Introduction
Congestive heart failure (HF) is a leading cause of
morbidity and mortality worldwide (1). Despite advances in medical therapy,
mechanical support and heart transplantation, nearly half of all
patients with HF succumb to the disease within five years of the
initial diagnosis. Therefore, novel strategies need to be
investigated to restore the structure and function of cardiac
muscle.
Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is
under evaluation as a regenerative therapeutic approach for HF
(2,3). In previous studies, MSCs showed
marginal improvement of cardiac function in animals and humans with
HF (4,5). In addition, MSCs have the potential for
clinical benefit in cardiovascular disease based on their
characteristics of anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and
proangiogenic properties (6,7), and their ability to stimulate
endogenous progenitor cells (8).
Moreover, MSCs can be isolated from bone marrow, umbilical cord
(UC) blood, and connective tissue (Wharton's jelly) (9), and can be expanded in culture to use as
a source of stem cells to elicit cardiac repair. In previous
studies, we investigated the safety and efficacy of human UC-MSCs
(HUC-MSCs) in rat (10–12) and human bone non-union (13).
In the present study, we describe our experience
using HUC-MSCs to treat patients with HF. The effect of HUC-MSCs on
the HF was then assessed in the following 12 months.
Materials and methods
Basic principles and ethical
considerations
The protocol of the present study was approved by
the Institutional Review Board and the Ethics Committee of Siping
Hospital of China Medical University. The study was conducted in
compliance with current Good Clinical Practice standards and in
accordance with the principles set forth under the Declaration of
Helsinki (1989).
Isolation and propagation of
HUC-MSCs
The HUC-MSC doses used in this study were derived
from two donated UCs obtained from healthy mothers during routine
term elective caesarean section birth. Fully informed consent was
obtained several weeks prior to delivery. HUC-MSC were isolated and
propagated as previously described (10–13). UCs
were filled with 0.1% collagenase (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO,
USA) in PBS and incubated at 37°C for 20 min. Each UC was washed
with proliferation medium [a-minimal essential medium (MEM), 10%
human AB serum; Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA], and the detached
cells were harvested after gentle massage of the UC. The cells were
centrifuged at 300 × g for 10 min, resuspended in proliferation
medium to seed in 75-cm 2 flasks at the density of 5×107
cells/ml. After 24 h of incubation, non-adherent cells were removed
and the culture medium was replaced every 3 days. The adherent
cells were cultured until they reached 80–90% confluence.
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry was performed to analyze the
cell-surface expression of typical protein markers. The adherent
cells were incubated with the following anti-human primary
antibodies CD31-phycoerythrin (PE), CD45-fluorescein isothiocyanate
(FITC), CD90-R-PE, HLA-DR-R-PE (Becton-Dickinson, Franklin Lakes,
NJ, USA). The total of 10,000 labeled cells were analyzed using a
Guava easyCyte flow cytometer running Guava Express Plus software
(Guava Technologies, Inc., Hayward, CA, USA).
Patients
The inclusion criteria were stable symptomatic
patients of ischemic cardiomyopathy [New York Heart Association
(NYHA) functional class II/III], older than 18 years, left
ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <40%. The exclusion
criteria were non-cardiac serious diseases expected to reduce the
patients's short-time survival, recent (<6 months) myocardial
infarction or an implanted pacemaker. The patients provided written
informed consent stating agreement to the treatment according to
the Siping Hospital of China Medical University. The general
characteristics of the patients are shown in Table I.
 | Table I.Baseline characteristics of the study
population. |
Table I.
Baseline characteristics of the study
population.
|
| Patient no. |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|
| Age (years) | 65 | 37 | 53 |
| Gender (M/F) | F | M | M |
| BMI
(kg/m2) | 23.62 | 27.39 | 27.85 |
| Duration of disease
(months) | 3 | 6 | 12 |
| Hypertension | Yes | No | No |
| Active smoker | Yes | No | No |
| Diabetes
mellitus | Yes | No | No |
| Family history of any
heart disease | No | No | No |
|
Hypercholesterolaemia | Yes | No | No |
| Medical therapy |
|
|
|
|
ACEI/ARB | Enalapril | Irbesartan | Enalapril |
|
β-blockers | Metoprolol | Bisoprolol |
|
Diuretics | Furosemide | Furosemide |
| Aldosterone
antagonists | Spironolactone | Spironolactone |
|
| Digoxin | Digoxin |
|
HUC-MSC intravenous infusion
HUC-MSCs (10 ml) with a cell density of
5×106-1×107/ml was given intravenously at a
rate of no more than 12.5×106/min and flushed with 20 ml
saline to ensure full cell dose delivery. Once the needle was fully
withdrawn, the puncture site was wrapped with sterilized dressing.
