prog Neurobio.
115:64–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pluta RM, Hansen-Schwartz J, Dreier J,
Vajkoczy P, Macdonald RL, Nishizawa S, Kasuya H, Wellman G, Keller
E, Zauner A and Dorsch N: Cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid
hemorrhage: Time for a new world of thought. Neurol Res.
31:151–158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cahill J, Calvert JW and Zhang JH:
Mechanisms of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 26:1341–1353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vajkoczy P, Meyer B, Weidauer S, Raabe A,
Thome C, Ringel F, Breu V and Schmiedek P: Clazosentan
(AXV-034343), a selective endothelin A receptor antagonist, in the
prevention of cerebral vasospasm following severe aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage: Results of a randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, multicenter phase IIa study. J Neurosurg.
103:9–17. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Macdonald RL, Kassell NF, Mayer S,
Ruefenacht D, Schmiedek P, Weidauer S, Frey A, Roux S and Pasqualin
A: CONSCIOUS-1 Investigators: Clazosentan to overcome neurological
ischemia and infarction occurring after subarachnoid hemorrhage
(CONSCIOUS-1): Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2
dose-finding trial. Stroke. 39:3015–3021. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hansen-Schwartz J, Vajkoczy P, Macdonald
RL, Pluta RM and Zhang JH: Cerebral vasospasm: Looking beyond
vasoconstriction. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 28:252–256. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rabinstein AA: Secondary brain injury
after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: More than vasospasm.
Lancet Neurol. 10:593–595. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Broderick JP, Brott TG, Duldner JE,
Tomsick T and Leach A: Initial and recurrent bleeding are the major
causes of death following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke.
25:1342–1347. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sehba FA and Bederson JB: Mechanisms of
acute brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Res.
28:381–398. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gaetani P, Pasqualin A, Rodriguezy Baena
R, Borasio E and Marzatico F: Oxidative stress in the human brain
after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 89:748–754. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Claassen J, Carhuapoma JR, Kreiter KT, Du
EY, Connolly ES and Mayer SA: Global cerebral edema after
subarachnoid hemorrhage: frequency, predictors and impact on
outcome. Stroke. 33:1225–1232. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cahill J and Zhang JH: Subarachnoid
hemorrhage: Is it time for a new direction? Stroke. 40(Suppl 3):
S86–S87. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
László FA, Varga C and Dóczi T: Cerebral
oedema after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Pathogenetic significance of
vasopressin. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 133:122–133. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dóczi T, Joó F, Adám G, Bozóky B and
Szerdahelyi P: Blood-brain barrier damage during the acute stage of
subarachnoid hemorrhage, as exemplified by a new animal model.
Neurosurgery. 18:733–739. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Palade C, Ciurea AV, Nica DA, Savu R and
Moisa HA: Interference of apoptosis in the pathophysiology of
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Asian J Neurosurg. 8:106–111. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gilgun-Sherki Y, Rosenbaum Z, Melamed E
and Offen D: Antioxidant therapy in acute central nervous system
injury: Current state. Pharmacol Rev. 54:271–284. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de la Torre R, Covas MI, Pujadas MA, Fitó
M and Farré M: Is dopamine behind the health benefits of red wine?
Eur J Nutr. 45:307–310. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Auñon-Calles D, Canut L and Visioli F:
Toxicological evaluation of pure hydroxytyrosol. Food Chem Toxicol.
55:498–504. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
González-Correa JA, Navas MD,
Lopez-Villodres JA, Trujillo M, Espartero JL and De La Cruz JP:
Neuroprotective effect of hydroxytyrosol and hydroxytyrosol acetate
in rat brain slices subjected to hypoxia-reoxygenation. Neurosci
Lett. 446:143–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ristagno G, Fumagalli F,
Porretta-Serapiglia C, Orrù A, Cassina C, Pesaresi M, Masson S,
Villanova L, Merendino A, Villanova A, et al: Hydroxytyrosol
attenuates peripheral neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetes
in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 60:5859–5865. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Granados-Principal S, El-Azem N, Pamplona
R, Ramirez-Tortosa C, Pulido-Moran M, Vera-Ramirez L, Quiles JL,
Sanchez-Rovira P, Naudí A, Portero-Otin M, et al: Hydroxytyrosol
ameliorates oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats with breast cancer.
