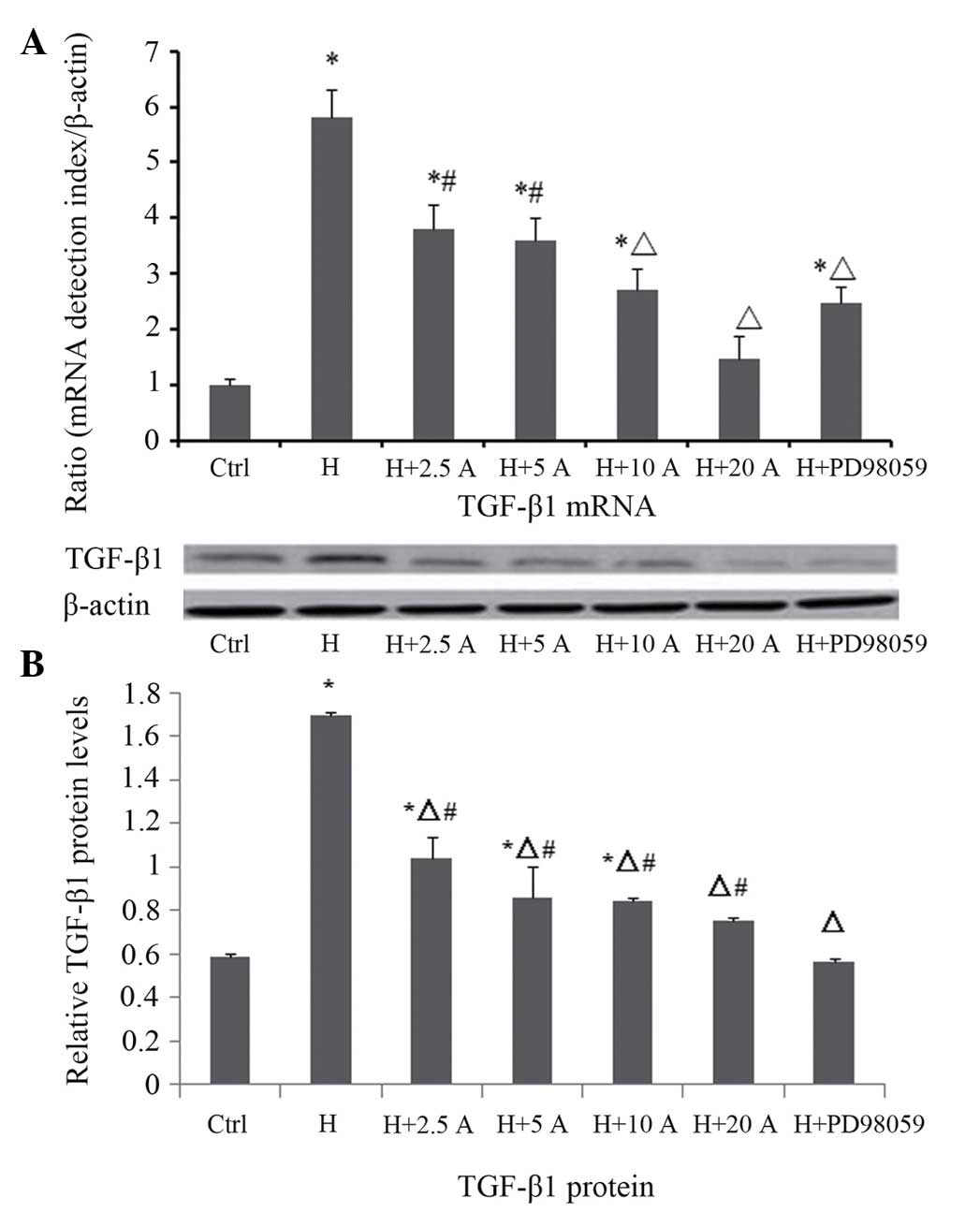
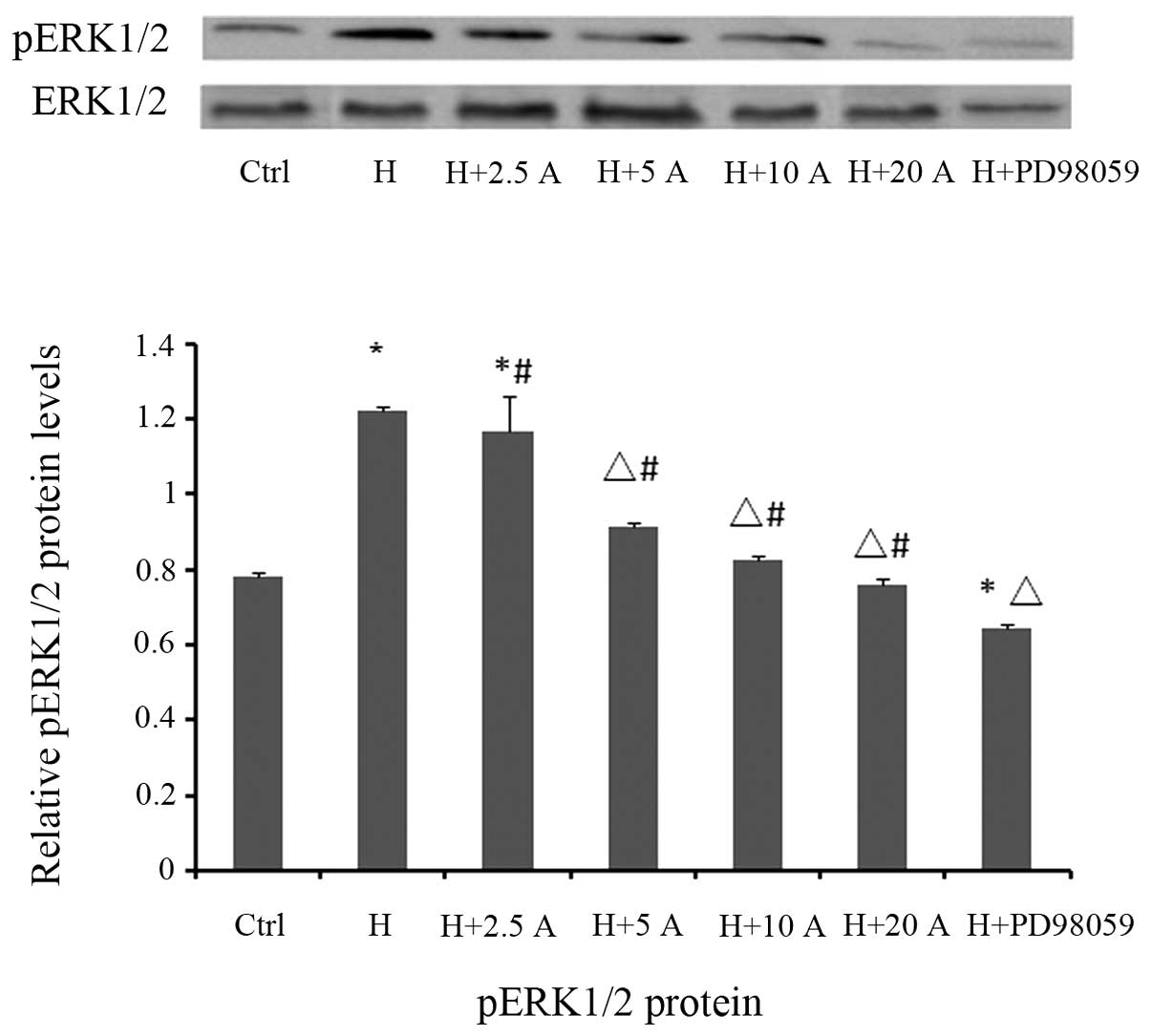
|
1
|
Liu Y: Renal fibrosis: New insights into
the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int. 69:213–217. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee JH, Kim JH, Kim JS, Chang JW, Kim SB,
Park JS and Lee SK: AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits TGF-β-,
angiotensin II-, aldosterone-, high glucose-, and albumin-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
304:F686–F697. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang WC, Liu SF, Chang WT, Shiue YL, Hsieh
PF, Hung TJ, Hung CY, Hung YJ, Chen MF and Yang YL: The effects of
diosgenin in the regulation of renal proximal tubular fibrosis. Exp
Cell Res. 323:255–262. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei J, Shi Y, Hou Y, Ren Y, Du C, Zhang L,
Li Y and Duan H: Knockdown of thioredoxin-interacting protein
ameliorates high glucose-induced epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in renal tubular epithelial cells. Cell Signal.