The patients remained in the supine decubitus on the operation bed
for another 30 min before off-bed activities. The patient was
monitored [temperature, blood pressure, pulse and
electrocardiograph (ECG)] at 0, 15, 30, 45 and 60 min, and then
hourly for a minimum of 4 h.
Six-minute walk test
Patients underwent exercise testing using six-minute
walk test a modified Bruce treadmill test. The patients were
monitored throughout with tests being terminated by physiological
markers (ST changes, arrhythmias, or chest pain) or by patient
request.
Clinical, functional assessment and
definitions
i) Primary safety assessments included monitoring
and recording of all adverse and serious adverse events. All
patient were monitored (temperature, blood pressure, pulse and
oxygen saturation) at 15, 30, 45 and 60 min, and then hourly for a
minimum of 4 h. They were discharged 24-h post-transplantation
given that the patient was afebrile and hemodynamically stable with
no signs of infection or any type of allergic reaction. Mortality
and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) defined as all-cause
death, myocardial infarction, hospitalization for HF, or major
arrhythmias were assessed at 3 months and 1 year.
ii) As exploratory secondary endpoints we
investigated the efficacy of HUC-MSC infusion as follows: The
change in global LVEF at 3, 6 and 12 months compared with baseline
as assessed by advanced cardiac imaging and changes in left
ventricular (LV) volumes; exercise capacity (six-minute walk test),
and NYHA classification at 3, 6 and 12 months compared with
baseline.
Pharmacological therapy protocol
The patient's pharmacological therapy consisted of:
i) Digoxin, 0.125 mg, once daily, p.o.; ii) β-acceptor blockers:
Metoprolol, 6.25 mg, twice daily, p.o., or bisoprolol 2.5 mg once
daily, p.o.; iii) diuretic: Furosemide, 20 mg once daily, i.v.;
and/or spironolactone: 20 mg once daily, p.o.; and iv)
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: Enalapril, 5 mg orally
twice daily; irbesartan: 150 mg orally once daily.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 16.0
software (Chicago, IL, USA). Safety and exploratory efficacy
secondary endpoints were observed for each patient against the
baseline values. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
Evaluation of HUC-MSCs
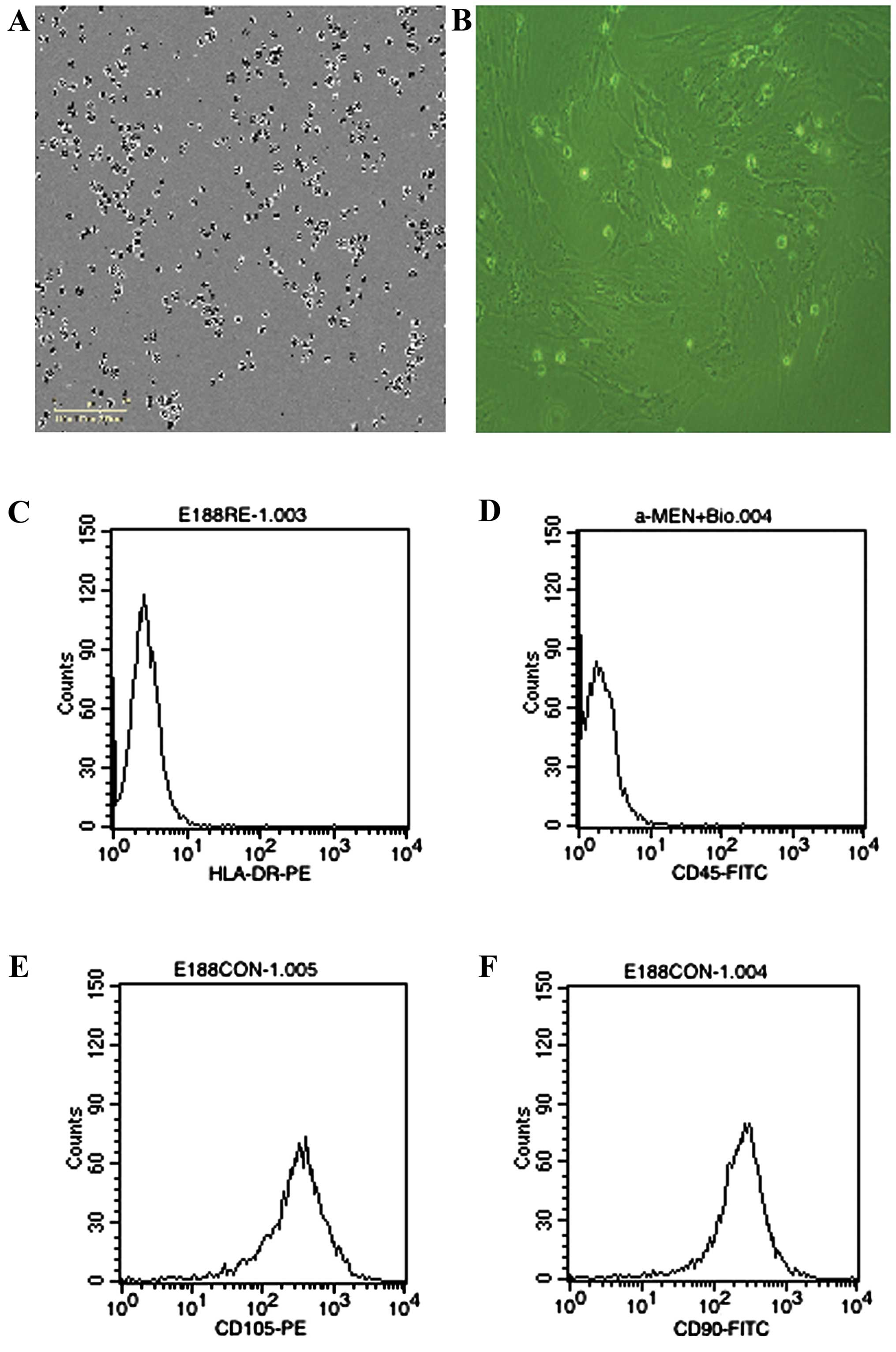
The cells derived from UC were observed 24 h after
seeding (Fig. 1A), when part of the
round mononuclear cells was adherent. Three days after inoculation,
small colonies of the adherent cells with typical fibroblast-shaped
morphology were obtained (Fig. 1B).