Biochem Pharmacol. 90:25–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rouissi K, Hamrita B, Kouidi S, Messai Y,
Jaouadi B, Hamden K, Medimegh I, Ouerhani S, Cherif M and Elgaaied
AB: In vivo prevention of bladder urotoxicity: Purified
hydroxytyrosol ameliorates urotoxic effects of cyclophosphamide and
buthionine sulfoximine in mice. Int J Toxicol. 30:419–427. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Capasso G, Di Gennaro CI, Della Ragione F,
Manna C, Ciarcia R, Florio S, Perna A, Pollastro RM, Damiano S,
Mazzoni O, et al: In vivo effect of the natural antioxidant
hydroxytyrosol on cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in rats. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 23:1186–1195. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pan S, Liu L, Pan H, Ma Y, Wang D, Kang K,
Wang J, Sun B, Sun X and Jiang H: Protective effects of
hydroxytyrosol on liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 57:1218–1227. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cao K, Xu J, Zou X, Li Y, Chen C, Zheng A,
Li H, Li H, Szeto IM, Shi Y, et al: Hydroxytyrosol prevents
diet-induced metabolic syndrome and attenuates mitochondrial
abnormalities in obese mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 67:396–407. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hagiwara K, Goto T, Araki M, Miyazaki H
and Hagiwara H: Olive polyphenol hydroxytyrosol prevents bone loss.
Eur J Pharmacol. 662:78–84. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de la Puerta R, Ruiz Gutierrez V and Hoult
JR: Inhibition of leukocyte 5-lipoxygenase by phenolics from virgin
olive oil. Biochem Pharmacol. 57:445–449. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
González-Santiago M, Martín-Bautista E,
Carrero JJ, Fonollá J, Baró L, Bartolomé MV, Gil-Loyzaga P and
López-Huertas E: One month administration of hydroxytyrosol,
phenolic antioxidant present in olive oil, to hyperlipemic rabbits
improves blood lipid profile, antioxidant status and reduces
atherosclerosis development. Atherosclerosis. 188:35–42. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao B, Ma Y, Xu Z, Wang J, Wang F, Wang
D, Pan S, Wu Y, Pan H, Xu D, et al: Hydroxytyrosol, a natural
molecule from olive oil, suppresses the growth of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inactivating AKT and nuclear
factor-kappa B pathways. Cancer Lett. 347:79–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee-Huang S and Huang PL, Zhang D, Lee JW,
Bao J, Sun Y, Chang YT, Zhang J and Huang PL: Discovery of
small-molecule HIV-1 fusion and integrase inhibitors oleuropein and
hydroxytyrosol: Part I. fusion (corrected) inhibition. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 354:872–878. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cabrerizo S, De La Cruz JP,
López-Villodres JA, Muñoz-Marín J, Guerrero A, Reyes JJ, Labajos MT
and González-Correa JA: Role of the inhibition of oxidative stress
and inflammatory mediators in the neuroprotective effects of
hydroxytyrosol in rat brain slices subjected to hypoxia
reoxygenation. J Nutr Biochem. 24:2152–2157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
St-Laurent-Thibault C, Arseneault M,
Longpré F and Ramassamy C: Tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol, two main
components of olive oil, protect N2a cells against
amyloid-β-induced toxicity. Involvement of the NF-κB signaling.
Curr Alzheimer Res. 8:543–551. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schaffer S, Podstawa M, Visioli F, Bogani
P, Müller WE and Eckert GP: Hydroxytyrosol-rich olive mill
wastewater extract protects brain cells in vitro and ex vivo. J
Agric Food Chem. 55:5043–5049. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Park S, Yamaguchi M, Zhou C, Calvert JW,
Tang J and Zhang JH: Neurovascular protection reduces early brain
injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 35:2412–2417. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF and Hu XJ:
Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable
to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical
validation. Stroke. 26:627–634; discussion 635. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xi G, Hua Y, Keep RF, Younger JG and Hoff
JT: Brain edema after intracerebral Hemorrhage: The effects of
systemic complement depletion. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 81:253–256.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tsubokawa T, Jadhav V, Solaroglu I,
Shiokawa Y, Konishi Y and Zhang JH: Lecithinized superoxide
dismutase improves outcomes and attenuates focal cerebral ischemic
injury via antiapoptotic mechanisms in rats. Stroke. 38:1057–1062.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wallace DC: A mitochondrial paradigm of
metabolic and degenerative diseases, aging and cancer: A dawn for
evolutionary medicine. Annu Rev Genet. 39:359–407. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Winterbourn CC: Biological reactivity and
biomarkers of the neutrophil oxidant, hypochlorous acid.
Toxicology. 181-182:223–227. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Macdonald RL and Weir BK: Cerebral
vasospasm and free radicals. Free Radic Biol Med. 16:633–643. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi Watanabe
M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S and Ohta
S: Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively
reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 13:688–694. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Floyd RA and Carney JM: Free radical
damage to protein and DNA: mechanisms involved and relevant
observations on brain undergoing oxidative stress. Ann Neurol.
32(Suppl): S22–S27. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Asano T: Oxyhemoglobin as the principal
cause of cerebral vasospasm: A holistic view of its actions. Crit
Rev Neurosurg. 9:303–318. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rodriguez y Baena R, Gaetani P, Silvani V,
Spanu G and Marzatico F: Effect of nimodipine on mitochondrial
respiration in different rat brain areas after subarachnoid
haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 43:177–181.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kaynar MY, Tanriverdi T, Kafadar AM,
Kacira T, Uzun H, Aydin S, Gumustas K, Dirican A and Kuday C:
Detection of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular
cell adhesion molecule-1 in both cerebrospinal fluid and serum of
patients after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg.