25:2788–2796. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ban CR and Twigg SM: Fibrosis in diabetes
complications: Pathogenic mechanisms and circulating and urinary
markers. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 4:575–596. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Simonson MS: Phenotypic transitions and
fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 71:846–854. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Burns WC and Thomas MC: The molecular
mediators of type 2 epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and
their role in renal pathophysiology. Expert Rev Mol Med.
12:e172010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y: Epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in renal fibrogenesis: Pathologic significance,
molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 15:1–12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kalluri R and Neilson EG:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 112:1776–1784. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rastaldi MP, Ferrario F, Giardino L,
Dell'Antonio G, Grillo C, Grillo P, Strutz F, Müller GA, Colasanti
G and D'Amico G: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tubular
epithelial cells in human renal biopsies. Kidney Int. 62:137–146.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y and Yang J: Hepatocyte growth
factor: New arsenal in the fights against renal fibrosis? Kidney
Int. 70:238–240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gonzalez DM and Medici D: Signaling
mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal.
7:2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Y, Zhang J, Fang L, Luo P, Peng J and
Du X: Lefty A attenuates the TGF-beta1-induced epithelial to
mesenchymal transition of human renal proximal epithelial tubular
cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 339:263–270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang W, Koka V and Lan HY: Transforming
growth factor-beta and Smad signalling in kidney diseases.
Nephrology (Carlton). 10:48–56. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
El Mesallamy HO, Ahmed HH, Bassyouni AA
and Ahmed AS: Clinical significance of inflammatory and fibrogenic
cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. Clin Biochem. 45:646–650. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang W and Liu H: MAPK signal pathways in
the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Research. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jang HS, Han SJ, Kim JI, Lee S, Lipschutz
JH and Park KM: Activation of ERK accelerates repair of renal
tubular epithelial cells, whereas it inhibits progression of
fibrosis following ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1832:1998–2008. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rhyu DY, Yang Y, Ha H, Lee GT, Song JS, Uh
ST and Lee HB: Role of reactive oxygen species in TGF-beta1-induced
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial
cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:667–675. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ali M, Thomson M and Afzal M: Garlic and
onions: Their effect on eicosanoid metabolism and its clinical
relevance. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids. 62:55–73. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cutler RR and Wilson P: Antibacterial
activity of a new, stable, aqueous extract of allicin against
methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Br J Biomed Sci.
61:71–74. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Goncagul G and Ayaz E: Antimicrobial
effect of garlic (Allium sativum). Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug
Discov. 5:91–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Davis SR: An overview of the antifungal
properties of allicin and its breakdown products-the possibility of
a safe and effective antifungal prophylactic. Mycoses. 48:95–100.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ramoutar RR and Brumaghim JL: Antioxidant
and anticancer properties and mechanisms of inorganic selenium,
oxo-sulfur and oxo-selenium compounds. Cell Biochem Biophys.
58:1–23. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Elkayam A, Mirelman D, Peleg E, Wilchek M,
Miron T, Rabinkov A, Sadetzki S and Rosenthal T: The effects of
allicin and enalapril in fructose-induced hyperinsulinemic
hyperlipidemic hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens. 14:377–381. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eilat S, Oestraicher Y, Rabinkov A, Ohad
D, Mirelman D, Battler A, Eldar M and Vered Z: Alteration of lipid
profile in hyperlipidemic rabbits by allicin, an active constituent
of garlic. Coron Artery Dis. 6:985–990. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Abramovitz D, Gavri S, Harats D, Levkovitz
H, Mirelman D, Miron T, Eilat-Adar S, Rabinkov A, Wilchek M, Eldar
M and Vered Z: Allicin-induced decrease in formation of fatty
streaks (atherosclerosis) in mice fed a cholesterol-rich diet.
Coron Artery Dis. 10:515–519. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gonen A, Harats D, Rabinkov A, Miron T,
Mirelman D, Wilchek M, Weiner L, Ulman E, Levkovitz H, Ben-Shushan
D and Shaish A: The antiatherogenic effect of allicin: Possible
mode of action. Pathobiology. 72:325–334. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lang A, Lahav M, Sakhnini E, Barshack I,
Fidder HH, Avidan B, Bardan E, Hershkoviz R, Bar-Meir S and Chowers
Y: Allicin inhibits spontaneous and TNF-alpha induced secretion of
proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines from intestinal epithelial
cells. Clin Nutr. 23:1199–1208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Antony ML and Singh SV: Molecular
mechanisms and targets of cancer chemoprevention by garlic-derived
bioactive compound diallyl trisulfide. Indian J Exp Biol.