These primary cells reached monolayer confluence, after planting
for 5–6 days, when passaged for the first time. The fifth passage
cells were analyzed by flow cytometry, and were strongly positive
for CD105 and CD90, but negative for CD45 and HLA-DR (Fig. 1C-F).
General characteristics of the HF
patients
The general characteristics of the patients are
shown in Table I. The patients
included 2 males and 1 female with a mean age of 51.7 years (range,
37–65 years) at HUC-MSCs infusion. The patients were enrolled
between January 2010 and January 2012. The etiology of the HF was
ischemic cardiomyopathy. All the patients reached the 3, 6 and 12
months primary endpoint (Table
I).
LVEF
Two patients demonstrated a 65.1% increase in LVEF
at the end of 3 months, which was maintained increasing to 47.8% at
the end of 12 months post-HUC-MSC intravenous infusion. LVEF of
patient 1 decreased slowly in the observation period (Table II).
 | Table II.LVEF and cardiac dimensions. |
Table II.
LVEF and cardiac dimensions.
|
| Patient no. |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|
| Primary endpoint
(LVEF) |
|
|
|
| Baseline
(%) | 39.1 | 20.3 | 31.6 |
|
Post-transplantation 3 months
(%) | 29.9 | 60.1 | 52.2 |
|
Post-transplantation 6 months
(%) | 25.3 | 57.6 | 52.6 |
|
Post-transplantation 12 months
(%) | 23.1 | 56.3 | 46.7 |
| Secondary
endpoint |
|
|
|
|
LVEDV |
| Baseline
(mls) | 90.2 | 98 | 78.2 |
|
Post-transplantation 3
months | 145.1 | 110 | 79.6 |
|
Post-transplantation 6
months | 106.5 | 115 | 69.1 |
|
Post-transplantation 12
months | 164.4 | 203 | 98.5 |
| LVESV |
|
|
|
| Baseline
(mls) | 55.6 | 78 | 54.4 |
|
Post-transplantation 3
months | 103.4 | 44 | 38.2 |
|
Post-transplantation 6
months | 76.1 | 80 | 33.1 |
|
Post-transplantation 12
months | 134.1 | 88 | 53.5 |
| Six-minute walk
test |
|
|
|
| Baseline
(ml) | 211.5 | 460.5 | 310.2 |
|
Post-transplantation 3 months
(ml) | 196.5 | 462 | 365.3 |
|
Post-transplantation 6 months
(ml) | 267.0 | 457.5 | 347.5 |
|
Post-transplantation 12 months
(ml) | 245.6 | 447 | 332.5 |
| NYHA functional
class |
|
|
|
|
Baseline | III | III | II |
|
Post-transplantation 3
months | III | III | II |
|
Post-transplantation 6
months | II | II | I |
|
Post-transplantation 12
months | II | I | I |
Exercise capacity
All the patients underwent a six-minute walk test at
baseline, 3, 6 and 12 months. Patient 1 got a transient decrease at
the end of 3 months, patient 2 got a transient increase at the end
of 3 months, and then decreased slowly. After 12 months, there was
significant improvement in six-minute walk test in two patients
post-transplantation (Table
II).