101:1030–1036. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rossi R, Dalle-Donne I, Milzani A and
Giustarini D: Oxidized forms of glutathione in peripheral blood as
biomarkers of oxidative stress. Clin Chem. 52:1406–1414. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Erşahin M, Ozsavcı D, Sener A, Ozakpınar
OB, Toklu HZ, Akakin D, Sener G and Yeğen BÇ: Obestatin alleviates
subarachnoid haemorrhage-induced oxidative injury in rats via its
anti-apoptotic and antioxidant effects. Brain Inj. 27:1181–1189.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Faine LA, Rodrigues HG, Galhardi CM, Ebaid
GM, Diniz YS, Padovani CR and Novelli EL: Effects of olive oil and
its minor constituents on serum lipids, oxidative stress, and
energy metabolism in cardiac muscle. Can J Physiol Pharml.
84:239–245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Deiana M, Incani A, Rosa A, Corona G,
Atzeri A, Loru D, Paola Melis M and Assunta Dessì M: Protective
effect of hydroxytyrosol and its metabolite homovanillic alcohol on
H(2)O(2) induced lipid peroxidation in renal tubular epithelial
cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 46:2984–2990. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Erşahin M, Toklu HZ, Erzik C, Cetinel S,
Akakin D, Velioğlu-Oğünç A, Tetik S, Ozdemir ZN, Sener G and Yeğen
BC: The anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of ghrelin in
subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced oxidative brain damage in rats. J
Neurotrauma. 27:1143–1155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P and Mahajan
RT: Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of
upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 7:65–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kandhare AD, Raygude KS, Ghosh P, Ghule AE
and Bodhankar SL: Neuroprotective effect of naringin by modulation
of endogenous biomarkers in streptozotocin induced painful diabetic
neuropathy. Fitoterapia. 83:650–659. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Pastore A, Federici G, Bertini E and
Piemonte F: Analysis of glutathione: Implication in redox and
detoxification. Clinica Chim Acta. 333:19–39. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Gutierrez VR, de la Puerta R and Catalá A:
The effect of tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein on the
non-enzymatic lipid peroxidation of rat liver microsomes. Mol Cell
Biochem. 217:35–41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Graham DI, McIntosh TK, Maxwell WL and
Nicoll JA: Recent advances in neurotrauma. J Neuropathol Exp
Neurol. 59:641–651. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Katzman R, Clasen R, Klatzo I, Meyer JS,
Pappius HM and Waltz AG: Report of joint committee for stroke
resources. IV. Brain edema in stroke. Stroke. 8:512–540. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kimelberg HK: Current concepts of brain
edema. Review of laboratory investigations. J Neurosurg.
83:1051–1059. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Feillet-Coudray C, Sutra T, Fouret G,
Ramos J, Wrutniak-Cabello C, Cabello G, Cristol JP and Coudray C:
Oxidative stress in rats fed a high-fat high-sucrose diet and
preventive effect of polyphenols: Involvement of mitochondrial and
NAD(P)H oxidase systems. Free Radic Biol Med. 46:624–632. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Fukuhara T, Douville CM, Eliott JP, Newell
DW and Winn HR: Relationship between intracranial pressure and the
development of vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 38:710–715; discussion 716–717. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Imperatore C, Germanò A, d'Avella D,
Tomasello F and Costa G: Effects of the radical scavenger AVS on
behavioral and BBB changes after experimental subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Life Sci. 66:779–790. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Dóczi T: The pathogenetic and prognostic
significance of blood-brain barrier damage at the acute stage of
aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Clinical and experimental
studies. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 77:110–132. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Fornezza U, Carraro R, Demo P, Zamperetti
N, Volpin L, Landi A, De Luca GP and Benedetti A: The transcranial
Doppler ultrasonography in the evaluation of vasospasm and of
intracranial hypertension after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Agressologie. 31:259–261. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Mohagheghi F, Bigdeli MR, Rasoulian B,
Zeinanloo AA and Khoshbaten A: Dietary virgin olive oil reduces
blood brain barrier permeability, brain edema and brain injury in
rats subjected to ischemia-reperfusion. Scientific World Journal.
10:1180–1191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ayer RE and Zhang JH: Oxidative stress in
subarachnoid haemorrhage: Signifi-cance in acute brain injury and
vasospasm. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 104:33–41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Cregan SP, MacLaurin JG, Craig C,
Robertson GS, Nicholson DW, Park DS and Slack RS: Bax-dependent
caspase-3 activation is a key determinant in p53-induced apoptosis
in neurons. J Neurosci. 19:7860–7869. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Simard JM, Geng Z, Woo SK, Ivanova S,
Tosun C, Melnichenko L and Gerzanich V: Glibenclamide reduces
inflammation, vasogenic edema and caspase-3 activation after
subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:317–330.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|