|
1
|
Zhang P, Yang Y, Lv R, Zhang Y, Xie W and
Chen J: Effect of the intensity of continuous renal replacement
therapy in patients with sepsis and acute kidney injury: a
single-center randomized clinical trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
27:967–973. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang N, Jiang L, Zhu B, Wen Y and Xi X-M:
Beijing Acute Kidney Injury Trial (BAKIT) Workgroup: Fluid balance
and mortality in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury:
a multicenter prospective epidemiological study. Crit Care.
19:3712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Smith OM, Wald R, Adhikari NKJ, Pope K,
Weir MA and Bagshaw SM: Canadian Critical Care Trials Group:
Standard versus accelerated initiation of renal replacement therapy
in acute kidney injury (STARRT-AKI): study protocol for a
randomized controlled trial. Trials. 14:3202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chou YH, Huang TM, Wu VC, Wang CY, Shiao
CC, Lai CF, Tsai HB, Chao CT, Young GH, Wang WJ, et al: NSARF Study
Group: Impact of timing of renal replacement therapy initiation on
outcome of septic acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 15:R1342011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vesconi S, Cruz DN, Fumagalli R,
Kindgen-Milles D, Monti G, Marinho A, Mariano F, Formica M,
Marchesi M, René R, et al: DOse REsponse Multicentre International
collaborative Initiative (DO-RE-MI Study Group): Delivered dose of
renal replacement therapy and mortality in critically ill patients
with acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 13:R572009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yasuda H, Uchino S, Uji M, Ohnuma T, Namba
Y, Katayama S, Kawarazaki H, Toki N, Takeda K, Izawa J, et al:
Japanese Society for Physicians and Trainees in Intensive Care
Clinical Trial Group: The lower limit of intensity to control
uremia during continuous renal replacement therapy. Crit Care.
18:5392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Limaye AP, Kirby KA, Rubenfeld GD,
Leisenring WM, Bulger EM, Neff MJ, Gibran NS, Huang ML, Hayes TK
Santo, Corey L, et al: Cytomegalovirus reactivation in critically
ill immunocompetent patients. JAMA. 300:413–422. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ronco C, Tetta C, Mariano F, Wratten ML,
Bonello M, Bordoni V, Cardona X, Inguaggiato P, Pilotto L, d'Intini