NYHA
Each patient who showed improvement in the NYHA
classification improved within 3 months of post-transplantation.
After 12 months, this pattern continued with the three (100%)
patients improving (Table II).
Safety
There were no complications or adverse events
associated with HUC-MSC transplantation. No cases of distal
coronary artery occlusion, acute cardiac dysfunction, and
ventricular arrhythmia occurred.
Discussion
In the present study, we reported the safety and
efficacy of HUC-MSCs in the treatment of HF caused by ischemic
cardiomyopathy in the 12 month follow-up duration. Two patients
demonstrated a 65.1% increase in LVEF at the end of 3 months, which
was maintained increasing to 47.8% at the end of 12 months
post-HUC-MSC intravenous infusion. Our data provided significant
evidence for the short-term safety of the cell therapy approach in
at least moderate HF, and provided novel insights into the
improvement of cardiac function.
NYHA class improvement was observed in all the
patients, while LVEF improvement was observed in two patients at
the end of the 12 month post-HUC-MSC transplantation. Thus, our
data indicate that HUC-MSC intravenous infusion was beneficial. In
the present study, we did not observe any improvement in
intermediate and clinical endpoints. Similar beneficial effects on
cardiac function with BMC therapy have been shown in other early
phase studies with the most recent demonstrating improvements to 5
years post-cell therapy (14,15).
Thus, HUC-MSC transplantation attenuation of the HF process was
related to cardiac regeneration.
The pathophysiology of HF and the related syndrome
is complex, and many factors contribute to diastolic dysfunction,
including vascular and myocardial stiffening (1). Generalized stiffening that occurs
throughout the cardiovascular system, and LV diastolic dysfunction
may be associated with changes in intrinsic myocyte stiffness. In
previous studies, we investigated the safety and efficacy of
HUC-MSCs in rat liver fibrosis (13), a fibrosic score that was reduced 8
weeks post-translation. Thus, our data suggest HUC-MSCs used in the
present study are capable of attenuating cardiac fibrosis process.
The results shown herein supported the hypothesis that the
beneficial effects of HUC-MSC transplantation in part mediated by
antifibrotics.
There are several limitations of the present study.
The HF patients received allogeneic HUC-MSCs; thus, we could not
investigate the effect of autologous MSCs in this specific HF
population. Furthermore, the patients with HF received the same
number of cells, and no control group/patients were included in the
present study. Despite these limitations, our data provided novel
insights into the positive cardiac function effect of HUC-MSC
transplantation in patients with HF. Rigorous study design
involving appropriate control arms are required, as previously
suggested (16).
In conclusion, the study has demonstrated a potent
and clinically relevant efficacy outcome of HUC-MSC transplantation
to treat patients with advanced HF, and the procedure is safe and
associated with improvement in LVEF 3 months after therapy, which
is maintained at 12 months. Our data supported a potential clinical
benefit of this therapy. Future large-scale randomized clinical
trials are likely to be designed to elucidate the efficacy of
HUC-MSC transplantation therapy on HF.