49:805–816. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nagini S: Cancer chemoprevention by garlic
and its organosulfur compounds-panacea or promise? Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 8:313–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park BJ, Cho SJ, Kwon HC, Lee KR, Rhee DK
and Pyo S: Caspase independent cell death by allicin in human
epithelial carcinoma cells: Involvement of PKA. Cancer Lett.
224:123–132. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oommen S, Anto RJ, Srinivas G and
Karunagaran D: Allicin (from garlic) induces caspase-mediated
apoptosis in cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 485:97–103. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang HX, Shi ZX and Jia HZ: Effect of
allicin on NIH3T3 cells on the proliferation and collagen
synthesis. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 27:431–434.
2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Zhang HX, Jia HZ and Li G: Effect of
allicin on myocardial fibrosis in rats with pressure overload.
Zhongguo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue. 14:149–151. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Zhu LX, Cheng WC and Liu SZ: Effect of
allicin on experimental hepatic fibrosis in rats. Chin J Dig Dis.
7:441–443. 2003.
|
|
36
|
Zhang DX, Ren YS and Liu B: Effect of
allicin on angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation. Zhong Guo Xiandai Yi Xue Za Zhi. 15:2136–2138.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
37
|
Zhu LX, Chen WC, Liu SZ and Gu ZL: Effect
of allicin on experimental liver fibrosis in rats. Chin J Digest.
23:441–443. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
38
|
Xu C, Ding W, Zhang M and Gu Y: Protective
effects of angiotensin-(1–7) administered with an
angiotensin-receptor blocker in a rat model of chronic kidney
disease. Nephrology (Carlton). 18:761–769. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu J, Ma KL, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Hu ZB, Lv LL,
Tang RN, Liu H, Ruan XZ and Liu BC: Activation of mTORC1 disrupted
LDL receptor pathway: A potential new mechanism for the progression
of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
61:8–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in
signaling, development and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Strutz F, Okada H, Lo CW, Danoff T, Carone
RL, Tomaszewski JE and Neilson EG: Identification and
characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J Cell Biol.
130:393–405. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Barnes JL and Glass WF: Renal Interstitial
Fibrosis: A Critical Evaluation of the Origin of Myofibroblasts.
Contrib Nephrol. 169:73–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Iwano M, Plieth D, Danoff TM, Xue C, Okada
H and Neilson EG: Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium
during tissue fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 110:341–350. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li MX and Liu BC: Epithelial to
mesenchymal transition in the progression of tubulointerstitial
fibrosis. Chin Med J (Engl). 120:1925–1930. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang J and Liu Y: Blockage of tubular
epithelial to myofibroblast transition by hepatocyte growth factor
prevents renal interstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:96–107.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Burns WC, Kantharidis P and Thomas MC: The
role of tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition in progressive
kidney disease. Cells Tissues Organs. 185:222–231. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fan JM, Huang XR, Ng YY, Nikolic-Paterson
DJ, Mu W, Atkins RC and Lan HY: Interleukin-1 induces tubular
epithelial- myofibroblast transdifferentiation through a
transforming growth factor-beta1-dependent mechanism in vitro. Am J
Kidney Dis. 37:820–831. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jinde K, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Huang XR,
Sakai H, Kurokawa K, Atkins RC and Lan HY: Tubular phenotypic
change in progressive tubulointerstitial fibrosis in human
glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 38:761–769. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lan HY: Tubular epithelial-myofibroblast
transdifferentiation mechanisms in proximal tubule cells. Curr Opin
Nephrol Hypertens. 12:25–29. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Oldfield MD, Bach LA, Forbes JM,
Nikolic-Paterson D, McRobert A, Thallas V, Atkins RC, Osicka T,
Jerums G and Cooper ME: Advanced glycation end products cause
epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation via the receptor for
advanced glycation end products (RAGE). J Clin Invest.