V, et al: Interpreting the mechanisms of continuous renal
replacement therapy in sepsis: the peak concentration hypothesis.
Artif Organs. 27:792–801. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hattori N, Oda S, Sadahiro T, Nakamura M,
Abe R, Shinozaki K, Nomura F, Tomonaga T, Matsushita K, Kodera Y,
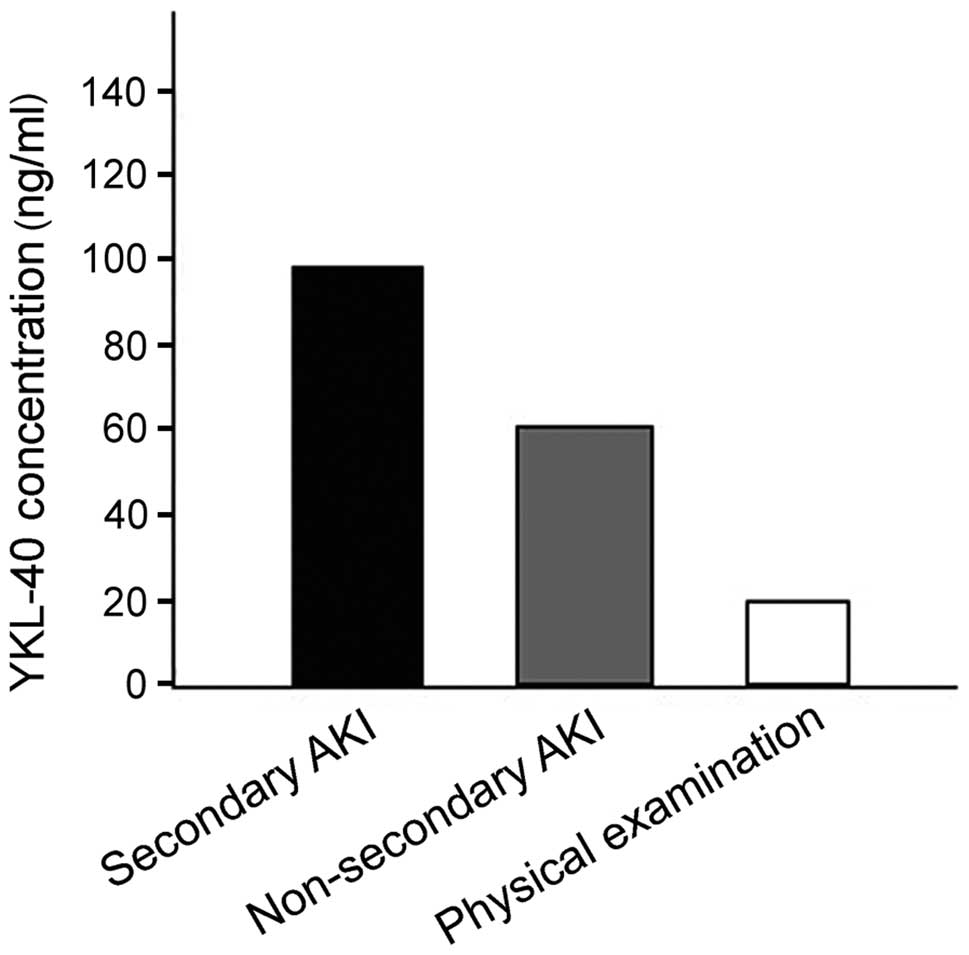
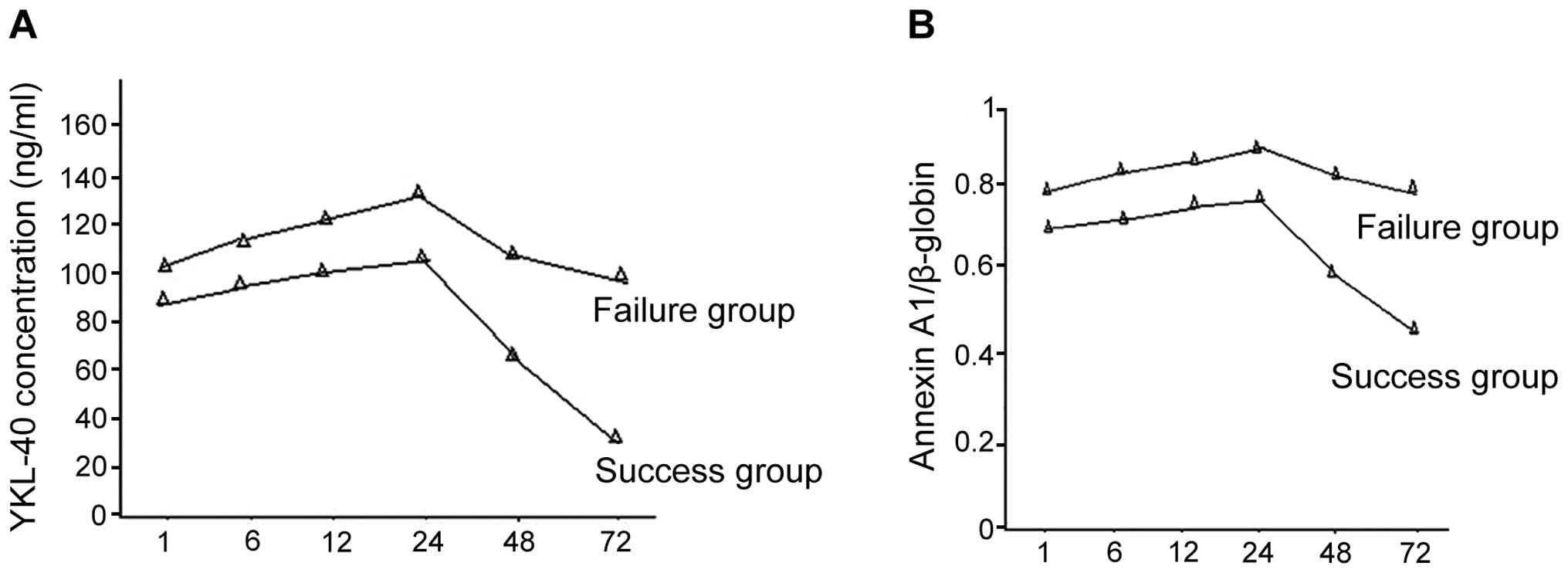
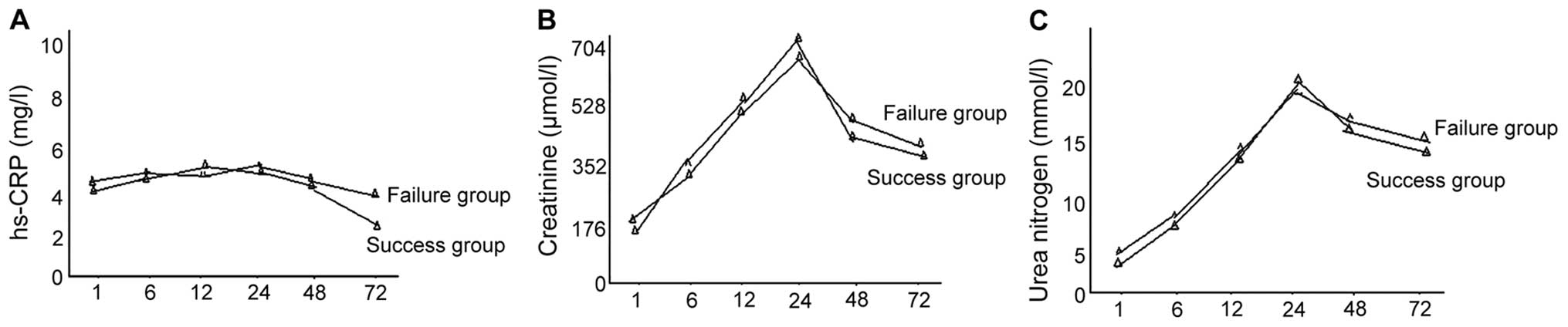
et al: YKL-40 identified by proteomic analysis as a biomarker of
sepsis. Shock. 32:393–400. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kliger AS, Foley RN, Goldfarb DS,
Goldstein SL, Johansen K, Singh A and Szczech L: KDOQI US
commentary on the 2012 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Anemia
in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 62:849–859. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmidt IM, Hall IE, Kale S, Lee S, He CH,
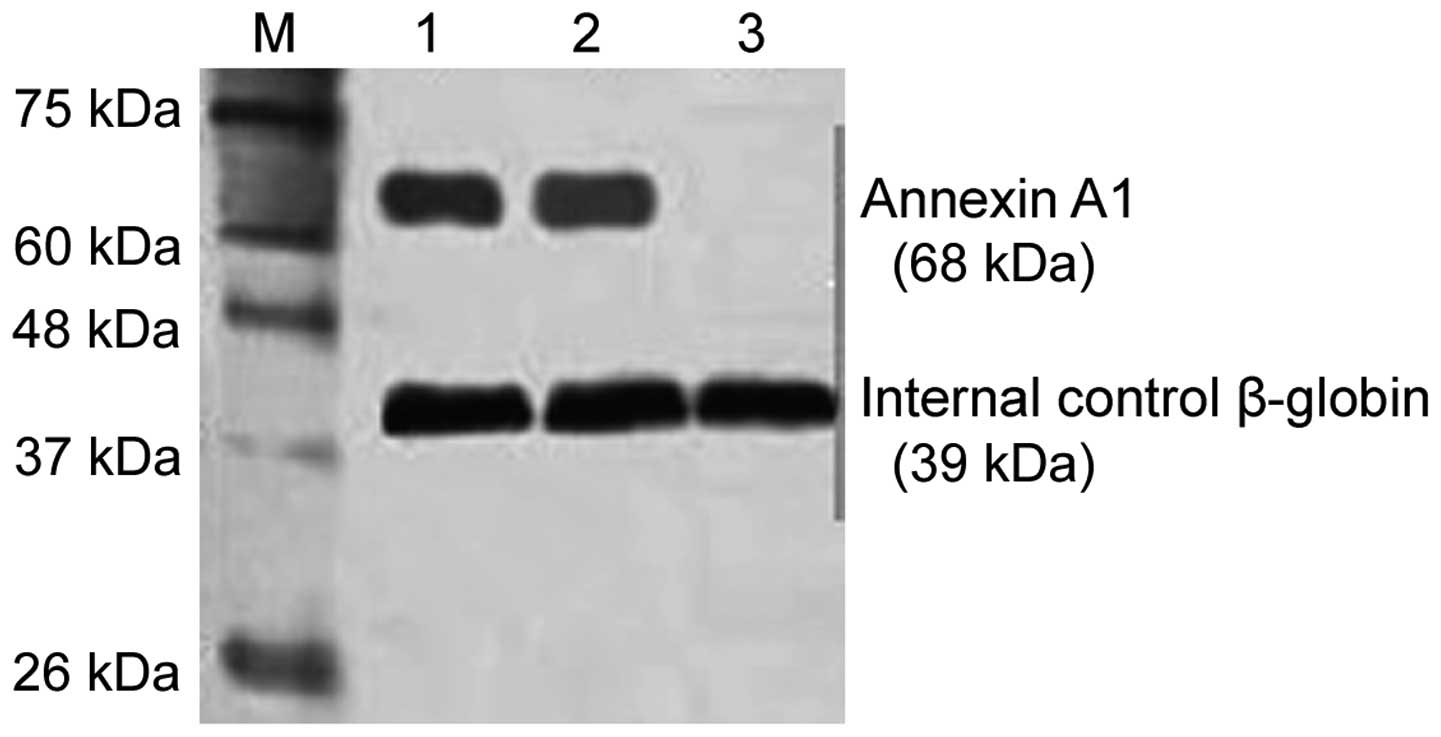
Lee Y, Chupp GL, Moeckel GW, Lee CG, Elias JA, et al:
Chitinase-like protein Brp-39/YKL-40 modulates the renal response
to ischemic injury and predicts delayed allograft function. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 24:309–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang L, He H, Wang J and Sheng D:
Expression of cartilage glycoprotein 39 in peripheral blood
monocytes of septic rat and its role in TLR 4-NF-κB signaling
pathways. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:2459–2464. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Horlacher T, Noti C, de Paz JL,
Bindschädler P, Hecht ML, Smith DF, Fukuda MN and Seeberger PH:
Characterization of annexin A1 glycan binding reveals binding to
highly sulfated glycans with preference for highly sulfated heparan
sulfate and heparin. Biochemistry. 50:2650–2659. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McArthur S, Cristante E, Paterno M,
Christian H, Roncaroli F, Gillies GE and Solito E: Annexin A1: A
central player in the anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective role of
microglia. J Immunol. 185:6317–6328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brooks AC, Rickards KJ and Cunningham FM:
Modulation of equine neutrophil adherence and migration by the
annexin-1 derived N-terminal peptide, Ac2-26. Vet Immunol
Immunopathol. 145:214–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|