References
|
1
|
Senni M, Paulus WJ, Gavazzi A, Fraser AG,
Díez J, Solomon SD, Smiseth OA, Guazzi M, Lam CS, Maggioni AP, et
al: New strategies for heart failure with preserved ejection
fraction: the importance of targeted therapies for heart failure
phenotypes. Eur Heart J. 35:2797–2815. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hare JM, Fishman JE, Gerstenblith G,
Velazquez DL DiFede, Zambrano JP, Suncion VY, Tracy M, Ghersin E,
Johnston PV, Brinker JA, et al: Comparison of allogeneic vs
autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells delivered by
transendocardial injection in patients with ischemic
cardiomyopathy: the POSEIDON randomized trial. JAMA. 308:2369–2379.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Heldman AW, DiFede DL, Fishman JE,
Zambrano JP, Trachtenberg BH, Karantalis V, Mushtaq M, Williams AR,
Suncion VY, McNiece IK, et al: Transendocardial mesenchymal stem
cells and mononuclear bone marrow cells for ischemic
cardiomyopathy: the TAC-HFT randomized trial. JAMA. 311:62–73.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Perin EC, Willerson JT, Pepine CJ, Henry
TD, Ellis SG, Zhao DX, Silva GV, Lai D, Thomas JD, Kronenberg MW,
et al: Cardiovascular Cell Therapy Research Network (CCTRN): Effect
of transendocardial delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear
cells on functional capacity, left ventricular function, and
perfusion in chronic heart failure: the FOCUS-CCTRN trial. JAMA.
307:1717–1726. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mathiasen AB, Jørgensen E, Qayyum AA,
Haack-Sørensen M, Ekblond A and Kastrup J: Rationale and design of
the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
intramyocardial injection of autologous bone-marrow derived
mesenchymal stromal cells in chronic ischemic heart failure (MSC-HF
Trial). Am Heart J. 164:285–291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Williams AR and Hare JM: Mesenchymal stem
cells: biology, pathophysiology, translational findings, and
therapeutic implications for cardiac disease. Circ Res.
109:923–940. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cao Y, Gomes SA, Rangel EB, Paulino EC,
Fonseca TL, Li J, Teixeira MB, Gouveia CH, Bianco AC, Kapiloff MS,
et al: S-nitrosoglutathione reductase-dependent PPARγ
denitrosylation participates in MSC-derived adipogenesis and
osteogenesis. J Clin Invest. 125:1679–1691. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Premer C, Blum A, Bellio MA, Schulman IH,
Hurwitz BE, Parker M, Dermarkarian CR, DiFede DL, Balkan W, Khan A,
et al: Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells restore endothelial
function in heart failure by stimulating endothelial progenitor
cells. EBioMedicine. 2:467–475. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Castro-Manrreza ME, Mayani H,
Monroy-García A, Flores-Figueroa E, Chávez-Rueda K,
Legorreta-Haquet V, Santiago-Osorio E and Montesinos JJ: Human
mesenchymal stromal cells from adult and neonatal sources: a
comparative in vitro analysis of their immunosuppressive properties
against T cells. Stem Cells Dev. 23:1217–1232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qu Z, Guo S, Fang G, Cui Z and Liu Y: AKT
pathway affects bone regeneration in nonunion treated with
umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 71:1542–1551. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Qu Z, Guo L, Fang G, Cui Z, Guo S and Liu
Y: Biological characteristics and effect of human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) grafting with blood plasma on
bone regeneration in rats. Cell Biochem Biophys. 63:171–181. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y, Shi ZL and Zhao Z: Transplantation
of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves
hepatic fibrosis in rats with carbon etrachloride-induced hepatic
cirrhosis. Chinese J Tissue Engineering Res. 16:1837–1840. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Qu Z, Fang G, Cui Z and Liu Y: Cell
therapy for bone nonunion: a retrospective study. Minerva Med.
106:315–321. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seth S, Bhargava B, Narang R, Ray R,
Mohanty S, Gulati G, Kumar L, Airan B and Venugopal P: AIIMS Stem
Cell Study Group: The ABCD (autologous bone marrow cells in dilated
cardiomyopathy) trial a long-term follow-up study. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 55:1643–1644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fischer-Rasokat U, Assmus B, Seeger FH,
Honold J, Leistner D, Fichtlscherer S, Schächinger V, Tonn T,
Martin H, Dimmeler S, et al: A pilot trial to assess potential
effects of selective intracoronary bone marrow-derived progenitor
cell infusion in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy:
final 1-year results of the transplantation of progenitor cells and
functional regeneration enhancement pilot trial in patients with
nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Heart Fail. 2:417–423.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gho JM, Kummeling GJ, Koudstaal S, Of
Lorkeers SJ Jansen, Doevendans PA, Asselbergs FW and Chamuleau SA:
Cell therapy, a novel remedy for dilated cardiomyopathy? A
systematic review. J Card Fail. 19:494–502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|