108:1853–1863. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li JH, Wang W, Huang XR, Oldfield M,
Schmidt AM, Cooper ME and Lan HY: Advanced glycation end products
induce tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transition through the
RAGE-ERK1/2 MAP kinase signaling pathway. Am J Pathol.
164:1389–1397. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ye X, Li H and Zhang JH: Phenotypic
conversion of renal cortex cells in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats. Zhong Guo Bing Li Sheng Li Za Zhi. 23:1645–1647. 2007.(In
Chinese).
|
|
54
|
Liu RY, Zeng YY, Lei Z, Wang LQ, Yang HP,
Liu ZY, Zhao J and Zhang HT: JAK/STAT3 signaling is required for
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 2:1643–1651. 2014.
|
|
55
|
Nakerakanti S and Trojanowska M: The role
of TGF-β receptors in fibrosis. Open Rheumat J. 6:156–162. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhou L, Xue H, Yuan P, Ni J, Yu C, Huang Y
and Lu LM: Angiotensin AT1 receptor activation mediates high
glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal proximal
tubular cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 37:e152–e157. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cheng X, Gao W, Dang Y, Liu X, Li Y, Peng
X and Ye X: Both ERK/MAPK and TGF-Beta/Smad signaling pathways play
a role in the kidney fibrosis of diabetic mice accelerated by blood
glucose fluctuation. J Diabetes Res. 2013:4637402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dai B, Cui M, Zhu M, Su WL, Qiu MC and
Zhang H: STAT1/3 and ERK1/2 synergistically regulate cardiac
fibrosis induced by high glucose. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:960–971.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nakasatomi M, Maeshima A, Mishima K,
Ikeuchi H, Sakairi T, Kaneko Y, Hiromura K and Nojima Y: Novel
approach for the detection of tubular cell migration into the
interstitium during renal fibrosis in rats. Fibrogenesis Tissue
Repair. 8:122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
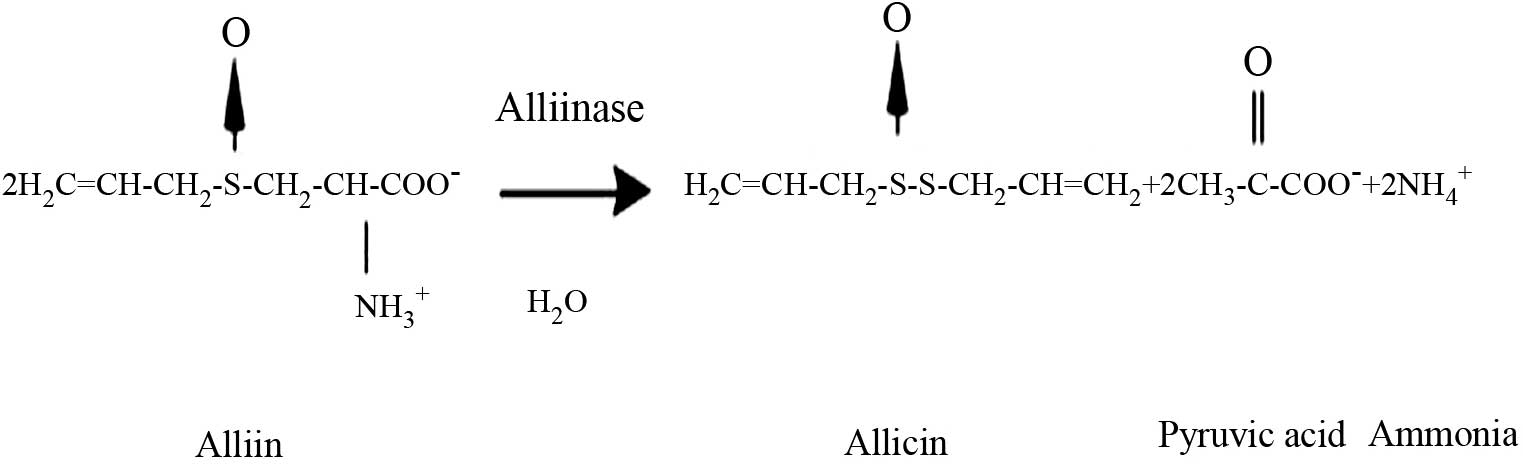
Block E: The chemistry of garlic and
onions. Sci Am. 252:114–119. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|