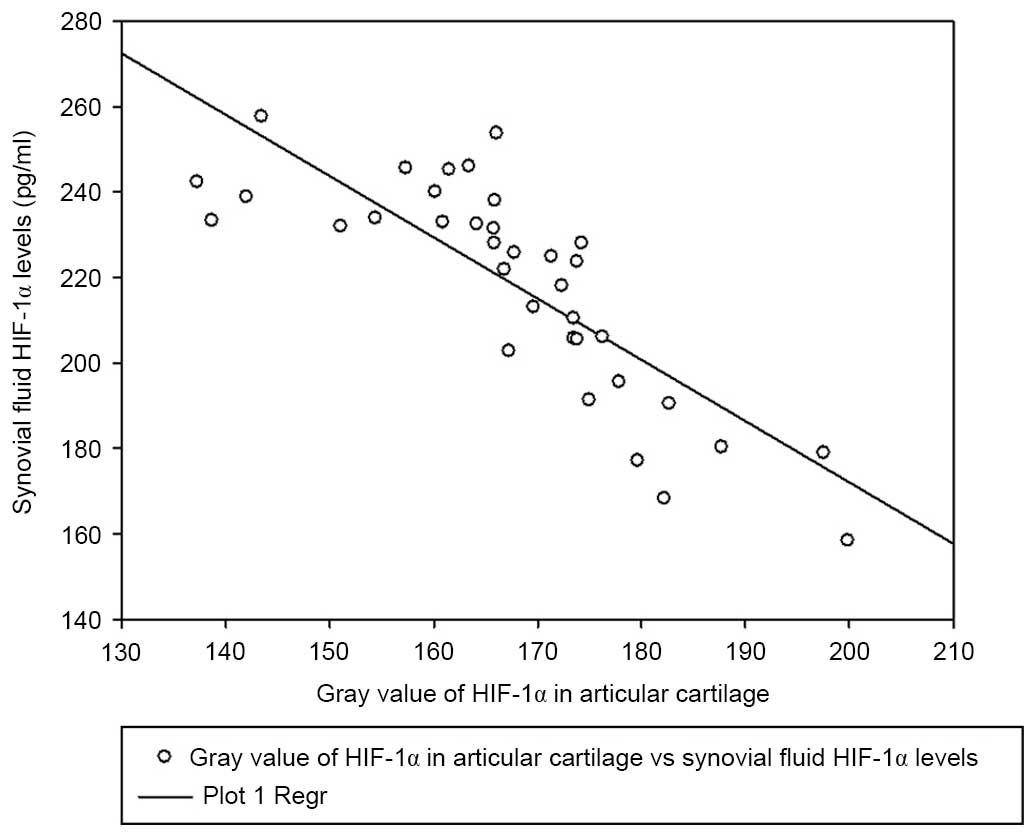
|
1
|
Gallo J, Goodman SB, Konttinen YT, Wimmer
MA and Holinka M: Osteolysis around total knee arthroplasty: A
review of pathogenetic mechanisms. Acta Biomaterialia. 9:8046–8058.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van den Berg WB: Osteoarthritis yearn
review: Pathomechanisms. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 19:338–341.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saito T and Kawaguchi H: HIF-2α as a
possible therapeutic target of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis
Cartilag. 18:1552–1556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lotz M: Osteoarthritis yearn review:
Biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:192–196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tonge DP, Pearson MJ and Jones SW: The
hallmarks of osteoarthritis and the potential to develop
personalised disease-modifying pharmacological therapeutics.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 22:609–621. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alcaraz MJ, Megías J, García-Arnandis I,
Clérigues V and Guillén MI: New molecular targets for the treatment
of osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:13–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Araldi E and Schipani E: Hypoxia, HIFs and
bone development. Bone. 47:190–196. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Coimbra IB, Jimenez SA, Hawkins DF,
Piera-Velazquez S and Stokes DG: Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha
expression in human normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 12:336–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cramer T, Schipani E, Johnson RS, Swoboda
B and Pfander D: Expression of VEGF isoforms by epiphyseal
chondrocytes during low-oxygen tension is HIF-1alpha dependent.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 12:433–439. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Duval E, Baugé C, Andriamanalijaona R,
Bénateau H, Leclercq S, Dutoit S, Poulain L, Galéra P and
Boumédiene K: Molecular mechanism of hypoxia-induced chondrogenesis
and its application in in vivo cartilage tissue engineering.
Biomaterialsm. 33:6042–6051. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gelse K, Mühle C, Knaup K, Swoboda B,
Wiesener M, Henning F, Olk A and Schneider H: Chondrogenic
differentiation of growth factor-stimulated precursor cells in
cartilage repair tissue is associated with increased HIF-1alpha
activity. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 16:1457–1465. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hong YH, Park CW, Kim HS, Won KC, Kim YW
and Lee CK: Effects of hypoxia/ischemia on catabolic mediators of
cartilage in a human chondrocyte, SW1353. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 431:478–483. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hatta TK, Kishimoto KN, Okuno H and Itoi
E: Lubricin expression is suppressed by hypoxia through HIF-1
mediated pathway. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:S137–S138. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Henrotin Y, Kurz B and Aigner T: Oxygen
and reactive oxygen species in cartilage degradation: Friends or
foes? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 13:643–654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li G, Zhang Y, Qian Y, Zhang H, Guo S,
Sunagawa M, Hisamitsu T and Liu Y: Interleukin-17A promotes
rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes migration and invasion under
hypoxia by increasing MMP2 and MMP9 expression through NF-κB/HIF-1α
pathway. Mol Immunol. 53:227–236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koh MY and Powis G: Passing the baton: the
HIF switch. Trends Biochem Sci. 37:364–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang C, Yang F, Cornelia R, Tang W,
Swisher S and Kim H: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 is a positive
regulator of Sox9 activity in femoral head osteonecrosis. Bone.
48:507–513. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Grimmer C, Balbus N, Lang U, Aigner T,
Cramer T, Müller L, Swoboda B and Pfander D: Regulation of Type II
collagen synthesis during osteoarthritis by prolyl-4-hydroxylases:
Possible influence of low oxygen levels. Am J Pathol. 169:491–502.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kellgren JH and Lawrence JS: Radiological
assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 16:494–502. 1957.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Van der Sluijs JA, Geesink RG, Van der
Linden AJ, Bulstra SK, Kuyer R and Drukker J: The reliability of
the Mankin scores for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 10:58–61. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang RX, Ren K and Dubner R:
Osteoarthritis pain mechanisms: Basic studies in animal models.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:1308–1315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meretoja VV, Dahlin RL, Wright S, Kasper
FK and Mikos SG: The effect of hypoxia on the chondrogenic
differentiation of co-cultured articular chondrocytes and
mesenchymal stem cells in scaffolds. Biomaterials. 34:4266–4273.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nomura T, Aoyama M, Waguri-Nagaya Y, Goto
Y, Suzuki M, Miyazawa K, Asai K and Goto S: Tumor necrosis factor
stimulates osteoclastogenesis from human bone marrow cells under
hypoxic conditions. Exp Cell Res. 321:167–177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin JL, Wang MJ, Lee DC, Liang CC and Lin
SK: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha regulates matrix
metalloproteinase-1 activity in human bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. FEBS Lett. 582:2615–2619. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Makris EA, Hu JC and Athanasiou KA:
Hypoxia-induced collagen crosslinking as a mechanism for enhancing
mechanical properties of engineered articular cartilage.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:634–641. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ren BF, Deng LF, Wang J, Zhu YP, Wei L and
Zhou Q: Hypoxia regulation of facilitated glucose transporter-1 and
glucose transporter-3 in mouse chondrocytes mediated by HIF-1alpha.
Joint Bone Spine. 75:176–181. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Murata M, Yudoh K and Masuko K: The
potential role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in
cartilage: How the angiogenic factor could be involved in the
pathogenesis of osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
16:279–286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu G, Tang Y, Liang X, Zheng M, Yang J,
Zhou H, Li L and Qin T: Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in
the regulation of plasminogen activator activity in rat knee joint
chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17:1494–1502. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu M, Feng Q and Bian LM: Differential
effect of hypoxia on human mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis and
hypertrophy in hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Acta Biomater.
10:1333–1340. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chim SM, Tickner J, Chow ST, Kuek V, Guo
BS, Zhang G, Rosen V, Erber W and Xu JK: Angiogenic factors in bone
local environment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:297–310. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matsuki TY, Arai Y, Tsuchida S, Terauchi
R, Inoue H, Nakagawa S, Inoue A, Mazda O and Kubo T: The roles of
heat shock protein 70 on chondrocyte. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
21:S1272013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pfander D, Swobodal B and Cramer T: The
role of HIF-1alpha in maintaining cartilage homeostasis and during
the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 8:1042006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Neve A, Cantatore FP, Corrado A, Gaudio A,
Ruggieri S and Ribatti D: In vitro and in vivo angiogenic activity
of osteoarthritic and osteoporotic osteoblasts is modulated by VEGF
and vitamin D3 treatment. Regul Pept. 184:81–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pufe T, Lemke A, Kurz B, Petersen W,
Tillmann B, Grodzinsky AJ and Mentlerin R: Mechanical overload
induces VEGF in cartilage discs via hypoxia-inducible factor. Am J
Pathol. 164:185–192. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Okada KY, Hosaka Y, Kobayashi H, Sugita S,
Chang S, Mori Y, Akiyama H, Tanaka S, Kawaguchi H and Saito T:
HIF-1α regulates configuration and maintenance of articular
cartilage through induction of anabolic factors and suppression of
catabolic factors. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 22:S164–S165. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sakamoto J, Origuchi T, Okita M, Nakano J,
Kato K, Yoshimura T, Izumi S, Komori T, Nakamura H, Ida H, et al:
Immobilization-induced cartilage degeneration mediated through
expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, vascular endothelial
growth factor, and chondromodulin-I. Connect Tissue Res. 50:37–45.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang C, Wei X, Chen C, Cao K, Li Y, Jiao
Q, Ding J, Zhou J, Fleming BC, Chen Q, et al: Indian hedgehog in
synovial fluid is a novel marker for early cartilage lesions in
human knee joint. Int J Mol Sci. 15:7250–7265. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Walsh DA, Bonnet CS, Turner EL, Wilson D,
Situ M and Mcwilliams SF: Angiogenesis in the synovium and at the
osteochondral junction in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
15:743–751. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|